User login
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Robotic hysterectomy combined with extraction of the uterus via mini-laparotomy led to significantly shorter lengths of stay, lower estimated blood loss, and fewer postoperative complications compared with open hysterectomy when the uterus weighed more than 250 grams.
Gynecologic surgeons are seeking ways to safely perform minimally invasive hysterectomy on patients with larger uteri in light of the 2014 Food and Drug Administration admonition regarding power morcellation. To this end, Natasha Gupta, MD, and her colleagues at the University of Tennessee, Chattanooga, retrospectively reviewed all patients with uterine sizes larger than 250 grams undergoing hysterectomy at their institution between 2012 and 2015.
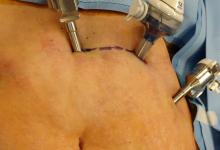
“For the mini-laparotomy, the technique utilizes a customized incision connecting the two left port sites, followed by the removal of the specimen via this incision,” Dr. Gupta said at the AAGL Global Congress.
Patient factors and outcomes were compared via Student t-tests and Chi-square analysis.
Mean length of stay was significantly shorter for patients who underwent robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy, at 1.4 days vs. 5.4 days for those with open hysterectomy (P = .000) as was mean estimated blood loss – 119.9 mL vs. 547.5 mL, respectively (P = .000). Postoperative complications were seen in fewer patients who underwent robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy, 9 of 82 patients vs. 15 of 58 open hysterectomy patients.
Mean operative time was significantly longer in robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy patients – 191.6 minutes vs. 162.8 minutes (P = .005) – but that was expected, Dr. Gupta noted. Patient factors such as hypertension, diabetes, history of spontaneous vaginal delivery and/or cesarean delivery, and body mass index, as well as uterine pathology, were not significantly different between the groups.
“Mini-laparotomy combined with minimally invasive hysterectomy is a very safe and feasible technique for tissue extraction where contained morcellation is either not preferred or not available,” Dr. Gupta said.
Dr. Gupta reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
[email protected]
On Twitter @denisefulton
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Robotic hysterectomy combined with extraction of the uterus via mini-laparotomy led to significantly shorter lengths of stay, lower estimated blood loss, and fewer postoperative complications compared with open hysterectomy when the uterus weighed more than 250 grams.
Gynecologic surgeons are seeking ways to safely perform minimally invasive hysterectomy on patients with larger uteri in light of the 2014 Food and Drug Administration admonition regarding power morcellation. To this end, Natasha Gupta, MD, and her colleagues at the University of Tennessee, Chattanooga, retrospectively reviewed all patients with uterine sizes larger than 250 grams undergoing hysterectomy at their institution between 2012 and 2015.
“For the mini-laparotomy, the technique utilizes a customized incision connecting the two left port sites, followed by the removal of the specimen via this incision,” Dr. Gupta said at the AAGL Global Congress.
Patient factors and outcomes were compared via Student t-tests and Chi-square analysis.
Mean length of stay was significantly shorter for patients who underwent robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy, at 1.4 days vs. 5.4 days for those with open hysterectomy (P = .000) as was mean estimated blood loss – 119.9 mL vs. 547.5 mL, respectively (P = .000). Postoperative complications were seen in fewer patients who underwent robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy, 9 of 82 patients vs. 15 of 58 open hysterectomy patients.
Mean operative time was significantly longer in robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy patients – 191.6 minutes vs. 162.8 minutes (P = .005) – but that was expected, Dr. Gupta noted. Patient factors such as hypertension, diabetes, history of spontaneous vaginal delivery and/or cesarean delivery, and body mass index, as well as uterine pathology, were not significantly different between the groups.
“Mini-laparotomy combined with minimally invasive hysterectomy is a very safe and feasible technique for tissue extraction where contained morcellation is either not preferred or not available,” Dr. Gupta said.
Dr. Gupta reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
[email protected]
On Twitter @denisefulton
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Robotic hysterectomy combined with extraction of the uterus via mini-laparotomy led to significantly shorter lengths of stay, lower estimated blood loss, and fewer postoperative complications compared with open hysterectomy when the uterus weighed more than 250 grams.
Gynecologic surgeons are seeking ways to safely perform minimally invasive hysterectomy on patients with larger uteri in light of the 2014 Food and Drug Administration admonition regarding power morcellation. To this end, Natasha Gupta, MD, and her colleagues at the University of Tennessee, Chattanooga, retrospectively reviewed all patients with uterine sizes larger than 250 grams undergoing hysterectomy at their institution between 2012 and 2015.
“For the mini-laparotomy, the technique utilizes a customized incision connecting the two left port sites, followed by the removal of the specimen via this incision,” Dr. Gupta said at the AAGL Global Congress.
Patient factors and outcomes were compared via Student t-tests and Chi-square analysis.
Mean length of stay was significantly shorter for patients who underwent robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy, at 1.4 days vs. 5.4 days for those with open hysterectomy (P = .000) as was mean estimated blood loss – 119.9 mL vs. 547.5 mL, respectively (P = .000). Postoperative complications were seen in fewer patients who underwent robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy, 9 of 82 patients vs. 15 of 58 open hysterectomy patients.
Mean operative time was significantly longer in robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy patients – 191.6 minutes vs. 162.8 minutes (P = .005) – but that was expected, Dr. Gupta noted. Patient factors such as hypertension, diabetes, history of spontaneous vaginal delivery and/or cesarean delivery, and body mass index, as well as uterine pathology, were not significantly different between the groups.
“Mini-laparotomy combined with minimally invasive hysterectomy is a very safe and feasible technique for tissue extraction where contained morcellation is either not preferred or not available,” Dr. Gupta said.
Dr. Gupta reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
[email protected]
On Twitter @denisefulton
AT AAGL 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Mean length of stay was 1.4 days with robotic hysterectomy/mini-laparotomy vs. 5.4 days for open hysterectomy (P = .000).
Data source: A single-center retrospective review of all hysterectomies with uteri larger than 250 grams from the period of 2012-2015.
Disclosures: The study had no outside funding. Dr. Gupta reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.