User login
While U.S. death rates have declined overall, marked geographic disparities exist at the state level in burden of disease, injuries, and risk factors, according to a comprehensive analysis.
Life expectancy varies substantially, for example, ranging from a high of 81.3 years in Hawaii to a low of 74.7 years in Mississippi, according to results from the analysis of data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study (JAMA. 2018;319[14]:1444-72).
Previously decreasing death rates for adults have reversed in 19 states, according to the analysis, which covers the years 1990 to 2016.
Hardest hit were Kentucky, New Mexico, Oklahoma, West Virginia, and Wyoming, which had mortality increases of more than 10% among adults aged 20-55 years. Those increases were largely due to causes such as substance use disorders, self-harm, and cirrhosis, according to the US Burden of Disease Collaborators, who authored the report.
“These findings should be used to examine the causes of health variations and to plan, develop, and implement programs and policies to improve health overall and eliminate disparities in the United States,” the authors wrote.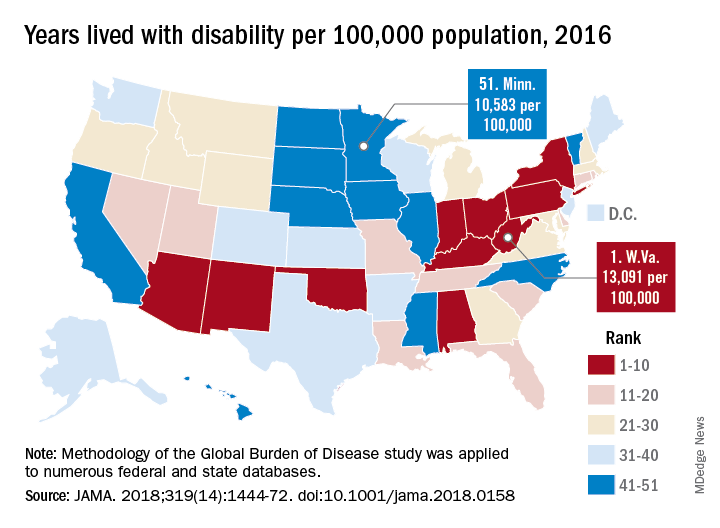
Overall, U.S. death rates have declined from 745.2 per 100,000 persons in 1990 to 578.0 per 100,000 persons in 2016, according to the report.
Likewise, health outcomes throughout the United States have improved over time for some conditions, such as ischemic heart disease, lung cancer, and neonatal preterm complications, the report says.
However, those gains are offset by rising death rates due to drug-use disorders, chronic kidney disease, cirrhosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, and self-harm.

The three most important risk factors in the United States are high body mass index, smoking, and high fasting plasma glucose, the analysis showed. Of those risk factors, only smoking is decreasing, authors noted.
Many risk factors contributing to disparities in burden among states are amenable to medical treatment that emphasizes supportive behavioral and lifestyle changes, according to the authors.
“Expanding health coverage for certain conditions and medications should be considered and adopted to reduce burden,” they said.
Substance abuse disorders, cirrhosis, and self-harm, the causes of the mortality reversal in Kentucky, New Mexico, and other states, could be addressed via a wide range of interventions, according to the investigators.
Prevention programs could address the root causes of substance use and causes of relapse, while physicians can play a “major role” in addiction control through counseling of patients on pain control medication, they said.
Interventions to treat hepatitis C and decrease excessive alcohol consumption could help address cirrhosis, while for self-harm, the most promising approaches focus on restricting access to lethal means, they said, noting that a large proportion of U.S. suicides are due to firearms.
“While multiple strategies are available for dealing with these problems, they have not until very recently garnered attention,” investigators wrote.
The study was supported in part by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Some individual study collaborators reported disclosures related to Savient, Takeda, Crealta/Horizon, Regeneron, Allergan, and others.
SOURCE: The US Burden of Disease Collaborators. JAMA 2018;319(14):1444-72.
This report on Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study data profoundly and powerfully illuminates U.S. health trends over time and by geography. There is much unfinished business for us, nationally and at the state level.
Clinicians and policy makers can use the rankings to evaluate why many individuals are still experiencing injury, disease, and deaths that are preventable; in doing so, the entire nation could move closely resemble a United States of health.
Clinicians could use the results to help guide patients through evidence-based disease prevention and early intervention, a strategy that has led to decreases in death due to cancer and cardiovascular disease over the past few decades.
At the same time, policy makers could use GBD 2016 results to reevaluate current national attitudes toward disease prevention.
Howard K. Koh, MD, MPH, is with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. Anand K. Parekh, MD, MPH, is with the Bipartisan Policy Center in Washington. The comments above are derived from an editorial accompanying the report from the US Burden of Disease Collaborators ( JAMA. 2018;319[14]:1438-40 ). Dr. Koh and Dr. Parekh reported no conflicts of interest related to the editorial.
This report on Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study data profoundly and powerfully illuminates U.S. health trends over time and by geography. There is much unfinished business for us, nationally and at the state level.
Clinicians and policy makers can use the rankings to evaluate why many individuals are still experiencing injury, disease, and deaths that are preventable; in doing so, the entire nation could move closely resemble a United States of health.
Clinicians could use the results to help guide patients through evidence-based disease prevention and early intervention, a strategy that has led to decreases in death due to cancer and cardiovascular disease over the past few decades.
At the same time, policy makers could use GBD 2016 results to reevaluate current national attitudes toward disease prevention.
Howard K. Koh, MD, MPH, is with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. Anand K. Parekh, MD, MPH, is with the Bipartisan Policy Center in Washington. The comments above are derived from an editorial accompanying the report from the US Burden of Disease Collaborators ( JAMA. 2018;319[14]:1438-40 ). Dr. Koh and Dr. Parekh reported no conflicts of interest related to the editorial.
This report on Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study data profoundly and powerfully illuminates U.S. health trends over time and by geography. There is much unfinished business for us, nationally and at the state level.
Clinicians and policy makers can use the rankings to evaluate why many individuals are still experiencing injury, disease, and deaths that are preventable; in doing so, the entire nation could move closely resemble a United States of health.
Clinicians could use the results to help guide patients through evidence-based disease prevention and early intervention, a strategy that has led to decreases in death due to cancer and cardiovascular disease over the past few decades.
At the same time, policy makers could use GBD 2016 results to reevaluate current national attitudes toward disease prevention.
Howard K. Koh, MD, MPH, is with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. Anand K. Parekh, MD, MPH, is with the Bipartisan Policy Center in Washington. The comments above are derived from an editorial accompanying the report from the US Burden of Disease Collaborators ( JAMA. 2018;319[14]:1438-40 ). Dr. Koh and Dr. Parekh reported no conflicts of interest related to the editorial.
While U.S. death rates have declined overall, marked geographic disparities exist at the state level in burden of disease, injuries, and risk factors, according to a comprehensive analysis.
Life expectancy varies substantially, for example, ranging from a high of 81.3 years in Hawaii to a low of 74.7 years in Mississippi, according to results from the analysis of data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study (JAMA. 2018;319[14]:1444-72).
Previously decreasing death rates for adults have reversed in 19 states, according to the analysis, which covers the years 1990 to 2016.
Hardest hit were Kentucky, New Mexico, Oklahoma, West Virginia, and Wyoming, which had mortality increases of more than 10% among adults aged 20-55 years. Those increases were largely due to causes such as substance use disorders, self-harm, and cirrhosis, according to the US Burden of Disease Collaborators, who authored the report.
“These findings should be used to examine the causes of health variations and to plan, develop, and implement programs and policies to improve health overall and eliminate disparities in the United States,” the authors wrote.
Overall, U.S. death rates have declined from 745.2 per 100,000 persons in 1990 to 578.0 per 100,000 persons in 2016, according to the report.
Likewise, health outcomes throughout the United States have improved over time for some conditions, such as ischemic heart disease, lung cancer, and neonatal preterm complications, the report says.
However, those gains are offset by rising death rates due to drug-use disorders, chronic kidney disease, cirrhosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, and self-harm.

The three most important risk factors in the United States are high body mass index, smoking, and high fasting plasma glucose, the analysis showed. Of those risk factors, only smoking is decreasing, authors noted.
Many risk factors contributing to disparities in burden among states are amenable to medical treatment that emphasizes supportive behavioral and lifestyle changes, according to the authors.
“Expanding health coverage for certain conditions and medications should be considered and adopted to reduce burden,” they said.
Substance abuse disorders, cirrhosis, and self-harm, the causes of the mortality reversal in Kentucky, New Mexico, and other states, could be addressed via a wide range of interventions, according to the investigators.
Prevention programs could address the root causes of substance use and causes of relapse, while physicians can play a “major role” in addiction control through counseling of patients on pain control medication, they said.
Interventions to treat hepatitis C and decrease excessive alcohol consumption could help address cirrhosis, while for self-harm, the most promising approaches focus on restricting access to lethal means, they said, noting that a large proportion of U.S. suicides are due to firearms.
“While multiple strategies are available for dealing with these problems, they have not until very recently garnered attention,” investigators wrote.
The study was supported in part by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Some individual study collaborators reported disclosures related to Savient, Takeda, Crealta/Horizon, Regeneron, Allergan, and others.
SOURCE: The US Burden of Disease Collaborators. JAMA 2018;319(14):1444-72.
While U.S. death rates have declined overall, marked geographic disparities exist at the state level in burden of disease, injuries, and risk factors, according to a comprehensive analysis.
Life expectancy varies substantially, for example, ranging from a high of 81.3 years in Hawaii to a low of 74.7 years in Mississippi, according to results from the analysis of data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study (JAMA. 2018;319[14]:1444-72).
Previously decreasing death rates for adults have reversed in 19 states, according to the analysis, which covers the years 1990 to 2016.
Hardest hit were Kentucky, New Mexico, Oklahoma, West Virginia, and Wyoming, which had mortality increases of more than 10% among adults aged 20-55 years. Those increases were largely due to causes such as substance use disorders, self-harm, and cirrhosis, according to the US Burden of Disease Collaborators, who authored the report.
“These findings should be used to examine the causes of health variations and to plan, develop, and implement programs and policies to improve health overall and eliminate disparities in the United States,” the authors wrote.
Overall, U.S. death rates have declined from 745.2 per 100,000 persons in 1990 to 578.0 per 100,000 persons in 2016, according to the report.
Likewise, health outcomes throughout the United States have improved over time for some conditions, such as ischemic heart disease, lung cancer, and neonatal preterm complications, the report says.
However, those gains are offset by rising death rates due to drug-use disorders, chronic kidney disease, cirrhosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, and self-harm.

The three most important risk factors in the United States are high body mass index, smoking, and high fasting plasma glucose, the analysis showed. Of those risk factors, only smoking is decreasing, authors noted.
Many risk factors contributing to disparities in burden among states are amenable to medical treatment that emphasizes supportive behavioral and lifestyle changes, according to the authors.
“Expanding health coverage for certain conditions and medications should be considered and adopted to reduce burden,” they said.
Substance abuse disorders, cirrhosis, and self-harm, the causes of the mortality reversal in Kentucky, New Mexico, and other states, could be addressed via a wide range of interventions, according to the investigators.
Prevention programs could address the root causes of substance use and causes of relapse, while physicians can play a “major role” in addiction control through counseling of patients on pain control medication, they said.
Interventions to treat hepatitis C and decrease excessive alcohol consumption could help address cirrhosis, while for self-harm, the most promising approaches focus on restricting access to lethal means, they said, noting that a large proportion of U.S. suicides are due to firearms.
“While multiple strategies are available for dealing with these problems, they have not until very recently garnered attention,” investigators wrote.
The study was supported in part by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Some individual study collaborators reported disclosures related to Savient, Takeda, Crealta/Horizon, Regeneron, Allergan, and others.
SOURCE: The US Burden of Disease Collaborators. JAMA 2018;319(14):1444-72.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: While U.S. death rates have declined overall, marked geographic disparities exist at the state level in burden of disease, injuries, and risk factors.
Major finding: Life expectancy ranged from a high of 81.3 years in Hawaii to a low of 74.7 years in Mississippi, and previously decreasing death rates for adults have reversed in 19 states.
Study details: A U.S. state-level analysis of results from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study illustrating trends in diseases, injuries, risk factors, and deaths from 1990 to 2016.
Disclosures: The study was supported in part by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Study authors reported disclosures related to Savient, Takeda, Crealta/Horizon, Regeneron, Allergan, and others.
Source: The US Burden of Disease Collaborators. JAMA 2018;319(14):1444-1472.