User login
Fever in the youngest of infants creates a challenge for the pediatric clinician. Fever is a common presentation for serious bacterial infection (SBI) although most fevers are due to viral infection. However, the clinical presentation does not necessarily differ, and the risk for a poor outcome in this age group is substantial.
In the early stages of my pediatric career, most febrile infants less than 90 days of age were evaluated for sepsis, admitted, and treated with antibiotics pending culture results. Group B streptococcal sepsis or Escherichia coli sepsis were common in the first month of life, and Haemophilus influenza type B or Streptococcus pneumoniae in the second and third months of life. The approach to fever in the first 90 days has changed following both the introduction of haemophilus and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines, the experience with risk stratification criteria for identifying infants at low risk for SBI, and the recognition of urinary tract infection (UTI) as a common source of infection in this age group as well as development of criteria for diagnosis.
A further nuance was subsequently added with the introduction of rapid diagnostics for viral infection. Byington et al. found that the majority of febrile infants less than 90 days of age had viral infection with enterovirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza or rotavirus.1 Using the Rochester risk stratification and the presence or absence of viral infection, she demonstrated that the risk of SBI was reduced in both high- and low-risk infants in the presence of viral infection; in low risk infants with viral infection, SBI was identified in 1.8%, compared with 3.1% in those without viral infection, and in high-risk infants. 5.5% has SBI when viral infection was found, compared to 16.7% in the absence of viral infection. She also proposed risk features to identify those infected with herpes simplex virus; age less than 42 days, vesicular rash, elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), CSF pleocytosis, and seizure or twitching.
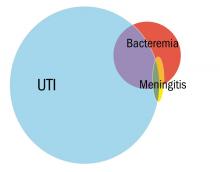
Greenhow et al. reported on the experience with “serious” bacterial infection in infants less than 90 days of age receiving care at Northern California Kaiser Permanente during the period 2005-2011.2 As pictured, the majority of children have UTI, and smaller numbers have bacteremia or meningitis. A small group of children with UTI have urosepsis as well; those with urosepsis can be differentiated from those with only UTI by age (less than 21 days), clinical exam (ill appearing), and elevated C reactive protein (greater than 20 mg/L) or elevated procalcitonin (greater than 0.5 ng/mL).3 Further evaluation of procalcitonin by other groups appears to validate its role in identifying children at low risk of SBI (procalcitonin less than 0.3 ng/mL).4
Currently, studies of febrile infants less than 90 days of age demonstrate that E. coli dominates in bacteremia, UTI, and meningitis, with Group B streptococcus as the next most frequent pathogen identified.2 Increasingly ampicillin resistance has been reported among E. coli isolates from both early- and late-onset disease as well as rare isolates that are resistant to third generation cephalosporins or gentamicin. Surveillance to identify changes in antimicrobial susceptibility will need to be ongoing to ensure that current approaches for initial therapy in high-risk infants aligns with current susceptibility patterns.
Dr. Pelton is chief of the section of pediatric infectious diseases and coordinator of the maternal-child HIV program at Boston Medical Center. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2004 Jun;113(6):1662-6.
2. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Jun;33(6):595-9.
3. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015 Jan;34(1):17-21.
4. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170(1):17-18.
5. “AAP Proposes Update to Evaluating, Managing Febrile Infants Guideline,” The Hospitalist, 2016.
Fever in the youngest of infants creates a challenge for the pediatric clinician. Fever is a common presentation for serious bacterial infection (SBI) although most fevers are due to viral infection. However, the clinical presentation does not necessarily differ, and the risk for a poor outcome in this age group is substantial.
In the early stages of my pediatric career, most febrile infants less than 90 days of age were evaluated for sepsis, admitted, and treated with antibiotics pending culture results. Group B streptococcal sepsis or Escherichia coli sepsis were common in the first month of life, and Haemophilus influenza type B or Streptococcus pneumoniae in the second and third months of life. The approach to fever in the first 90 days has changed following both the introduction of haemophilus and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines, the experience with risk stratification criteria for identifying infants at low risk for SBI, and the recognition of urinary tract infection (UTI) as a common source of infection in this age group as well as development of criteria for diagnosis.
A further nuance was subsequently added with the introduction of rapid diagnostics for viral infection. Byington et al. found that the majority of febrile infants less than 90 days of age had viral infection with enterovirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza or rotavirus.1 Using the Rochester risk stratification and the presence or absence of viral infection, she demonstrated that the risk of SBI was reduced in both high- and low-risk infants in the presence of viral infection; in low risk infants with viral infection, SBI was identified in 1.8%, compared with 3.1% in those without viral infection, and in high-risk infants. 5.5% has SBI when viral infection was found, compared to 16.7% in the absence of viral infection. She also proposed risk features to identify those infected with herpes simplex virus; age less than 42 days, vesicular rash, elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), CSF pleocytosis, and seizure or twitching.
Greenhow et al. reported on the experience with “serious” bacterial infection in infants less than 90 days of age receiving care at Northern California Kaiser Permanente during the period 2005-2011.2 As pictured, the majority of children have UTI, and smaller numbers have bacteremia or meningitis. A small group of children with UTI have urosepsis as well; those with urosepsis can be differentiated from those with only UTI by age (less than 21 days), clinical exam (ill appearing), and elevated C reactive protein (greater than 20 mg/L) or elevated procalcitonin (greater than 0.5 ng/mL).3 Further evaluation of procalcitonin by other groups appears to validate its role in identifying children at low risk of SBI (procalcitonin less than 0.3 ng/mL).4
Currently, studies of febrile infants less than 90 days of age demonstrate that E. coli dominates in bacteremia, UTI, and meningitis, with Group B streptococcus as the next most frequent pathogen identified.2 Increasingly ampicillin resistance has been reported among E. coli isolates from both early- and late-onset disease as well as rare isolates that are resistant to third generation cephalosporins or gentamicin. Surveillance to identify changes in antimicrobial susceptibility will need to be ongoing to ensure that current approaches for initial therapy in high-risk infants aligns with current susceptibility patterns.
Dr. Pelton is chief of the section of pediatric infectious diseases and coordinator of the maternal-child HIV program at Boston Medical Center. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2004 Jun;113(6):1662-6.
2. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Jun;33(6):595-9.
3. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015 Jan;34(1):17-21.
4. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170(1):17-18.
5. “AAP Proposes Update to Evaluating, Managing Febrile Infants Guideline,” The Hospitalist, 2016.
Fever in the youngest of infants creates a challenge for the pediatric clinician. Fever is a common presentation for serious bacterial infection (SBI) although most fevers are due to viral infection. However, the clinical presentation does not necessarily differ, and the risk for a poor outcome in this age group is substantial.
In the early stages of my pediatric career, most febrile infants less than 90 days of age were evaluated for sepsis, admitted, and treated with antibiotics pending culture results. Group B streptococcal sepsis or Escherichia coli sepsis were common in the first month of life, and Haemophilus influenza type B or Streptococcus pneumoniae in the second and third months of life. The approach to fever in the first 90 days has changed following both the introduction of haemophilus and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines, the experience with risk stratification criteria for identifying infants at low risk for SBI, and the recognition of urinary tract infection (UTI) as a common source of infection in this age group as well as development of criteria for diagnosis.
A further nuance was subsequently added with the introduction of rapid diagnostics for viral infection. Byington et al. found that the majority of febrile infants less than 90 days of age had viral infection with enterovirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza or rotavirus.1 Using the Rochester risk stratification and the presence or absence of viral infection, she demonstrated that the risk of SBI was reduced in both high- and low-risk infants in the presence of viral infection; in low risk infants with viral infection, SBI was identified in 1.8%, compared with 3.1% in those without viral infection, and in high-risk infants. 5.5% has SBI when viral infection was found, compared to 16.7% in the absence of viral infection. She also proposed risk features to identify those infected with herpes simplex virus; age less than 42 days, vesicular rash, elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), CSF pleocytosis, and seizure or twitching.
Greenhow et al. reported on the experience with “serious” bacterial infection in infants less than 90 days of age receiving care at Northern California Kaiser Permanente during the period 2005-2011.2 As pictured, the majority of children have UTI, and smaller numbers have bacteremia or meningitis. A small group of children with UTI have urosepsis as well; those with urosepsis can be differentiated from those with only UTI by age (less than 21 days), clinical exam (ill appearing), and elevated C reactive protein (greater than 20 mg/L) or elevated procalcitonin (greater than 0.5 ng/mL).3 Further evaluation of procalcitonin by other groups appears to validate its role in identifying children at low risk of SBI (procalcitonin less than 0.3 ng/mL).4
Currently, studies of febrile infants less than 90 days of age demonstrate that E. coli dominates in bacteremia, UTI, and meningitis, with Group B streptococcus as the next most frequent pathogen identified.2 Increasingly ampicillin resistance has been reported among E. coli isolates from both early- and late-onset disease as well as rare isolates that are resistant to third generation cephalosporins or gentamicin. Surveillance to identify changes in antimicrobial susceptibility will need to be ongoing to ensure that current approaches for initial therapy in high-risk infants aligns with current susceptibility patterns.
Dr. Pelton is chief of the section of pediatric infectious diseases and coordinator of the maternal-child HIV program at Boston Medical Center. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2004 Jun;113(6):1662-6.
2. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Jun;33(6):595-9.
3. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015 Jan;34(1):17-21.
4. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170(1):17-18.
5. “AAP Proposes Update to Evaluating, Managing Febrile Infants Guideline,” The Hospitalist, 2016.