User login
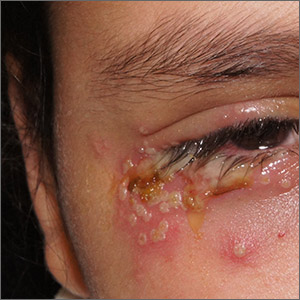
This patient was given a diagnosis of primary herpes simplex virus (HSV) based on the appearance of her eyelid. Swabs were performed for bacterial culture, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing was done for HSV and varicella, but results were pending prior to her transfer to the Emergency Department (ED).
The patient was given a single dose of 800 mg oral acyclovir (200 mg/5mL) and 500 mg of oral cephalexin (250 mg/5mL) and referred to the ED for a more detailed eye exam and to exclude orbital erosions.
HSV classically causes clustered vesicles on an erythematous base. Superinfection with skin flora can cause pustules instead of vesicles. Severe complications of HSV can include widespread skin involvement, eczema herpeticum, local destruction, central nervous system involvement, throat infections (affecting airway and oral intake), and dissemination in immunocompromised hosts. Ocular or periorbital infections increase the risk of keratitis, corneal ulcers, and loss of sight. Viral involvement of the cornea is best seen with fluorescein staining.
In cases like this one, PCR is the preferred method of testing over viral cultures or serology, given its speed, accuracy, and temporal relevance. Ophthalmology referral is warranted, although it should not delay treatment. Topical and oral antivirals are both effective when treating corneal disease; patient preference should be considered.
Most cases of HSV may resolve without treatment; however, treatment started while vesicles are present and within 72 hours of infection may shorten the time of viral replication and prevent progression to stromal involvement.
After a 12-hour wait in the ED, this patient was seen by an ophthalmology resident who did not observe orbital erosions but did note umbilication and misdiagnosed molluscum contagiosum. Umbilication is not pathognomonic for molluscum; few experienced in diagnosing molluscum contagiosum would make this error.
The patient was instructed to stop the acyclovir. Two days later when the PCR came back positive for HSV-1 and the bacterial culture confirmed growth of superimposed Staphylococcus aureus, the patient had been lost to follow-up. A better approach would have been for the ophthalmology resident to continue the acyclovir until PCR excluded herpetic disease.
Text courtesy of Tristan Reynolds, DO, Maine Dartmouth Family Medicine Residency, and Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
Barker NH. Ocular herpes simplex. BMJ Clin Evid. 2008;2008:0707.

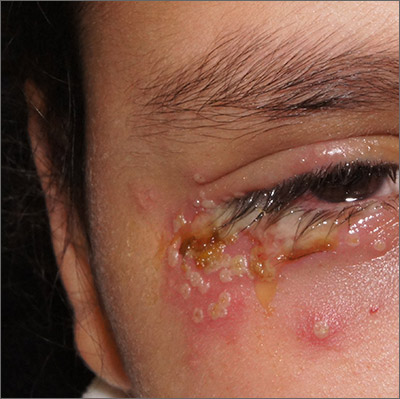
This patient was given a diagnosis of primary herpes simplex virus (HSV) based on the appearance of her eyelid. Swabs were performed for bacterial culture, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing was done for HSV and varicella, but results were pending prior to her transfer to the Emergency Department (ED).
The patient was given a single dose of 800 mg oral acyclovir (200 mg/5mL) and 500 mg of oral cephalexin (250 mg/5mL) and referred to the ED for a more detailed eye exam and to exclude orbital erosions.
HSV classically causes clustered vesicles on an erythematous base. Superinfection with skin flora can cause pustules instead of vesicles. Severe complications of HSV can include widespread skin involvement, eczema herpeticum, local destruction, central nervous system involvement, throat infections (affecting airway and oral intake), and dissemination in immunocompromised hosts. Ocular or periorbital infections increase the risk of keratitis, corneal ulcers, and loss of sight. Viral involvement of the cornea is best seen with fluorescein staining.
In cases like this one, PCR is the preferred method of testing over viral cultures or serology, given its speed, accuracy, and temporal relevance. Ophthalmology referral is warranted, although it should not delay treatment. Topical and oral antivirals are both effective when treating corneal disease; patient preference should be considered.
Most cases of HSV may resolve without treatment; however, treatment started while vesicles are present and within 72 hours of infection may shorten the time of viral replication and prevent progression to stromal involvement.
After a 12-hour wait in the ED, this patient was seen by an ophthalmology resident who did not observe orbital erosions but did note umbilication and misdiagnosed molluscum contagiosum. Umbilication is not pathognomonic for molluscum; few experienced in diagnosing molluscum contagiosum would make this error.
The patient was instructed to stop the acyclovir. Two days later when the PCR came back positive for HSV-1 and the bacterial culture confirmed growth of superimposed Staphylococcus aureus, the patient had been lost to follow-up. A better approach would have been for the ophthalmology resident to continue the acyclovir until PCR excluded herpetic disease.
Text courtesy of Tristan Reynolds, DO, Maine Dartmouth Family Medicine Residency, and Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

This patient was given a diagnosis of primary herpes simplex virus (HSV) based on the appearance of her eyelid. Swabs were performed for bacterial culture, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing was done for HSV and varicella, but results were pending prior to her transfer to the Emergency Department (ED).
The patient was given a single dose of 800 mg oral acyclovir (200 mg/5mL) and 500 mg of oral cephalexin (250 mg/5mL) and referred to the ED for a more detailed eye exam and to exclude orbital erosions.
HSV classically causes clustered vesicles on an erythematous base. Superinfection with skin flora can cause pustules instead of vesicles. Severe complications of HSV can include widespread skin involvement, eczema herpeticum, local destruction, central nervous system involvement, throat infections (affecting airway and oral intake), and dissemination in immunocompromised hosts. Ocular or periorbital infections increase the risk of keratitis, corneal ulcers, and loss of sight. Viral involvement of the cornea is best seen with fluorescein staining.
In cases like this one, PCR is the preferred method of testing over viral cultures or serology, given its speed, accuracy, and temporal relevance. Ophthalmology referral is warranted, although it should not delay treatment. Topical and oral antivirals are both effective when treating corneal disease; patient preference should be considered.
Most cases of HSV may resolve without treatment; however, treatment started while vesicles are present and within 72 hours of infection may shorten the time of viral replication and prevent progression to stromal involvement.
After a 12-hour wait in the ED, this patient was seen by an ophthalmology resident who did not observe orbital erosions but did note umbilication and misdiagnosed molluscum contagiosum. Umbilication is not pathognomonic for molluscum; few experienced in diagnosing molluscum contagiosum would make this error.
The patient was instructed to stop the acyclovir. Two days later when the PCR came back positive for HSV-1 and the bacterial culture confirmed growth of superimposed Staphylococcus aureus, the patient had been lost to follow-up. A better approach would have been for the ophthalmology resident to continue the acyclovir until PCR excluded herpetic disease.
Text courtesy of Tristan Reynolds, DO, Maine Dartmouth Family Medicine Residency, and Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
Barker NH. Ocular herpes simplex. BMJ Clin Evid. 2008;2008:0707.
Barker NH. Ocular herpes simplex. BMJ Clin Evid. 2008;2008:0707.