User login
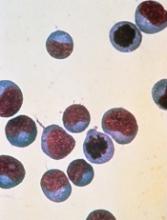
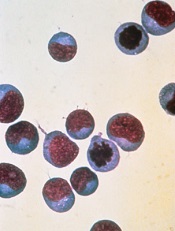
The US Food and Drug Administrated (FDA) placed a clinical hold on the phase 1 trial of the Sleeping Beauty (SB)-generated CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed or refractory leukemia and lymphoma patients.
The Sleeping Beauty platform was designed to very rapidly manufacture CD19-specific CAR T cells at the point of care.
All SB-CAR T-cell processing is planned to take place within 2 days at the healthcare facility, thus eliminating shipping cells from hospitals to production sites and back again.
The FDA is requesting more chemistry, manufacturing, and control (CMC) information before allowing the trial to proceed.
The Sleeping Beauty technology, a non-viral transposon/transposase system, has the potential to reduce the costs and complexity associated with recombinant viral vector-based immunotherapy, according to developers.
Ziopharm Oncology, Precigen, Inc, a wholly owned subsidiary of Intrexon Corporation, and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, are developing the Sleeping Beauty CAR T cell therapy.
“We know what is needed to address the hold issues and are looking forward to responding to the agency in a timely manner,” said Laurence Cooper, MD, PhD, chief executive officer of Ziopharm, in a corporate release.
“We are undertaking cutting-edge science and are on the verge of a paradigm shift based on our approach to very rapidly manufacture CD19-specific T cells within 2 days using our non-viral approach to CAR-T therapy based on the Sleeping Beauty platform.”
The phase 1 trial in question is a third-generation trial in which the CAR T cells are designed to co-express CD19-specific CAR, membrane-bound interleukin 15, and a safety switch.
The findings from earlier generation phase 1 trials have been previously reported in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The US Food and Drug Administrated (FDA) placed a clinical hold on the phase 1 trial of the Sleeping Beauty (SB)-generated CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed or refractory leukemia and lymphoma patients.
The Sleeping Beauty platform was designed to very rapidly manufacture CD19-specific CAR T cells at the point of care.
All SB-CAR T-cell processing is planned to take place within 2 days at the healthcare facility, thus eliminating shipping cells from hospitals to production sites and back again.
The FDA is requesting more chemistry, manufacturing, and control (CMC) information before allowing the trial to proceed.
The Sleeping Beauty technology, a non-viral transposon/transposase system, has the potential to reduce the costs and complexity associated with recombinant viral vector-based immunotherapy, according to developers.
Ziopharm Oncology, Precigen, Inc, a wholly owned subsidiary of Intrexon Corporation, and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, are developing the Sleeping Beauty CAR T cell therapy.
“We know what is needed to address the hold issues and are looking forward to responding to the agency in a timely manner,” said Laurence Cooper, MD, PhD, chief executive officer of Ziopharm, in a corporate release.
“We are undertaking cutting-edge science and are on the verge of a paradigm shift based on our approach to very rapidly manufacture CD19-specific T cells within 2 days using our non-viral approach to CAR-T therapy based on the Sleeping Beauty platform.”
The phase 1 trial in question is a third-generation trial in which the CAR T cells are designed to co-express CD19-specific CAR, membrane-bound interleukin 15, and a safety switch.
The findings from earlier generation phase 1 trials have been previously reported in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The US Food and Drug Administrated (FDA) placed a clinical hold on the phase 1 trial of the Sleeping Beauty (SB)-generated CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed or refractory leukemia and lymphoma patients.
The Sleeping Beauty platform was designed to very rapidly manufacture CD19-specific CAR T cells at the point of care.
All SB-CAR T-cell processing is planned to take place within 2 days at the healthcare facility, thus eliminating shipping cells from hospitals to production sites and back again.
The FDA is requesting more chemistry, manufacturing, and control (CMC) information before allowing the trial to proceed.
The Sleeping Beauty technology, a non-viral transposon/transposase system, has the potential to reduce the costs and complexity associated with recombinant viral vector-based immunotherapy, according to developers.
Ziopharm Oncology, Precigen, Inc, a wholly owned subsidiary of Intrexon Corporation, and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, are developing the Sleeping Beauty CAR T cell therapy.
“We know what is needed to address the hold issues and are looking forward to responding to the agency in a timely manner,” said Laurence Cooper, MD, PhD, chief executive officer of Ziopharm, in a corporate release.
“We are undertaking cutting-edge science and are on the verge of a paradigm shift based on our approach to very rapidly manufacture CD19-specific T cells within 2 days using our non-viral approach to CAR-T therapy based on the Sleeping Beauty platform.”
The phase 1 trial in question is a third-generation trial in which the CAR T cells are designed to co-express CD19-specific CAR, membrane-bound interleukin 15, and a safety switch.
The findings from earlier generation phase 1 trials have been previously reported in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.