User login
A 51-year-old woman is referred to dermatology for multiple problems she has had for several months—and, in some cases, years. The most immediate is a new nodule on the side of one thumb. Although it is asymptomatic, the fact that it simply “appeared” worries her, because her favorite uncle recently died of melanoma.
Several new lesions also materialized on her finger pads and chest. These do not cause symptoms either, but their newness makes them worrisome.
When asked about her health in general, the patient initially states it is “fine”—until her husband corrects her. She then recalls that she is being seen by various specialists, including a gastroenterologist for dysphagia-like symptoms and a rheumatologist for vague joint pains and what sounds like Raynaud disease.
EXAMINATION
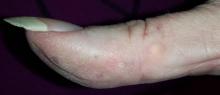
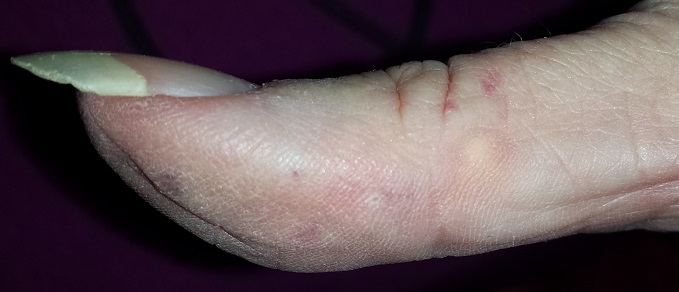
On the lateral right thumb is a shallow, intradermal, white lesion. It is firm and round and measures 5 mm. No overlying skin changes (eg, redness or disruption of the skin surface) are observed. Under local anesthesia, a small incision is made in the lesion’s surface, allowing for exploration with small forceps; granular, gritty, white material is extracted.
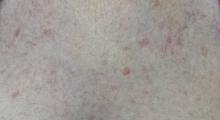
On the affected thumb and two other fingers, telangiectasias can be seen. There are additional patches on the patient’s chest, but none around her mouth.
No sign of Raynaud disease is seen. However, the patient is adamant that this only appears when her hands are quite cold.
What is the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
Connecting these dots leads to the likelihood of CREST syndrome, a variant of systemic sclerosis (SS); the acronym stands for calcinosis, Raynaud disease, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia. The classification of CREST in the spectrum of SS is still open to discussion, but it is widely recognized as a real and distinct condition.
SS shares with CREST the involvement of anticentromere antibodies, but there are significant differences in the clinical course of each condition. Raynaud disease is often the first sign of CREST and can precede the other findings by years. Unlike SS, CREST typically spares the kidneys, and if it affects the lungs at all, it is through pulmonary artery hypertension and not fibrosis (the latter of which is seen in SS). Both conditions, however, can present with swelling of the hands and dysphagia.
Interpretation of these disparate findings requires the skill of a rheumatologist, who often shares management with other specialists.
As for differential diagnoses: Any one of these components can be a stand-alone diagnosis or can manifest with other diseases or syndromes. But when found together, they are highly suggestive of CREST. In this patient’s case, more testing needs to be done before a definitive diagnosis can be made.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
• CREST syndrome is considered a variant of systemic sclerosis but has significantly different features and clinical course.
• The components of CREST (calcinosis, Raynaud disease, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia) are often viewed as isolated phenomena by those unfamiliar with the condition.
• Raynaud disease is often the initial sign of CREST, preceding the rest by years.
• The telangiectasias seen with CREST often manifest on the hands and chest but can also be found on mucosal surfaces.
A 51-year-old woman is referred to dermatology for multiple problems she has had for several months—and, in some cases, years. The most immediate is a new nodule on the side of one thumb. Although it is asymptomatic, the fact that it simply “appeared” worries her, because her favorite uncle recently died of melanoma.
Several new lesions also materialized on her finger pads and chest. These do not cause symptoms either, but their newness makes them worrisome.
When asked about her health in general, the patient initially states it is “fine”—until her husband corrects her. She then recalls that she is being seen by various specialists, including a gastroenterologist for dysphagia-like symptoms and a rheumatologist for vague joint pains and what sounds like Raynaud disease.
EXAMINATION
On the lateral right thumb is a shallow, intradermal, white lesion. It is firm and round and measures 5 mm. No overlying skin changes (eg, redness or disruption of the skin surface) are observed. Under local anesthesia, a small incision is made in the lesion’s surface, allowing for exploration with small forceps; granular, gritty, white material is extracted.
On the affected thumb and two other fingers, telangiectasias can be seen. There are additional patches on the patient’s chest, but none around her mouth.
No sign of Raynaud disease is seen. However, the patient is adamant that this only appears when her hands are quite cold.
What is the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
Connecting these dots leads to the likelihood of CREST syndrome, a variant of systemic sclerosis (SS); the acronym stands for calcinosis, Raynaud disease, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia. The classification of CREST in the spectrum of SS is still open to discussion, but it is widely recognized as a real and distinct condition.
SS shares with CREST the involvement of anticentromere antibodies, but there are significant differences in the clinical course of each condition. Raynaud disease is often the first sign of CREST and can precede the other findings by years. Unlike SS, CREST typically spares the kidneys, and if it affects the lungs at all, it is through pulmonary artery hypertension and not fibrosis (the latter of which is seen in SS). Both conditions, however, can present with swelling of the hands and dysphagia.
Interpretation of these disparate findings requires the skill of a rheumatologist, who often shares management with other specialists.
As for differential diagnoses: Any one of these components can be a stand-alone diagnosis or can manifest with other diseases or syndromes. But when found together, they are highly suggestive of CREST. In this patient’s case, more testing needs to be done before a definitive diagnosis can be made.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
• CREST syndrome is considered a variant of systemic sclerosis but has significantly different features and clinical course.
• The components of CREST (calcinosis, Raynaud disease, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia) are often viewed as isolated phenomena by those unfamiliar with the condition.
• Raynaud disease is often the initial sign of CREST, preceding the rest by years.
• The telangiectasias seen with CREST often manifest on the hands and chest but can also be found on mucosal surfaces.
A 51-year-old woman is referred to dermatology for multiple problems she has had for several months—and, in some cases, years. The most immediate is a new nodule on the side of one thumb. Although it is asymptomatic, the fact that it simply “appeared” worries her, because her favorite uncle recently died of melanoma.
Several new lesions also materialized on her finger pads and chest. These do not cause symptoms either, but their newness makes them worrisome.
When asked about her health in general, the patient initially states it is “fine”—until her husband corrects her. She then recalls that she is being seen by various specialists, including a gastroenterologist for dysphagia-like symptoms and a rheumatologist for vague joint pains and what sounds like Raynaud disease.
EXAMINATION
On the lateral right thumb is a shallow, intradermal, white lesion. It is firm and round and measures 5 mm. No overlying skin changes (eg, redness or disruption of the skin surface) are observed. Under local anesthesia, a small incision is made in the lesion’s surface, allowing for exploration with small forceps; granular, gritty, white material is extracted.
On the affected thumb and two other fingers, telangiectasias can be seen. There are additional patches on the patient’s chest, but none around her mouth.
No sign of Raynaud disease is seen. However, the patient is adamant that this only appears when her hands are quite cold.
What is the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
Connecting these dots leads to the likelihood of CREST syndrome, a variant of systemic sclerosis (SS); the acronym stands for calcinosis, Raynaud disease, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia. The classification of CREST in the spectrum of SS is still open to discussion, but it is widely recognized as a real and distinct condition.
SS shares with CREST the involvement of anticentromere antibodies, but there are significant differences in the clinical course of each condition. Raynaud disease is often the first sign of CREST and can precede the other findings by years. Unlike SS, CREST typically spares the kidneys, and if it affects the lungs at all, it is through pulmonary artery hypertension and not fibrosis (the latter of which is seen in SS). Both conditions, however, can present with swelling of the hands and dysphagia.
Interpretation of these disparate findings requires the skill of a rheumatologist, who often shares management with other specialists.
As for differential diagnoses: Any one of these components can be a stand-alone diagnosis or can manifest with other diseases or syndromes. But when found together, they are highly suggestive of CREST. In this patient’s case, more testing needs to be done before a definitive diagnosis can be made.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
• CREST syndrome is considered a variant of systemic sclerosis but has significantly different features and clinical course.
• The components of CREST (calcinosis, Raynaud disease, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia) are often viewed as isolated phenomena by those unfamiliar with the condition.
• Raynaud disease is often the initial sign of CREST, preceding the rest by years.
• The telangiectasias seen with CREST often manifest on the hands and chest but can also be found on mucosal surfaces.