User login
Several of the core medications for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) come with a well-known risk of causing hyperkalemia, to which many clinicians respond by pulling back on dosing or withdrawing the culprit drug.
But accompanying renin-angiotensin system–inhibiting agents with the potassium-sequestrant patiromer (Veltassa, Vifor Pharma) appears to shield patients against hyperkalemia enough that they can take more RASI medications at higher doses, suggests a randomized, a controlled study.
The DIAMOND trial’s HFrEF patients, who had current or a history of RASI-related hyperkalemia, added either patiromer or placebo to their guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT), which includes, even emphasizes, the culprit medication. They include ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs), angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs), and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs).
Those taking patiromer tolerated more intense RASI therapy – including MRAs, which are especially prone to causing hyperkalemia – than the patients assigned to placebo. They also maintained lower potassium concentrations and experienced fewer clinically important hyperkalemia episodes, reported Javed Butler, MD, MPH, MBA, Baylor Scott and White Research Institute, Dallas, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The apparent benefit from patiromer came in part from an advantage for a composite hyperkalemia-event endpoint that included mortality, Dr. Butler noted. That advantage seemed to hold regardless of age, sex, body mass index, HFrEF symptom severity, or initial natriuretic peptide levels.
Patients who took patiromer, compared with those who took placebo, showed a 37% reduction in risk for hyperkalemia (P = .006), defined as potassium levels exceeding 5.5 mEq/L, over a median follow-up of 27 weeks. They were 38% less likely to have their MRA dosage reduced to below target level (P = .006).
More patients in the patiromer group than in the control group attained at least 50% of target dosage for MRAs and ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or ARNIs (92% vs. 87%; P = .015).
Patients with HFrEF are unlikely to achieve best possible outcomes without GDMT optimization, but failure to optimize is often attributed to hyperkalemia concerns. DIAMOND, Dr. Butler said, suggests that, by adding the potassium sequestrant to GDMT, “you can simultaneously control potassium and optimize RASI therapy.” Many clinicians seem to believe they can achieve only one or the other.
DIAMOND was too underpowered to show whether preventing hyperkalemia with patiromer could improve clinical outcomes. But failure to optimize RASI medication in HFrEF can worsen risk for heart failure events and death. So “it stands to reason that optimization of RASI therapy without a concomitant risk of hyperkalemia may, in the long run, lead to better outcomes for these patients,” Dr. Butler said in an interview.
Given the drug’s ability to keep potassium levels in check during RASI therapy, Dr. Butler said, “hypokalemia should not be a reason for suboptimal therapy.”
Patiromer and other potassium sequestrants have been available in the United States and Europe for 4-6 years, but their value as adjuncts to RASI medication in HFrEF or other heart failure has been unclear.
“There’s a good opportunity to expand the use of the drug. The question is, in whom and when?” James L. Januzzi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
Some HFrEF patients on GDMT “should be treated with patiromer. The bigger question is, should we give someone who has a history of hyperkalemia another chance at GDMT before we treat them with patiromer? Because they may not necessarily develop hyperkalemia a second time,” said Dr. Januzzi, who was on the DIAMOND endpoint-adjudication committee.
Among the most notable findings of the trial, he said, is that the number of people who developed hyperkalemia on RASI medication, although significantly elevated, “wasn’t as high as they expected it would be,” he said. “The data from DIAMOND argue that if a really significant majority does not become hyperkalemic on rechallenge, jumping straight to a potassium-binding drug may be premature.”
Physicians across specialties can differ in how they interpret potassium-level elevation and can use various cut points to flag when to stop RASI medication or at least hold back on up-titration, Dr. Butler observed. “Cardiologists have a different threshold of potassium that they tolerate than say, for instance, a nephrologist.”
Useful, then, might be a way to tell which patients are most likely to develop hyperkalemia with RASI up-titration and so might benefit from a potassium-binding agent right away. But DIAMOND, Dr. Butler said, “does not necessarily define any patient phenotype or any potassium level where we would say that you should use a potassium binder.”
The trial entered 1,642 patients with HFrEF and current or past RASI-related hyperkalemia to a 12-week run-in phase for optimization of GDMT with patiromer. The trial was conducted at nearly 400 centers in 21 countries.
RASI medication could be optimized in 85% of the cohort, from which 878 patients were randomly assigned either to continue optimized GDMT with patiromer or to have the potassium-sequestrant replaced with a placebo.
The patients on patiromer showed a 0.03-mEq/L mean rise in serum potassium levels from randomization to the end of the study, the primary endpoint, compared with a 0.13 mEq/L mean increase for those in the control group (P < .001), Dr. Butler reported.
The win ratio for a RASI-use score hierarchically featuring cardiovascular death and CV hospitalization for hyperkalemia at several levels of severity was 1.25 (95% confidence interval, 1.003-1.564; P = .048), favoring the patiromer group. The win ratio solely for hyperkalemia-related events also favored patients on patiromer, at 1.53 (95% CI, 1.23-1.91; P < .001).
Patiromer also seemed well tolerated, Dr. Butler said.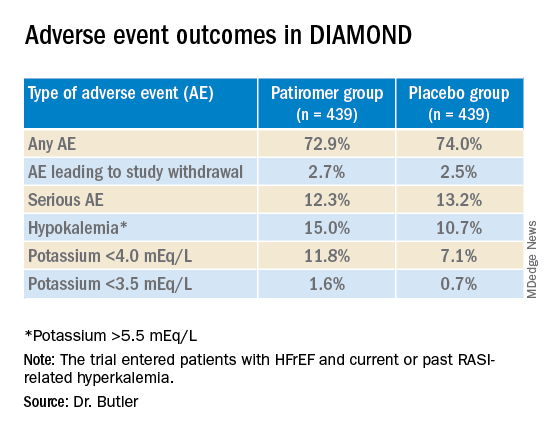
Hyperkalemia is “one of the most common excuses” from clinicians for failing to up-titrate RASI medicine in patients with heart failure, Dr. Januzzi said. DIAMOND was less about patiromer itself than about ways “to facilitate better GDMT, where we’re really falling short of the mark. During the run-in phase they were able to get the vast majority of individuals to target, which to me is a critically important point, and emblematic of the need for things that facilitate this kind of excellent care.”
DIAMOND was funded by Vifor Pharma. Dr. Butler disclosed receiving consulting fees from Abbott, Adrenomed, Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, Array, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, G3 Pharma, Impulse Dynamics, Innolife, Janssen, LivaNova, Luitpold, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Relypsa, Sequana Medical, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Januzzi disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Abbott Laboratories, Imbria, Jana Care, Novartis, Prevencio, and Roche Diagnostics; serving on a data safety monitoring board for AbbVie, Amgen, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, Beyer, CVRx, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals North America; and receiving research grants from Abbott Laboratories, Janssen, and Vifor Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Several of the core medications for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) come with a well-known risk of causing hyperkalemia, to which many clinicians respond by pulling back on dosing or withdrawing the culprit drug.
But accompanying renin-angiotensin system–inhibiting agents with the potassium-sequestrant patiromer (Veltassa, Vifor Pharma) appears to shield patients against hyperkalemia enough that they can take more RASI medications at higher doses, suggests a randomized, a controlled study.
The DIAMOND trial’s HFrEF patients, who had current or a history of RASI-related hyperkalemia, added either patiromer or placebo to their guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT), which includes, even emphasizes, the culprit medication. They include ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs), angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs), and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs).
Those taking patiromer tolerated more intense RASI therapy – including MRAs, which are especially prone to causing hyperkalemia – than the patients assigned to placebo. They also maintained lower potassium concentrations and experienced fewer clinically important hyperkalemia episodes, reported Javed Butler, MD, MPH, MBA, Baylor Scott and White Research Institute, Dallas, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The apparent benefit from patiromer came in part from an advantage for a composite hyperkalemia-event endpoint that included mortality, Dr. Butler noted. That advantage seemed to hold regardless of age, sex, body mass index, HFrEF symptom severity, or initial natriuretic peptide levels.
Patients who took patiromer, compared with those who took placebo, showed a 37% reduction in risk for hyperkalemia (P = .006), defined as potassium levels exceeding 5.5 mEq/L, over a median follow-up of 27 weeks. They were 38% less likely to have their MRA dosage reduced to below target level (P = .006).
More patients in the patiromer group than in the control group attained at least 50% of target dosage for MRAs and ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or ARNIs (92% vs. 87%; P = .015).
Patients with HFrEF are unlikely to achieve best possible outcomes without GDMT optimization, but failure to optimize is often attributed to hyperkalemia concerns. DIAMOND, Dr. Butler said, suggests that, by adding the potassium sequestrant to GDMT, “you can simultaneously control potassium and optimize RASI therapy.” Many clinicians seem to believe they can achieve only one or the other.
DIAMOND was too underpowered to show whether preventing hyperkalemia with patiromer could improve clinical outcomes. But failure to optimize RASI medication in HFrEF can worsen risk for heart failure events and death. So “it stands to reason that optimization of RASI therapy without a concomitant risk of hyperkalemia may, in the long run, lead to better outcomes for these patients,” Dr. Butler said in an interview.
Given the drug’s ability to keep potassium levels in check during RASI therapy, Dr. Butler said, “hypokalemia should not be a reason for suboptimal therapy.”
Patiromer and other potassium sequestrants have been available in the United States and Europe for 4-6 years, but their value as adjuncts to RASI medication in HFrEF or other heart failure has been unclear.
“There’s a good opportunity to expand the use of the drug. The question is, in whom and when?” James L. Januzzi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
Some HFrEF patients on GDMT “should be treated with patiromer. The bigger question is, should we give someone who has a history of hyperkalemia another chance at GDMT before we treat them with patiromer? Because they may not necessarily develop hyperkalemia a second time,” said Dr. Januzzi, who was on the DIAMOND endpoint-adjudication committee.
Among the most notable findings of the trial, he said, is that the number of people who developed hyperkalemia on RASI medication, although significantly elevated, “wasn’t as high as they expected it would be,” he said. “The data from DIAMOND argue that if a really significant majority does not become hyperkalemic on rechallenge, jumping straight to a potassium-binding drug may be premature.”
Physicians across specialties can differ in how they interpret potassium-level elevation and can use various cut points to flag when to stop RASI medication or at least hold back on up-titration, Dr. Butler observed. “Cardiologists have a different threshold of potassium that they tolerate than say, for instance, a nephrologist.”
Useful, then, might be a way to tell which patients are most likely to develop hyperkalemia with RASI up-titration and so might benefit from a potassium-binding agent right away. But DIAMOND, Dr. Butler said, “does not necessarily define any patient phenotype or any potassium level where we would say that you should use a potassium binder.”
The trial entered 1,642 patients with HFrEF and current or past RASI-related hyperkalemia to a 12-week run-in phase for optimization of GDMT with patiromer. The trial was conducted at nearly 400 centers in 21 countries.
RASI medication could be optimized in 85% of the cohort, from which 878 patients were randomly assigned either to continue optimized GDMT with patiromer or to have the potassium-sequestrant replaced with a placebo.
The patients on patiromer showed a 0.03-mEq/L mean rise in serum potassium levels from randomization to the end of the study, the primary endpoint, compared with a 0.13 mEq/L mean increase for those in the control group (P < .001), Dr. Butler reported.
The win ratio for a RASI-use score hierarchically featuring cardiovascular death and CV hospitalization for hyperkalemia at several levels of severity was 1.25 (95% confidence interval, 1.003-1.564; P = .048), favoring the patiromer group. The win ratio solely for hyperkalemia-related events also favored patients on patiromer, at 1.53 (95% CI, 1.23-1.91; P < .001).
Patiromer also seemed well tolerated, Dr. Butler said.
Hyperkalemia is “one of the most common excuses” from clinicians for failing to up-titrate RASI medicine in patients with heart failure, Dr. Januzzi said. DIAMOND was less about patiromer itself than about ways “to facilitate better GDMT, where we’re really falling short of the mark. During the run-in phase they were able to get the vast majority of individuals to target, which to me is a critically important point, and emblematic of the need for things that facilitate this kind of excellent care.”
DIAMOND was funded by Vifor Pharma. Dr. Butler disclosed receiving consulting fees from Abbott, Adrenomed, Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, Array, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, G3 Pharma, Impulse Dynamics, Innolife, Janssen, LivaNova, Luitpold, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Relypsa, Sequana Medical, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Januzzi disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Abbott Laboratories, Imbria, Jana Care, Novartis, Prevencio, and Roche Diagnostics; serving on a data safety monitoring board for AbbVie, Amgen, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, Beyer, CVRx, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals North America; and receiving research grants from Abbott Laboratories, Janssen, and Vifor Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Several of the core medications for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) come with a well-known risk of causing hyperkalemia, to which many clinicians respond by pulling back on dosing or withdrawing the culprit drug.
But accompanying renin-angiotensin system–inhibiting agents with the potassium-sequestrant patiromer (Veltassa, Vifor Pharma) appears to shield patients against hyperkalemia enough that they can take more RASI medications at higher doses, suggests a randomized, a controlled study.
The DIAMOND trial’s HFrEF patients, who had current or a history of RASI-related hyperkalemia, added either patiromer or placebo to their guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT), which includes, even emphasizes, the culprit medication. They include ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs), angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs), and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs).
Those taking patiromer tolerated more intense RASI therapy – including MRAs, which are especially prone to causing hyperkalemia – than the patients assigned to placebo. They also maintained lower potassium concentrations and experienced fewer clinically important hyperkalemia episodes, reported Javed Butler, MD, MPH, MBA, Baylor Scott and White Research Institute, Dallas, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The apparent benefit from patiromer came in part from an advantage for a composite hyperkalemia-event endpoint that included mortality, Dr. Butler noted. That advantage seemed to hold regardless of age, sex, body mass index, HFrEF symptom severity, or initial natriuretic peptide levels.
Patients who took patiromer, compared with those who took placebo, showed a 37% reduction in risk for hyperkalemia (P = .006), defined as potassium levels exceeding 5.5 mEq/L, over a median follow-up of 27 weeks. They were 38% less likely to have their MRA dosage reduced to below target level (P = .006).
More patients in the patiromer group than in the control group attained at least 50% of target dosage for MRAs and ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or ARNIs (92% vs. 87%; P = .015).
Patients with HFrEF are unlikely to achieve best possible outcomes without GDMT optimization, but failure to optimize is often attributed to hyperkalemia concerns. DIAMOND, Dr. Butler said, suggests that, by adding the potassium sequestrant to GDMT, “you can simultaneously control potassium and optimize RASI therapy.” Many clinicians seem to believe they can achieve only one or the other.
DIAMOND was too underpowered to show whether preventing hyperkalemia with patiromer could improve clinical outcomes. But failure to optimize RASI medication in HFrEF can worsen risk for heart failure events and death. So “it stands to reason that optimization of RASI therapy without a concomitant risk of hyperkalemia may, in the long run, lead to better outcomes for these patients,” Dr. Butler said in an interview.
Given the drug’s ability to keep potassium levels in check during RASI therapy, Dr. Butler said, “hypokalemia should not be a reason for suboptimal therapy.”
Patiromer and other potassium sequestrants have been available in the United States and Europe for 4-6 years, but their value as adjuncts to RASI medication in HFrEF or other heart failure has been unclear.
“There’s a good opportunity to expand the use of the drug. The question is, in whom and when?” James L. Januzzi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
Some HFrEF patients on GDMT “should be treated with patiromer. The bigger question is, should we give someone who has a history of hyperkalemia another chance at GDMT before we treat them with patiromer? Because they may not necessarily develop hyperkalemia a second time,” said Dr. Januzzi, who was on the DIAMOND endpoint-adjudication committee.
Among the most notable findings of the trial, he said, is that the number of people who developed hyperkalemia on RASI medication, although significantly elevated, “wasn’t as high as they expected it would be,” he said. “The data from DIAMOND argue that if a really significant majority does not become hyperkalemic on rechallenge, jumping straight to a potassium-binding drug may be premature.”
Physicians across specialties can differ in how they interpret potassium-level elevation and can use various cut points to flag when to stop RASI medication or at least hold back on up-titration, Dr. Butler observed. “Cardiologists have a different threshold of potassium that they tolerate than say, for instance, a nephrologist.”
Useful, then, might be a way to tell which patients are most likely to develop hyperkalemia with RASI up-titration and so might benefit from a potassium-binding agent right away. But DIAMOND, Dr. Butler said, “does not necessarily define any patient phenotype or any potassium level where we would say that you should use a potassium binder.”
The trial entered 1,642 patients with HFrEF and current or past RASI-related hyperkalemia to a 12-week run-in phase for optimization of GDMT with patiromer. The trial was conducted at nearly 400 centers in 21 countries.
RASI medication could be optimized in 85% of the cohort, from which 878 patients were randomly assigned either to continue optimized GDMT with patiromer or to have the potassium-sequestrant replaced with a placebo.
The patients on patiromer showed a 0.03-mEq/L mean rise in serum potassium levels from randomization to the end of the study, the primary endpoint, compared with a 0.13 mEq/L mean increase for those in the control group (P < .001), Dr. Butler reported.
The win ratio for a RASI-use score hierarchically featuring cardiovascular death and CV hospitalization for hyperkalemia at several levels of severity was 1.25 (95% confidence interval, 1.003-1.564; P = .048), favoring the patiromer group. The win ratio solely for hyperkalemia-related events also favored patients on patiromer, at 1.53 (95% CI, 1.23-1.91; P < .001).
Patiromer also seemed well tolerated, Dr. Butler said.
Hyperkalemia is “one of the most common excuses” from clinicians for failing to up-titrate RASI medicine in patients with heart failure, Dr. Januzzi said. DIAMOND was less about patiromer itself than about ways “to facilitate better GDMT, where we’re really falling short of the mark. During the run-in phase they were able to get the vast majority of individuals to target, which to me is a critically important point, and emblematic of the need for things that facilitate this kind of excellent care.”
DIAMOND was funded by Vifor Pharma. Dr. Butler disclosed receiving consulting fees from Abbott, Adrenomed, Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, Array, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, G3 Pharma, Impulse Dynamics, Innolife, Janssen, LivaNova, Luitpold, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Relypsa, Sequana Medical, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Januzzi disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Abbott Laboratories, Imbria, Jana Care, Novartis, Prevencio, and Roche Diagnostics; serving on a data safety monitoring board for AbbVie, Amgen, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, Beyer, CVRx, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals North America; and receiving research grants from Abbott Laboratories, Janssen, and Vifor Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2022


