User login
Editor’s Note: This article has been adapted from an article originally published in Federal Practitioner (Tavakoli HR, et al. Kratom: a new product in an expanding substance abuse market. Fed Prac. 2016;33[11]:132-136. http://www.fedprac.com).
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, the last decade saw an alarming rise in the use of recreational substances.1 There was an escalation not only in the use of the more well-known street drugs (cannabis, stimulants, opioids, and hallucinogens), but also an exponential increase in the abuse of novel psychoactive substances. Although most emergency physicians (EPs) are at least relatively familiar with some of these designer drugs—often synthesized analogues of common street drugs—region-specific herbal products with psychoactive properties are now entering the market worldwide. Certainly, the cause of this increased use is multifactorial: Ease of access to these drugs and ambiguous legality are believed to be among the largest contributors. Infrastructure established through globalization promotes easy drug transportation and distribution across borders, and widespread Internet use makes knowledge of and accessibility to such substances exceedingly simple.2,3
In particular, widespread online access has permanently altered the acquisition of knowledge in all realms—including drug use. Although Erowid Center remains one of the oldest and best-known of this type of Web site and bills itself as providing “harm reduction,” others have cropped up online and disseminate information about many forms of potentially psychoactive substances. Despite the purported raison d’être of these Web sites, recent studies have demonstrated these sites’ efficacy in promoting drug use under the guise of safety, particularly among adolescents and young adults. Among these is a qualitative study by Boyer et al4 of 12 drug users admitted to a pediatric psychiatry unit. Through extensive questioning about the patients’ digital habits, the researchers demonstrated that the majority of subjects used these Web sites and, as a result, either increased their drug use or learned about (and tried) new substances.
One drug that has benefited from globalization and the Internet is kratom (Mitragyna speciosa korth). This formerly regionally confined herbal psychoactive substance is native to Southeast Asia, where it has been used (and abused) for centuries as a mild stimulant, to prevent opioid withdrawal, and for recreational purposes. In recent years, kratom has been marketed as a psychotropic drug and has become increasingly popular in the United States and in the United Kingdom.2,5,6 In the United States, this poses a problem for EPs who often are unaware of this plant’s existence, much less its abuse potential or health effects.2 Also known as ketum, kakuam, thang, thom, or biak, kratom is marketed in stores and online as a cheap, safe alternative to opioids.
Although considered a “substance of concern” without any approved medical use by the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA
To that end, users consider kratom a legal high, and it is easily purchased online. A 2010 study in the United Kingdom examined Web sites where kratom and many other quasilegal substances (including Salvia divinorum and legal precursors to LSD) could be purchased for an average of £10 (about $13 US currency).5 This study’s authors also noted a significant lack of product information on these marketplaces. As these products are not overseen by any regulatory body, the risk of overdose or adulteration is extremely high.2,3,6-8 In fact, Krypton, a kratom product sold online, was found to be adulterated with O-desmethyltramadol—the active metabolite of the synthetic opiate tramadol—and implicated in at least nine deaths.7
This article presents a case of kratom abuse. It describes a brief history of the substance, its pharmacological characteristics, the clinical presentation of kratom abuse, and the treatment of kratom-related illness and evaluation of potential toxic sequelae. In light of the rapid proliferation of kratom in the United States, a basic working knowledge of the drug is quickly becoming a must for EPs.
Case Presentation
At his employer’s request, a 33-year-old man presented to his family physician for a worsening of his uncontrolled back pain from a herniated lumbar disk resulting from a motor vehicle collision 3 months before. At his physician’s office he stated, “I don’t care if I live or die, I’m tired of the pain,” and “I’m going to go off on somebody if I can’t get this pain under control.” He also endorsed having auditory hallucinations for several years and a history of violence and homicide. The problem arose precipitously after he became concerned that he was abusing his opioid medication, and it was discontinued. The patient was transferred to the local ED and admitted to the psychiatric service for his suicidal ideations and risk of harming self and others.
On admission to the psychiatric service, the patient complained of body aches, chills, rhinorrhea, and significantly worsened irritability from his baseline, consistent with opioid withdrawal. Initial point-of-care (POC) admission drug testing had been negative as had expanded urine tests looking for synthetic opioids, cannabinoids, and cathinones. The patient reported no opioid use but was unable to explain his current symptom patterns, which were worsening his chronic pain and hampering any attempt to build rapport. On hospital day 3, the patient’s opioid withdrawal resolved, and psychiatric treatment was able to progress fully. On hospital day 4, the inpatient treatment team received a message from the patient’s primary care manager stating that a friend of the patient had found a bottle of herbal pills in the patient’s car. This was later revealed to be a kratom formulation that he had purchased online.
Background
Kratom is the colloquial name of a tree that is native to Thailand, Malaysia, and other countries in Southeast Asia. These trees, which can grow to 50 feet high and 15 feet wide, have long been the source of herbal remedies in Southeast Asia.2,3 The leaves of these trees contain psychoactive substances that have a variety of effects when consumed. At low doses, kratom causes a stimulant effect (akin to the leaves of the coca plant in South America); laborers and farmers often use it to help boost their energy. At higher doses, kratom causes an opioid-like effect, which at mega doses produces an intense euphoric state and has led to a steady growth in abuse worldwide. Although the government of Thailand banned the planting of Mitragyna speciosa as early as 1943, its continued proliferation in Southeast Asia and throughout the world has not ceased.2,3,6
In the United Kingdom, kratom is currently the second most common drug that is considered a legal high, only behind salvia (Salvia divinorum), a hallucinogenic herb that is better known as a result of its use by young celebrities over the past decade.5,8
Kratom can be taken in a variety of ways: Crushed leaves often are placed in gel caps and swallowed; it can be drunk as a tea, juice, or boiled syrup; and it can be smoked or insufflated.2,3,5,6
Pharmacology and Clinical Presentation
More than 20 psychoactive compounds have been isolated from kratom. Although a discussion of all these compounds is beyond the scope of this review, the two major compounds are mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine.
Mitragynine
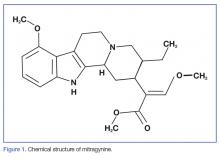
Mitragynine, the most abundant psychoactive compound found in kratom, is an indole alkaloid (Figure 1). Extraction and analysis of this compound has demonstrated numerous effects on multiple receptors, including mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors, leading to its opioid-like effects, including analgesia and euphoria. Also similar to common opioids, withdrawal symptomatology can present after only 5 days of daily use. There is limited evidence that mitragynine can activate postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, which may act synergistically with the mu-agonist with regard to its analgesic effect.2,5
7-Hydroxymitragynine
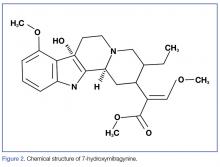
7-hydroxymitragynine, despite being far less concentrated in kratom preparations, is about 13 times more potent than morphine and 46 times more potent than mitragynine. It is thought that its hydroxyl side chain added to C7 (Figure 2) adds to its lipophilicity and ability to cross the blood-brain barrier at a far more rapid rate than that of mitragynine.2
Mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine remain the best-studied psychoactive components of kratom at this time. Other compounds that have been isolated, such as speciociliatine, paynantheine, and speciogynine, may play a role in kratom’s analgesic and psychoactive effects. Animal studies have demonstrated antimuscarinic properties in these compounds, but the properties do not seem to have any demonstrable effect at the opioid receptors.2
Intoxication and Withdrawal
Due to its increasing worldwide popularity, it is now imperative for EPs to be aware of the presentation of patients with kratom abuse as well as the management of withdrawal in light of its dependence potential. However, large-scale studies have not been performed, and much of the evidence comes not from the medical literature but from Web sites such as Erowid or SageWisdom.2,5-9 To that end, such information will be discussed along with the limited research and expert consensuses available in peer-reviewed medical literature.
Kratom seems to have dose-dependent effects. At low doses (1-5 g of raw crushed leaves), kratom abusers often report a mild energizing effect, thought to be secondary to the stimulant properties of kratom’s multiple alkaloids. Users have reported mild euphoria and highs similar to those of the abuse of methylphenidate or modafinil.2,9,10 Also similar to abuse of those substances, users have reported anxiety, irritability, and aggressiveness as a result of the stimulant-like effects.
At moderate-to-high doses (5-15 g of raw crushed leaves), it is believed that the mu-opiate receptor agonism overtakes the stimulant effects, leading to the euphoria, relaxation, and analgesia seen with conventional opioid use and abuse.2,10 In light of the drug’s substantial binding and agonism of all opioid receptors, constipation and itching also are seen.2 As such, if an individual is intoxicated, he or she should be managed with supportive and symptomatic care and continuous monitoring of heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation.2,10 Kratom intoxication can precipitate psychotic episodes similar to those caused by opiate intoxication, so monitoring for agitation or psychotic behaviors is also indicated.9,10
The medical management of a patient with an acute kratom overdose (typically requiring ingestion of >15 g of crushed leaves) begins with addressing airway support, breathing, and circulation along with continuous vital sign monitoring and laboratory testing, including POC glucose testing, complete blood count, electrolytes, lactate, venous blood gas, and measurable drug levels (ethanol, acetaminophen, tricyclic antidepressants, as indicated).11 If it is determined that kratom was the intoxicant, the greatest concern of death is similar to that of opioid overdose: respiratory depression. Although there are no large-scale human studies demonstrating efficacy, multiple authors suggest the use of naloxone in kratom-related hypoventilation.9,10
The development of dependence on kratom and its subsequent withdrawal phenomena are thought to be similar to that of opioids, in light of its strong mu agonism.2,5,9,10 Indeed, kratom has a long history of being used by opioid-dependent patients as an attempt to quit drug abuse or stave off debilitating withdrawal symptoms when they are unable to acquire their substance of choice.2,5-10 As such, withdrawal and the treatment thereof will also mimic that of opioid withdrawal.
The kratom-dependent individual will often present with rhinorrhea, lacrimation, dry mouth, hostility, aggression, and emotional lability similar to the case study described earlier.2,9,10 Kratom withdrawal, much like intoxication, also may precipitate or worsen psychotic symptoms, and monitoring is necessary throughout the detoxification process.2,5,10 Withdrawal management should proceed along ambulatory clinic or hospital opioid withdrawal protocols that include step-down administration of opioids or with nonopioid medications for symptomatic relief, including muscle relaxants, alpha-2 agonists, and antidiarrheal agents.5,9,10
Kratom Toxicity
A review of the available medical literature has demonstrated a number of toxic effects with kratom abuse, either as the sole agent or in concert with prescribed medications, recreational coingestants, or as a result of manufacturer’s adulteration with other chemicals or drugs. Of particular interest to EPs are manic or psychotic episode precipitation, seizure, hypothyroidism, intrahepatic cholestatic injury, and even sudden cardiac death.2,3,5-10 In addition to the basic history, physical, and laboratory examination, the workup of patients identified as kratom users should include the following:
- Fastidious medication reconciliation with drug-interaction check;
- Exhaustive substance abuse history;
- Identification of the brand name and source of kratom purchased, to determine whether there are advertised coingestants or reports of adulteration;
- Electrocardiogram;
- Thyroid function testing;
- Hepatic function testing; and
- Comprehensive neurological and mental status examinations.
In chronic users of kratom, a number of effects have been seen whose etiologies have not yet been determined. These effects include depression, anxiety, tremulousness, weight loss, and psychosis.3-7 Additionally, a study by Kittirattanapaiboon et al12 correlated drug use by those with concurrent mental health disorders (in particular, kratom, which was used in 59% of the ≥14,000 individuals included in the study sample) with statistically significant higher suicide risk.
Detection
Because kratom is a relatively new compound in the United States, medical and forensic laboratories are only now implementing kratom detection protocols. Many laboratories now use high-performance liquid chromatography to analyze for mitragynine, 7-hydroxymitragynine, and two metabolites of mitragynine in urine.7 Le et al13 were able to detect mitragynine in the urine in levels as low as 1 ng/mL, which is clinically useful as mitragynine has a half-life determined in animal studies to be 3.85 hours. Similar detection limits for mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine are used only at the Naval Medical Center Portsmouth in Virginia; however, kratom was not detected in the case study patient’s urine because a urine test was not done until hospital day 5.
Case Conclusion
When gently confronted about the kratom found in his car, the case study patient admitted that he had purchased kratom online after he was “cut off” from prescription opioids for his pain. He admitted that although it was beneficial for his pain, he did notice worsening in his aggression toward his spouse and coworkers. This progressed to an exacerbation of his psychotic symptoms of hallucinations and persecutory delusions. These symptoms remained well hidden—but were present for years prior to his presentation at the hospital. The patient was discharged from the inpatient psychiatric unit on hospital day 16 with a diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder, depressive type in addition to opioid-use disorder. The patient agreed to seek a pain management specialist and discontinue kratom use.
Conclusion
Kratom is an emerging drug of abuse in the Western world. Although significant research is being conducted on its possible medical uses, little is known about kratom beyond the “trip reports” of kratom users posted online. Because of its technically legal status in the United States and multiple other Western countries, kratom is easily accessible. Emergency physicians need to be aware of kratom, and during their evaluations, question appropriate patients about kratom and other legal highs.
1. United Nations Office of Drug and Crime. World Drug Report 2014. https://www.unodc.org/documents/wdr2014/World_Drug_Report_2014_web.pdf. Published June 2014. Accessed September 26, 2016.
2. Prozialeck WC, Jivan JK, Andurkar SV. Pharmacology of kratom: an emerging botanical agent with stimulant, analgesic and opioid-like effects. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012;112(12):792-799.
3. U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, Office of Diversion Control. Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa korth). http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drug _chem_info/kratom.pdf. Published January 2013. Accessed September 26, 2016.
4. Boyer EW, Shannon M, Hibberd PL. The Internet and psychoactive substance use among innovative drug users. Pediatrics. 2005;115(2):302-305.
5. Yusoff NH, Suhaimi FW, Vadivelu RK, et al. Abuse potential and adverse cognitive effects of mitragynine (kratom). Addict Biol. 2016;21(1):98-110.
6. Schmidt MM, Sharma A, Schifano F, Feinmann C. “Legal highs” on the net-evaluation of UK-based websites, products and product information. Forensic Sci Int. 2011;206(1-3):92-97.
7. Kronstrand R, Roman M, Thelander G, Eriksson A. Unintentional fatal intoxications with mitragynine and O-desmethyltramadol from the herbal blend Krypton. J Anal Toxicol. 2011;35(4):242-247.
8. Holler JM, Vorce SP, McDonough-Bender PC, Magluilo J Jr, Solomon CJ, Levine B. A drug toxicity death involving propylhexedrine and mitragynine. J Anal Toxicol. 2011;35(1):54-59.
9. Rosenbaum CD, Carreiro SP, Babu KM. Here today, gone tomorrow…and back again? A review of herbal marijuana alternatives (K2, Spice), synthetic cathinones (bath salts), kratom, Salvia divinorum, methoxetamine, and piperazines. J Med Toxicol. 2012;8(1):15-32.
10. Rech MA, Donahey E, Cappiello Dziedzic JM, Oh L, Greenhalgh E. New drugs of abuse. Pharmacotherapy. 2015;35(2):189-197.
11. Silvilotti MLA. Initial management of the critically ill adult with an unknown overdose. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/initial-management-of-the -critically-ill-adult-with-an-unknown-overdose. Updated August 27, 2015. Accessed September 26, 2016.
12. Kittirattanapaiboon P, Suttajit S, Junsirimongkol B, Likhitsathian S, Srisurapanont M. Suicide risk among Thai illicit drug users with and without mental/alcohol use disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014;10:453-458.
13. Le D, Goggin MM, Janis GC. Analysis of mitragynine and metabolites in human urine for detecting the use of the psychoactive plant kratom. J Anal Toxicol. 2012;36(9):616-625.
Editor’s Note: This article has been adapted from an article originally published in Federal Practitioner (Tavakoli HR, et al. Kratom: a new product in an expanding substance abuse market. Fed Prac. 2016;33[11]:132-136. http://www.fedprac.com).
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, the last decade saw an alarming rise in the use of recreational substances.1 There was an escalation not only in the use of the more well-known street drugs (cannabis, stimulants, opioids, and hallucinogens), but also an exponential increase in the abuse of novel psychoactive substances. Although most emergency physicians (EPs) are at least relatively familiar with some of these designer drugs—often synthesized analogues of common street drugs—region-specific herbal products with psychoactive properties are now entering the market worldwide. Certainly, the cause of this increased use is multifactorial: Ease of access to these drugs and ambiguous legality are believed to be among the largest contributors. Infrastructure established through globalization promotes easy drug transportation and distribution across borders, and widespread Internet use makes knowledge of and accessibility to such substances exceedingly simple.2,3
In particular, widespread online access has permanently altered the acquisition of knowledge in all realms—including drug use. Although Erowid Center remains one of the oldest and best-known of this type of Web site and bills itself as providing “harm reduction,” others have cropped up online and disseminate information about many forms of potentially psychoactive substances. Despite the purported raison d’être of these Web sites, recent studies have demonstrated these sites’ efficacy in promoting drug use under the guise of safety, particularly among adolescents and young adults. Among these is a qualitative study by Boyer et al4 of 12 drug users admitted to a pediatric psychiatry unit. Through extensive questioning about the patients’ digital habits, the researchers demonstrated that the majority of subjects used these Web sites and, as a result, either increased their drug use or learned about (and tried) new substances.
One drug that has benefited from globalization and the Internet is kratom (Mitragyna speciosa korth). This formerly regionally confined herbal psychoactive substance is native to Southeast Asia, where it has been used (and abused) for centuries as a mild stimulant, to prevent opioid withdrawal, and for recreational purposes. In recent years, kratom has been marketed as a psychotropic drug and has become increasingly popular in the United States and in the United Kingdom.2,5,6 In the United States, this poses a problem for EPs who often are unaware of this plant’s existence, much less its abuse potential or health effects.2 Also known as ketum, kakuam, thang, thom, or biak, kratom is marketed in stores and online as a cheap, safe alternative to opioids.
Although considered a “substance of concern” without any approved medical use by the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA
To that end, users consider kratom a legal high, and it is easily purchased online. A 2010 study in the United Kingdom examined Web sites where kratom and many other quasilegal substances (including Salvia divinorum and legal precursors to LSD) could be purchased for an average of £10 (about $13 US currency).5 This study’s authors also noted a significant lack of product information on these marketplaces. As these products are not overseen by any regulatory body, the risk of overdose or adulteration is extremely high.2,3,6-8 In fact, Krypton, a kratom product sold online, was found to be adulterated with O-desmethyltramadol—the active metabolite of the synthetic opiate tramadol—and implicated in at least nine deaths.7
This article presents a case of kratom abuse. It describes a brief history of the substance, its pharmacological characteristics, the clinical presentation of kratom abuse, and the treatment of kratom-related illness and evaluation of potential toxic sequelae. In light of the rapid proliferation of kratom in the United States, a basic working knowledge of the drug is quickly becoming a must for EPs.
Case Presentation
At his employer’s request, a 33-year-old man presented to his family physician for a worsening of his uncontrolled back pain from a herniated lumbar disk resulting from a motor vehicle collision 3 months before. At his physician’s office he stated, “I don’t care if I live or die, I’m tired of the pain,” and “I’m going to go off on somebody if I can’t get this pain under control.” He also endorsed having auditory hallucinations for several years and a history of violence and homicide. The problem arose precipitously after he became concerned that he was abusing his opioid medication, and it was discontinued. The patient was transferred to the local ED and admitted to the psychiatric service for his suicidal ideations and risk of harming self and others.
On admission to the psychiatric service, the patient complained of body aches, chills, rhinorrhea, and significantly worsened irritability from his baseline, consistent with opioid withdrawal. Initial point-of-care (POC) admission drug testing had been negative as had expanded urine tests looking for synthetic opioids, cannabinoids, and cathinones. The patient reported no opioid use but was unable to explain his current symptom patterns, which were worsening his chronic pain and hampering any attempt to build rapport. On hospital day 3, the patient’s opioid withdrawal resolved, and psychiatric treatment was able to progress fully. On hospital day 4, the inpatient treatment team received a message from the patient’s primary care manager stating that a friend of the patient had found a bottle of herbal pills in the patient’s car. This was later revealed to be a kratom formulation that he had purchased online.
Background
Kratom is the colloquial name of a tree that is native to Thailand, Malaysia, and other countries in Southeast Asia. These trees, which can grow to 50 feet high and 15 feet wide, have long been the source of herbal remedies in Southeast Asia.2,3 The leaves of these trees contain psychoactive substances that have a variety of effects when consumed. At low doses, kratom causes a stimulant effect (akin to the leaves of the coca plant in South America); laborers and farmers often use it to help boost their energy. At higher doses, kratom causes an opioid-like effect, which at mega doses produces an intense euphoric state and has led to a steady growth in abuse worldwide. Although the government of Thailand banned the planting of Mitragyna speciosa as early as 1943, its continued proliferation in Southeast Asia and throughout the world has not ceased.2,3,6
In the United Kingdom, kratom is currently the second most common drug that is considered a legal high, only behind salvia (Salvia divinorum), a hallucinogenic herb that is better known as a result of its use by young celebrities over the past decade.5,8
Kratom can be taken in a variety of ways: Crushed leaves often are placed in gel caps and swallowed; it can be drunk as a tea, juice, or boiled syrup; and it can be smoked or insufflated.2,3,5,6
Pharmacology and Clinical Presentation
More than 20 psychoactive compounds have been isolated from kratom. Although a discussion of all these compounds is beyond the scope of this review, the two major compounds are mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine.
Mitragynine
Mitragynine, the most abundant psychoactive compound found in kratom, is an indole alkaloid (Figure 1). Extraction and analysis of this compound has demonstrated numerous effects on multiple receptors, including mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors, leading to its opioid-like effects, including analgesia and euphoria. Also similar to common opioids, withdrawal symptomatology can present after only 5 days of daily use. There is limited evidence that mitragynine can activate postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, which may act synergistically with the mu-agonist with regard to its analgesic effect.2,5
7-Hydroxymitragynine
7-hydroxymitragynine, despite being far less concentrated in kratom preparations, is about 13 times more potent than morphine and 46 times more potent than mitragynine. It is thought that its hydroxyl side chain added to C7 (Figure 2) adds to its lipophilicity and ability to cross the blood-brain barrier at a far more rapid rate than that of mitragynine.2
Mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine remain the best-studied psychoactive components of kratom at this time. Other compounds that have been isolated, such as speciociliatine, paynantheine, and speciogynine, may play a role in kratom’s analgesic and psychoactive effects. Animal studies have demonstrated antimuscarinic properties in these compounds, but the properties do not seem to have any demonstrable effect at the opioid receptors.2
Intoxication and Withdrawal
Due to its increasing worldwide popularity, it is now imperative for EPs to be aware of the presentation of patients with kratom abuse as well as the management of withdrawal in light of its dependence potential. However, large-scale studies have not been performed, and much of the evidence comes not from the medical literature but from Web sites such as Erowid or SageWisdom.2,5-9 To that end, such information will be discussed along with the limited research and expert consensuses available in peer-reviewed medical literature.
Kratom seems to have dose-dependent effects. At low doses (1-5 g of raw crushed leaves), kratom abusers often report a mild energizing effect, thought to be secondary to the stimulant properties of kratom’s multiple alkaloids. Users have reported mild euphoria and highs similar to those of the abuse of methylphenidate or modafinil.2,9,10 Also similar to abuse of those substances, users have reported anxiety, irritability, and aggressiveness as a result of the stimulant-like effects.
At moderate-to-high doses (5-15 g of raw crushed leaves), it is believed that the mu-opiate receptor agonism overtakes the stimulant effects, leading to the euphoria, relaxation, and analgesia seen with conventional opioid use and abuse.2,10 In light of the drug’s substantial binding and agonism of all opioid receptors, constipation and itching also are seen.2 As such, if an individual is intoxicated, he or she should be managed with supportive and symptomatic care and continuous monitoring of heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation.2,10 Kratom intoxication can precipitate psychotic episodes similar to those caused by opiate intoxication, so monitoring for agitation or psychotic behaviors is also indicated.9,10
The medical management of a patient with an acute kratom overdose (typically requiring ingestion of >15 g of crushed leaves) begins with addressing airway support, breathing, and circulation along with continuous vital sign monitoring and laboratory testing, including POC glucose testing, complete blood count, electrolytes, lactate, venous blood gas, and measurable drug levels (ethanol, acetaminophen, tricyclic antidepressants, as indicated).11 If it is determined that kratom was the intoxicant, the greatest concern of death is similar to that of opioid overdose: respiratory depression. Although there are no large-scale human studies demonstrating efficacy, multiple authors suggest the use of naloxone in kratom-related hypoventilation.9,10
The development of dependence on kratom and its subsequent withdrawal phenomena are thought to be similar to that of opioids, in light of its strong mu agonism.2,5,9,10 Indeed, kratom has a long history of being used by opioid-dependent patients as an attempt to quit drug abuse or stave off debilitating withdrawal symptoms when they are unable to acquire their substance of choice.2,5-10 As such, withdrawal and the treatment thereof will also mimic that of opioid withdrawal.
The kratom-dependent individual will often present with rhinorrhea, lacrimation, dry mouth, hostility, aggression, and emotional lability similar to the case study described earlier.2,9,10 Kratom withdrawal, much like intoxication, also may precipitate or worsen psychotic symptoms, and monitoring is necessary throughout the detoxification process.2,5,10 Withdrawal management should proceed along ambulatory clinic or hospital opioid withdrawal protocols that include step-down administration of opioids or with nonopioid medications for symptomatic relief, including muscle relaxants, alpha-2 agonists, and antidiarrheal agents.5,9,10
Kratom Toxicity
A review of the available medical literature has demonstrated a number of toxic effects with kratom abuse, either as the sole agent or in concert with prescribed medications, recreational coingestants, or as a result of manufacturer’s adulteration with other chemicals or drugs. Of particular interest to EPs are manic or psychotic episode precipitation, seizure, hypothyroidism, intrahepatic cholestatic injury, and even sudden cardiac death.2,3,5-10 In addition to the basic history, physical, and laboratory examination, the workup of patients identified as kratom users should include the following:
- Fastidious medication reconciliation with drug-interaction check;
- Exhaustive substance abuse history;
- Identification of the brand name and source of kratom purchased, to determine whether there are advertised coingestants or reports of adulteration;
- Electrocardiogram;
- Thyroid function testing;
- Hepatic function testing; and
- Comprehensive neurological and mental status examinations.
In chronic users of kratom, a number of effects have been seen whose etiologies have not yet been determined. These effects include depression, anxiety, tremulousness, weight loss, and psychosis.3-7 Additionally, a study by Kittirattanapaiboon et al12 correlated drug use by those with concurrent mental health disorders (in particular, kratom, which was used in 59% of the ≥14,000 individuals included in the study sample) with statistically significant higher suicide risk.
Detection
Because kratom is a relatively new compound in the United States, medical and forensic laboratories are only now implementing kratom detection protocols. Many laboratories now use high-performance liquid chromatography to analyze for mitragynine, 7-hydroxymitragynine, and two metabolites of mitragynine in urine.7 Le et al13 were able to detect mitragynine in the urine in levels as low as 1 ng/mL, which is clinically useful as mitragynine has a half-life determined in animal studies to be 3.85 hours. Similar detection limits for mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine are used only at the Naval Medical Center Portsmouth in Virginia; however, kratom was not detected in the case study patient’s urine because a urine test was not done until hospital day 5.
Case Conclusion
When gently confronted about the kratom found in his car, the case study patient admitted that he had purchased kratom online after he was “cut off” from prescription opioids for his pain. He admitted that although it was beneficial for his pain, he did notice worsening in his aggression toward his spouse and coworkers. This progressed to an exacerbation of his psychotic symptoms of hallucinations and persecutory delusions. These symptoms remained well hidden—but were present for years prior to his presentation at the hospital. The patient was discharged from the inpatient psychiatric unit on hospital day 16 with a diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder, depressive type in addition to opioid-use disorder. The patient agreed to seek a pain management specialist and discontinue kratom use.
Conclusion
Kratom is an emerging drug of abuse in the Western world. Although significant research is being conducted on its possible medical uses, little is known about kratom beyond the “trip reports” of kratom users posted online. Because of its technically legal status in the United States and multiple other Western countries, kratom is easily accessible. Emergency physicians need to be aware of kratom, and during their evaluations, question appropriate patients about kratom and other legal highs.
Editor’s Note: This article has been adapted from an article originally published in Federal Practitioner (Tavakoli HR, et al. Kratom: a new product in an expanding substance abuse market. Fed Prac. 2016;33[11]:132-136. http://www.fedprac.com).
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, the last decade saw an alarming rise in the use of recreational substances.1 There was an escalation not only in the use of the more well-known street drugs (cannabis, stimulants, opioids, and hallucinogens), but also an exponential increase in the abuse of novel psychoactive substances. Although most emergency physicians (EPs) are at least relatively familiar with some of these designer drugs—often synthesized analogues of common street drugs—region-specific herbal products with psychoactive properties are now entering the market worldwide. Certainly, the cause of this increased use is multifactorial: Ease of access to these drugs and ambiguous legality are believed to be among the largest contributors. Infrastructure established through globalization promotes easy drug transportation and distribution across borders, and widespread Internet use makes knowledge of and accessibility to such substances exceedingly simple.2,3
In particular, widespread online access has permanently altered the acquisition of knowledge in all realms—including drug use. Although Erowid Center remains one of the oldest and best-known of this type of Web site and bills itself as providing “harm reduction,” others have cropped up online and disseminate information about many forms of potentially psychoactive substances. Despite the purported raison d’être of these Web sites, recent studies have demonstrated these sites’ efficacy in promoting drug use under the guise of safety, particularly among adolescents and young adults. Among these is a qualitative study by Boyer et al4 of 12 drug users admitted to a pediatric psychiatry unit. Through extensive questioning about the patients’ digital habits, the researchers demonstrated that the majority of subjects used these Web sites and, as a result, either increased their drug use or learned about (and tried) new substances.
One drug that has benefited from globalization and the Internet is kratom (Mitragyna speciosa korth). This formerly regionally confined herbal psychoactive substance is native to Southeast Asia, where it has been used (and abused) for centuries as a mild stimulant, to prevent opioid withdrawal, and for recreational purposes. In recent years, kratom has been marketed as a psychotropic drug and has become increasingly popular in the United States and in the United Kingdom.2,5,6 In the United States, this poses a problem for EPs who often are unaware of this plant’s existence, much less its abuse potential or health effects.2 Also known as ketum, kakuam, thang, thom, or biak, kratom is marketed in stores and online as a cheap, safe alternative to opioids.
Although considered a “substance of concern” without any approved medical use by the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA
To that end, users consider kratom a legal high, and it is easily purchased online. A 2010 study in the United Kingdom examined Web sites where kratom and many other quasilegal substances (including Salvia divinorum and legal precursors to LSD) could be purchased for an average of £10 (about $13 US currency).5 This study’s authors also noted a significant lack of product information on these marketplaces. As these products are not overseen by any regulatory body, the risk of overdose or adulteration is extremely high.2,3,6-8 In fact, Krypton, a kratom product sold online, was found to be adulterated with O-desmethyltramadol—the active metabolite of the synthetic opiate tramadol—and implicated in at least nine deaths.7
This article presents a case of kratom abuse. It describes a brief history of the substance, its pharmacological characteristics, the clinical presentation of kratom abuse, and the treatment of kratom-related illness and evaluation of potential toxic sequelae. In light of the rapid proliferation of kratom in the United States, a basic working knowledge of the drug is quickly becoming a must for EPs.
Case Presentation
At his employer’s request, a 33-year-old man presented to his family physician for a worsening of his uncontrolled back pain from a herniated lumbar disk resulting from a motor vehicle collision 3 months before. At his physician’s office he stated, “I don’t care if I live or die, I’m tired of the pain,” and “I’m going to go off on somebody if I can’t get this pain under control.” He also endorsed having auditory hallucinations for several years and a history of violence and homicide. The problem arose precipitously after he became concerned that he was abusing his opioid medication, and it was discontinued. The patient was transferred to the local ED and admitted to the psychiatric service for his suicidal ideations and risk of harming self and others.
On admission to the psychiatric service, the patient complained of body aches, chills, rhinorrhea, and significantly worsened irritability from his baseline, consistent with opioid withdrawal. Initial point-of-care (POC) admission drug testing had been negative as had expanded urine tests looking for synthetic opioids, cannabinoids, and cathinones. The patient reported no opioid use but was unable to explain his current symptom patterns, which were worsening his chronic pain and hampering any attempt to build rapport. On hospital day 3, the patient’s opioid withdrawal resolved, and psychiatric treatment was able to progress fully. On hospital day 4, the inpatient treatment team received a message from the patient’s primary care manager stating that a friend of the patient had found a bottle of herbal pills in the patient’s car. This was later revealed to be a kratom formulation that he had purchased online.
Background
Kratom is the colloquial name of a tree that is native to Thailand, Malaysia, and other countries in Southeast Asia. These trees, which can grow to 50 feet high and 15 feet wide, have long been the source of herbal remedies in Southeast Asia.2,3 The leaves of these trees contain psychoactive substances that have a variety of effects when consumed. At low doses, kratom causes a stimulant effect (akin to the leaves of the coca plant in South America); laborers and farmers often use it to help boost their energy. At higher doses, kratom causes an opioid-like effect, which at mega doses produces an intense euphoric state and has led to a steady growth in abuse worldwide. Although the government of Thailand banned the planting of Mitragyna speciosa as early as 1943, its continued proliferation in Southeast Asia and throughout the world has not ceased.2,3,6
In the United Kingdom, kratom is currently the second most common drug that is considered a legal high, only behind salvia (Salvia divinorum), a hallucinogenic herb that is better known as a result of its use by young celebrities over the past decade.5,8
Kratom can be taken in a variety of ways: Crushed leaves often are placed in gel caps and swallowed; it can be drunk as a tea, juice, or boiled syrup; and it can be smoked or insufflated.2,3,5,6
Pharmacology and Clinical Presentation
More than 20 psychoactive compounds have been isolated from kratom. Although a discussion of all these compounds is beyond the scope of this review, the two major compounds are mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine.
Mitragynine
Mitragynine, the most abundant psychoactive compound found in kratom, is an indole alkaloid (Figure 1). Extraction and analysis of this compound has demonstrated numerous effects on multiple receptors, including mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors, leading to its opioid-like effects, including analgesia and euphoria. Also similar to common opioids, withdrawal symptomatology can present after only 5 days of daily use. There is limited evidence that mitragynine can activate postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, which may act synergistically with the mu-agonist with regard to its analgesic effect.2,5
7-Hydroxymitragynine
7-hydroxymitragynine, despite being far less concentrated in kratom preparations, is about 13 times more potent than morphine and 46 times more potent than mitragynine. It is thought that its hydroxyl side chain added to C7 (Figure 2) adds to its lipophilicity and ability to cross the blood-brain barrier at a far more rapid rate than that of mitragynine.2
Mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine remain the best-studied psychoactive components of kratom at this time. Other compounds that have been isolated, such as speciociliatine, paynantheine, and speciogynine, may play a role in kratom’s analgesic and psychoactive effects. Animal studies have demonstrated antimuscarinic properties in these compounds, but the properties do not seem to have any demonstrable effect at the opioid receptors.2
Intoxication and Withdrawal
Due to its increasing worldwide popularity, it is now imperative for EPs to be aware of the presentation of patients with kratom abuse as well as the management of withdrawal in light of its dependence potential. However, large-scale studies have not been performed, and much of the evidence comes not from the medical literature but from Web sites such as Erowid or SageWisdom.2,5-9 To that end, such information will be discussed along with the limited research and expert consensuses available in peer-reviewed medical literature.
Kratom seems to have dose-dependent effects. At low doses (1-5 g of raw crushed leaves), kratom abusers often report a mild energizing effect, thought to be secondary to the stimulant properties of kratom’s multiple alkaloids. Users have reported mild euphoria and highs similar to those of the abuse of methylphenidate or modafinil.2,9,10 Also similar to abuse of those substances, users have reported anxiety, irritability, and aggressiveness as a result of the stimulant-like effects.
At moderate-to-high doses (5-15 g of raw crushed leaves), it is believed that the mu-opiate receptor agonism overtakes the stimulant effects, leading to the euphoria, relaxation, and analgesia seen with conventional opioid use and abuse.2,10 In light of the drug’s substantial binding and agonism of all opioid receptors, constipation and itching also are seen.2 As such, if an individual is intoxicated, he or she should be managed with supportive and symptomatic care and continuous monitoring of heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation.2,10 Kratom intoxication can precipitate psychotic episodes similar to those caused by opiate intoxication, so monitoring for agitation or psychotic behaviors is also indicated.9,10
The medical management of a patient with an acute kratom overdose (typically requiring ingestion of >15 g of crushed leaves) begins with addressing airway support, breathing, and circulation along with continuous vital sign monitoring and laboratory testing, including POC glucose testing, complete blood count, electrolytes, lactate, venous blood gas, and measurable drug levels (ethanol, acetaminophen, tricyclic antidepressants, as indicated).11 If it is determined that kratom was the intoxicant, the greatest concern of death is similar to that of opioid overdose: respiratory depression. Although there are no large-scale human studies demonstrating efficacy, multiple authors suggest the use of naloxone in kratom-related hypoventilation.9,10
The development of dependence on kratom and its subsequent withdrawal phenomena are thought to be similar to that of opioids, in light of its strong mu agonism.2,5,9,10 Indeed, kratom has a long history of being used by opioid-dependent patients as an attempt to quit drug abuse or stave off debilitating withdrawal symptoms when they are unable to acquire their substance of choice.2,5-10 As such, withdrawal and the treatment thereof will also mimic that of opioid withdrawal.
The kratom-dependent individual will often present with rhinorrhea, lacrimation, dry mouth, hostility, aggression, and emotional lability similar to the case study described earlier.2,9,10 Kratom withdrawal, much like intoxication, also may precipitate or worsen psychotic symptoms, and monitoring is necessary throughout the detoxification process.2,5,10 Withdrawal management should proceed along ambulatory clinic or hospital opioid withdrawal protocols that include step-down administration of opioids or with nonopioid medications for symptomatic relief, including muscle relaxants, alpha-2 agonists, and antidiarrheal agents.5,9,10
Kratom Toxicity
A review of the available medical literature has demonstrated a number of toxic effects with kratom abuse, either as the sole agent or in concert with prescribed medications, recreational coingestants, or as a result of manufacturer’s adulteration with other chemicals or drugs. Of particular interest to EPs are manic or psychotic episode precipitation, seizure, hypothyroidism, intrahepatic cholestatic injury, and even sudden cardiac death.2,3,5-10 In addition to the basic history, physical, and laboratory examination, the workup of patients identified as kratom users should include the following:
- Fastidious medication reconciliation with drug-interaction check;
- Exhaustive substance abuse history;
- Identification of the brand name and source of kratom purchased, to determine whether there are advertised coingestants or reports of adulteration;
- Electrocardiogram;
- Thyroid function testing;
- Hepatic function testing; and
- Comprehensive neurological and mental status examinations.
In chronic users of kratom, a number of effects have been seen whose etiologies have not yet been determined. These effects include depression, anxiety, tremulousness, weight loss, and psychosis.3-7 Additionally, a study by Kittirattanapaiboon et al12 correlated drug use by those with concurrent mental health disorders (in particular, kratom, which was used in 59% of the ≥14,000 individuals included in the study sample) with statistically significant higher suicide risk.
Detection
Because kratom is a relatively new compound in the United States, medical and forensic laboratories are only now implementing kratom detection protocols. Many laboratories now use high-performance liquid chromatography to analyze for mitragynine, 7-hydroxymitragynine, and two metabolites of mitragynine in urine.7 Le et al13 were able to detect mitragynine in the urine in levels as low as 1 ng/mL, which is clinically useful as mitragynine has a half-life determined in animal studies to be 3.85 hours. Similar detection limits for mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine are used only at the Naval Medical Center Portsmouth in Virginia; however, kratom was not detected in the case study patient’s urine because a urine test was not done until hospital day 5.
Case Conclusion
When gently confronted about the kratom found in his car, the case study patient admitted that he had purchased kratom online after he was “cut off” from prescription opioids for his pain. He admitted that although it was beneficial for his pain, he did notice worsening in his aggression toward his spouse and coworkers. This progressed to an exacerbation of his psychotic symptoms of hallucinations and persecutory delusions. These symptoms remained well hidden—but were present for years prior to his presentation at the hospital. The patient was discharged from the inpatient psychiatric unit on hospital day 16 with a diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder, depressive type in addition to opioid-use disorder. The patient agreed to seek a pain management specialist and discontinue kratom use.
Conclusion
Kratom is an emerging drug of abuse in the Western world. Although significant research is being conducted on its possible medical uses, little is known about kratom beyond the “trip reports” of kratom users posted online. Because of its technically legal status in the United States and multiple other Western countries, kratom is easily accessible. Emergency physicians need to be aware of kratom, and during their evaluations, question appropriate patients about kratom and other legal highs.
1. United Nations Office of Drug and Crime. World Drug Report 2014. https://www.unodc.org/documents/wdr2014/World_Drug_Report_2014_web.pdf. Published June 2014. Accessed September 26, 2016.
2. Prozialeck WC, Jivan JK, Andurkar SV. Pharmacology of kratom: an emerging botanical agent with stimulant, analgesic and opioid-like effects. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012;112(12):792-799.
3. U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, Office of Diversion Control. Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa korth). http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drug _chem_info/kratom.pdf. Published January 2013. Accessed September 26, 2016.
4. Boyer EW, Shannon M, Hibberd PL. The Internet and psychoactive substance use among innovative drug users. Pediatrics. 2005;115(2):302-305.
5. Yusoff NH, Suhaimi FW, Vadivelu RK, et al. Abuse potential and adverse cognitive effects of mitragynine (kratom). Addict Biol. 2016;21(1):98-110.
6. Schmidt MM, Sharma A, Schifano F, Feinmann C. “Legal highs” on the net-evaluation of UK-based websites, products and product information. Forensic Sci Int. 2011;206(1-3):92-97.
7. Kronstrand R, Roman M, Thelander G, Eriksson A. Unintentional fatal intoxications with mitragynine and O-desmethyltramadol from the herbal blend Krypton. J Anal Toxicol. 2011;35(4):242-247.
8. Holler JM, Vorce SP, McDonough-Bender PC, Magluilo J Jr, Solomon CJ, Levine B. A drug toxicity death involving propylhexedrine and mitragynine. J Anal Toxicol. 2011;35(1):54-59.
9. Rosenbaum CD, Carreiro SP, Babu KM. Here today, gone tomorrow…and back again? A review of herbal marijuana alternatives (K2, Spice), synthetic cathinones (bath salts), kratom, Salvia divinorum, methoxetamine, and piperazines. J Med Toxicol. 2012;8(1):15-32.
10. Rech MA, Donahey E, Cappiello Dziedzic JM, Oh L, Greenhalgh E. New drugs of abuse. Pharmacotherapy. 2015;35(2):189-197.
11. Silvilotti MLA. Initial management of the critically ill adult with an unknown overdose. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/initial-management-of-the -critically-ill-adult-with-an-unknown-overdose. Updated August 27, 2015. Accessed September 26, 2016.
12. Kittirattanapaiboon P, Suttajit S, Junsirimongkol B, Likhitsathian S, Srisurapanont M. Suicide risk among Thai illicit drug users with and without mental/alcohol use disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014;10:453-458.
13. Le D, Goggin MM, Janis GC. Analysis of mitragynine and metabolites in human urine for detecting the use of the psychoactive plant kratom. J Anal Toxicol. 2012;36(9):616-625.
1. United Nations Office of Drug and Crime. World Drug Report 2014. https://www.unodc.org/documents/wdr2014/World_Drug_Report_2014_web.pdf. Published June 2014. Accessed September 26, 2016.
2. Prozialeck WC, Jivan JK, Andurkar SV. Pharmacology of kratom: an emerging botanical agent with stimulant, analgesic and opioid-like effects. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012;112(12):792-799.
3. U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, Office of Diversion Control. Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa korth). http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drug _chem_info/kratom.pdf. Published January 2013. Accessed September 26, 2016.
4. Boyer EW, Shannon M, Hibberd PL. The Internet and psychoactive substance use among innovative drug users. Pediatrics. 2005;115(2):302-305.
5. Yusoff NH, Suhaimi FW, Vadivelu RK, et al. Abuse potential and adverse cognitive effects of mitragynine (kratom). Addict Biol. 2016;21(1):98-110.
6. Schmidt MM, Sharma A, Schifano F, Feinmann C. “Legal highs” on the net-evaluation of UK-based websites, products and product information. Forensic Sci Int. 2011;206(1-3):92-97.
7. Kronstrand R, Roman M, Thelander G, Eriksson A. Unintentional fatal intoxications with mitragynine and O-desmethyltramadol from the herbal blend Krypton. J Anal Toxicol. 2011;35(4):242-247.
8. Holler JM, Vorce SP, McDonough-Bender PC, Magluilo J Jr, Solomon CJ, Levine B. A drug toxicity death involving propylhexedrine and mitragynine. J Anal Toxicol. 2011;35(1):54-59.
9. Rosenbaum CD, Carreiro SP, Babu KM. Here today, gone tomorrow…and back again? A review of herbal marijuana alternatives (K2, Spice), synthetic cathinones (bath salts), kratom, Salvia divinorum, methoxetamine, and piperazines. J Med Toxicol. 2012;8(1):15-32.
10. Rech MA, Donahey E, Cappiello Dziedzic JM, Oh L, Greenhalgh E. New drugs of abuse. Pharmacotherapy. 2015;35(2):189-197.
11. Silvilotti MLA. Initial management of the critically ill adult with an unknown overdose. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/initial-management-of-the -critically-ill-adult-with-an-unknown-overdose. Updated August 27, 2015. Accessed September 26, 2016.
12. Kittirattanapaiboon P, Suttajit S, Junsirimongkol B, Likhitsathian S, Srisurapanont M. Suicide risk among Thai illicit drug users with and without mental/alcohol use disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014;10:453-458.
13. Le D, Goggin MM, Janis GC. Analysis of mitragynine and metabolites in human urine for detecting the use of the psychoactive plant kratom. J Anal Toxicol. 2012;36(9):616-625.