User login
The new breakfast of champions
We love a good ranking system here at LOTME world headquarters, especially the food-based ones. Luckily for us (and our readers), a new study published in Nature Food offers a food-based ranking system.
Sadly, unlike the last food-related ranking we covered, the Food Compass doesn’t tell you how much life you gain or lose from each food you eat down to the precise minute. Instead, it favors a more simple rating system from 1 to 100, with healthier foods scoring higher, and even incorporates mixed foods, not just single ingredients. This makes it better at assessing and comparing food combinations, rather than trying to mix and match the many ingredients that go into even relatively simple recipes.
The top and bottom of the rankings contain the usual suspects. Legumes and nuts, at 78.6, had the highest average score among the broad food groups, followed by fruits and then vegetables. Rounding out the bottom were sweets and savory snacks at 16.4. Among the individual foods, there were perfect scores in both directions: 100 for raw raspberries, while instant noodle soup and nonchocolate, ready-to-eat, nonfat pudding (very specific there) each earned a 1.
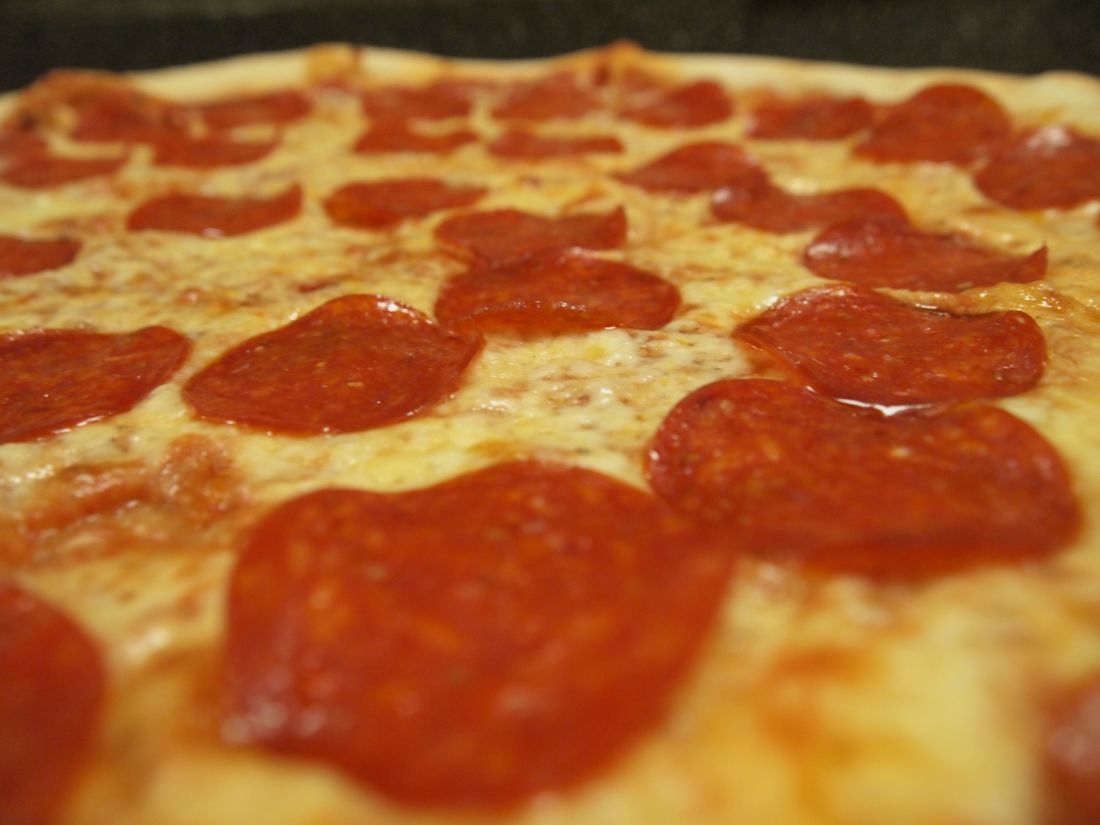
There are a few surprises in between. Nonfat cappuccino received a green light from the investigators, great news for the coffee drinkers out there. A serving of sweet potato chips scored better than a simple grilled chicken breast, and a slice of pizza, loaded up with extra meat and a thick crust, is still more nutritious than a bowl of corn flakes.
Neither is good for you, of course, but we’re still going to take this as a sign that pizza is the ideal breakfast food. Add that to your morning coffee, and you’re ready to start the day. Move over Wheaties, there’s a new breakfast of champions.
COVID-19 resisters, please step forward
Some people have all the luck with good genes, both inside and out.
Genetically speaking, humans are 99.9% the same, but that 0.1% is where things get interesting. Because of that 0.1% difference, some people are more likely to contract diseases such as HIV, while others might be more resistant. These small differences in genetic code could be the key to finding treatments for COVID-19.
“The introduction of SARS-CoV-2 to a naive population, on a global scale, has provided yet another demonstration of the remarkable clinical variability between individuals in the course of infection, ranging from asymptomatic infections to life-threatening disease,” the researchers said in Nature Immunology.
The investigators have been scouring the world to find people who might be resistant to SARS-CoV-2 and have enrolled over 400 individuals in a “dedicated resistance study cohort,” according to ScienceAlert.
The investigators are looking at households in which families were infected but one member did not show severe symptoms, or for individuals who have been around the virus multiple times and haven’t contracted it. They are also looking at blood types.
Enrollment is ongoing, so if you’ve been in contact with COVID-19 multiple times and have not gotten sick, scientists would like to hear from you.
Better living through parasitization
How would you like to triple your life span, while maintaining a youthful appearance and gaining special social standing and privileges?
Sounds pretty good, right, so what’s the catch? Well, you have to be infected with a tapeworm ... and you have to be an ant.
If you are an ant, here’s the deal: Workers of the species Temnothorax nylanderi that have tapeworms live much longer than uninfected workers, and while living out those longer lives they do less work and receive gifts of food.
In a study conducted at Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz, Germany, infected ants’ metabolic rates and lipid levels were similar to those of younger ants, and they appeared to remain in a permanent juvenile stage as a result of the infection, the investigators reported.
They tracked Temnothorax colonies for 3 years, at which point 95% of the uninfected workers had died but over half of the infected ants were still alive. Pretty great, right? Wrong. There was no joy in antville, for the uninfected workers had struck out. “Strained by the additional burden of their wormed-up nestmates, they seemed to be shunting care away from their queen. They were dying sooner than they might have if the colonies had remained parasite-free,” according to an article in the Atlantic.
Does this situation seem just a wee bit familiar? A small group lives longer, healthier lives and enjoys special privileges while the majority of that society works harder to support them? We’ll put it into the form of a chicken-and-egg argument: Which came first, the tapeworms or the one-percenters?
Laughing the pandemic stress away
Doomscrolling on social media has become one of the world’s favorite pastimes during the pandemic, but research shows that those memes about COVID-19 might combat the doom and gloom of the outside world.
A study recently published in Psychology of Popular Media showed that viewing memes, specifically those that were COVID-19 related, actually lessened the stress of the pandemic.
The researchers conducted a survey of 748 people aged 18-88 years. Each participant viewed three memes with text or three memes with text but no images. All three memes had similar cuteness levels (baby or adult), subject (animal or human), and caption (COVID-19–related or not). The participants were then asked to report on their stress levels and feelings before and after the memes.
The people who looked at memes felt less stressed and a higher humor level, especially the participants who received the COVID-19 memes. Study Finds said that they had more “pandemic-coping confidence” than those who got regular memes.
“While the World Health Organization recommended that people avoid too much COVID-related media for the benefit of their mental health, our research reveals that memes about COVID-19 could help people feel more confident in their ability to deal with the pandemic,” lead author Jessica Gall Myrick, PhD, said in a written statement. “The positive emotions associated with this type of content may make people feel psychologically safer and therefore better able to pay attention to the underlying messages related to health threats.”
So if you think you’ve been wasting time looking at memes during this pandemic, think again. It actually might keep you sane. Keep on scrolling!
Giving the gift of stress reduction
It’s a big week here at LOTME. You’ve just read our 100th edition, and to help celebrate that milestone – along with Count Your Buttons Day, Celebration of the Mind Day, and the International Day of the Nacho – we’re presenting an extra-special bonus feature, courtesy of Sad and Useless: The most depressive humor site on the Internet.
We hope you’ll stop your doomscrolling long enough to enjoy this stress-reducing meme. Thanks for reading!
The new breakfast of champions
We love a good ranking system here at LOTME world headquarters, especially the food-based ones. Luckily for us (and our readers), a new study published in Nature Food offers a food-based ranking system.
Sadly, unlike the last food-related ranking we covered, the Food Compass doesn’t tell you how much life you gain or lose from each food you eat down to the precise minute. Instead, it favors a more simple rating system from 1 to 100, with healthier foods scoring higher, and even incorporates mixed foods, not just single ingredients. This makes it better at assessing and comparing food combinations, rather than trying to mix and match the many ingredients that go into even relatively simple recipes.
The top and bottom of the rankings contain the usual suspects. Legumes and nuts, at 78.6, had the highest average score among the broad food groups, followed by fruits and then vegetables. Rounding out the bottom were sweets and savory snacks at 16.4. Among the individual foods, there were perfect scores in both directions: 100 for raw raspberries, while instant noodle soup and nonchocolate, ready-to-eat, nonfat pudding (very specific there) each earned a 1.
There are a few surprises in between. Nonfat cappuccino received a green light from the investigators, great news for the coffee drinkers out there. A serving of sweet potato chips scored better than a simple grilled chicken breast, and a slice of pizza, loaded up with extra meat and a thick crust, is still more nutritious than a bowl of corn flakes.
Neither is good for you, of course, but we’re still going to take this as a sign that pizza is the ideal breakfast food. Add that to your morning coffee, and you’re ready to start the day. Move over Wheaties, there’s a new breakfast of champions.
COVID-19 resisters, please step forward
Some people have all the luck with good genes, both inside and out.
Genetically speaking, humans are 99.9% the same, but that 0.1% is where things get interesting. Because of that 0.1% difference, some people are more likely to contract diseases such as HIV, while others might be more resistant. These small differences in genetic code could be the key to finding treatments for COVID-19.
“The introduction of SARS-CoV-2 to a naive population, on a global scale, has provided yet another demonstration of the remarkable clinical variability between individuals in the course of infection, ranging from asymptomatic infections to life-threatening disease,” the researchers said in Nature Immunology.
The investigators have been scouring the world to find people who might be resistant to SARS-CoV-2 and have enrolled over 400 individuals in a “dedicated resistance study cohort,” according to ScienceAlert.
The investigators are looking at households in which families were infected but one member did not show severe symptoms, or for individuals who have been around the virus multiple times and haven’t contracted it. They are also looking at blood types.
Enrollment is ongoing, so if you’ve been in contact with COVID-19 multiple times and have not gotten sick, scientists would like to hear from you.
Better living through parasitization
How would you like to triple your life span, while maintaining a youthful appearance and gaining special social standing and privileges?
Sounds pretty good, right, so what’s the catch? Well, you have to be infected with a tapeworm ... and you have to be an ant.
If you are an ant, here’s the deal: Workers of the species Temnothorax nylanderi that have tapeworms live much longer than uninfected workers, and while living out those longer lives they do less work and receive gifts of food.
In a study conducted at Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz, Germany, infected ants’ metabolic rates and lipid levels were similar to those of younger ants, and they appeared to remain in a permanent juvenile stage as a result of the infection, the investigators reported.
They tracked Temnothorax colonies for 3 years, at which point 95% of the uninfected workers had died but over half of the infected ants were still alive. Pretty great, right? Wrong. There was no joy in antville, for the uninfected workers had struck out. “Strained by the additional burden of their wormed-up nestmates, they seemed to be shunting care away from their queen. They were dying sooner than they might have if the colonies had remained parasite-free,” according to an article in the Atlantic.
Does this situation seem just a wee bit familiar? A small group lives longer, healthier lives and enjoys special privileges while the majority of that society works harder to support them? We’ll put it into the form of a chicken-and-egg argument: Which came first, the tapeworms or the one-percenters?
Laughing the pandemic stress away
Doomscrolling on social media has become one of the world’s favorite pastimes during the pandemic, but research shows that those memes about COVID-19 might combat the doom and gloom of the outside world.
A study recently published in Psychology of Popular Media showed that viewing memes, specifically those that were COVID-19 related, actually lessened the stress of the pandemic.
The researchers conducted a survey of 748 people aged 18-88 years. Each participant viewed three memes with text or three memes with text but no images. All three memes had similar cuteness levels (baby or adult), subject (animal or human), and caption (COVID-19–related or not). The participants were then asked to report on their stress levels and feelings before and after the memes.
The people who looked at memes felt less stressed and a higher humor level, especially the participants who received the COVID-19 memes. Study Finds said that they had more “pandemic-coping confidence” than those who got regular memes.
“While the World Health Organization recommended that people avoid too much COVID-related media for the benefit of their mental health, our research reveals that memes about COVID-19 could help people feel more confident in their ability to deal with the pandemic,” lead author Jessica Gall Myrick, PhD, said in a written statement. “The positive emotions associated with this type of content may make people feel psychologically safer and therefore better able to pay attention to the underlying messages related to health threats.”
So if you think you’ve been wasting time looking at memes during this pandemic, think again. It actually might keep you sane. Keep on scrolling!
Giving the gift of stress reduction
It’s a big week here at LOTME. You’ve just read our 100th edition, and to help celebrate that milestone – along with Count Your Buttons Day, Celebration of the Mind Day, and the International Day of the Nacho – we’re presenting an extra-special bonus feature, courtesy of Sad and Useless: The most depressive humor site on the Internet.
We hope you’ll stop your doomscrolling long enough to enjoy this stress-reducing meme. Thanks for reading!
The new breakfast of champions
We love a good ranking system here at LOTME world headquarters, especially the food-based ones. Luckily for us (and our readers), a new study published in Nature Food offers a food-based ranking system.
Sadly, unlike the last food-related ranking we covered, the Food Compass doesn’t tell you how much life you gain or lose from each food you eat down to the precise minute. Instead, it favors a more simple rating system from 1 to 100, with healthier foods scoring higher, and even incorporates mixed foods, not just single ingredients. This makes it better at assessing and comparing food combinations, rather than trying to mix and match the many ingredients that go into even relatively simple recipes.
The top and bottom of the rankings contain the usual suspects. Legumes and nuts, at 78.6, had the highest average score among the broad food groups, followed by fruits and then vegetables. Rounding out the bottom were sweets and savory snacks at 16.4. Among the individual foods, there were perfect scores in both directions: 100 for raw raspberries, while instant noodle soup and nonchocolate, ready-to-eat, nonfat pudding (very specific there) each earned a 1.
There are a few surprises in between. Nonfat cappuccino received a green light from the investigators, great news for the coffee drinkers out there. A serving of sweet potato chips scored better than a simple grilled chicken breast, and a slice of pizza, loaded up with extra meat and a thick crust, is still more nutritious than a bowl of corn flakes.
Neither is good for you, of course, but we’re still going to take this as a sign that pizza is the ideal breakfast food. Add that to your morning coffee, and you’re ready to start the day. Move over Wheaties, there’s a new breakfast of champions.
COVID-19 resisters, please step forward
Some people have all the luck with good genes, both inside and out.
Genetically speaking, humans are 99.9% the same, but that 0.1% is where things get interesting. Because of that 0.1% difference, some people are more likely to contract diseases such as HIV, while others might be more resistant. These small differences in genetic code could be the key to finding treatments for COVID-19.
“The introduction of SARS-CoV-2 to a naive population, on a global scale, has provided yet another demonstration of the remarkable clinical variability between individuals in the course of infection, ranging from asymptomatic infections to life-threatening disease,” the researchers said in Nature Immunology.
The investigators have been scouring the world to find people who might be resistant to SARS-CoV-2 and have enrolled over 400 individuals in a “dedicated resistance study cohort,” according to ScienceAlert.
The investigators are looking at households in which families were infected but one member did not show severe symptoms, or for individuals who have been around the virus multiple times and haven’t contracted it. They are also looking at blood types.
Enrollment is ongoing, so if you’ve been in contact with COVID-19 multiple times and have not gotten sick, scientists would like to hear from you.
Better living through parasitization
How would you like to triple your life span, while maintaining a youthful appearance and gaining special social standing and privileges?
Sounds pretty good, right, so what’s the catch? Well, you have to be infected with a tapeworm ... and you have to be an ant.
If you are an ant, here’s the deal: Workers of the species Temnothorax nylanderi that have tapeworms live much longer than uninfected workers, and while living out those longer lives they do less work and receive gifts of food.
In a study conducted at Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz, Germany, infected ants’ metabolic rates and lipid levels were similar to those of younger ants, and they appeared to remain in a permanent juvenile stage as a result of the infection, the investigators reported.
They tracked Temnothorax colonies for 3 years, at which point 95% of the uninfected workers had died but over half of the infected ants were still alive. Pretty great, right? Wrong. There was no joy in antville, for the uninfected workers had struck out. “Strained by the additional burden of their wormed-up nestmates, they seemed to be shunting care away from their queen. They were dying sooner than they might have if the colonies had remained parasite-free,” according to an article in the Atlantic.
Does this situation seem just a wee bit familiar? A small group lives longer, healthier lives and enjoys special privileges while the majority of that society works harder to support them? We’ll put it into the form of a chicken-and-egg argument: Which came first, the tapeworms or the one-percenters?
Laughing the pandemic stress away
Doomscrolling on social media has become one of the world’s favorite pastimes during the pandemic, but research shows that those memes about COVID-19 might combat the doom and gloom of the outside world.
A study recently published in Psychology of Popular Media showed that viewing memes, specifically those that were COVID-19 related, actually lessened the stress of the pandemic.
The researchers conducted a survey of 748 people aged 18-88 years. Each participant viewed three memes with text or three memes with text but no images. All three memes had similar cuteness levels (baby or adult), subject (animal or human), and caption (COVID-19–related or not). The participants were then asked to report on their stress levels and feelings before and after the memes.
The people who looked at memes felt less stressed and a higher humor level, especially the participants who received the COVID-19 memes. Study Finds said that they had more “pandemic-coping confidence” than those who got regular memes.
“While the World Health Organization recommended that people avoid too much COVID-related media for the benefit of their mental health, our research reveals that memes about COVID-19 could help people feel more confident in their ability to deal with the pandemic,” lead author Jessica Gall Myrick, PhD, said in a written statement. “The positive emotions associated with this type of content may make people feel psychologically safer and therefore better able to pay attention to the underlying messages related to health threats.”
So if you think you’ve been wasting time looking at memes during this pandemic, think again. It actually might keep you sane. Keep on scrolling!
Giving the gift of stress reduction
It’s a big week here at LOTME. You’ve just read our 100th edition, and to help celebrate that milestone – along with Count Your Buttons Day, Celebration of the Mind Day, and the International Day of the Nacho – we’re presenting an extra-special bonus feature, courtesy of Sad and Useless: The most depressive humor site on the Internet.
We hope you’ll stop your doomscrolling long enough to enjoy this stress-reducing meme. Thanks for reading!