User login
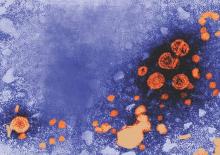
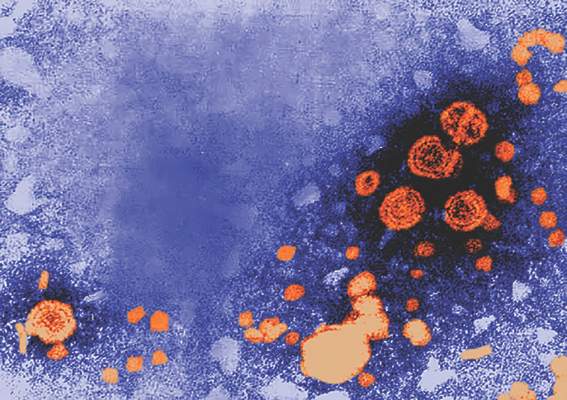
Pediatric doses of hepatitis B vaccine can provide long-term protection against hepatitis B up to 15-16 years, and also can produce strong immune memory, according to Dr. Olivier Van Der Meeren of GlaxoSmithKline Vaccines, Wavre, Belgium, and his associates.
The researchers looked at 303 healthy adolescents who had received three doses of monovalent pediatric hepatitis B vaccine (containing 10 mcg hepatitis B surface antigen, HBsAg) in infancy. Of the 293 patients analyzed, 71% were seropositive (anti-HBs antibodies greater than or equal to 6.2 mIU/mL) before the challenge dose and 65% remained seroprotected (anti-HBs antibodies greater than or equal to 10 mIU/mL) after challenge. One month after the challenge dose, the percentage of seroprotected subjects increased to 99%, and 91% of those patients had anti-HBs antibody concentrations greater than or equal to 100 mIU/mL.
The study also looked at safety and reactogenicity. The researchers stated that it was well tolerated, with pain and fatigue the most frequently reported adverse effects.
“Despite declining levels of circulating anti-HBs antibodies, the vast majority of subjects in our study were able to mount a rapid and robust anamnestic response after a challenge dose (more than 150-fold increase in GMC [geometric mean concentration]) regardless of their pre-challenge serostatus,” the researchers concluded. “This confirms that maintaining anti-HBs antibody concentrations greater than 10 mIU/mL may not be essential for protection against clinically significant breakthrough hepatitis B infection.”
Find the study in Vaccine (doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.04.013).
Pediatric doses of hepatitis B vaccine can provide long-term protection against hepatitis B up to 15-16 years, and also can produce strong immune memory, according to Dr. Olivier Van Der Meeren of GlaxoSmithKline Vaccines, Wavre, Belgium, and his associates.
The researchers looked at 303 healthy adolescents who had received three doses of monovalent pediatric hepatitis B vaccine (containing 10 mcg hepatitis B surface antigen, HBsAg) in infancy. Of the 293 patients analyzed, 71% were seropositive (anti-HBs antibodies greater than or equal to 6.2 mIU/mL) before the challenge dose and 65% remained seroprotected (anti-HBs antibodies greater than or equal to 10 mIU/mL) after challenge. One month after the challenge dose, the percentage of seroprotected subjects increased to 99%, and 91% of those patients had anti-HBs antibody concentrations greater than or equal to 100 mIU/mL.
The study also looked at safety and reactogenicity. The researchers stated that it was well tolerated, with pain and fatigue the most frequently reported adverse effects.
“Despite declining levels of circulating anti-HBs antibodies, the vast majority of subjects in our study were able to mount a rapid and robust anamnestic response after a challenge dose (more than 150-fold increase in GMC [geometric mean concentration]) regardless of their pre-challenge serostatus,” the researchers concluded. “This confirms that maintaining anti-HBs antibody concentrations greater than 10 mIU/mL may not be essential for protection against clinically significant breakthrough hepatitis B infection.”
Find the study in Vaccine (doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.04.013).
Pediatric doses of hepatitis B vaccine can provide long-term protection against hepatitis B up to 15-16 years, and also can produce strong immune memory, according to Dr. Olivier Van Der Meeren of GlaxoSmithKline Vaccines, Wavre, Belgium, and his associates.
The researchers looked at 303 healthy adolescents who had received three doses of monovalent pediatric hepatitis B vaccine (containing 10 mcg hepatitis B surface antigen, HBsAg) in infancy. Of the 293 patients analyzed, 71% were seropositive (anti-HBs antibodies greater than or equal to 6.2 mIU/mL) before the challenge dose and 65% remained seroprotected (anti-HBs antibodies greater than or equal to 10 mIU/mL) after challenge. One month after the challenge dose, the percentage of seroprotected subjects increased to 99%, and 91% of those patients had anti-HBs antibody concentrations greater than or equal to 100 mIU/mL.
The study also looked at safety and reactogenicity. The researchers stated that it was well tolerated, with pain and fatigue the most frequently reported adverse effects.
“Despite declining levels of circulating anti-HBs antibodies, the vast majority of subjects in our study were able to mount a rapid and robust anamnestic response after a challenge dose (more than 150-fold increase in GMC [geometric mean concentration]) regardless of their pre-challenge serostatus,” the researchers concluded. “This confirms that maintaining anti-HBs antibody concentrations greater than 10 mIU/mL may not be essential for protection against clinically significant breakthrough hepatitis B infection.”
Find the study in Vaccine (doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.04.013).
FROM VACCINE