User login
The Internet has been a transformative means of transmitting information. Alas, the information is often not vetted, so the effects on science, truth, and health literacy have been mixed. Unfortunately, Facebook spawned a billion dollar industry that transmits gossip. Twitter distributes information based on celebrity rather than intelligence or expertise.
Listservs and Google groups have allowed small communities to form unrestricted by the physical locations of the members. A listserv for pediatric hospitalists, with 3,800 members, provides quick access to a vast body of knowledge, an extensive array of experience, and insightful clinical wisdom. Discussions on this listserv resource have inspired several of my columns, including this one. The professionalism of the listserv members ensures the accuracy of the messages. Because many of the members work nights, it is possible to post a question and receive five consults from peers, even at 1 a.m. When I first started office practice in rural areas, all I had available was my memory, Rudolph’s Pediatrics textbook, and The Harriet Lane Handbook.
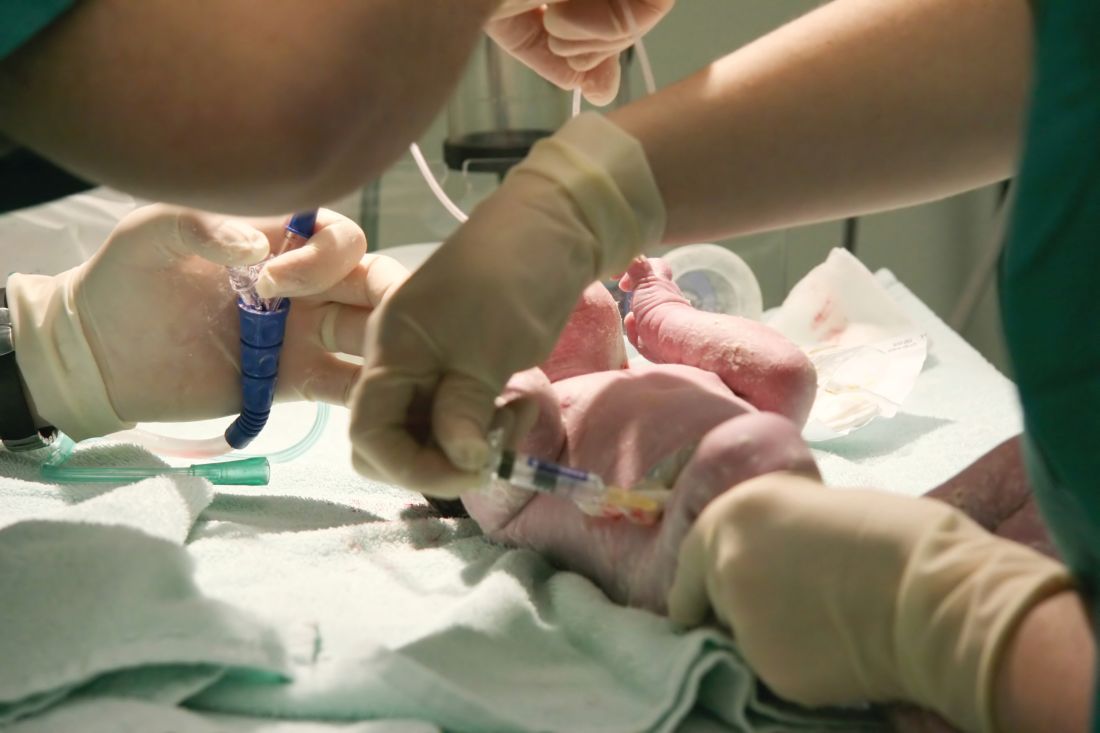
Misinformation has led to vaccine hesitancy and the reemergence of diseases such as measles that had been essentially eliminated. Because people haven’t seen these diseases, they are prone to believing any critique about the risk of vaccines. More recently, parents have been refusing the vitamin K shot that is provided to all newborns to prevent hemorrhagic disease of the newborn, now called vitamin K deficiency bleeding. The incidence of this bleeding disorder is relatively rare. However, when it occurs, the results can be disastrous, with life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeds and disabling brain hemorrhages. As with vaccine hesitancy, the corruption of scientific knowledge has led to bad outcomes that once were nearly eliminated by modern health care.
Part of being a professional is communicating in a manner that helps parents understand small risks. I compare newborn vitamin K deficiency to the risk of driving the newborn around for the first 30 days of life without a car seat. The vast majority of people will not have an accident in that time and their babies will be fine. But emergency department doctors would see so many preventable cases of injury that they would strongly advocate for car seats. I also note that if the baby has a stroke due to vitamin K deficiency, we can’t catch it early and fix it.
One issue that comes up in the nursery is whether the physician should refuse to perform a circumcision on a newborn who has not received vitamin K. The risk of bleeding is increased further when circumcisions are done as outpatient procedures a few days after birth. When this topic was discussed on the hospitalist’s listserv, most respondents took a hard line and would not perform the procedure. I am more ambivalent because of my strong personal value of accommodating diverse views and perhaps because I have never experienced a severe case of postop bleeding. The absolute risk is low.
The ethical issues are similar to those involved in maintaining or dismissing families from your practice panel if they refuse vaccines. Some physicians think the threat of having to find another doctor is the only way to appear credible when advocating the use of vaccines. Actions speak louder than words. Other physicians are dedicated to accommodating diverse viewpoints. They try to persuade over time. This is a complex subject and the American Academy of Pediatrics’ position on this changed 2 years ago to consider dismissal as a viable option as long as it adheres to relevant state laws that prohibit abandonment of patients.1
Respect for science has diminished since the era when men walked on the moon. There are myriad reasons for this. They exceed what can be covered here. All human endeavors wax and wane in their prestige and credibility. The 1960s was an era of great technological progress in many areas, including space flight and medicine. Since then, the credibility of science has been harmed by mercenary scientists who do research not to illuminate truth but to sow doubt.2 This doubt has impeded educating the public about the risks of smoking, lead paint, and climate change.
Physicians themselves have contributed to this diminished credibility of scientists. Recommendations have been published and later withdrawn in areas such as dietary cholesterol, salt, and saturated fats, estrogen replacement therapy, and screening for prostate and breast cancers. In modern America, even small inconsistencies and errors get blown up into conspiracy plots.
The era of expecting patients to blindly follow a doctor’s orders has long since passed. Parents will search the Internet for answers. The modern physician needs to guide them to good ones.
Dr. Powell is a pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2016 Aug. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-2146.
2. “Doubt is Their Product,” by David Michaels, Oxford University Press, 2008, and “Merchants of Doubt,” by Naomi Oreskes and Erik M. Conway, Bloomsbury Press, 2011.
The Internet has been a transformative means of transmitting information. Alas, the information is often not vetted, so the effects on science, truth, and health literacy have been mixed. Unfortunately, Facebook spawned a billion dollar industry that transmits gossip. Twitter distributes information based on celebrity rather than intelligence or expertise.
Listservs and Google groups have allowed small communities to form unrestricted by the physical locations of the members. A listserv for pediatric hospitalists, with 3,800 members, provides quick access to a vast body of knowledge, an extensive array of experience, and insightful clinical wisdom. Discussions on this listserv resource have inspired several of my columns, including this one. The professionalism of the listserv members ensures the accuracy of the messages. Because many of the members work nights, it is possible to post a question and receive five consults from peers, even at 1 a.m. When I first started office practice in rural areas, all I had available was my memory, Rudolph’s Pediatrics textbook, and The Harriet Lane Handbook.
Misinformation has led to vaccine hesitancy and the reemergence of diseases such as measles that had been essentially eliminated. Because people haven’t seen these diseases, they are prone to believing any critique about the risk of vaccines. More recently, parents have been refusing the vitamin K shot that is provided to all newborns to prevent hemorrhagic disease of the newborn, now called vitamin K deficiency bleeding. The incidence of this bleeding disorder is relatively rare. However, when it occurs, the results can be disastrous, with life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeds and disabling brain hemorrhages. As with vaccine hesitancy, the corruption of scientific knowledge has led to bad outcomes that once were nearly eliminated by modern health care.
Part of being a professional is communicating in a manner that helps parents understand small risks. I compare newborn vitamin K deficiency to the risk of driving the newborn around for the first 30 days of life without a car seat. The vast majority of people will not have an accident in that time and their babies will be fine. But emergency department doctors would see so many preventable cases of injury that they would strongly advocate for car seats. I also note that if the baby has a stroke due to vitamin K deficiency, we can’t catch it early and fix it.
One issue that comes up in the nursery is whether the physician should refuse to perform a circumcision on a newborn who has not received vitamin K. The risk of bleeding is increased further when circumcisions are done as outpatient procedures a few days after birth. When this topic was discussed on the hospitalist’s listserv, most respondents took a hard line and would not perform the procedure. I am more ambivalent because of my strong personal value of accommodating diverse views and perhaps because I have never experienced a severe case of postop bleeding. The absolute risk is low.
The ethical issues are similar to those involved in maintaining or dismissing families from your practice panel if they refuse vaccines. Some physicians think the threat of having to find another doctor is the only way to appear credible when advocating the use of vaccines. Actions speak louder than words. Other physicians are dedicated to accommodating diverse viewpoints. They try to persuade over time. This is a complex subject and the American Academy of Pediatrics’ position on this changed 2 years ago to consider dismissal as a viable option as long as it adheres to relevant state laws that prohibit abandonment of patients.1
Respect for science has diminished since the era when men walked on the moon. There are myriad reasons for this. They exceed what can be covered here. All human endeavors wax and wane in their prestige and credibility. The 1960s was an era of great technological progress in many areas, including space flight and medicine. Since then, the credibility of science has been harmed by mercenary scientists who do research not to illuminate truth but to sow doubt.2 This doubt has impeded educating the public about the risks of smoking, lead paint, and climate change.
Physicians themselves have contributed to this diminished credibility of scientists. Recommendations have been published and later withdrawn in areas such as dietary cholesterol, salt, and saturated fats, estrogen replacement therapy, and screening for prostate and breast cancers. In modern America, even small inconsistencies and errors get blown up into conspiracy plots.
The era of expecting patients to blindly follow a doctor’s orders has long since passed. Parents will search the Internet for answers. The modern physician needs to guide them to good ones.
Dr. Powell is a pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2016 Aug. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-2146.
2. “Doubt is Their Product,” by David Michaels, Oxford University Press, 2008, and “Merchants of Doubt,” by Naomi Oreskes and Erik M. Conway, Bloomsbury Press, 2011.
The Internet has been a transformative means of transmitting information. Alas, the information is often not vetted, so the effects on science, truth, and health literacy have been mixed. Unfortunately, Facebook spawned a billion dollar industry that transmits gossip. Twitter distributes information based on celebrity rather than intelligence or expertise.
Listservs and Google groups have allowed small communities to form unrestricted by the physical locations of the members. A listserv for pediatric hospitalists, with 3,800 members, provides quick access to a vast body of knowledge, an extensive array of experience, and insightful clinical wisdom. Discussions on this listserv resource have inspired several of my columns, including this one. The professionalism of the listserv members ensures the accuracy of the messages. Because many of the members work nights, it is possible to post a question and receive five consults from peers, even at 1 a.m. When I first started office practice in rural areas, all I had available was my memory, Rudolph’s Pediatrics textbook, and The Harriet Lane Handbook.
Misinformation has led to vaccine hesitancy and the reemergence of diseases such as measles that had been essentially eliminated. Because people haven’t seen these diseases, they are prone to believing any critique about the risk of vaccines. More recently, parents have been refusing the vitamin K shot that is provided to all newborns to prevent hemorrhagic disease of the newborn, now called vitamin K deficiency bleeding. The incidence of this bleeding disorder is relatively rare. However, when it occurs, the results can be disastrous, with life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeds and disabling brain hemorrhages. As with vaccine hesitancy, the corruption of scientific knowledge has led to bad outcomes that once were nearly eliminated by modern health care.
Part of being a professional is communicating in a manner that helps parents understand small risks. I compare newborn vitamin K deficiency to the risk of driving the newborn around for the first 30 days of life without a car seat. The vast majority of people will not have an accident in that time and their babies will be fine. But emergency department doctors would see so many preventable cases of injury that they would strongly advocate for car seats. I also note that if the baby has a stroke due to vitamin K deficiency, we can’t catch it early and fix it.
One issue that comes up in the nursery is whether the physician should refuse to perform a circumcision on a newborn who has not received vitamin K. The risk of bleeding is increased further when circumcisions are done as outpatient procedures a few days after birth. When this topic was discussed on the hospitalist’s listserv, most respondents took a hard line and would not perform the procedure. I am more ambivalent because of my strong personal value of accommodating diverse views and perhaps because I have never experienced a severe case of postop bleeding. The absolute risk is low.
The ethical issues are similar to those involved in maintaining or dismissing families from your practice panel if they refuse vaccines. Some physicians think the threat of having to find another doctor is the only way to appear credible when advocating the use of vaccines. Actions speak louder than words. Other physicians are dedicated to accommodating diverse viewpoints. They try to persuade over time. This is a complex subject and the American Academy of Pediatrics’ position on this changed 2 years ago to consider dismissal as a viable option as long as it adheres to relevant state laws that prohibit abandonment of patients.1
Respect for science has diminished since the era when men walked on the moon. There are myriad reasons for this. They exceed what can be covered here. All human endeavors wax and wane in their prestige and credibility. The 1960s was an era of great technological progress in many areas, including space flight and medicine. Since then, the credibility of science has been harmed by mercenary scientists who do research not to illuminate truth but to sow doubt.2 This doubt has impeded educating the public about the risks of smoking, lead paint, and climate change.
Physicians themselves have contributed to this diminished credibility of scientists. Recommendations have been published and later withdrawn in areas such as dietary cholesterol, salt, and saturated fats, estrogen replacement therapy, and screening for prostate and breast cancers. In modern America, even small inconsistencies and errors get blown up into conspiracy plots.
The era of expecting patients to blindly follow a doctor’s orders has long since passed. Parents will search the Internet for answers. The modern physician needs to guide them to good ones.
Dr. Powell is a pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2016 Aug. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-2146.
2. “Doubt is Their Product,” by David Michaels, Oxford University Press, 2008, and “Merchants of Doubt,” by Naomi Oreskes and Erik M. Conway, Bloomsbury Press, 2011.