User login
The new guideline on management of heart failure (HF) from the European Society of Cardiology seemed to bear an asterisk or footnote even before its full unveiling in the early hours of ESC Congress 2021.
The document would offer little new in the arena of HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), so understandably the fast-approaching presentation of a major HFpEF trial – arguably the conference’s marquee event – would feel to some like the elephant in the room.
“I’d like to highlight this unfortunate timing of the guideline, because it’s an hour or 2 before we hear the full story from EMPEROR-Preserved, which I’m sure will change the guidelines,” Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, University of Lorraine, Vandoeuvre-Les-Nancy, France, said wryly.
Anticipation of the trial’s full presentation was intense as the ESC congress got underway, in part because the top-line and incomplete message from EMPEROR-Preserved had already been released: Patients with HFpEF treated with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF hospitalization.
Although empagliflozin is the first medication to achieve that status in a major HFpEF trial, conspicuously absent from the early announcement were the magnitude of “benefit” and any data. Still, the tantalizing top-line results mean that technically, at least, “we have a drug which is effective in reduced and preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. Zannad said.
But the new guideline, published online Aug. 27, 2021, in the European Heart Journal and comprehensively described that day at the congress, was never really expected to consider results from EMPEROR-Reduced. “These new indications do need to go through the regulatory authorities,” such as the European Medicines Agency and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, observed Carlos Aguiar, MD, Hospital Santa Cruz, Carnaxide, Portugal.
“It does take some time for the whole process to be concluded and, finally, as physicians, being able to implement it in clinical practice,” Dr. Aguiar said as moderator of press briefing prior to the ESC congress.
The ESC guideline’s next iteration or update could well include an SGLT2 inhibitor recommendation that applies beyond the ejection fraction limits of HFrEF. Still, the document summarized that day reflects a number of pivotal concepts with profound treatment implications. Among them are the field’s latest paradigm for medical therapy of HFrEF and the increasingly accepted division of traditional HFpEF into two entities: HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF); and HFpEF, with its left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) threshold raised to 50%.
In fact, HFmrEF in the new document is a drug-therapy indication that barely existed a few years ago but grew in prominence after secondary findings from trials like TOPCAT for spironolactone and PARAGON-HF for sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), an angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI). Still, the HFmrEF recommendations come with different class and level-of-evidence designations.
Those new guideline features and others in the realm of pharmacologic therapy were summarized by the document’s authors at the 2021 Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) meeting, and covered at the time by this news organization
The ‘fantastic four’
One of the document’s central recommendations specifies which contemporary drug classes should be initiated, and when, in patients with HFrEF. An ACE inhibitor or ARNI, a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and an SGLT2 inhibitor collectively earned a class I recommendation, “given the importance of these key HFrEF therapies, some of which have been shown to improve outcomes within a month of initiation,” observed Roy S. Gardner, MBChB, MD.
An agent from each of the four classes is to be “commenced and up-titrated as quickly and as safely as possible, whilst using the lowest effective dose of loop diuretic to relieve congestion,” said Dr. Gardner, from Golden Jubilee National Hospital, Clydebank, Scotland, when presenting the full HFrEF portion of the guidelines.
The oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo, Merck), which recently emerged from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization, gained a class IIb recommendation.
The document’s “simplified algorithm” for managing such patients overall and the advent of SGLT2 inhibitors are new twists in ESC guidelines for HF. But the way the four drug classes are started in patients is key and could take some practitioners time to get used to. There is no prespecified order of initiation.
“We’ve left the door open for clinicians to evaluate the evidence to make sure these four drugs are started, and to tailor how to do it according to the patient,” based on clinical considerations such as blood pressure or renal function, said Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, cochair of the guideline task force.
“The SGLT2 inhibitor trials were done on top of therapy with ACE inhibitors or ARNI, beta-blockers, and MRAs, so some people no doubt will choose to follow a sequenced approach,” Dr. McDonagh said. Other practitioners will consider each patient and attempt to get all four started “as quickly and safely as possible based on the phenotype.”
Importantly, clinicians “should not wait for weeks, months, or years until you have the four drugs in the patient, but you should do this within weeks,” cautioned Johann Bauersachs, MD, Hannover (Germany) Medical School, a discussant for the guideline presentation who is listed as a reviewer on the document.
Although angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors are sometimes thought of as interchangeable, the new guideline does not give them the same weight. “The angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan is a constituent of the ARNI,” Dr. McDonagh noted. “So, the place of ARBs in heart failure has been downgraded in HFrEF. They are really for those who are intolerant of an ACE inhibitor or an ARNI.”
In practice, ARBs are likely to be used as first-line therapy in some circumstances, observed Dr. Bauersachs. They are “the default option in, unfortunately, many low-income countries that may not afford sacubitril-valsartan. And I know that there are many of them.”
Tweaks to device recommendations
The new document contains several new wrinkles in the recommendations for HF device therapy, which should usually be considered only if still appropriate after at least 3 months of optimal medical therapy, Dr. Gardner said.
For example, use of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) has been demoted from its previous class I recommendation to class II, level of evidence A, in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy “in light of the data from the DANISH study,” Dr. Gardner said.
The 2016 DANISH trial was noteworthy for questioning the survival benefits of ICDs in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy, whether or not they were also receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
The new document also puts greater emphasis on a range of specific CRT patient-selection criteria. Beyond the conventional recommended standards of an LVEF of 35% or less, QRS of at least 150 ms, and left-bundle-branch block on optimal meds, consideration can be given to CRT if the QRS is only 130 ms or greater. “And where it’s appropriate to do so, an ICD could be an option,” Dr. Gardner said.
It also recommends CRT as a replacement for right ventricular pacing in patients with high-degree atrioventricular block. “And this, for the first time, includes patients with atrial fibrillation,” he said. “The previous indications for CRT were in individuals in sinus rhythm.”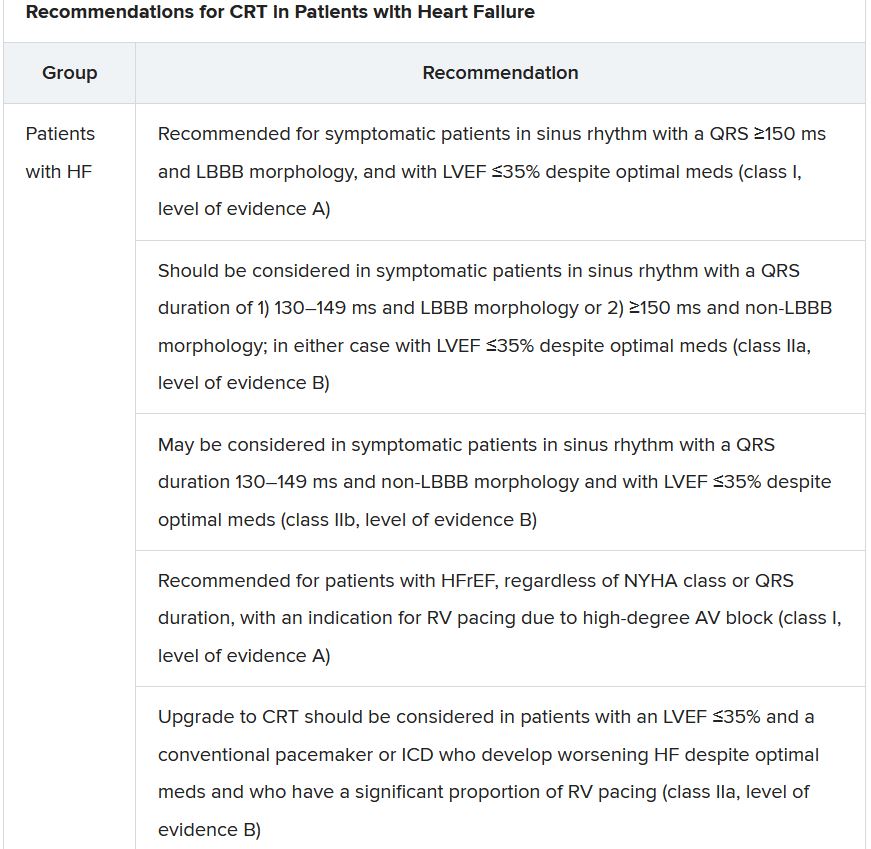
The new document recommends that HF in any patient be classified as HFrEF, defined by an LVEF of ≤40%; HFmrEF, defined by an LVEF of 41%-49%; or HFpEF, defined by an LVEF of at least 50%. “Importantly, for all forms, the presence of the clinical syndrome of heart failure is a prerequisite,” observed Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School, Singapore, at the presentation.
In a critical update from previous guidelines, the term HF with “mid-range” ejection fraction was replaced by the term specifying “mildly reduced” ejection fraction, Dr. Lam noted. The shift retains the acronym but now reflects growing appreciation that HFmrEF patients can benefit from treatments also used in HFrEF, including ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, MRAs, and sacubitril-valsartan, she said.
Support for that relationship comes largely from post hoc subgroup analyses of trials that featured some patients with LVEF 40%-49%. That includes most HFpEF trials represented in the guideline document, but also EMPEROR-Preserved, which saw gains for the primary outcome across the entire range of LVEF above 40%.
The LVEF-based definitions are consistent with a recent HF classification proposal endorsed by the ESC and subspecialty societies in Europe, North America, Japan, India, Australia, New Zealand, and China.
The document doesn’t update recommendations for HFpEF, in which “no treatment has been shown to convincingly reduce mortality or morbidity,” Dr. Lam observed. Still, she noted, the guideline task force “acknowledges that treatment options for HFpEF are being revised even as the guidelines have been published.”
That could be a reference to empagliflozin in EMPEROR-Preserved, but it also refers to the strikingly broad wording of an expanded indication for sacubitril-valsartan in the United States – “to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure” – without specific restrictions on the basis of LVEF. The new indication was announced in early 2021, too late to be considered in the new guidelines.
Whither LVEF-based definitions?
During discussion after the guideline presentation, Dr. Zannad speculated on the future of HF classifications based on ventricular function, given trial evidence in recent years that some agents – notably spironolactone, sacubitril-valsartan, and now, apparently, empagliflozin – might be effective in HFpEF as well as HFrEF.
Will the field continue with “LVEF-centric” distinctions across the range of HF, or transition to “some definition in which drug therapies can be used independently across the full spectrum of ejection fraction?” Dr. Zannad posed.
“I think we need to wait and see what some of these trials with the SGLT2 inhibitors are going to show in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. McDonagh replied. “And I think that will be a step for the next guideline, completely redefining heart failure.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guideline on management of heart failure (HF) from the European Society of Cardiology seemed to bear an asterisk or footnote even before its full unveiling in the early hours of ESC Congress 2021.
The document would offer little new in the arena of HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), so understandably the fast-approaching presentation of a major HFpEF trial – arguably the conference’s marquee event – would feel to some like the elephant in the room.
“I’d like to highlight this unfortunate timing of the guideline, because it’s an hour or 2 before we hear the full story from EMPEROR-Preserved, which I’m sure will change the guidelines,” Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, University of Lorraine, Vandoeuvre-Les-Nancy, France, said wryly.
Anticipation of the trial’s full presentation was intense as the ESC congress got underway, in part because the top-line and incomplete message from EMPEROR-Preserved had already been released: Patients with HFpEF treated with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF hospitalization.
Although empagliflozin is the first medication to achieve that status in a major HFpEF trial, conspicuously absent from the early announcement were the magnitude of “benefit” and any data. Still, the tantalizing top-line results mean that technically, at least, “we have a drug which is effective in reduced and preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. Zannad said.
But the new guideline, published online Aug. 27, 2021, in the European Heart Journal and comprehensively described that day at the congress, was never really expected to consider results from EMPEROR-Reduced. “These new indications do need to go through the regulatory authorities,” such as the European Medicines Agency and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, observed Carlos Aguiar, MD, Hospital Santa Cruz, Carnaxide, Portugal.
“It does take some time for the whole process to be concluded and, finally, as physicians, being able to implement it in clinical practice,” Dr. Aguiar said as moderator of press briefing prior to the ESC congress.
The ESC guideline’s next iteration or update could well include an SGLT2 inhibitor recommendation that applies beyond the ejection fraction limits of HFrEF. Still, the document summarized that day reflects a number of pivotal concepts with profound treatment implications. Among them are the field’s latest paradigm for medical therapy of HFrEF and the increasingly accepted division of traditional HFpEF into two entities: HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF); and HFpEF, with its left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) threshold raised to 50%.
In fact, HFmrEF in the new document is a drug-therapy indication that barely existed a few years ago but grew in prominence after secondary findings from trials like TOPCAT for spironolactone and PARAGON-HF for sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), an angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI). Still, the HFmrEF recommendations come with different class and level-of-evidence designations.
Those new guideline features and others in the realm of pharmacologic therapy were summarized by the document’s authors at the 2021 Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) meeting, and covered at the time by this news organization
The ‘fantastic four’
One of the document’s central recommendations specifies which contemporary drug classes should be initiated, and when, in patients with HFrEF. An ACE inhibitor or ARNI, a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and an SGLT2 inhibitor collectively earned a class I recommendation, “given the importance of these key HFrEF therapies, some of which have been shown to improve outcomes within a month of initiation,” observed Roy S. Gardner, MBChB, MD.
An agent from each of the four classes is to be “commenced and up-titrated as quickly and as safely as possible, whilst using the lowest effective dose of loop diuretic to relieve congestion,” said Dr. Gardner, from Golden Jubilee National Hospital, Clydebank, Scotland, when presenting the full HFrEF portion of the guidelines.
The oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo, Merck), which recently emerged from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization, gained a class IIb recommendation.
The document’s “simplified algorithm” for managing such patients overall and the advent of SGLT2 inhibitors are new twists in ESC guidelines for HF. But the way the four drug classes are started in patients is key and could take some practitioners time to get used to. There is no prespecified order of initiation.
“We’ve left the door open for clinicians to evaluate the evidence to make sure these four drugs are started, and to tailor how to do it according to the patient,” based on clinical considerations such as blood pressure or renal function, said Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, cochair of the guideline task force.
“The SGLT2 inhibitor trials were done on top of therapy with ACE inhibitors or ARNI, beta-blockers, and MRAs, so some people no doubt will choose to follow a sequenced approach,” Dr. McDonagh said. Other practitioners will consider each patient and attempt to get all four started “as quickly and safely as possible based on the phenotype.”
Importantly, clinicians “should not wait for weeks, months, or years until you have the four drugs in the patient, but you should do this within weeks,” cautioned Johann Bauersachs, MD, Hannover (Germany) Medical School, a discussant for the guideline presentation who is listed as a reviewer on the document.
Although angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors are sometimes thought of as interchangeable, the new guideline does not give them the same weight. “The angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan is a constituent of the ARNI,” Dr. McDonagh noted. “So, the place of ARBs in heart failure has been downgraded in HFrEF. They are really for those who are intolerant of an ACE inhibitor or an ARNI.”
In practice, ARBs are likely to be used as first-line therapy in some circumstances, observed Dr. Bauersachs. They are “the default option in, unfortunately, many low-income countries that may not afford sacubitril-valsartan. And I know that there are many of them.”
Tweaks to device recommendations
The new document contains several new wrinkles in the recommendations for HF device therapy, which should usually be considered only if still appropriate after at least 3 months of optimal medical therapy, Dr. Gardner said.
For example, use of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) has been demoted from its previous class I recommendation to class II, level of evidence A, in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy “in light of the data from the DANISH study,” Dr. Gardner said.
The 2016 DANISH trial was noteworthy for questioning the survival benefits of ICDs in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy, whether or not they were also receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
The new document also puts greater emphasis on a range of specific CRT patient-selection criteria. Beyond the conventional recommended standards of an LVEF of 35% or less, QRS of at least 150 ms, and left-bundle-branch block on optimal meds, consideration can be given to CRT if the QRS is only 130 ms or greater. “And where it’s appropriate to do so, an ICD could be an option,” Dr. Gardner said.
It also recommends CRT as a replacement for right ventricular pacing in patients with high-degree atrioventricular block. “And this, for the first time, includes patients with atrial fibrillation,” he said. “The previous indications for CRT were in individuals in sinus rhythm.”
The new document recommends that HF in any patient be classified as HFrEF, defined by an LVEF of ≤40%; HFmrEF, defined by an LVEF of 41%-49%; or HFpEF, defined by an LVEF of at least 50%. “Importantly, for all forms, the presence of the clinical syndrome of heart failure is a prerequisite,” observed Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School, Singapore, at the presentation.
In a critical update from previous guidelines, the term HF with “mid-range” ejection fraction was replaced by the term specifying “mildly reduced” ejection fraction, Dr. Lam noted. The shift retains the acronym but now reflects growing appreciation that HFmrEF patients can benefit from treatments also used in HFrEF, including ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, MRAs, and sacubitril-valsartan, she said.
Support for that relationship comes largely from post hoc subgroup analyses of trials that featured some patients with LVEF 40%-49%. That includes most HFpEF trials represented in the guideline document, but also EMPEROR-Preserved, which saw gains for the primary outcome across the entire range of LVEF above 40%.
The LVEF-based definitions are consistent with a recent HF classification proposal endorsed by the ESC and subspecialty societies in Europe, North America, Japan, India, Australia, New Zealand, and China.
The document doesn’t update recommendations for HFpEF, in which “no treatment has been shown to convincingly reduce mortality or morbidity,” Dr. Lam observed. Still, she noted, the guideline task force “acknowledges that treatment options for HFpEF are being revised even as the guidelines have been published.”
That could be a reference to empagliflozin in EMPEROR-Preserved, but it also refers to the strikingly broad wording of an expanded indication for sacubitril-valsartan in the United States – “to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure” – without specific restrictions on the basis of LVEF. The new indication was announced in early 2021, too late to be considered in the new guidelines.
Whither LVEF-based definitions?
During discussion after the guideline presentation, Dr. Zannad speculated on the future of HF classifications based on ventricular function, given trial evidence in recent years that some agents – notably spironolactone, sacubitril-valsartan, and now, apparently, empagliflozin – might be effective in HFpEF as well as HFrEF.
Will the field continue with “LVEF-centric” distinctions across the range of HF, or transition to “some definition in which drug therapies can be used independently across the full spectrum of ejection fraction?” Dr. Zannad posed.
“I think we need to wait and see what some of these trials with the SGLT2 inhibitors are going to show in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. McDonagh replied. “And I think that will be a step for the next guideline, completely redefining heart failure.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guideline on management of heart failure (HF) from the European Society of Cardiology seemed to bear an asterisk or footnote even before its full unveiling in the early hours of ESC Congress 2021.
The document would offer little new in the arena of HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), so understandably the fast-approaching presentation of a major HFpEF trial – arguably the conference’s marquee event – would feel to some like the elephant in the room.
“I’d like to highlight this unfortunate timing of the guideline, because it’s an hour or 2 before we hear the full story from EMPEROR-Preserved, which I’m sure will change the guidelines,” Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, University of Lorraine, Vandoeuvre-Les-Nancy, France, said wryly.
Anticipation of the trial’s full presentation was intense as the ESC congress got underway, in part because the top-line and incomplete message from EMPEROR-Preserved had already been released: Patients with HFpEF treated with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF hospitalization.
Although empagliflozin is the first medication to achieve that status in a major HFpEF trial, conspicuously absent from the early announcement were the magnitude of “benefit” and any data. Still, the tantalizing top-line results mean that technically, at least, “we have a drug which is effective in reduced and preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. Zannad said.
But the new guideline, published online Aug. 27, 2021, in the European Heart Journal and comprehensively described that day at the congress, was never really expected to consider results from EMPEROR-Reduced. “These new indications do need to go through the regulatory authorities,” such as the European Medicines Agency and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, observed Carlos Aguiar, MD, Hospital Santa Cruz, Carnaxide, Portugal.
“It does take some time for the whole process to be concluded and, finally, as physicians, being able to implement it in clinical practice,” Dr. Aguiar said as moderator of press briefing prior to the ESC congress.
The ESC guideline’s next iteration or update could well include an SGLT2 inhibitor recommendation that applies beyond the ejection fraction limits of HFrEF. Still, the document summarized that day reflects a number of pivotal concepts with profound treatment implications. Among them are the field’s latest paradigm for medical therapy of HFrEF and the increasingly accepted division of traditional HFpEF into two entities: HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF); and HFpEF, with its left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) threshold raised to 50%.
In fact, HFmrEF in the new document is a drug-therapy indication that barely existed a few years ago but grew in prominence after secondary findings from trials like TOPCAT for spironolactone and PARAGON-HF for sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), an angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI). Still, the HFmrEF recommendations come with different class and level-of-evidence designations.
Those new guideline features and others in the realm of pharmacologic therapy were summarized by the document’s authors at the 2021 Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) meeting, and covered at the time by this news organization
The ‘fantastic four’
One of the document’s central recommendations specifies which contemporary drug classes should be initiated, and when, in patients with HFrEF. An ACE inhibitor or ARNI, a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and an SGLT2 inhibitor collectively earned a class I recommendation, “given the importance of these key HFrEF therapies, some of which have been shown to improve outcomes within a month of initiation,” observed Roy S. Gardner, MBChB, MD.
An agent from each of the four classes is to be “commenced and up-titrated as quickly and as safely as possible, whilst using the lowest effective dose of loop diuretic to relieve congestion,” said Dr. Gardner, from Golden Jubilee National Hospital, Clydebank, Scotland, when presenting the full HFrEF portion of the guidelines.
The oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo, Merck), which recently emerged from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization, gained a class IIb recommendation.
The document’s “simplified algorithm” for managing such patients overall and the advent of SGLT2 inhibitors are new twists in ESC guidelines for HF. But the way the four drug classes are started in patients is key and could take some practitioners time to get used to. There is no prespecified order of initiation.
“We’ve left the door open for clinicians to evaluate the evidence to make sure these four drugs are started, and to tailor how to do it according to the patient,” based on clinical considerations such as blood pressure or renal function, said Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, cochair of the guideline task force.
“The SGLT2 inhibitor trials were done on top of therapy with ACE inhibitors or ARNI, beta-blockers, and MRAs, so some people no doubt will choose to follow a sequenced approach,” Dr. McDonagh said. Other practitioners will consider each patient and attempt to get all four started “as quickly and safely as possible based on the phenotype.”
Importantly, clinicians “should not wait for weeks, months, or years until you have the four drugs in the patient, but you should do this within weeks,” cautioned Johann Bauersachs, MD, Hannover (Germany) Medical School, a discussant for the guideline presentation who is listed as a reviewer on the document.
Although angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors are sometimes thought of as interchangeable, the new guideline does not give them the same weight. “The angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan is a constituent of the ARNI,” Dr. McDonagh noted. “So, the place of ARBs in heart failure has been downgraded in HFrEF. They are really for those who are intolerant of an ACE inhibitor or an ARNI.”
In practice, ARBs are likely to be used as first-line therapy in some circumstances, observed Dr. Bauersachs. They are “the default option in, unfortunately, many low-income countries that may not afford sacubitril-valsartan. And I know that there are many of them.”
Tweaks to device recommendations
The new document contains several new wrinkles in the recommendations for HF device therapy, which should usually be considered only if still appropriate after at least 3 months of optimal medical therapy, Dr. Gardner said.
For example, use of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) has been demoted from its previous class I recommendation to class II, level of evidence A, in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy “in light of the data from the DANISH study,” Dr. Gardner said.
The 2016 DANISH trial was noteworthy for questioning the survival benefits of ICDs in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy, whether or not they were also receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
The new document also puts greater emphasis on a range of specific CRT patient-selection criteria. Beyond the conventional recommended standards of an LVEF of 35% or less, QRS of at least 150 ms, and left-bundle-branch block on optimal meds, consideration can be given to CRT if the QRS is only 130 ms or greater. “And where it’s appropriate to do so, an ICD could be an option,” Dr. Gardner said.
It also recommends CRT as a replacement for right ventricular pacing in patients with high-degree atrioventricular block. “And this, for the first time, includes patients with atrial fibrillation,” he said. “The previous indications for CRT were in individuals in sinus rhythm.”
The new document recommends that HF in any patient be classified as HFrEF, defined by an LVEF of ≤40%; HFmrEF, defined by an LVEF of 41%-49%; or HFpEF, defined by an LVEF of at least 50%. “Importantly, for all forms, the presence of the clinical syndrome of heart failure is a prerequisite,” observed Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School, Singapore, at the presentation.
In a critical update from previous guidelines, the term HF with “mid-range” ejection fraction was replaced by the term specifying “mildly reduced” ejection fraction, Dr. Lam noted. The shift retains the acronym but now reflects growing appreciation that HFmrEF patients can benefit from treatments also used in HFrEF, including ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, MRAs, and sacubitril-valsartan, she said.
Support for that relationship comes largely from post hoc subgroup analyses of trials that featured some patients with LVEF 40%-49%. That includes most HFpEF trials represented in the guideline document, but also EMPEROR-Preserved, which saw gains for the primary outcome across the entire range of LVEF above 40%.
The LVEF-based definitions are consistent with a recent HF classification proposal endorsed by the ESC and subspecialty societies in Europe, North America, Japan, India, Australia, New Zealand, and China.
The document doesn’t update recommendations for HFpEF, in which “no treatment has been shown to convincingly reduce mortality or morbidity,” Dr. Lam observed. Still, she noted, the guideline task force “acknowledges that treatment options for HFpEF are being revised even as the guidelines have been published.”
That could be a reference to empagliflozin in EMPEROR-Preserved, but it also refers to the strikingly broad wording of an expanded indication for sacubitril-valsartan in the United States – “to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure” – without specific restrictions on the basis of LVEF. The new indication was announced in early 2021, too late to be considered in the new guidelines.
Whither LVEF-based definitions?
During discussion after the guideline presentation, Dr. Zannad speculated on the future of HF classifications based on ventricular function, given trial evidence in recent years that some agents – notably spironolactone, sacubitril-valsartan, and now, apparently, empagliflozin – might be effective in HFpEF as well as HFrEF.
Will the field continue with “LVEF-centric” distinctions across the range of HF, or transition to “some definition in which drug therapies can be used independently across the full spectrum of ejection fraction?” Dr. Zannad posed.
“I think we need to wait and see what some of these trials with the SGLT2 inhibitors are going to show in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. McDonagh replied. “And I think that will be a step for the next guideline, completely redefining heart failure.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

