User login
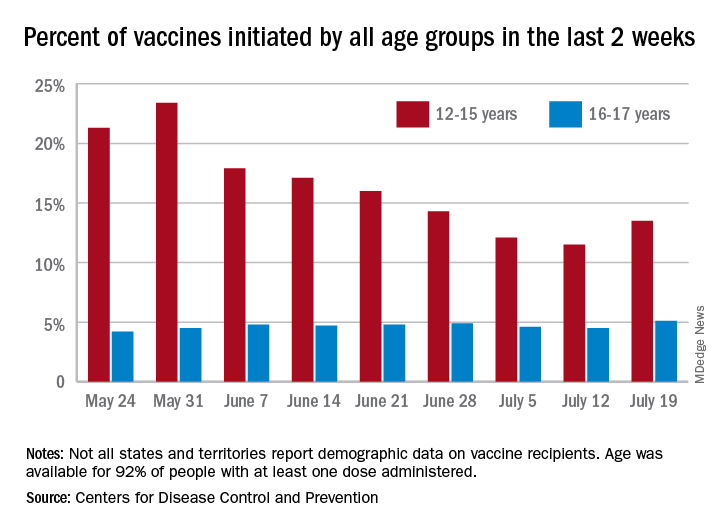
Children aged 12-15 years represented 13.5% of all first vaccinations received during the 2 weeks ending July 19, compared with 11.5% for the 2 weeks ending July 12, marking the first increase since the end of May. First vaccinations in 16- and 17-year-olds, who make up a much smaller share of the U.S. population, also went up, topping 5%, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in its COVID Data Tracker.
The total number of vaccine initiations was almost 250,000 for the week ending July 19, after dropping to a low of 201,000 the previous week. Before that, first vaccinations had fallen in 5 of the previous 6 weeks, going from 1.4 million on May 24 to 307,000 on July 5, the CDC said.
New cases of COVID-19, unfortunately, continued to follow the trend among the larger population: As of July 15, weekly cases in children were up by 179% since dropping to 8,400 on June 24, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in a joint report. The 23,551 new cases in children for the week ending July 15 were 15.9% of all cases reported.
With those new cases, the total number of children infected with COVID-19 comes to almost 4.1 million since the start of the pandemic, the AAP and CHA said. The CDC data indicate that just over 5.35 million children aged 12-15 years and 3.53 million 16- and 17-year-olds have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine and that 6.8 million children aged 12-17 are fully vaccinated.
Fully vaccinated children represent 26.4% of all 12- to 15-year-olds and 38.3% of the 16- 17-year-olds as of July 19. The corresponding numbers for those who have received at least one dose are 35.2% (ages 12-15) and 46.8% (16-17), the CDC said.
The AAP recently recommended in-person learning with universal masking in schools this fall “because a significant portion of the student population is not yet eligible for vaccines. ... Many schools will not have a system to monitor vaccine status of students, teachers and staff, and some communities overall have low vaccination uptake where the virus may be circulating more prominently.”

Children aged 12-15 years represented 13.5% of all first vaccinations received during the 2 weeks ending July 19, compared with 11.5% for the 2 weeks ending July 12, marking the first increase since the end of May. First vaccinations in 16- and 17-year-olds, who make up a much smaller share of the U.S. population, also went up, topping 5%, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in its COVID Data Tracker.
The total number of vaccine initiations was almost 250,000 for the week ending July 19, after dropping to a low of 201,000 the previous week. Before that, first vaccinations had fallen in 5 of the previous 6 weeks, going from 1.4 million on May 24 to 307,000 on July 5, the CDC said.
New cases of COVID-19, unfortunately, continued to follow the trend among the larger population: As of July 15, weekly cases in children were up by 179% since dropping to 8,400 on June 24, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in a joint report. The 23,551 new cases in children for the week ending July 15 were 15.9% of all cases reported.
With those new cases, the total number of children infected with COVID-19 comes to almost 4.1 million since the start of the pandemic, the AAP and CHA said. The CDC data indicate that just over 5.35 million children aged 12-15 years and 3.53 million 16- and 17-year-olds have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine and that 6.8 million children aged 12-17 are fully vaccinated.
Fully vaccinated children represent 26.4% of all 12- to 15-year-olds and 38.3% of the 16- 17-year-olds as of July 19. The corresponding numbers for those who have received at least one dose are 35.2% (ages 12-15) and 46.8% (16-17), the CDC said.
The AAP recently recommended in-person learning with universal masking in schools this fall “because a significant portion of the student population is not yet eligible for vaccines. ... Many schools will not have a system to monitor vaccine status of students, teachers and staff, and some communities overall have low vaccination uptake where the virus may be circulating more prominently.”

Children aged 12-15 years represented 13.5% of all first vaccinations received during the 2 weeks ending July 19, compared with 11.5% for the 2 weeks ending July 12, marking the first increase since the end of May. First vaccinations in 16- and 17-year-olds, who make up a much smaller share of the U.S. population, also went up, topping 5%, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in its COVID Data Tracker.
The total number of vaccine initiations was almost 250,000 for the week ending July 19, after dropping to a low of 201,000 the previous week. Before that, first vaccinations had fallen in 5 of the previous 6 weeks, going from 1.4 million on May 24 to 307,000 on July 5, the CDC said.
New cases of COVID-19, unfortunately, continued to follow the trend among the larger population: As of July 15, weekly cases in children were up by 179% since dropping to 8,400 on June 24, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in a joint report. The 23,551 new cases in children for the week ending July 15 were 15.9% of all cases reported.
With those new cases, the total number of children infected with COVID-19 comes to almost 4.1 million since the start of the pandemic, the AAP and CHA said. The CDC data indicate that just over 5.35 million children aged 12-15 years and 3.53 million 16- and 17-year-olds have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine and that 6.8 million children aged 12-17 are fully vaccinated.
Fully vaccinated children represent 26.4% of all 12- to 15-year-olds and 38.3% of the 16- 17-year-olds as of July 19. The corresponding numbers for those who have received at least one dose are 35.2% (ages 12-15) and 46.8% (16-17), the CDC said.
The AAP recently recommended in-person learning with universal masking in schools this fall “because a significant portion of the student population is not yet eligible for vaccines. ... Many schools will not have a system to monitor vaccine status of students, teachers and staff, and some communities overall have low vaccination uptake where the virus may be circulating more prominently.”