User login
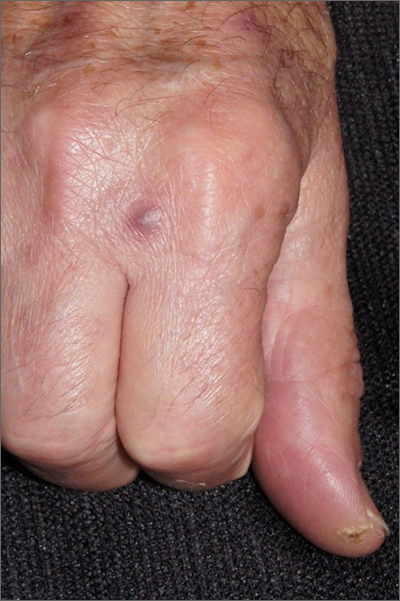
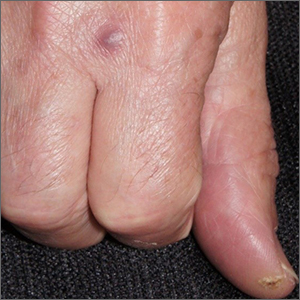
A biopsy was performed to exclude squamous cell carcinoma and an additional biopsy was sent for tissue culture for aerobic and acid-fast bacteria. The culture revealed a surprising diagnosis: cutaneous mycobacterium marinum.
Mycobacterium marinum is one of many nontuberculosis mycobacteria that may rarely cause infections in immunocompetent patients. M marinum is found worldwide in saltwater and freshwater. Infections may occur in individuals working in fisheries or fish markets, natural marine environments, or with aquariums. The infection may gain access through small, even unnoticed breaks in the skin. Papules, pustules, or abscesses caused by M marinum develop a few weeks after exposure and share many features with other common skin infections, including Staphylococcus aureus. Lymphatic involvement and sporotrichoid spread may occur. Immunocompromised patients can experience deeper involvement into tendons. Patients with significant soft tissue pain should undergo computed tomography, or preferably magnetic resonance imaging, to determine the extent of disease.
For immunocompetent patients and those with limited disease, as in this case, spontaneous resolution can occur after a year or more. However, because of the potential risk of more severe disease, treatment is recommended. M marinum is resistant to multiple antibiotics and there are no standardized treatment guidelines. Minocycline 100 mg bid for 3 weeks to 3 months is 1 accepted regimen for limited disease; treatment should be continued for 3 to 4 weeks following clinical resolution.1 Patients with more widespread disease benefit from evaluation by Infectious Diseases. Patients exposed to atypical mycobacteria may have false positive QuantiFERON-TB Gold tests that are commonly performed prior to biologic therapies.2
This patient achieved complete resolution of his signs and symptoms after receiving minocycline 100 mg bid for 6 weeks. He continues to fish recreationally.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Rallis E, Koumantaki-Mathioudaki E. Treatment of Mycobacterium marinum cutaneous infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007;8:2965-2978. doi: 10.1517/14656566.8.17.2965
2. Gajurel K, Subramanian AK. False-positive QuantiFERON TB-Gold test due to Mycobacterium gordonae. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016;84:315-317. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2015.10.020

A biopsy was performed to exclude squamous cell carcinoma and an additional biopsy was sent for tissue culture for aerobic and acid-fast bacteria. The culture revealed a surprising diagnosis: cutaneous mycobacterium marinum.
Mycobacterium marinum is one of many nontuberculosis mycobacteria that may rarely cause infections in immunocompetent patients. M marinum is found worldwide in saltwater and freshwater. Infections may occur in individuals working in fisheries or fish markets, natural marine environments, or with aquariums. The infection may gain access through small, even unnoticed breaks in the skin. Papules, pustules, or abscesses caused by M marinum develop a few weeks after exposure and share many features with other common skin infections, including Staphylococcus aureus. Lymphatic involvement and sporotrichoid spread may occur. Immunocompromised patients can experience deeper involvement into tendons. Patients with significant soft tissue pain should undergo computed tomography, or preferably magnetic resonance imaging, to determine the extent of disease.
For immunocompetent patients and those with limited disease, as in this case, spontaneous resolution can occur after a year or more. However, because of the potential risk of more severe disease, treatment is recommended. M marinum is resistant to multiple antibiotics and there are no standardized treatment guidelines. Minocycline 100 mg bid for 3 weeks to 3 months is 1 accepted regimen for limited disease; treatment should be continued for 3 to 4 weeks following clinical resolution.1 Patients with more widespread disease benefit from evaluation by Infectious Diseases. Patients exposed to atypical mycobacteria may have false positive QuantiFERON-TB Gold tests that are commonly performed prior to biologic therapies.2
This patient achieved complete resolution of his signs and symptoms after receiving minocycline 100 mg bid for 6 weeks. He continues to fish recreationally.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

A biopsy was performed to exclude squamous cell carcinoma and an additional biopsy was sent for tissue culture for aerobic and acid-fast bacteria. The culture revealed a surprising diagnosis: cutaneous mycobacterium marinum.
Mycobacterium marinum is one of many nontuberculosis mycobacteria that may rarely cause infections in immunocompetent patients. M marinum is found worldwide in saltwater and freshwater. Infections may occur in individuals working in fisheries or fish markets, natural marine environments, or with aquariums. The infection may gain access through small, even unnoticed breaks in the skin. Papules, pustules, or abscesses caused by M marinum develop a few weeks after exposure and share many features with other common skin infections, including Staphylococcus aureus. Lymphatic involvement and sporotrichoid spread may occur. Immunocompromised patients can experience deeper involvement into tendons. Patients with significant soft tissue pain should undergo computed tomography, or preferably magnetic resonance imaging, to determine the extent of disease.
For immunocompetent patients and those with limited disease, as in this case, spontaneous resolution can occur after a year or more. However, because of the potential risk of more severe disease, treatment is recommended. M marinum is resistant to multiple antibiotics and there are no standardized treatment guidelines. Minocycline 100 mg bid for 3 weeks to 3 months is 1 accepted regimen for limited disease; treatment should be continued for 3 to 4 weeks following clinical resolution.1 Patients with more widespread disease benefit from evaluation by Infectious Diseases. Patients exposed to atypical mycobacteria may have false positive QuantiFERON-TB Gold tests that are commonly performed prior to biologic therapies.2
This patient achieved complete resolution of his signs and symptoms after receiving minocycline 100 mg bid for 6 weeks. He continues to fish recreationally.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Rallis E, Koumantaki-Mathioudaki E. Treatment of Mycobacterium marinum cutaneous infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007;8:2965-2978. doi: 10.1517/14656566.8.17.2965
2. Gajurel K, Subramanian AK. False-positive QuantiFERON TB-Gold test due to Mycobacterium gordonae. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016;84:315-317. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2015.10.020
1. Rallis E, Koumantaki-Mathioudaki E. Treatment of Mycobacterium marinum cutaneous infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007;8:2965-2978. doi: 10.1517/14656566.8.17.2965
2. Gajurel K, Subramanian AK. False-positive QuantiFERON TB-Gold test due to Mycobacterium gordonae. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016;84:315-317. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2015.10.020