User login
CHICAGO – Atrial fibrillation with good heart rate control in patients who have heart failure with preserved ejection fraction is independently associated with exercise intolerance, impaired contractile reserve, and a sharply higher mortality rate than in matched HFpEF patients without the arrhythmia, a retrospective analysis showed.
“Our study, the largest of its kind, provides mechanistic evidence from cardiopulmonary testing that a rhythm control strategy may potentially improve peak exercise capacity and survival in this patient population, a finding that of course requires future prospective appraisal in randomized trials comparing rate and rhythm control of atrial fibrillation in HFpEF,” Dr. Mohamed Badreldin Elshazly reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
In the meantime, his study also shows the useful role cardiopulmonary stress testing can play in the setting of atrial fibrillation (AF) in HFpEF, he added.
“Cardiopulmonary stress tests are cheap and easy to do. They’re a big asset for personalized medicine. Using an objective measure like cardiopulmonary stress testing to define the physiologic and hemodynamic consequences of atrial fibrillation in individual patients may help identify those in whom rhythm control may improve exercise tolerance and quality of life, and those who may be okay with rate control,” according to Dr. Elshazly of the Cleveland Clinic.
He noted that while it’s well established that atrial fibrillation is associated with exercise intolerance in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and that restoration of sinus rhythm in such patients has a positive impact on exercise hemodynamics, symptom severity, and quality of life, the situation is murkier regarding AF in patients with HFpEF. Prior studies were generally small and unable to establish whether AF was independently associated with exercise intolerance or if HFpEF patients who developed AF were sicker and higher risk.
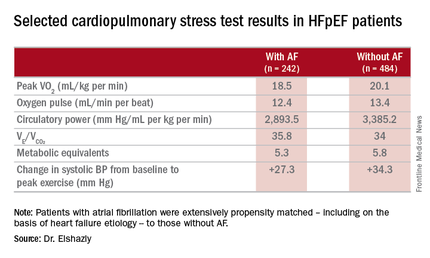
He presented a retrospective, case-control study in a cohort of 1,825 patients with HFpEF referred for maximal, symptom-limited cardiopulmonary stress testing at the Cleveland Clinic. Among these were 242 patients with AF. They were extensively propensity matched – including on the basis of heart failure etiology – to 484 HFpEF patients without AF.
“That’s what makes our study strong. We were the first to be able to do propensity matching and therefore account for other risk factors in our analysis,” Dr. Elshazly explained.
The investigators measured peak oxygen uptake (VO2), the minute ventilation–carbon dioxide production relationship (VE/VCO2) as an indicator of ventilatory efficiency, metabolic equivalents (METS), ventilatory anaerobic threshold, circulatory power as a proxy for cardiac power, peak oxygen pulse as a surrogate for stroke volume, and resting and peak heart rate and systolic blood pressure. The patients with AF were in fibrillation at the time of their cardiopulmonary stress testing.
The HFpEF patients with AF had a mean resting heart rate of 70 beats per minute and a peak rate of 130 bpm. This group showed evidence of impaired peak exercise tolerance as reflected in lower peak VO2, oxygen pulse, and circulatory power at peak exercise. Their VE/VCO2 was higher, indicating impaired ventilatory efficiency. Notably, however, their submaximal exercise capacity was similar to the non-AF controls.
“Atrial fibrillation in these patients is really more of a disease that shows itself in patients when you take them to their peak exercise capacity,” he observed.
All-cause mortality was significantly higher in the AF as compared with no-AF patients with HFpEF. The mortality curves separated early and the divergence grew larger over the course of 8 years of follow-up.
One audience member pointed out that the large mortality difference between the two groups seems disproportionate to the rather modest differences in exercise capacity.
“It brings up an interesting point,” Dr. Elshazly replied. “Maybe the increase in total mortality that we see is being driven by other things besides cardiovascular mortality. Our data doesn’t capture the specific cause of death, be it cancer, for example, but it does raise the idea that this mortality difference is not all driven by cardiovascular mortality, but by atrial fibrillation.”
Dr. Elshazly reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his institutionally supported study.
CHICAGO – Atrial fibrillation with good heart rate control in patients who have heart failure with preserved ejection fraction is independently associated with exercise intolerance, impaired contractile reserve, and a sharply higher mortality rate than in matched HFpEF patients without the arrhythmia, a retrospective analysis showed.
“Our study, the largest of its kind, provides mechanistic evidence from cardiopulmonary testing that a rhythm control strategy may potentially improve peak exercise capacity and survival in this patient population, a finding that of course requires future prospective appraisal in randomized trials comparing rate and rhythm control of atrial fibrillation in HFpEF,” Dr. Mohamed Badreldin Elshazly reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
In the meantime, his study also shows the useful role cardiopulmonary stress testing can play in the setting of atrial fibrillation (AF) in HFpEF, he added.
“Cardiopulmonary stress tests are cheap and easy to do. They’re a big asset for personalized medicine. Using an objective measure like cardiopulmonary stress testing to define the physiologic and hemodynamic consequences of atrial fibrillation in individual patients may help identify those in whom rhythm control may improve exercise tolerance and quality of life, and those who may be okay with rate control,” according to Dr. Elshazly of the Cleveland Clinic.
He noted that while it’s well established that atrial fibrillation is associated with exercise intolerance in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and that restoration of sinus rhythm in such patients has a positive impact on exercise hemodynamics, symptom severity, and quality of life, the situation is murkier regarding AF in patients with HFpEF. Prior studies were generally small and unable to establish whether AF was independently associated with exercise intolerance or if HFpEF patients who developed AF were sicker and higher risk.
He presented a retrospective, case-control study in a cohort of 1,825 patients with HFpEF referred for maximal, symptom-limited cardiopulmonary stress testing at the Cleveland Clinic. Among these were 242 patients with AF. They were extensively propensity matched – including on the basis of heart failure etiology – to 484 HFpEF patients without AF.
“That’s what makes our study strong. We were the first to be able to do propensity matching and therefore account for other risk factors in our analysis,” Dr. Elshazly explained.
The investigators measured peak oxygen uptake (VO2), the minute ventilation–carbon dioxide production relationship (VE/VCO2) as an indicator of ventilatory efficiency, metabolic equivalents (METS), ventilatory anaerobic threshold, circulatory power as a proxy for cardiac power, peak oxygen pulse as a surrogate for stroke volume, and resting and peak heart rate and systolic blood pressure. The patients with AF were in fibrillation at the time of their cardiopulmonary stress testing.
The HFpEF patients with AF had a mean resting heart rate of 70 beats per minute and a peak rate of 130 bpm. This group showed evidence of impaired peak exercise tolerance as reflected in lower peak VO2, oxygen pulse, and circulatory power at peak exercise. Their VE/VCO2 was higher, indicating impaired ventilatory efficiency. Notably, however, their submaximal exercise capacity was similar to the non-AF controls.

“Atrial fibrillation in these patients is really more of a disease that shows itself in patients when you take them to their peak exercise capacity,” he observed.
All-cause mortality was significantly higher in the AF as compared with no-AF patients with HFpEF. The mortality curves separated early and the divergence grew larger over the course of 8 years of follow-up.
One audience member pointed out that the large mortality difference between the two groups seems disproportionate to the rather modest differences in exercise capacity.
“It brings up an interesting point,” Dr. Elshazly replied. “Maybe the increase in total mortality that we see is being driven by other things besides cardiovascular mortality. Our data doesn’t capture the specific cause of death, be it cancer, for example, but it does raise the idea that this mortality difference is not all driven by cardiovascular mortality, but by atrial fibrillation.”
Dr. Elshazly reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his institutionally supported study.
CHICAGO – Atrial fibrillation with good heart rate control in patients who have heart failure with preserved ejection fraction is independently associated with exercise intolerance, impaired contractile reserve, and a sharply higher mortality rate than in matched HFpEF patients without the arrhythmia, a retrospective analysis showed.
“Our study, the largest of its kind, provides mechanistic evidence from cardiopulmonary testing that a rhythm control strategy may potentially improve peak exercise capacity and survival in this patient population, a finding that of course requires future prospective appraisal in randomized trials comparing rate and rhythm control of atrial fibrillation in HFpEF,” Dr. Mohamed Badreldin Elshazly reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
In the meantime, his study also shows the useful role cardiopulmonary stress testing can play in the setting of atrial fibrillation (AF) in HFpEF, he added.
“Cardiopulmonary stress tests are cheap and easy to do. They’re a big asset for personalized medicine. Using an objective measure like cardiopulmonary stress testing to define the physiologic and hemodynamic consequences of atrial fibrillation in individual patients may help identify those in whom rhythm control may improve exercise tolerance and quality of life, and those who may be okay with rate control,” according to Dr. Elshazly of the Cleveland Clinic.
He noted that while it’s well established that atrial fibrillation is associated with exercise intolerance in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and that restoration of sinus rhythm in such patients has a positive impact on exercise hemodynamics, symptom severity, and quality of life, the situation is murkier regarding AF in patients with HFpEF. Prior studies were generally small and unable to establish whether AF was independently associated with exercise intolerance or if HFpEF patients who developed AF were sicker and higher risk.
He presented a retrospective, case-control study in a cohort of 1,825 patients with HFpEF referred for maximal, symptom-limited cardiopulmonary stress testing at the Cleveland Clinic. Among these were 242 patients with AF. They were extensively propensity matched – including on the basis of heart failure etiology – to 484 HFpEF patients without AF.
“That’s what makes our study strong. We were the first to be able to do propensity matching and therefore account for other risk factors in our analysis,” Dr. Elshazly explained.
The investigators measured peak oxygen uptake (VO2), the minute ventilation–carbon dioxide production relationship (VE/VCO2) as an indicator of ventilatory efficiency, metabolic equivalents (METS), ventilatory anaerobic threshold, circulatory power as a proxy for cardiac power, peak oxygen pulse as a surrogate for stroke volume, and resting and peak heart rate and systolic blood pressure. The patients with AF were in fibrillation at the time of their cardiopulmonary stress testing.
The HFpEF patients with AF had a mean resting heart rate of 70 beats per minute and a peak rate of 130 bpm. This group showed evidence of impaired peak exercise tolerance as reflected in lower peak VO2, oxygen pulse, and circulatory power at peak exercise. Their VE/VCO2 was higher, indicating impaired ventilatory efficiency. Notably, however, their submaximal exercise capacity was similar to the non-AF controls.

“Atrial fibrillation in these patients is really more of a disease that shows itself in patients when you take them to their peak exercise capacity,” he observed.
All-cause mortality was significantly higher in the AF as compared with no-AF patients with HFpEF. The mortality curves separated early and the divergence grew larger over the course of 8 years of follow-up.
One audience member pointed out that the large mortality difference between the two groups seems disproportionate to the rather modest differences in exercise capacity.
“It brings up an interesting point,” Dr. Elshazly replied. “Maybe the increase in total mortality that we see is being driven by other things besides cardiovascular mortality. Our data doesn’t capture the specific cause of death, be it cancer, for example, but it does raise the idea that this mortality difference is not all driven by cardiovascular mortality, but by atrial fibrillation.”
Dr. Elshazly reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his institutionally supported study.
AT ACC 16
Key clinical point: Atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction is associated with exercise intolerance and increased mortality.
Major finding: Mean peak VO2 was 18.5 mL/kg per minute in patients with HFpEF and atrial fibrillation, significantly less than the 20.1 mL/kg per minute in controls.
Data source: A retrospective, single-institution study of cardiopulmonary stress test findings and 8-year mortality in 242 patients with HFpEF and atrial fibrillation and 484 propensity-matched controls with HFpEF and no arrhythmia.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his institutionally supported study.

