User login
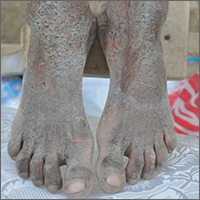
The FP diagnosed crusted scabies based on the patient’s clinical appearance and the distribution of crusting. He happened to have a dermatoscope and was able to see scabies mites moving and creating burrows under the skin. The mites generally appeared as dark triangles with light oval bodies. Crusted scabies is also known as "Norwegian scabies," but the preferred term is crusted scabies. Crusted scabies is more common in individuals who are immunosuppressed, chronically ill (for any reason), or who live in nursing homes.
The child's HIV test was negative and the FP never found out the cause of the cachexia. The diagnosis of crusted scabies was important for everyone involved in the transportation and care of this child. Once the diagnosis was known, everyone was careful to use gloves when caring for her so as to avoid acquiring scabies. The mother was almost certainly infested, along with other family members who’d been in direct contact with the child.
The recommended treatment for crusted scabies is oral ivermectin at a dose of 0.2 mg/kg (maximum dose, 12 mg) once for each infested person to be repeated in 10 days. Fortunately, the global health team had oral ivermectin to give to the child and the family. The FP also told the family to wash all of their clothes and bedclothes.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Usatine R, Chanoine P, Smith M. Scabies. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:575-580.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

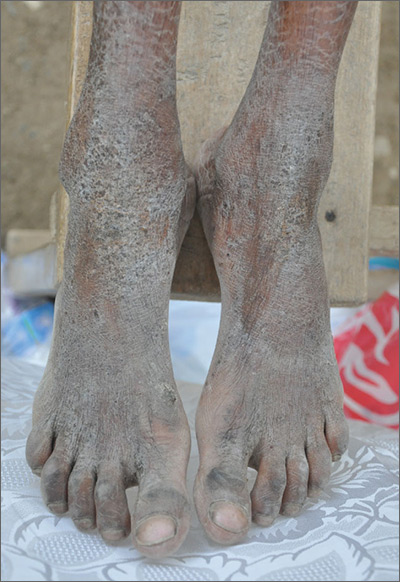
The FP diagnosed crusted scabies based on the patient’s clinical appearance and the distribution of crusting. He happened to have a dermatoscope and was able to see scabies mites moving and creating burrows under the skin. The mites generally appeared as dark triangles with light oval bodies. Crusted scabies is also known as "Norwegian scabies," but the preferred term is crusted scabies. Crusted scabies is more common in individuals who are immunosuppressed, chronically ill (for any reason), or who live in nursing homes.
The child's HIV test was negative and the FP never found out the cause of the cachexia. The diagnosis of crusted scabies was important for everyone involved in the transportation and care of this child. Once the diagnosis was known, everyone was careful to use gloves when caring for her so as to avoid acquiring scabies. The mother was almost certainly infested, along with other family members who’d been in direct contact with the child.
The recommended treatment for crusted scabies is oral ivermectin at a dose of 0.2 mg/kg (maximum dose, 12 mg) once for each infested person to be repeated in 10 days. Fortunately, the global health team had oral ivermectin to give to the child and the family. The FP also told the family to wash all of their clothes and bedclothes.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Usatine R, Chanoine P, Smith M. Scabies. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:575-580.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

The FP diagnosed crusted scabies based on the patient’s clinical appearance and the distribution of crusting. He happened to have a dermatoscope and was able to see scabies mites moving and creating burrows under the skin. The mites generally appeared as dark triangles with light oval bodies. Crusted scabies is also known as "Norwegian scabies," but the preferred term is crusted scabies. Crusted scabies is more common in individuals who are immunosuppressed, chronically ill (for any reason), or who live in nursing homes.
The child's HIV test was negative and the FP never found out the cause of the cachexia. The diagnosis of crusted scabies was important for everyone involved in the transportation and care of this child. Once the diagnosis was known, everyone was careful to use gloves when caring for her so as to avoid acquiring scabies. The mother was almost certainly infested, along with other family members who’d been in direct contact with the child.
The recommended treatment for crusted scabies is oral ivermectin at a dose of 0.2 mg/kg (maximum dose, 12 mg) once for each infested person to be repeated in 10 days. Fortunately, the global health team had oral ivermectin to give to the child and the family. The FP also told the family to wash all of their clothes and bedclothes.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Usatine R, Chanoine P, Smith M. Scabies. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:575-580.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com