User login
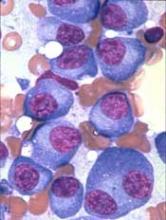
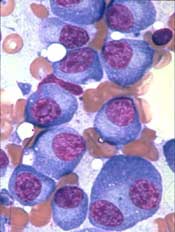
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to galinpepimut-S (GPS) as a treatment for multiple myeloma (MM).
GPS is an immunotherapeutic that targets malignancies characterized by overexpression of the Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) antigen.
GPS consists of 4 peptide chains, 2 of which are modified chains that induce an innate immune response (CD4+/CD8+) against the WT1 antigen and access a range of HLA types.
When GPS is administered to a patient, the induced immune response has the potential to recognize and destroy cancer cells and provide ongoing support to the immune system so it can continue to target and destroy residual cancer cells.
GPS also has orphan designation from the FDA for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and malignant plural mesothelioma.
Phase 2 trial
GPS has been investigated in a phase 2 trial of MM patients. Results from this trial were recently presented at the 44th Annual Meeting of the EBMT.
Researchers evaluated GPS in combination with lenalidomide as maintenance therapy in MM patients who received an autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
The study enrolled 19 patients who began receiving GPS within 22 days of ASCT. They received 6 doses every 2 weeks. (Injection sites were pre-stimulated with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.)
Patients received 6 additional monthly doses of GPS as well as lenalidomide maintenance (10 mg daily) starting on day 100 post-ASCT.
Twelve patients received all 12 doses of GPS. Eleven patients achieved a complete response or very good partial response. All of these patients had CD4 immune responses, and 9 of them had CD8 immune responses.
The progression-free survival was 81% at 12 months and 62% at 18 months. The median progression-free survival was 23.6 months (range, 15.2 to not reached).
The overall survival was 88% at 18 months, and the median overall survival was not reached.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to galinpepimut-S (GPS) as a treatment for multiple myeloma (MM).
GPS is an immunotherapeutic that targets malignancies characterized by overexpression of the Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) antigen.
GPS consists of 4 peptide chains, 2 of which are modified chains that induce an innate immune response (CD4+/CD8+) against the WT1 antigen and access a range of HLA types.
When GPS is administered to a patient, the induced immune response has the potential to recognize and destroy cancer cells and provide ongoing support to the immune system so it can continue to target and destroy residual cancer cells.
GPS also has orphan designation from the FDA for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and malignant plural mesothelioma.
Phase 2 trial
GPS has been investigated in a phase 2 trial of MM patients. Results from this trial were recently presented at the 44th Annual Meeting of the EBMT.
Researchers evaluated GPS in combination with lenalidomide as maintenance therapy in MM patients who received an autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
The study enrolled 19 patients who began receiving GPS within 22 days of ASCT. They received 6 doses every 2 weeks. (Injection sites were pre-stimulated with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.)
Patients received 6 additional monthly doses of GPS as well as lenalidomide maintenance (10 mg daily) starting on day 100 post-ASCT.
Twelve patients received all 12 doses of GPS. Eleven patients achieved a complete response or very good partial response. All of these patients had CD4 immune responses, and 9 of them had CD8 immune responses.
The progression-free survival was 81% at 12 months and 62% at 18 months. The median progression-free survival was 23.6 months (range, 15.2 to not reached).
The overall survival was 88% at 18 months, and the median overall survival was not reached.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to galinpepimut-S (GPS) as a treatment for multiple myeloma (MM).
GPS is an immunotherapeutic that targets malignancies characterized by overexpression of the Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) antigen.
GPS consists of 4 peptide chains, 2 of which are modified chains that induce an innate immune response (CD4+/CD8+) against the WT1 antigen and access a range of HLA types.
When GPS is administered to a patient, the induced immune response has the potential to recognize and destroy cancer cells and provide ongoing support to the immune system so it can continue to target and destroy residual cancer cells.
GPS also has orphan designation from the FDA for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and malignant plural mesothelioma.
Phase 2 trial
GPS has been investigated in a phase 2 trial of MM patients. Results from this trial were recently presented at the 44th Annual Meeting of the EBMT.
Researchers evaluated GPS in combination with lenalidomide as maintenance therapy in MM patients who received an autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
The study enrolled 19 patients who began receiving GPS within 22 days of ASCT. They received 6 doses every 2 weeks. (Injection sites were pre-stimulated with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.)
Patients received 6 additional monthly doses of GPS as well as lenalidomide maintenance (10 mg daily) starting on day 100 post-ASCT.
Twelve patients received all 12 doses of GPS. Eleven patients achieved a complete response or very good partial response. All of these patients had CD4 immune responses, and 9 of them had CD8 immune responses.
The progression-free survival was 81% at 12 months and 62% at 18 months. The median progression-free survival was 23.6 months (range, 15.2 to not reached).
The overall survival was 88% at 18 months, and the median overall survival was not reached.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.