User login
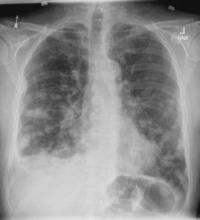
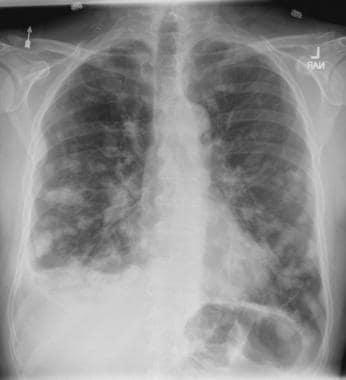
On the basis of the patient's presentation, history, and imaging results, the likely diagnosis is metastatic small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Most patients with SCLC present with hematogenous metastases; only about one third present with limited disease confined to the chest that is amenable to multimodal therapy. Patients with SCLC often present with symptoms of widespread metastases, including weight loss, bone pain, and neurologic compromise. It is uncommon for patients to present with a solitary peripheral nodule. In earlier stages, the differential diagnosis of SCLC spans other neuroendocrine lung tumors and NSCLC, in particular, basaloid carcinoma, extrapulmonary small cell tumors, and lymphoma.
Because the concentration of circulating tumor cells in SCLC is among the highest of any solid tumor, SCLC is characterized by a rapid doubling time, high growth fraction, and early development of widespread metastases. It is likely for this reason that CT screening does not seem effective in detecting early-stage SCLC. Common sites of SCLC metastasis are the contralateral lung, the brain, liver, adrenal glands, and bone. Most cases of SCLC are caused by smoking.
Metastatic spread is often evident on radiologic exam, sometimes showing pleural and pericardial effusions. In general, workup for SCLC includes imaging (contrast-enhanced CT or F-FDG PET–CT of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis and brain MRI with contrast), blood tests (cell count, liver and kidney function, and lactate dehydrogenase), and ECG. Biopsies are generally procured by bronchoscopy with or without endobronchial ultrasonography; if accessible, a biopsy of a distal metastatic site may be obtained. Diagnosis of SCLC is confirmed by histopathologic examination via cytology.
Patients with extensive-stage SCLC are typically treated with systemic chemotherapy with or without immunotherapy. In the early stages, SCLC is very responsive to cytotoxic therapies, with response rates over 60% even in patients with metastatic disease. Until recently, the only second-line therapy for recurrent metastatic SCLC was the topoisomerase I inhibitor topotecan. However, lurbinectedin was granted accelerated approval for second-line therapy after demonstrating a 35% response rate in a single-arm phase 2 study of 105 patients. In addition, the anti–programmed cell death protein 1 monoclonal antibodies nivolumab and pembrolizumab were granted accelerated approval for third-line use. Finally, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines note that participation in clinical trials should be strongly encouraged for all patients with SCLC.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient's presentation, history, and imaging results, the likely diagnosis is metastatic small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Most patients with SCLC present with hematogenous metastases; only about one third present with limited disease confined to the chest that is amenable to multimodal therapy. Patients with SCLC often present with symptoms of widespread metastases, including weight loss, bone pain, and neurologic compromise. It is uncommon for patients to present with a solitary peripheral nodule. In earlier stages, the differential diagnosis of SCLC spans other neuroendocrine lung tumors and NSCLC, in particular, basaloid carcinoma, extrapulmonary small cell tumors, and lymphoma.
Because the concentration of circulating tumor cells in SCLC is among the highest of any solid tumor, SCLC is characterized by a rapid doubling time, high growth fraction, and early development of widespread metastases. It is likely for this reason that CT screening does not seem effective in detecting early-stage SCLC. Common sites of SCLC metastasis are the contralateral lung, the brain, liver, adrenal glands, and bone. Most cases of SCLC are caused by smoking.
Metastatic spread is often evident on radiologic exam, sometimes showing pleural and pericardial effusions. In general, workup for SCLC includes imaging (contrast-enhanced CT or F-FDG PET–CT of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis and brain MRI with contrast), blood tests (cell count, liver and kidney function, and lactate dehydrogenase), and ECG. Biopsies are generally procured by bronchoscopy with or without endobronchial ultrasonography; if accessible, a biopsy of a distal metastatic site may be obtained. Diagnosis of SCLC is confirmed by histopathologic examination via cytology.
Patients with extensive-stage SCLC are typically treated with systemic chemotherapy with or without immunotherapy. In the early stages, SCLC is very responsive to cytotoxic therapies, with response rates over 60% even in patients with metastatic disease. Until recently, the only second-line therapy for recurrent metastatic SCLC was the topoisomerase I inhibitor topotecan. However, lurbinectedin was granted accelerated approval for second-line therapy after demonstrating a 35% response rate in a single-arm phase 2 study of 105 patients. In addition, the anti–programmed cell death protein 1 monoclonal antibodies nivolumab and pembrolizumab were granted accelerated approval for third-line use. Finally, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines note that participation in clinical trials should be strongly encouraged for all patients with SCLC.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient's presentation, history, and imaging results, the likely diagnosis is metastatic small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Most patients with SCLC present with hematogenous metastases; only about one third present with limited disease confined to the chest that is amenable to multimodal therapy. Patients with SCLC often present with symptoms of widespread metastases, including weight loss, bone pain, and neurologic compromise. It is uncommon for patients to present with a solitary peripheral nodule. In earlier stages, the differential diagnosis of SCLC spans other neuroendocrine lung tumors and NSCLC, in particular, basaloid carcinoma, extrapulmonary small cell tumors, and lymphoma.
Because the concentration of circulating tumor cells in SCLC is among the highest of any solid tumor, SCLC is characterized by a rapid doubling time, high growth fraction, and early development of widespread metastases. It is likely for this reason that CT screening does not seem effective in detecting early-stage SCLC. Common sites of SCLC metastasis are the contralateral lung, the brain, liver, adrenal glands, and bone. Most cases of SCLC are caused by smoking.
Metastatic spread is often evident on radiologic exam, sometimes showing pleural and pericardial effusions. In general, workup for SCLC includes imaging (contrast-enhanced CT or F-FDG PET–CT of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis and brain MRI with contrast), blood tests (cell count, liver and kidney function, and lactate dehydrogenase), and ECG. Biopsies are generally procured by bronchoscopy with or without endobronchial ultrasonography; if accessible, a biopsy of a distal metastatic site may be obtained. Diagnosis of SCLC is confirmed by histopathologic examination via cytology.
Patients with extensive-stage SCLC are typically treated with systemic chemotherapy with or without immunotherapy. In the early stages, SCLC is very responsive to cytotoxic therapies, with response rates over 60% even in patients with metastatic disease. Until recently, the only second-line therapy for recurrent metastatic SCLC was the topoisomerase I inhibitor topotecan. However, lurbinectedin was granted accelerated approval for second-line therapy after demonstrating a 35% response rate in a single-arm phase 2 study of 105 patients. In addition, the anti–programmed cell death protein 1 monoclonal antibodies nivolumab and pembrolizumab were granted accelerated approval for third-line use. Finally, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines note that participation in clinical trials should be strongly encouraged for all patients with SCLC.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 58-year-old man presents with a persistent dry cough that has developed over the past 8 weeks. He has lost about 8-10 lb in under 3 months. Height is 5 ft 10 in and weight is 172 lb (BMI 24.7). Although he quit smoking about 15 years ago, his wife still smokes. He has been screened twice for non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), most recently a year and a half ago. Chest radiograph shows multiple pulmonary nodules of varying sizes and a small right basal effusion.