User login
New COVID-19 cases in children soared by almost 86% over the course of just 1 week, while the number of 12- to 17-year-old children who have received at least one dose of vaccine rose by 5.4%, according to two separate sources.
Meanwhile, the increase over the past 2 weeks – from 23,551 new cases for July 16-22 to almost 72,000 – works out to almost 205%, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Children represented 19.0% of the cases reported during the week of July 23-29, and they have made up 14.3% of all cases since the pandemic began, with the total number of cases in children now approaching 4.2 million, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. About 22% of the U.S. population is under the age of 18 years.
As of Aug. 2, just over 9.8 million children aged 12-17 years had received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, which was up by about 500,000, or 5.4%, from a week earlier, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Children aged 16-17 have reached a notable milestone on the journey that started with vaccine approval in December: 50.2% have gotten at least one dose and 40.3% are fully vaccinated. Among children aged 12-15 years, the proportion with at least one dose of vaccine is up to 39.5%, compared with 37.1% the previous week, while 29.0% are fully vaccinated (27.8% the week before), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
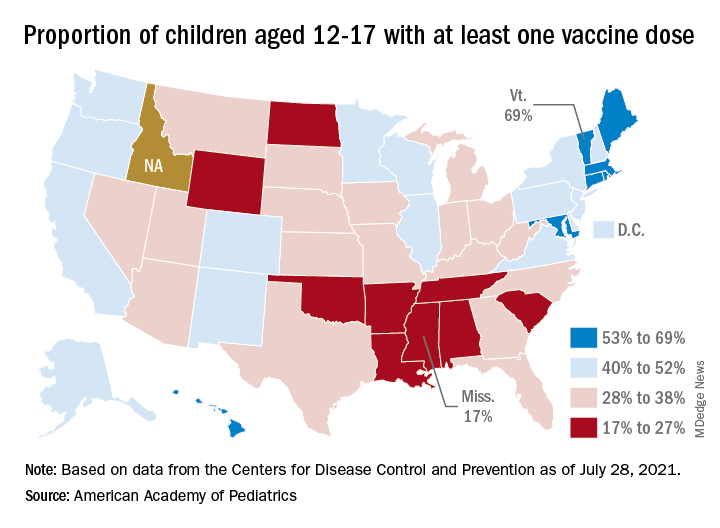
The national rates for child vaccination, however, tend to hide the disparities between states. There is a gap between Mississippi (lowest), where just 17% of children aged 12-17 years have gotten at least one dose, and Vermont (highest), which is up to 69%. Vermont also has the highest rate of vaccine completion (60%), while Alabama and Mississippi have the lowest (10%), according to a solo report from the AAP.
New COVID-19 cases in children soared by almost 86% over the course of just 1 week, while the number of 12- to 17-year-old children who have received at least one dose of vaccine rose by 5.4%, according to two separate sources.

Meanwhile, the increase over the past 2 weeks – from 23,551 new cases for July 16-22 to almost 72,000 – works out to almost 205%, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Children represented 19.0% of the cases reported during the week of July 23-29, and they have made up 14.3% of all cases since the pandemic began, with the total number of cases in children now approaching 4.2 million, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. About 22% of the U.S. population is under the age of 18 years.
As of Aug. 2, just over 9.8 million children aged 12-17 years had received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, which was up by about 500,000, or 5.4%, from a week earlier, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Children aged 16-17 have reached a notable milestone on the journey that started with vaccine approval in December: 50.2% have gotten at least one dose and 40.3% are fully vaccinated. Among children aged 12-15 years, the proportion with at least one dose of vaccine is up to 39.5%, compared with 37.1% the previous week, while 29.0% are fully vaccinated (27.8% the week before), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The national rates for child vaccination, however, tend to hide the disparities between states. There is a gap between Mississippi (lowest), where just 17% of children aged 12-17 years have gotten at least one dose, and Vermont (highest), which is up to 69%. Vermont also has the highest rate of vaccine completion (60%), while Alabama and Mississippi have the lowest (10%), according to a solo report from the AAP.
New COVID-19 cases in children soared by almost 86% over the course of just 1 week, while the number of 12- to 17-year-old children who have received at least one dose of vaccine rose by 5.4%, according to two separate sources.

Meanwhile, the increase over the past 2 weeks – from 23,551 new cases for July 16-22 to almost 72,000 – works out to almost 205%, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Children represented 19.0% of the cases reported during the week of July 23-29, and they have made up 14.3% of all cases since the pandemic began, with the total number of cases in children now approaching 4.2 million, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. About 22% of the U.S. population is under the age of 18 years.
As of Aug. 2, just over 9.8 million children aged 12-17 years had received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, which was up by about 500,000, or 5.4%, from a week earlier, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Children aged 16-17 have reached a notable milestone on the journey that started with vaccine approval in December: 50.2% have gotten at least one dose and 40.3% are fully vaccinated. Among children aged 12-15 years, the proportion with at least one dose of vaccine is up to 39.5%, compared with 37.1% the previous week, while 29.0% are fully vaccinated (27.8% the week before), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The national rates for child vaccination, however, tend to hide the disparities between states. There is a gap between Mississippi (lowest), where just 17% of children aged 12-17 years have gotten at least one dose, and Vermont (highest), which is up to 69%. Vermont also has the highest rate of vaccine completion (60%), while Alabama and Mississippi have the lowest (10%), according to a solo report from the AAP.