User login
Increases in hepatitis C–related inpatient stays for baby boomers from 2005 to 2014 far outpaced those of older adults, while younger adults saw their admissions drop over that period, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
For the baby boomers (adults aged 52-72 years), the rate of inpatient stays involving hepatitis C with or without hepatitis B, HIV, or alcoholic liver disease rose from 300.7 per 100,000 population in 2005 to 503.1 per 100,000 in 2014 – an increase of over 67%. For patients aged 73 years and older, that rate went from 104.4 in 2005 to 117.1 in 2014, which translates to a 12% increase, and for patients aged 18-51 years, it dropped 15%, from 182.5 to 155.4, the AHRQ said in a statistical brief.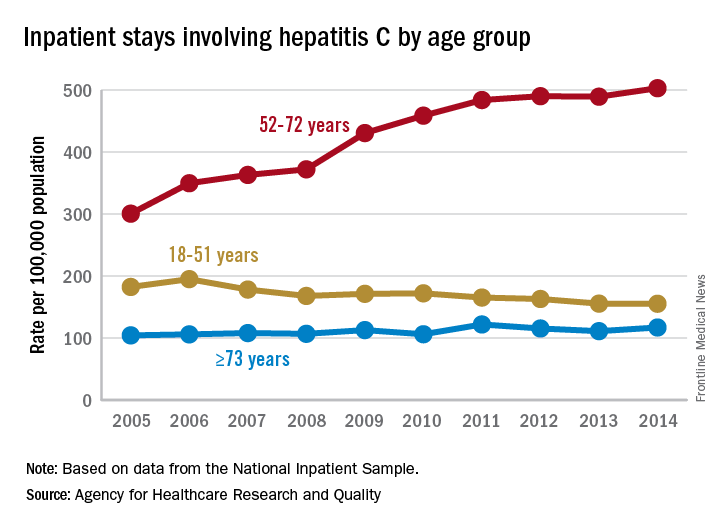
Along with the increased hospitalizations, “acute hepatitis C cases nearly tripled from 2010 through 2015,” the report noted, which was “likely the result of increasing injection drug use due to the growing opioid epidemic.”
Increases in hepatitis C–related inpatient stays for baby boomers from 2005 to 2014 far outpaced those of older adults, while younger adults saw their admissions drop over that period, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
For the baby boomers (adults aged 52-72 years), the rate of inpatient stays involving hepatitis C with or without hepatitis B, HIV, or alcoholic liver disease rose from 300.7 per 100,000 population in 2005 to 503.1 per 100,000 in 2014 – an increase of over 67%. For patients aged 73 years and older, that rate went from 104.4 in 2005 to 117.1 in 2014, which translates to a 12% increase, and for patients aged 18-51 years, it dropped 15%, from 182.5 to 155.4, the AHRQ said in a statistical brief.
Along with the increased hospitalizations, “acute hepatitis C cases nearly tripled from 2010 through 2015,” the report noted, which was “likely the result of increasing injection drug use due to the growing opioid epidemic.”
Increases in hepatitis C–related inpatient stays for baby boomers from 2005 to 2014 far outpaced those of older adults, while younger adults saw their admissions drop over that period, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
For the baby boomers (adults aged 52-72 years), the rate of inpatient stays involving hepatitis C with or without hepatitis B, HIV, or alcoholic liver disease rose from 300.7 per 100,000 population in 2005 to 503.1 per 100,000 in 2014 – an increase of over 67%. For patients aged 73 years and older, that rate went from 104.4 in 2005 to 117.1 in 2014, which translates to a 12% increase, and for patients aged 18-51 years, it dropped 15%, from 182.5 to 155.4, the AHRQ said in a statistical brief.
Along with the increased hospitalizations, “acute hepatitis C cases nearly tripled from 2010 through 2015,” the report noted, which was “likely the result of increasing injection drug use due to the growing opioid epidemic.”