User login
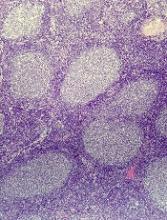
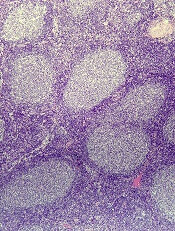
Autologous and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) both offer excellent long-term survival in follicular lymphoma (FL) patients who experience early treatment failure, an analysis of a large transplant registry suggests.
Five-year survival rates exceeded 70% for patients who received autologous or matched sibling donor (MSD) transplants, according to the analysis of the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) database. The database included 440 patients who underwent a procedure between 2002 and 2014.
“Until better risk-stratification tools are available for FL, auto-HCT and MSD allo-HCT should be considered as effective treatment options with excellent long-term survival for high-risk patients as defined by early treatment failure,” Sonali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago, and co-investigators wrote in the journal Cancer.
Early treatment failure in FL is associated with worse overall survival. In the National LymphoCare Study (NLCS), patients who received upfront R-CHOP therapy and progressed within 24 months had a 5-year overall survival of 50%, versus 90% for patients without early progression.
By contrast, survival figures in the present study are “provocatively higher” than those in the NLCS, in which only 8 out of 110 patients underwent HCT, Dr Smith and co-authors said.
Dr Smith’s study showed that with a median follow-up of 69 to 73 months, adjusted probability of 5-year overall survival was 70% for autologous and 73% for MSD HCT, versus 49% for matched unrelated donor HCT (P=0.0008).
Ryan C. Lynch, MD, and Ajay K. Gopal, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington, said that the finding “convincingly demonstrates” the benefit of transplant in the setting of early treatment failure.
“Select patients (particularly younger patients) with chemoresponsive disease who understand the risk-benefit ratio in comparison with currently approved and experimental therapies still remain good candidates for autologous HCT,” Drs Lynch and Gopal said in an editorial.
“For older patients or patients with comorbidities, we would continue to recommend clinical trials or treatment with an approved PI3K inhibitor,” they added.
The study by Dr Smith and colleagues is not the first to show a benefit of HCT in this clinical scenario. In a recent NLCS/CIBMTR analysis of FL patients, 5-year overall survival was 73% for those undergoing autologous HCT done within a year of early treatment failure, versus 60% for those who did not (P=0.05).
The two studies “collectively suggest that transplantation should be considered in this high-risk group of patients with early relapse,” Dr Smith and co-authors wrote.
Autologous and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) both offer excellent long-term survival in follicular lymphoma (FL) patients who experience early treatment failure, an analysis of a large transplant registry suggests.
Five-year survival rates exceeded 70% for patients who received autologous or matched sibling donor (MSD) transplants, according to the analysis of the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) database. The database included 440 patients who underwent a procedure between 2002 and 2014.
“Until better risk-stratification tools are available for FL, auto-HCT and MSD allo-HCT should be considered as effective treatment options with excellent long-term survival for high-risk patients as defined by early treatment failure,” Sonali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago, and co-investigators wrote in the journal Cancer.
Early treatment failure in FL is associated with worse overall survival. In the National LymphoCare Study (NLCS), patients who received upfront R-CHOP therapy and progressed within 24 months had a 5-year overall survival of 50%, versus 90% for patients without early progression.
By contrast, survival figures in the present study are “provocatively higher” than those in the NLCS, in which only 8 out of 110 patients underwent HCT, Dr Smith and co-authors said.
Dr Smith’s study showed that with a median follow-up of 69 to 73 months, adjusted probability of 5-year overall survival was 70% for autologous and 73% for MSD HCT, versus 49% for matched unrelated donor HCT (P=0.0008).
Ryan C. Lynch, MD, and Ajay K. Gopal, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington, said that the finding “convincingly demonstrates” the benefit of transplant in the setting of early treatment failure.
“Select patients (particularly younger patients) with chemoresponsive disease who understand the risk-benefit ratio in comparison with currently approved and experimental therapies still remain good candidates for autologous HCT,” Drs Lynch and Gopal said in an editorial.
“For older patients or patients with comorbidities, we would continue to recommend clinical trials or treatment with an approved PI3K inhibitor,” they added.
The study by Dr Smith and colleagues is not the first to show a benefit of HCT in this clinical scenario. In a recent NLCS/CIBMTR analysis of FL patients, 5-year overall survival was 73% for those undergoing autologous HCT done within a year of early treatment failure, versus 60% for those who did not (P=0.05).
The two studies “collectively suggest that transplantation should be considered in this high-risk group of patients with early relapse,” Dr Smith and co-authors wrote.
Autologous and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) both offer excellent long-term survival in follicular lymphoma (FL) patients who experience early treatment failure, an analysis of a large transplant registry suggests.
Five-year survival rates exceeded 70% for patients who received autologous or matched sibling donor (MSD) transplants, according to the analysis of the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) database. The database included 440 patients who underwent a procedure between 2002 and 2014.
“Until better risk-stratification tools are available for FL, auto-HCT and MSD allo-HCT should be considered as effective treatment options with excellent long-term survival for high-risk patients as defined by early treatment failure,” Sonali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago, and co-investigators wrote in the journal Cancer.
Early treatment failure in FL is associated with worse overall survival. In the National LymphoCare Study (NLCS), patients who received upfront R-CHOP therapy and progressed within 24 months had a 5-year overall survival of 50%, versus 90% for patients without early progression.
By contrast, survival figures in the present study are “provocatively higher” than those in the NLCS, in which only 8 out of 110 patients underwent HCT, Dr Smith and co-authors said.
Dr Smith’s study showed that with a median follow-up of 69 to 73 months, adjusted probability of 5-year overall survival was 70% for autologous and 73% for MSD HCT, versus 49% for matched unrelated donor HCT (P=0.0008).
Ryan C. Lynch, MD, and Ajay K. Gopal, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington, said that the finding “convincingly demonstrates” the benefit of transplant in the setting of early treatment failure.
“Select patients (particularly younger patients) with chemoresponsive disease who understand the risk-benefit ratio in comparison with currently approved and experimental therapies still remain good candidates for autologous HCT,” Drs Lynch and Gopal said in an editorial.
“For older patients or patients with comorbidities, we would continue to recommend clinical trials or treatment with an approved PI3K inhibitor,” they added.
The study by Dr Smith and colleagues is not the first to show a benefit of HCT in this clinical scenario. In a recent NLCS/CIBMTR analysis of FL patients, 5-year overall survival was 73% for those undergoing autologous HCT done within a year of early treatment failure, versus 60% for those who did not (P=0.05).
The two studies “collectively suggest that transplantation should be considered in this high-risk group of patients with early relapse,” Dr Smith and co-authors wrote.