User login
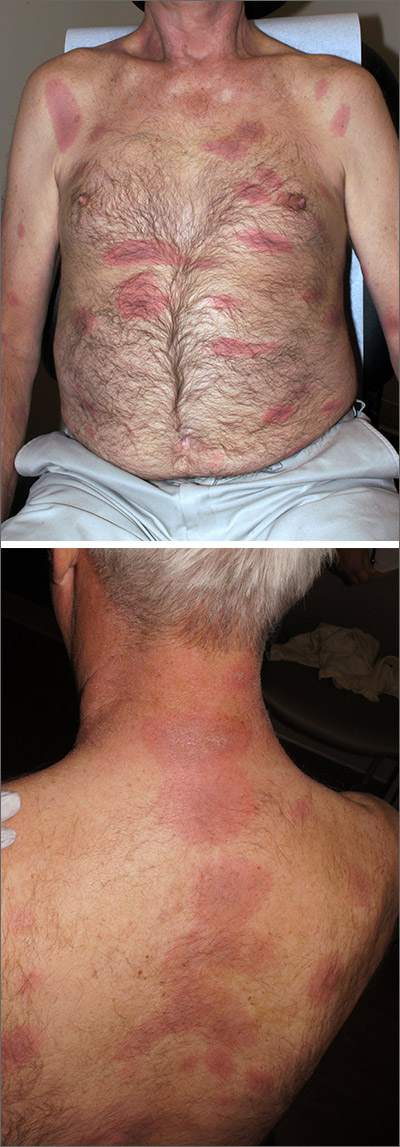
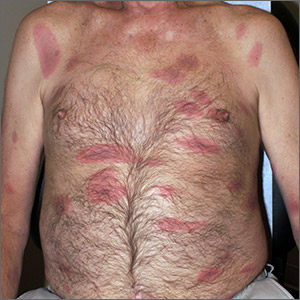
The constellation of symptoms was suggestive of Lyme disease, although connective tissue disease and syphilis were also considered. Two punch biopsies were performed in the office, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), complete blood cell count (CBC), international normalized ratio (INR), comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), Lyme enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) antibody panel, and rapid plasma reagin (RPR) laboratory tests were ordered.
Immediately available laboratory results included ESR, CBC, INR, and CMP. Findings were notable for elevated INR, as well as elevated alanine aminotransferase and aspartate transaminase. The transaminitis suggested myopathy and was consistent with clinical muscle weakness. RPR testing was negative.
Because of the confusion, severity of muscle weakness, and plausibility of early encephalopathy with Lyme disease, the patient was admitted to the hospital for further work-up. Lumbar puncture was delayed until his INR was reduced, but subsequently was found to be normal. He received intravenous (IV) ceftriaxone (2 g/d) empirically for possible early disseminated disease with neurologic complications. His confusion, muscle weakness, and transaminitis rapidly improved.
His Lyme antibody panel was positive for IgM after his third day of hospitalization. A reflexive confirmatory western blot for IgG was not positive on the initial set of labs but was positive when redrawn 4 weeks after this hospitalization, confirming Lyme disease.
Lyme disease is a vector-borne disease caused by the Borrelia genus of spirochete bacteria, most commonly Borrelia burgdorferi in North America. Transmission occurs through prolonged (typically 36-48 hours) attachment of a blacklegged tick.
The disease can be divided into 3 stages:
- localized (3-30 days): erythema migrans rash and flulike illness
- early disseminated (days to weeks; seen in this patient): multiple erythema migrans rashes, early neuroborreliosis, arthritis, carditis, and rarely hepatitis and uveitis
- late disseminated (months to years): chronic Lyme arthritis, chronic neurological disorders (eg, encephalopathy, radicular pain, and chronic neuropathy).
The initial erythema migrans rash is classically red and targetoid; it expands from the site of attachment. Early disseminated patches tend to be smaller and can occur on any body part. The rash is rarely itchy or painful but may be warm to the touch or sensitive. The rash resolves spontaneously within 3 to 4 weeks of onset.
Treatment of all early and early disseminated Lyme disease typically involves a 14- to 28-day course of doxycycline (100 mg bid for adults, 2.2 mg/kg bid [maximum 100 mg bid] for children). Patients with acute neurologic disease often can be treated with doxycycline, but patients who cannot tolerate doxycycline and those with parenchymal disease such as encephalitis should receive IV therapy with ceftriaxone 2 g/d.
In this case, the patient was discharged home on a 3-week course of doxycycline 100 mg bid and cleared without further symptoms.
Text courtesy of Tristan Reynolds, DO, Maine Dartmouth Family Medicine Residency, and Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
Lyme disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/healthcare/index.html. Accessed September 1, 2020.

The constellation of symptoms was suggestive of Lyme disease, although connective tissue disease and syphilis were also considered. Two punch biopsies were performed in the office, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), complete blood cell count (CBC), international normalized ratio (INR), comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), Lyme enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) antibody panel, and rapid plasma reagin (RPR) laboratory tests were ordered.
Immediately available laboratory results included ESR, CBC, INR, and CMP. Findings were notable for elevated INR, as well as elevated alanine aminotransferase and aspartate transaminase. The transaminitis suggested myopathy and was consistent with clinical muscle weakness. RPR testing was negative.
Because of the confusion, severity of muscle weakness, and plausibility of early encephalopathy with Lyme disease, the patient was admitted to the hospital for further work-up. Lumbar puncture was delayed until his INR was reduced, but subsequently was found to be normal. He received intravenous (IV) ceftriaxone (2 g/d) empirically for possible early disseminated disease with neurologic complications. His confusion, muscle weakness, and transaminitis rapidly improved.
His Lyme antibody panel was positive for IgM after his third day of hospitalization. A reflexive confirmatory western blot for IgG was not positive on the initial set of labs but was positive when redrawn 4 weeks after this hospitalization, confirming Lyme disease.
Lyme disease is a vector-borne disease caused by the Borrelia genus of spirochete bacteria, most commonly Borrelia burgdorferi in North America. Transmission occurs through prolonged (typically 36-48 hours) attachment of a blacklegged tick.
The disease can be divided into 3 stages:
- localized (3-30 days): erythema migrans rash and flulike illness
- early disseminated (days to weeks; seen in this patient): multiple erythema migrans rashes, early neuroborreliosis, arthritis, carditis, and rarely hepatitis and uveitis
- late disseminated (months to years): chronic Lyme arthritis, chronic neurological disorders (eg, encephalopathy, radicular pain, and chronic neuropathy).
The initial erythema migrans rash is classically red and targetoid; it expands from the site of attachment. Early disseminated patches tend to be smaller and can occur on any body part. The rash is rarely itchy or painful but may be warm to the touch or sensitive. The rash resolves spontaneously within 3 to 4 weeks of onset.
Treatment of all early and early disseminated Lyme disease typically involves a 14- to 28-day course of doxycycline (100 mg bid for adults, 2.2 mg/kg bid [maximum 100 mg bid] for children). Patients with acute neurologic disease often can be treated with doxycycline, but patients who cannot tolerate doxycycline and those with parenchymal disease such as encephalitis should receive IV therapy with ceftriaxone 2 g/d.
In this case, the patient was discharged home on a 3-week course of doxycycline 100 mg bid and cleared without further symptoms.
Text courtesy of Tristan Reynolds, DO, Maine Dartmouth Family Medicine Residency, and Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

The constellation of symptoms was suggestive of Lyme disease, although connective tissue disease and syphilis were also considered. Two punch biopsies were performed in the office, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), complete blood cell count (CBC), international normalized ratio (INR), comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), Lyme enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) antibody panel, and rapid plasma reagin (RPR) laboratory tests were ordered.
Immediately available laboratory results included ESR, CBC, INR, and CMP. Findings were notable for elevated INR, as well as elevated alanine aminotransferase and aspartate transaminase. The transaminitis suggested myopathy and was consistent with clinical muscle weakness. RPR testing was negative.
Because of the confusion, severity of muscle weakness, and plausibility of early encephalopathy with Lyme disease, the patient was admitted to the hospital for further work-up. Lumbar puncture was delayed until his INR was reduced, but subsequently was found to be normal. He received intravenous (IV) ceftriaxone (2 g/d) empirically for possible early disseminated disease with neurologic complications. His confusion, muscle weakness, and transaminitis rapidly improved.
His Lyme antibody panel was positive for IgM after his third day of hospitalization. A reflexive confirmatory western blot for IgG was not positive on the initial set of labs but was positive when redrawn 4 weeks after this hospitalization, confirming Lyme disease.
Lyme disease is a vector-borne disease caused by the Borrelia genus of spirochete bacteria, most commonly Borrelia burgdorferi in North America. Transmission occurs through prolonged (typically 36-48 hours) attachment of a blacklegged tick.
The disease can be divided into 3 stages:
- localized (3-30 days): erythema migrans rash and flulike illness
- early disseminated (days to weeks; seen in this patient): multiple erythema migrans rashes, early neuroborreliosis, arthritis, carditis, and rarely hepatitis and uveitis
- late disseminated (months to years): chronic Lyme arthritis, chronic neurological disorders (eg, encephalopathy, radicular pain, and chronic neuropathy).
The initial erythema migrans rash is classically red and targetoid; it expands from the site of attachment. Early disseminated patches tend to be smaller and can occur on any body part. The rash is rarely itchy or painful but may be warm to the touch or sensitive. The rash resolves spontaneously within 3 to 4 weeks of onset.
Treatment of all early and early disseminated Lyme disease typically involves a 14- to 28-day course of doxycycline (100 mg bid for adults, 2.2 mg/kg bid [maximum 100 mg bid] for children). Patients with acute neurologic disease often can be treated with doxycycline, but patients who cannot tolerate doxycycline and those with parenchymal disease such as encephalitis should receive IV therapy with ceftriaxone 2 g/d.
In this case, the patient was discharged home on a 3-week course of doxycycline 100 mg bid and cleared without further symptoms.
Text courtesy of Tristan Reynolds, DO, Maine Dartmouth Family Medicine Residency, and Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
Lyme disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/healthcare/index.html. Accessed September 1, 2020.
Lyme disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/healthcare/index.html. Accessed September 1, 2020.