User login
Over 6.3 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine have been administered to children aged 12-17 years as of June 7, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
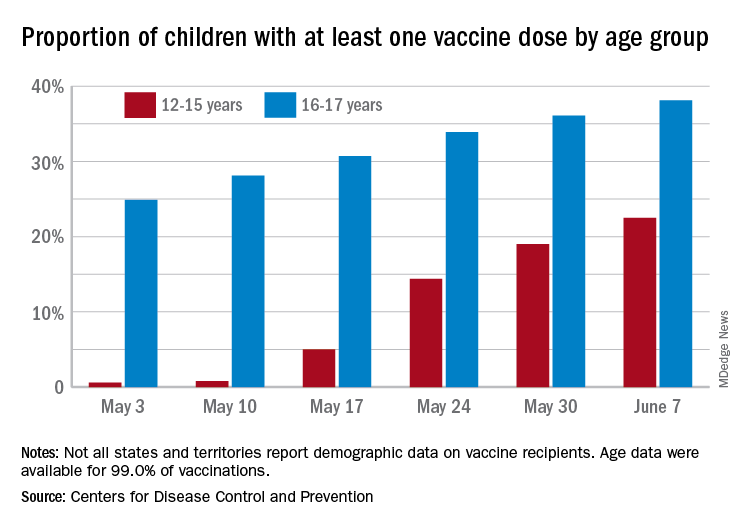
The latest results from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker show that , with the corresponding figures for vaccine completion coming in at 4.1% and 26.4%. Compared with a week earlier, those numbers are up by 15.4% (one dose) and 486% (completion) for the younger group and by 4.7% and 8.6%, respectively, for the older children.
Children aged 12-15 represented 17.9% of all persons who initiated vaccination in the last 14 days up to June 7, while children aged 16-17 made up 4.8% of vaccine initiation over that period. The 25- to 39-year-olds, at 23.7% of all vaccine initiators, were the only group ahead of those aged 12-15, and the 50- to 64-year-olds were just behind at 17.7%, the CDC data show.
Both groups of children were on the low side, however, when it came to vaccine completion in the last 14 days, with those aged 12-15 at 6.7% of the total and those aged 16-17 years at 4.3%. The only age groups lower than that were ≥75 at 3.5% and <12 at 0.2%, and the highest share of vaccine completion was 26.0% for those aged 25-39, which also happens to be the group with the largest share of the U.S. population (20.5%), the CDC said.
People considered fully vaccinated are those who have received the second dose of a two-dose series or one dose of a single-shot vaccine, but children under age 18 years are eligible only for the Pfizer-BioNTech version, the CDC noted.
Meanwhile, back on the incidence side of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of new cases in U.S. children for the week ending June 3 was at its lowest point (16,281) since mid-June of 2020, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Cases among children now total 3.99 million, which represents 14.1% of cases among all ages, a proportion that hasn’t increased since mid-May, which hasn’t happened since the two groups started keeping track in mid-April of 2020 in the 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam that report such data by age.
Less encouraging was the CDC’s report that “COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates among adolescents ages 12-17 years increased during March and April, following declines in January and February 2021.”
Children have been experiencing much lower rates of severe disease than those of adults throughout the pandemic, the CDC pointed out, but “recent increases in COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates and the potential for severe disease in adolescents reinforce the importance of continued prevention strategies, including vaccination and the correct and consistent use of masks in those who are not yet fully vaccinated.”
Over 6.3 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine have been administered to children aged 12-17 years as of June 7, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The latest results from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker show that , with the corresponding figures for vaccine completion coming in at 4.1% and 26.4%. Compared with a week earlier, those numbers are up by 15.4% (one dose) and 486% (completion) for the younger group and by 4.7% and 8.6%, respectively, for the older children.
Children aged 12-15 represented 17.9% of all persons who initiated vaccination in the last 14 days up to June 7, while children aged 16-17 made up 4.8% of vaccine initiation over that period. The 25- to 39-year-olds, at 23.7% of all vaccine initiators, were the only group ahead of those aged 12-15, and the 50- to 64-year-olds were just behind at 17.7%, the CDC data show.
Both groups of children were on the low side, however, when it came to vaccine completion in the last 14 days, with those aged 12-15 at 6.7% of the total and those aged 16-17 years at 4.3%. The only age groups lower than that were ≥75 at 3.5% and <12 at 0.2%, and the highest share of vaccine completion was 26.0% for those aged 25-39, which also happens to be the group with the largest share of the U.S. population (20.5%), the CDC said.
People considered fully vaccinated are those who have received the second dose of a two-dose series or one dose of a single-shot vaccine, but children under age 18 years are eligible only for the Pfizer-BioNTech version, the CDC noted.
Meanwhile, back on the incidence side of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of new cases in U.S. children for the week ending June 3 was at its lowest point (16,281) since mid-June of 2020, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Cases among children now total 3.99 million, which represents 14.1% of cases among all ages, a proportion that hasn’t increased since mid-May, which hasn’t happened since the two groups started keeping track in mid-April of 2020 in the 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam that report such data by age.
Less encouraging was the CDC’s report that “COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates among adolescents ages 12-17 years increased during March and April, following declines in January and February 2021.”
Children have been experiencing much lower rates of severe disease than those of adults throughout the pandemic, the CDC pointed out, but “recent increases in COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates and the potential for severe disease in adolescents reinforce the importance of continued prevention strategies, including vaccination and the correct and consistent use of masks in those who are not yet fully vaccinated.”
Over 6.3 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine have been administered to children aged 12-17 years as of June 7, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The latest results from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker show that , with the corresponding figures for vaccine completion coming in at 4.1% and 26.4%. Compared with a week earlier, those numbers are up by 15.4% (one dose) and 486% (completion) for the younger group and by 4.7% and 8.6%, respectively, for the older children.
Children aged 12-15 represented 17.9% of all persons who initiated vaccination in the last 14 days up to June 7, while children aged 16-17 made up 4.8% of vaccine initiation over that period. The 25- to 39-year-olds, at 23.7% of all vaccine initiators, were the only group ahead of those aged 12-15, and the 50- to 64-year-olds were just behind at 17.7%, the CDC data show.
Both groups of children were on the low side, however, when it came to vaccine completion in the last 14 days, with those aged 12-15 at 6.7% of the total and those aged 16-17 years at 4.3%. The only age groups lower than that were ≥75 at 3.5% and <12 at 0.2%, and the highest share of vaccine completion was 26.0% for those aged 25-39, which also happens to be the group with the largest share of the U.S. population (20.5%), the CDC said.
People considered fully vaccinated are those who have received the second dose of a two-dose series or one dose of a single-shot vaccine, but children under age 18 years are eligible only for the Pfizer-BioNTech version, the CDC noted.
Meanwhile, back on the incidence side of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of new cases in U.S. children for the week ending June 3 was at its lowest point (16,281) since mid-June of 2020, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Cases among children now total 3.99 million, which represents 14.1% of cases among all ages, a proportion that hasn’t increased since mid-May, which hasn’t happened since the two groups started keeping track in mid-April of 2020 in the 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam that report such data by age.
Less encouraging was the CDC’s report that “COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates among adolescents ages 12-17 years increased during March and April, following declines in January and February 2021.”
Children have been experiencing much lower rates of severe disease than those of adults throughout the pandemic, the CDC pointed out, but “recent increases in COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates and the potential for severe disease in adolescents reinforce the importance of continued prevention strategies, including vaccination and the correct and consistent use of masks in those who are not yet fully vaccinated.”