User login
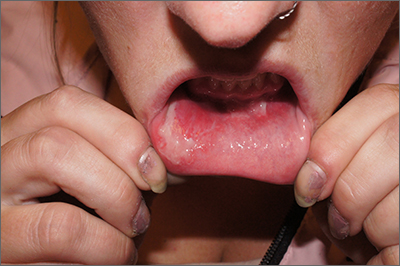
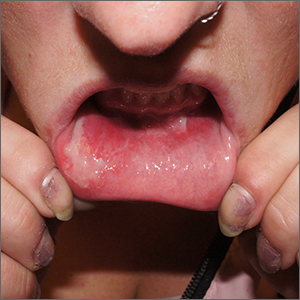
The patient was having a flare of pemphigus vulgaris (PV), a rare and sometimes life-threatening acquired autoimmune blistering disease that affects the skin and/or mucosa. Ashkenazi Jewish patients and patients from Mediterranean and Middle Eastern countries are more likely to be affected.
In PV, acquired autoantibodies target the desmosomes that connect epithelial cells together, weakening the intercellular adhesion. It can affect skin, mucosa, or both. Patients present with fragile bullae or ulcers. The connections between the cells are often so damaged that rubbing on the skin creates a new blister called “Nikolsky sign.” In the mouth, bullae erode rapidly. Look for disease affecting the ocular conjunctiva or sclera, as well. PV can also occasionally affect the nasopharynx and esophagus, usually manifesting as hemoptysis, dysphagia, and nosebleeds with ulcer seen on endoscopy or otolaryngoscopy.
Although PV is often severe (and can warrant hospitalization when significant body surface area is involved), some patients may have few active lesions and can be managed safely as outpatients.
The diagnosis requires 2 biopsies and serum for indirect immunofluorescence. One biopsy (either by punch or shave to the upper dermis) is taken from the edge of a bulla or ulcer. Another biopsy (by punch or shave) is taken from nearby normal-looking skin or mucosa for testing the direct immunofluorescence pattern. In the mucosa, a punch biopsy may be left open or closed with absorbable sutures. A serum sample is taken for indirect immunofluorescence to differentiate pemphigus vulgaris from other forms of pemphigus.1
PV is treated by suppressing the immune system. Focal disease may be treated with super-potent topical steroids, including clobetasol 0.05% ointment. Even in the mouth, topical clobetasol 0.05% may be used off-label twice daily until control is achieved. When topical treatment is used in the mouth, advise patients to apply the clobetasol ointment to a piece of gauze and place the gauze (ointment side down) over affected areas for 20 to 30 minutes twice daily.
Patients with widespread or severe disease should be hospitalized. In severe cases, supportive wound care is provided, and treatment is aimed at immunosuppression. Systemic options include high-dose prednisone 0.5 to 1 mg/kg daily until clear, a steroid-sparing immunosuppressant such as mycophenolate mofetil up to 1000 mg bid, or rituximab in 1 of several regimens.
Three years prior to this patient’s visit, she had been successfully treated for PV with a course of rituximab. To treat the current flare, she was started on prednisone 60 mg/d. In addition, the plan was for her to complete 2 infusions of 1000 mg rituximab 2 weeks apart.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, Maine.
1. Didona, D, Schmidt, MF, Maglie, R, et al. Pemphigus and pemphigoids: clinical presentation, diagnosis and therapy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023;1-20. doi: 10.1111/ddg.15174

The patient was having a flare of pemphigus vulgaris (PV), a rare and sometimes life-threatening acquired autoimmune blistering disease that affects the skin and/or mucosa. Ashkenazi Jewish patients and patients from Mediterranean and Middle Eastern countries are more likely to be affected.
In PV, acquired autoantibodies target the desmosomes that connect epithelial cells together, weakening the intercellular adhesion. It can affect skin, mucosa, or both. Patients present with fragile bullae or ulcers. The connections between the cells are often so damaged that rubbing on the skin creates a new blister called “Nikolsky sign.” In the mouth, bullae erode rapidly. Look for disease affecting the ocular conjunctiva or sclera, as well. PV can also occasionally affect the nasopharynx and esophagus, usually manifesting as hemoptysis, dysphagia, and nosebleeds with ulcer seen on endoscopy or otolaryngoscopy.
Although PV is often severe (and can warrant hospitalization when significant body surface area is involved), some patients may have few active lesions and can be managed safely as outpatients.
The diagnosis requires 2 biopsies and serum for indirect immunofluorescence. One biopsy (either by punch or shave to the upper dermis) is taken from the edge of a bulla or ulcer. Another biopsy (by punch or shave) is taken from nearby normal-looking skin or mucosa for testing the direct immunofluorescence pattern. In the mucosa, a punch biopsy may be left open or closed with absorbable sutures. A serum sample is taken for indirect immunofluorescence to differentiate pemphigus vulgaris from other forms of pemphigus.1
PV is treated by suppressing the immune system. Focal disease may be treated with super-potent topical steroids, including clobetasol 0.05% ointment. Even in the mouth, topical clobetasol 0.05% may be used off-label twice daily until control is achieved. When topical treatment is used in the mouth, advise patients to apply the clobetasol ointment to a piece of gauze and place the gauze (ointment side down) over affected areas for 20 to 30 minutes twice daily.
Patients with widespread or severe disease should be hospitalized. In severe cases, supportive wound care is provided, and treatment is aimed at immunosuppression. Systemic options include high-dose prednisone 0.5 to 1 mg/kg daily until clear, a steroid-sparing immunosuppressant such as mycophenolate mofetil up to 1000 mg bid, or rituximab in 1 of several regimens.
Three years prior to this patient’s visit, she had been successfully treated for PV with a course of rituximab. To treat the current flare, she was started on prednisone 60 mg/d. In addition, the plan was for her to complete 2 infusions of 1000 mg rituximab 2 weeks apart.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, Maine.

The patient was having a flare of pemphigus vulgaris (PV), a rare and sometimes life-threatening acquired autoimmune blistering disease that affects the skin and/or mucosa. Ashkenazi Jewish patients and patients from Mediterranean and Middle Eastern countries are more likely to be affected.
In PV, acquired autoantibodies target the desmosomes that connect epithelial cells together, weakening the intercellular adhesion. It can affect skin, mucosa, or both. Patients present with fragile bullae or ulcers. The connections between the cells are often so damaged that rubbing on the skin creates a new blister called “Nikolsky sign.” In the mouth, bullae erode rapidly. Look for disease affecting the ocular conjunctiva or sclera, as well. PV can also occasionally affect the nasopharynx and esophagus, usually manifesting as hemoptysis, dysphagia, and nosebleeds with ulcer seen on endoscopy or otolaryngoscopy.
Although PV is often severe (and can warrant hospitalization when significant body surface area is involved), some patients may have few active lesions and can be managed safely as outpatients.
The diagnosis requires 2 biopsies and serum for indirect immunofluorescence. One biopsy (either by punch or shave to the upper dermis) is taken from the edge of a bulla or ulcer. Another biopsy (by punch or shave) is taken from nearby normal-looking skin or mucosa for testing the direct immunofluorescence pattern. In the mucosa, a punch biopsy may be left open or closed with absorbable sutures. A serum sample is taken for indirect immunofluorescence to differentiate pemphigus vulgaris from other forms of pemphigus.1
PV is treated by suppressing the immune system. Focal disease may be treated with super-potent topical steroids, including clobetasol 0.05% ointment. Even in the mouth, topical clobetasol 0.05% may be used off-label twice daily until control is achieved. When topical treatment is used in the mouth, advise patients to apply the clobetasol ointment to a piece of gauze and place the gauze (ointment side down) over affected areas for 20 to 30 minutes twice daily.
Patients with widespread or severe disease should be hospitalized. In severe cases, supportive wound care is provided, and treatment is aimed at immunosuppression. Systemic options include high-dose prednisone 0.5 to 1 mg/kg daily until clear, a steroid-sparing immunosuppressant such as mycophenolate mofetil up to 1000 mg bid, or rituximab in 1 of several regimens.
Three years prior to this patient’s visit, she had been successfully treated for PV with a course of rituximab. To treat the current flare, she was started on prednisone 60 mg/d. In addition, the plan was for her to complete 2 infusions of 1000 mg rituximab 2 weeks apart.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, Maine.
1. Didona, D, Schmidt, MF, Maglie, R, et al. Pemphigus and pemphigoids: clinical presentation, diagnosis and therapy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023;1-20. doi: 10.1111/ddg.15174
1. Didona, D, Schmidt, MF, Maglie, R, et al. Pemphigus and pemphigoids: clinical presentation, diagnosis and therapy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023;1-20. doi: 10.1111/ddg.15174