User login
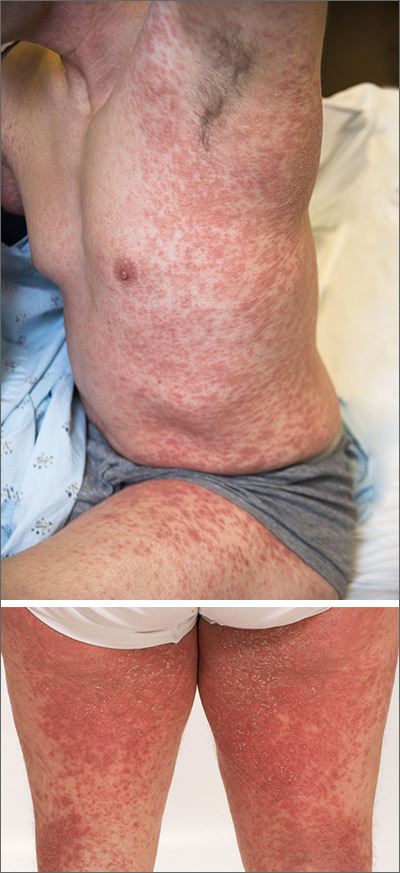
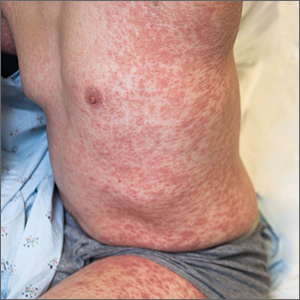
The acute rash with minute pustules and associated leukocytosis with neutrophilia and eosinophilia led to a diagnosis of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), which may have been triggered by azithromycin—the patient’s only recent medication. AGEP is a severe cutaneous eruption that may be associated with systemic involvement. Medications are usually implicated, and patients often seek urgent evaluation.
AGEP typically begins as an acute eruption in the intertriginous sites of the axilla, groin, and neck, but often becomes more generalized. The diagnosis is strongly suggested by the condition’s key features: fever (97% of cases) and leukocytosis (87%) with neutrophilia (91%) and eosinophilia (30%). Leukocytosis peaks 4 days after pustulosis occurs and lasts for about 12 days. Although common, fever is not always documented in patients with AGEP. (This patient was a case in point.)
In approximately 90% of AGEP cases, medications such as antibiotics and calcium channel blockers are implicated; however, the lack of such an association does not preclude the diagnosis. In cases of drug reactions, the eruption typically develops 1 to 2 days after a medication is begun, and the pustules typically resolve in fewer than 15 days. In 17% of patients, systemic involvement can occur and can include the liver, kidneys, bone marrow, and lungs. A physical exam, review of systems, and a laboratory evaluation can help rule out systemic involvement and guide additional testing.
AGEP has an incidence of 1 to 5 cases per million people per year, affecting women slightly more frequently than men. While the pathophysiology is not well understood, AGEP and its differential diagnoses are categorized as T cell-related inflammatory responses.
There are at least 4 severe cutaneous eruptions that might be confused with AGEP, all of which may be associated with fever. They include a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and pustular psoriasis. The clinical features that may help differentiate these conditions from AGEP include timeline, mucocutaneous features, organ system involvement, and histopathologic findings.
Patients who have AGEP, including those with systemic involvement, generally improve after the offending drug is discontinued and treatment with topical corticosteroids is initiated. A brief course of systemic corticosteroids can also be considered for patients with severe skin involvement or systemic involvement.
This patient was prescribed topical corticosteroid wet dressing treatments twice daily for 2 weeks. At the 2-week follow-up visit, the rash had completely cleared and only minimal residual erythema was noted. The patient was instructed to avoid azithromycin.
This case was adapted from: Tolkachjov SN, Wetter DA, Sandefur BJ. Generalized pustular eruption. J Fam Pract. 2018;67:309-310,312.

The acute rash with minute pustules and associated leukocytosis with neutrophilia and eosinophilia led to a diagnosis of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), which may have been triggered by azithromycin—the patient’s only recent medication. AGEP is a severe cutaneous eruption that may be associated with systemic involvement. Medications are usually implicated, and patients often seek urgent evaluation.
AGEP typically begins as an acute eruption in the intertriginous sites of the axilla, groin, and neck, but often becomes more generalized. The diagnosis is strongly suggested by the condition’s key features: fever (97% of cases) and leukocytosis (87%) with neutrophilia (91%) and eosinophilia (30%). Leukocytosis peaks 4 days after pustulosis occurs and lasts for about 12 days. Although common, fever is not always documented in patients with AGEP. (This patient was a case in point.)
In approximately 90% of AGEP cases, medications such as antibiotics and calcium channel blockers are implicated; however, the lack of such an association does not preclude the diagnosis. In cases of drug reactions, the eruption typically develops 1 to 2 days after a medication is begun, and the pustules typically resolve in fewer than 15 days. In 17% of patients, systemic involvement can occur and can include the liver, kidneys, bone marrow, and lungs. A physical exam, review of systems, and a laboratory evaluation can help rule out systemic involvement and guide additional testing.
AGEP has an incidence of 1 to 5 cases per million people per year, affecting women slightly more frequently than men. While the pathophysiology is not well understood, AGEP and its differential diagnoses are categorized as T cell-related inflammatory responses.
There are at least 4 severe cutaneous eruptions that might be confused with AGEP, all of which may be associated with fever. They include a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and pustular psoriasis. The clinical features that may help differentiate these conditions from AGEP include timeline, mucocutaneous features, organ system involvement, and histopathologic findings.
Patients who have AGEP, including those with systemic involvement, generally improve after the offending drug is discontinued and treatment with topical corticosteroids is initiated. A brief course of systemic corticosteroids can also be considered for patients with severe skin involvement or systemic involvement.
This patient was prescribed topical corticosteroid wet dressing treatments twice daily for 2 weeks. At the 2-week follow-up visit, the rash had completely cleared and only minimal residual erythema was noted. The patient was instructed to avoid azithromycin.
This case was adapted from: Tolkachjov SN, Wetter DA, Sandefur BJ. Generalized pustular eruption. J Fam Pract. 2018;67:309-310,312.

The acute rash with minute pustules and associated leukocytosis with neutrophilia and eosinophilia led to a diagnosis of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), which may have been triggered by azithromycin—the patient’s only recent medication. AGEP is a severe cutaneous eruption that may be associated with systemic involvement. Medications are usually implicated, and patients often seek urgent evaluation.
AGEP typically begins as an acute eruption in the intertriginous sites of the axilla, groin, and neck, but often becomes more generalized. The diagnosis is strongly suggested by the condition’s key features: fever (97% of cases) and leukocytosis (87%) with neutrophilia (91%) and eosinophilia (30%). Leukocytosis peaks 4 days after pustulosis occurs and lasts for about 12 days. Although common, fever is not always documented in patients with AGEP. (This patient was a case in point.)
In approximately 90% of AGEP cases, medications such as antibiotics and calcium channel blockers are implicated; however, the lack of such an association does not preclude the diagnosis. In cases of drug reactions, the eruption typically develops 1 to 2 days after a medication is begun, and the pustules typically resolve in fewer than 15 days. In 17% of patients, systemic involvement can occur and can include the liver, kidneys, bone marrow, and lungs. A physical exam, review of systems, and a laboratory evaluation can help rule out systemic involvement and guide additional testing.
AGEP has an incidence of 1 to 5 cases per million people per year, affecting women slightly more frequently than men. While the pathophysiology is not well understood, AGEP and its differential diagnoses are categorized as T cell-related inflammatory responses.
There are at least 4 severe cutaneous eruptions that might be confused with AGEP, all of which may be associated with fever. They include a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and pustular psoriasis. The clinical features that may help differentiate these conditions from AGEP include timeline, mucocutaneous features, organ system involvement, and histopathologic findings.
Patients who have AGEP, including those with systemic involvement, generally improve after the offending drug is discontinued and treatment with topical corticosteroids is initiated. A brief course of systemic corticosteroids can also be considered for patients with severe skin involvement or systemic involvement.
This patient was prescribed topical corticosteroid wet dressing treatments twice daily for 2 weeks. At the 2-week follow-up visit, the rash had completely cleared and only minimal residual erythema was noted. The patient was instructed to avoid azithromycin.
This case was adapted from: Tolkachjov SN, Wetter DA, Sandefur BJ. Generalized pustular eruption. J Fam Pract. 2018;67:309-310,312.