User login
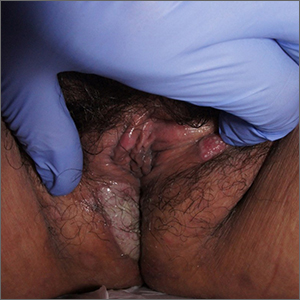
White-to-pink friable plaques occurring acutely in the vulva is concerning for one form of secondary syphilis that affects mucous membranes: condyloma lata.
Known as the great imitator for its variety of clinical presentations, syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. Three to 10 days following contact with the spirochete, a painless ulcer or chancre forms and subsequently resolves—sometimes without notice.
Secondary syphilis develops from hematogenous spread of bacteria taking many forms—most commonly a widespread rash over the whole body of many (although sometimes faint) macules or papules up to about 1 cm in size and haphazardly spread out about every 1 cm. Palms and soles may be affected, even if faintly. Another, less common form of secondary syphilis includes the friable plaques (often in the anogenital area, as pictured) that are highly concentrated with bacteria. These occur 3 to 12 weeks after the appearance of a primary chancre and are variably symptomatic.
The differential diagnosis includes genital warts, vulvar carcinoma, and pemphigus vegetans. The relatively rapid, multifocal presentation helps to separate this disorder from vulvar carcinoma. A biopsy can distinguish the 2. However, diagnosis is better made with serology using nontreponemal tests, such as the rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test. Treponemal tests (assaying immunoglobulin [Ig]M and IgG to Treponema pallidum) are also an option and are very specific. Following this, an RPR titer can help guide treatment. Darkfield microscopy, which can reveal spirochetes directly, isn’t readily available but could be used to diagnose condyloma lata.
Patients who have been given a diagnosis of syphilis should be offered screening for other STIs, including HIV. Anyone who has had sexual contact with the patient within the previous 90 days should be notified, tested, and treated. Patients with primary or secondary syphilis should be treated with 2.4 million units of intramuscular (IM) benzathine penicillin G in a single dose—regardless of whether they test positive for HIV. To exclude tertiary syphilis, a careful neurologic exam should take place at the time of diagnosis and again 6 and 12 months after treatment (sooner if follow-up may be uncertain). Consider treatment failure if RPR titers haven’t fallen fourfold in 12 months. In 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a notice that COVID-19-vaccinated patients may have false-positive RPR titers performed from Bio-Rad Laboratories (BioPlex 2200 Syphilis Total & RPR kit).1
In this case, the patient tested positive for treponemal antibodies and had an RPR titer of 1:128. She was treated with IM benzathine penicillin with lasting clearance.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Infection Treatment Guidelines, 2021. Reviewed December 22, 2021. Accessed February 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/syphilis.htm

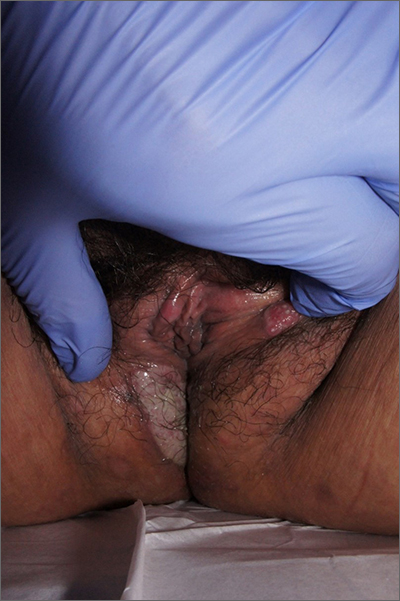
White-to-pink friable plaques occurring acutely in the vulva is concerning for one form of secondary syphilis that affects mucous membranes: condyloma lata.
Known as the great imitator for its variety of clinical presentations, syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. Three to 10 days following contact with the spirochete, a painless ulcer or chancre forms and subsequently resolves—sometimes without notice.
Secondary syphilis develops from hematogenous spread of bacteria taking many forms—most commonly a widespread rash over the whole body of many (although sometimes faint) macules or papules up to about 1 cm in size and haphazardly spread out about every 1 cm. Palms and soles may be affected, even if faintly. Another, less common form of secondary syphilis includes the friable plaques (often in the anogenital area, as pictured) that are highly concentrated with bacteria. These occur 3 to 12 weeks after the appearance of a primary chancre and are variably symptomatic.
The differential diagnosis includes genital warts, vulvar carcinoma, and pemphigus vegetans. The relatively rapid, multifocal presentation helps to separate this disorder from vulvar carcinoma. A biopsy can distinguish the 2. However, diagnosis is better made with serology using nontreponemal tests, such as the rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test. Treponemal tests (assaying immunoglobulin [Ig]M and IgG to Treponema pallidum) are also an option and are very specific. Following this, an RPR titer can help guide treatment. Darkfield microscopy, which can reveal spirochetes directly, isn’t readily available but could be used to diagnose condyloma lata.
Patients who have been given a diagnosis of syphilis should be offered screening for other STIs, including HIV. Anyone who has had sexual contact with the patient within the previous 90 days should be notified, tested, and treated. Patients with primary or secondary syphilis should be treated with 2.4 million units of intramuscular (IM) benzathine penicillin G in a single dose—regardless of whether they test positive for HIV. To exclude tertiary syphilis, a careful neurologic exam should take place at the time of diagnosis and again 6 and 12 months after treatment (sooner if follow-up may be uncertain). Consider treatment failure if RPR titers haven’t fallen fourfold in 12 months. In 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a notice that COVID-19-vaccinated patients may have false-positive RPR titers performed from Bio-Rad Laboratories (BioPlex 2200 Syphilis Total & RPR kit).1
In this case, the patient tested positive for treponemal antibodies and had an RPR titer of 1:128. She was treated with IM benzathine penicillin with lasting clearance.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

White-to-pink friable plaques occurring acutely in the vulva is concerning for one form of secondary syphilis that affects mucous membranes: condyloma lata.
Known as the great imitator for its variety of clinical presentations, syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. Three to 10 days following contact with the spirochete, a painless ulcer or chancre forms and subsequently resolves—sometimes without notice.
Secondary syphilis develops from hematogenous spread of bacteria taking many forms—most commonly a widespread rash over the whole body of many (although sometimes faint) macules or papules up to about 1 cm in size and haphazardly spread out about every 1 cm. Palms and soles may be affected, even if faintly. Another, less common form of secondary syphilis includes the friable plaques (often in the anogenital area, as pictured) that are highly concentrated with bacteria. These occur 3 to 12 weeks after the appearance of a primary chancre and are variably symptomatic.
The differential diagnosis includes genital warts, vulvar carcinoma, and pemphigus vegetans. The relatively rapid, multifocal presentation helps to separate this disorder from vulvar carcinoma. A biopsy can distinguish the 2. However, diagnosis is better made with serology using nontreponemal tests, such as the rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test. Treponemal tests (assaying immunoglobulin [Ig]M and IgG to Treponema pallidum) are also an option and are very specific. Following this, an RPR titer can help guide treatment. Darkfield microscopy, which can reveal spirochetes directly, isn’t readily available but could be used to diagnose condyloma lata.
Patients who have been given a diagnosis of syphilis should be offered screening for other STIs, including HIV. Anyone who has had sexual contact with the patient within the previous 90 days should be notified, tested, and treated. Patients with primary or secondary syphilis should be treated with 2.4 million units of intramuscular (IM) benzathine penicillin G in a single dose—regardless of whether they test positive for HIV. To exclude tertiary syphilis, a careful neurologic exam should take place at the time of diagnosis and again 6 and 12 months after treatment (sooner if follow-up may be uncertain). Consider treatment failure if RPR titers haven’t fallen fourfold in 12 months. In 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a notice that COVID-19-vaccinated patients may have false-positive RPR titers performed from Bio-Rad Laboratories (BioPlex 2200 Syphilis Total & RPR kit).1
In this case, the patient tested positive for treponemal antibodies and had an RPR titer of 1:128. She was treated with IM benzathine penicillin with lasting clearance.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Infection Treatment Guidelines, 2021. Reviewed December 22, 2021. Accessed February 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/syphilis.htm
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Infection Treatment Guidelines, 2021. Reviewed December 22, 2021. Accessed February 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/syphilis.htm