User login
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
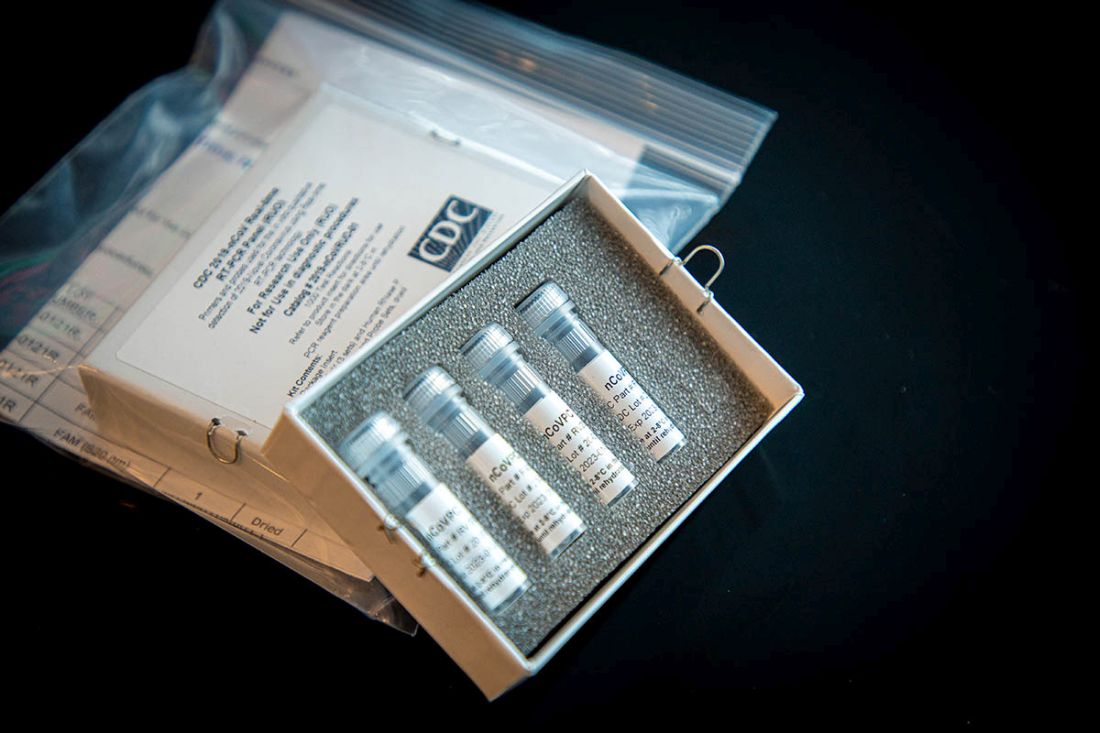
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.