User login
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
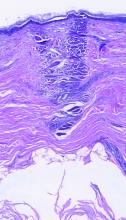
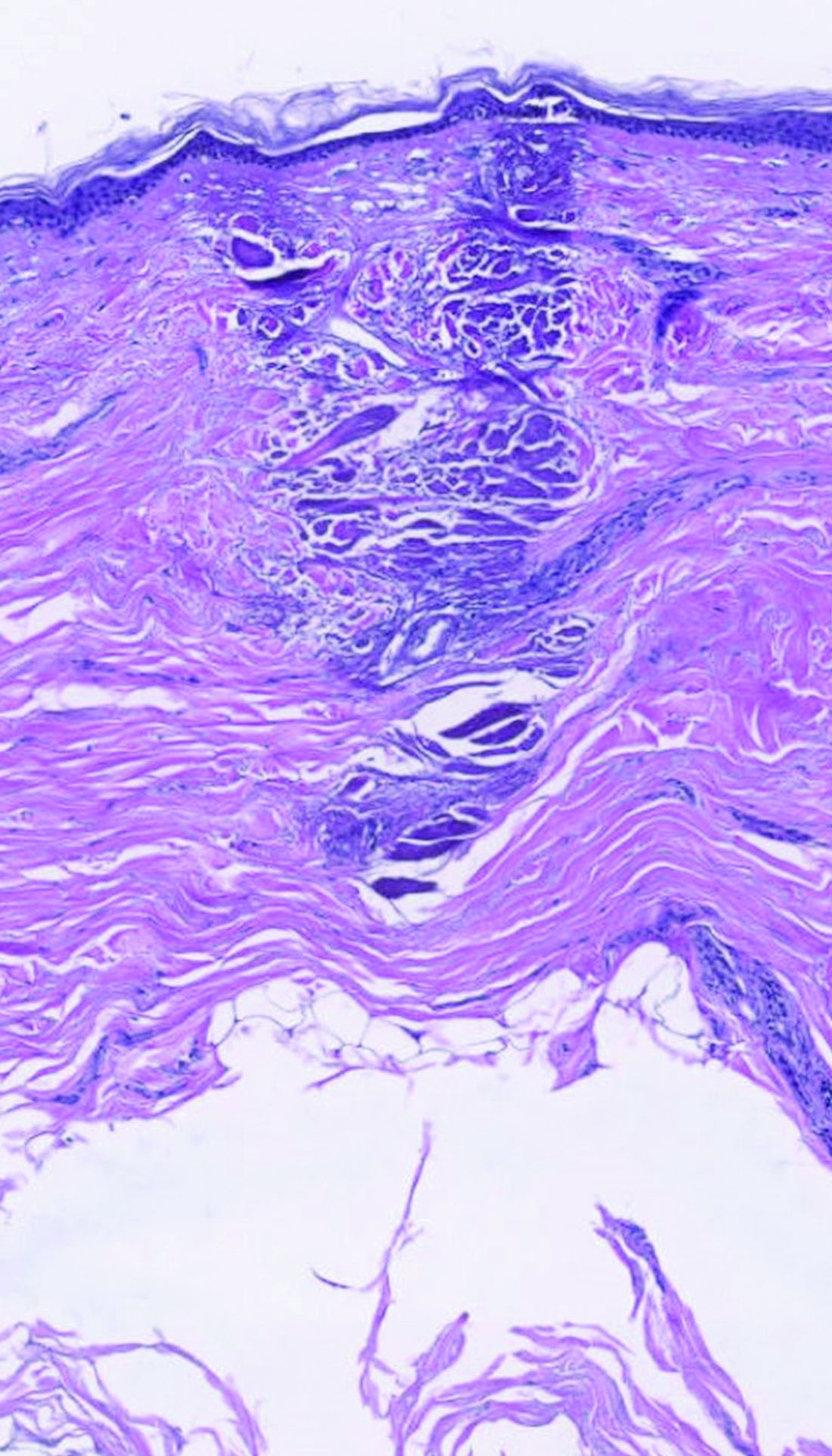
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE