User login
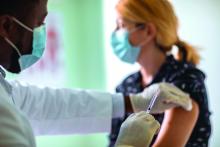
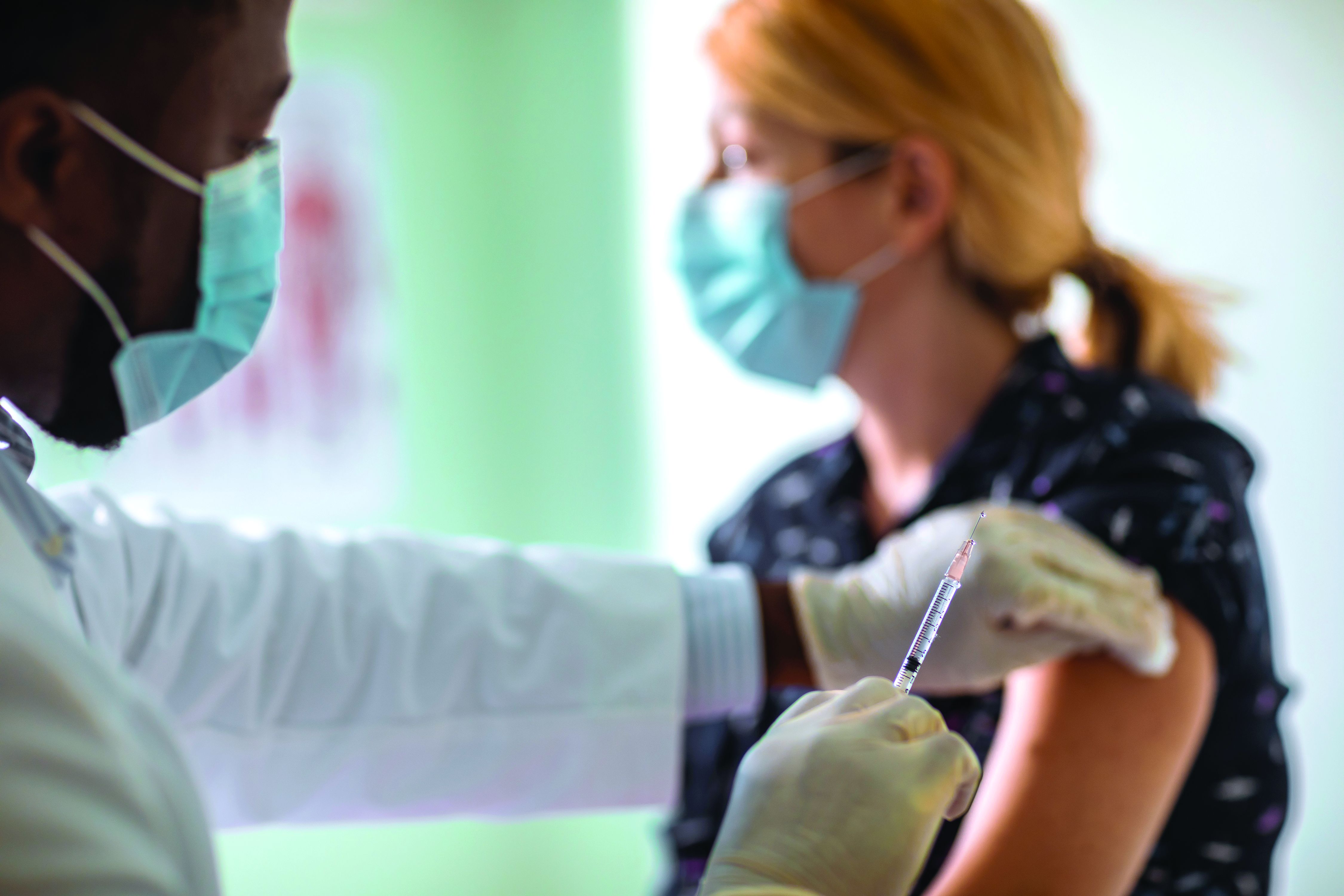
Moderna has released new data that it said support the argument for COVID-19 booster shots – specifically showing that people who received a first shot of their mRNA vaccine a median of 13 months ago are more likely to experience a breakthrough infection compared to individuals who received a first shot a median of 8 months ago.
The findings come from the ongoing phase 3 COVE clinical trial, the results of which the Food and Drug Administration considered in granting emergency use authorization for the vaccine. In the initial stage of the trial, people were randomly assigned to receive the company’s mRNA vaccine or placebo.
according to the analysis of the open-label extension of the study during which placebo participants could cross over and get immunized as well.
The updated COVE trial data show that 88 breakthrough cases of COVID-19 occurred among 11,431 participants vaccinated between December 2020 and March 2021 (49.0 cases per 1,000 person-years).
In contrast, there were 162 breakthrough cases among 14,746 people vaccinated between July and October 2020 (77.1 cases per 1,000 person-years).
The breakthrough infections include 19 severe cases. Although not statically different, there was a trend toward fewer severe cases among the more recently vaccinated, at a rate of 3.3 per 1,000 person-years, compared with 6.2 per 1,000 person-years in the group vaccinated in 2020
The findings were posted as a preprint to the medRxiv server and have not yet been peer reviewed.
“The increased risk of breakthrough infections in COVE study participants who were vaccinated last year compared to more recently illustrates the impact of waning immunity and supports the need for a booster to maintain high levels of protection,” Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said in a company statement.
An FDA advisory committee is meeting Sept. 17 to look at the available evidence on boosters to help the agency decide whether the additional shots are warranted.
There is still a lot of debate in the medical community about the need for boosters. U.S. physicians and nurses are divided about the need for them and about how the country should prioritize its vaccine supplies, according to a Medscape poll of more than 1,700 clinicians that collected responses from Aug. 25 to Sept. 6, 2020.
The research was funded by Moderna, and also supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderna has released new data that it said support the argument for COVID-19 booster shots – specifically showing that people who received a first shot of their mRNA vaccine a median of 13 months ago are more likely to experience a breakthrough infection compared to individuals who received a first shot a median of 8 months ago.
The findings come from the ongoing phase 3 COVE clinical trial, the results of which the Food and Drug Administration considered in granting emergency use authorization for the vaccine. In the initial stage of the trial, people were randomly assigned to receive the company’s mRNA vaccine or placebo.
according to the analysis of the open-label extension of the study during which placebo participants could cross over and get immunized as well.
The updated COVE trial data show that 88 breakthrough cases of COVID-19 occurred among 11,431 participants vaccinated between December 2020 and March 2021 (49.0 cases per 1,000 person-years).
In contrast, there were 162 breakthrough cases among 14,746 people vaccinated between July and October 2020 (77.1 cases per 1,000 person-years).
The breakthrough infections include 19 severe cases. Although not statically different, there was a trend toward fewer severe cases among the more recently vaccinated, at a rate of 3.3 per 1,000 person-years, compared with 6.2 per 1,000 person-years in the group vaccinated in 2020
The findings were posted as a preprint to the medRxiv server and have not yet been peer reviewed.
“The increased risk of breakthrough infections in COVE study participants who were vaccinated last year compared to more recently illustrates the impact of waning immunity and supports the need for a booster to maintain high levels of protection,” Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said in a company statement.
An FDA advisory committee is meeting Sept. 17 to look at the available evidence on boosters to help the agency decide whether the additional shots are warranted.
There is still a lot of debate in the medical community about the need for boosters. U.S. physicians and nurses are divided about the need for them and about how the country should prioritize its vaccine supplies, according to a Medscape poll of more than 1,700 clinicians that collected responses from Aug. 25 to Sept. 6, 2020.
The research was funded by Moderna, and also supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderna has released new data that it said support the argument for COVID-19 booster shots – specifically showing that people who received a first shot of their mRNA vaccine a median of 13 months ago are more likely to experience a breakthrough infection compared to individuals who received a first shot a median of 8 months ago.
The findings come from the ongoing phase 3 COVE clinical trial, the results of which the Food and Drug Administration considered in granting emergency use authorization for the vaccine. In the initial stage of the trial, people were randomly assigned to receive the company’s mRNA vaccine or placebo.
according to the analysis of the open-label extension of the study during which placebo participants could cross over and get immunized as well.
The updated COVE trial data show that 88 breakthrough cases of COVID-19 occurred among 11,431 participants vaccinated between December 2020 and March 2021 (49.0 cases per 1,000 person-years).
In contrast, there were 162 breakthrough cases among 14,746 people vaccinated between July and October 2020 (77.1 cases per 1,000 person-years).
The breakthrough infections include 19 severe cases. Although not statically different, there was a trend toward fewer severe cases among the more recently vaccinated, at a rate of 3.3 per 1,000 person-years, compared with 6.2 per 1,000 person-years in the group vaccinated in 2020
The findings were posted as a preprint to the medRxiv server and have not yet been peer reviewed.
“The increased risk of breakthrough infections in COVE study participants who were vaccinated last year compared to more recently illustrates the impact of waning immunity and supports the need for a booster to maintain high levels of protection,” Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said in a company statement.
An FDA advisory committee is meeting Sept. 17 to look at the available evidence on boosters to help the agency decide whether the additional shots are warranted.
There is still a lot of debate in the medical community about the need for boosters. U.S. physicians and nurses are divided about the need for them and about how the country should prioritize its vaccine supplies, according to a Medscape poll of more than 1,700 clinicians that collected responses from Aug. 25 to Sept. 6, 2020.
The research was funded by Moderna, and also supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.