User login
HOUSTON – Subspecialties such as urology and gynecology have seen a steady increase in robot-assisted surgery and an offsetting decline in open procedures, but in general surgery, robot-assisted procedures seem to be making gains at the expense of laparoscopy, according to researchers from the University of Nebraska.
In two specific operations, ventral and inguinal hernia repairs (VHR and IHR), the percentage of open procedures has increased or held steady over the 7-year study period while the share of laparoscopic operations declined and robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) increased, Priscila Rodrigues Armijo, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons.
This shift to RAS rather than laparoscopy could have significant implications because RAS is significantly more costly than laparoscopy, Dr. Armijo said. “In our study, the open procedures were the most expensive, followed by the robot-assisted surgeries and then laparoscopy,” she said. Median direct costs were $14,364 for open procedures, $11,376 for RAS and $7,945 for laparoscopy.
The Nebraska study retrospectively analyzed five different general surgery procedures: colectomy, cholecystectomy, and bariatric procedures in addition to VHR and IHR. The researchers analyzed 857,468 operations entered into the University HealthSystem Consortium Clinical Database Resource Manager from October 2008 to September 2015.
Dr. Armijo explained that the goal was to study trends in general surgery because while several studies have examined trends in urologic and gynecologic surgery, few studies have done so in general surgery.
“There was a significant increase in minimally invasive utilizations over time, and robotic surgery increased disproportionately compared to the laparoscope counterpart,” Dr. Armijo said. “And although we cannot prove where those patients are coming from, we believe that, especially for inguinal and ventral hernia repairs, they are coming from laparoscopic surgeons who now are adopting robotic techniques and not from open surgeons switching to the robotic approach.”
In 7 years, the study showed a significant decrease in the share of open procedures in colectomy (from 71.8% to 61.9%), cholecystectomy (35.7% to 27.1%), and bariatric surgery (20.1% to 10.1%), but an increase in both laparoscopic and RAS approaches in these surgeries.
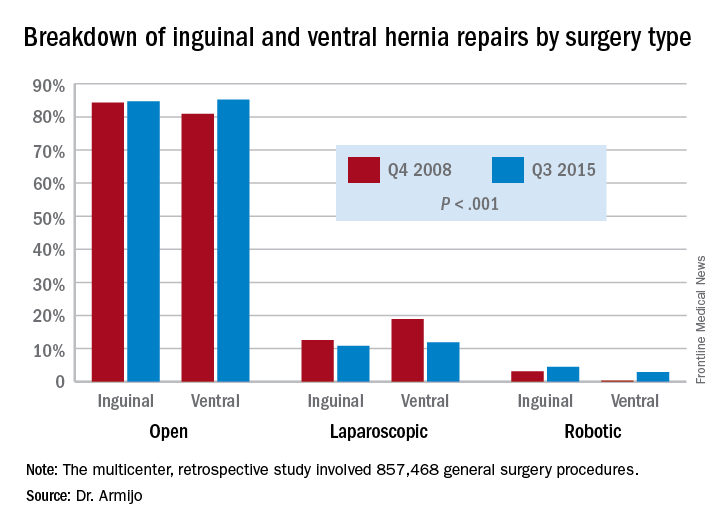
However, in IHR, open procedures held steady at around 84% through the study period, while laparoscopic procedures declined from 12.6% to 10.8% and RAS jumped 3.1% to 4.5%. For VHR, the share of open procedures actually jumped from 80.9% to 85.2%, while the proportion of laparoscopic procedures fell from 18.9% to 11.9% and RAS operations jumped more than tenfold, from 0.2% to 2.9%.
“For ventral hernia repair there was a significant decrease in the laparoscopic approach with a significant increase in both open and robotic procedures, which may be due to new open techniques, including component separation, that have been shown to be more durable as a repair,” Dr. Armijo said. “In addition, those repair techniques are more easily performed with the robotic approach. Laparoscopic surgeons are finding that robotic technology is enabling them to execute surgical tasks, such as suturing mesh.”
Coauthor Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, FACS, disclosed he is a stockholder in Virtual Incision Corp. Dr. Armijo and other coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
HOUSTON – Subspecialties such as urology and gynecology have seen a steady increase in robot-assisted surgery and an offsetting decline in open procedures, but in general surgery, robot-assisted procedures seem to be making gains at the expense of laparoscopy, according to researchers from the University of Nebraska.
In two specific operations, ventral and inguinal hernia repairs (VHR and IHR), the percentage of open procedures has increased or held steady over the 7-year study period while the share of laparoscopic operations declined and robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) increased, Priscila Rodrigues Armijo, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons.
This shift to RAS rather than laparoscopy could have significant implications because RAS is significantly more costly than laparoscopy, Dr. Armijo said. “In our study, the open procedures were the most expensive, followed by the robot-assisted surgeries and then laparoscopy,” she said. Median direct costs were $14,364 for open procedures, $11,376 for RAS and $7,945 for laparoscopy.
The Nebraska study retrospectively analyzed five different general surgery procedures: colectomy, cholecystectomy, and bariatric procedures in addition to VHR and IHR. The researchers analyzed 857,468 operations entered into the University HealthSystem Consortium Clinical Database Resource Manager from October 2008 to September 2015.
Dr. Armijo explained that the goal was to study trends in general surgery because while several studies have examined trends in urologic and gynecologic surgery, few studies have done so in general surgery.

“There was a significant increase in minimally invasive utilizations over time, and robotic surgery increased disproportionately compared to the laparoscope counterpart,” Dr. Armijo said. “And although we cannot prove where those patients are coming from, we believe that, especially for inguinal and ventral hernia repairs, they are coming from laparoscopic surgeons who now are adopting robotic techniques and not from open surgeons switching to the robotic approach.”
In 7 years, the study showed a significant decrease in the share of open procedures in colectomy (from 71.8% to 61.9%), cholecystectomy (35.7% to 27.1%), and bariatric surgery (20.1% to 10.1%), but an increase in both laparoscopic and RAS approaches in these surgeries.
However, in IHR, open procedures held steady at around 84% through the study period, while laparoscopic procedures declined from 12.6% to 10.8% and RAS jumped 3.1% to 4.5%. For VHR, the share of open procedures actually jumped from 80.9% to 85.2%, while the proportion of laparoscopic procedures fell from 18.9% to 11.9% and RAS operations jumped more than tenfold, from 0.2% to 2.9%.
“For ventral hernia repair there was a significant decrease in the laparoscopic approach with a significant increase in both open and robotic procedures, which may be due to new open techniques, including component separation, that have been shown to be more durable as a repair,” Dr. Armijo said. “In addition, those repair techniques are more easily performed with the robotic approach. Laparoscopic surgeons are finding that robotic technology is enabling them to execute surgical tasks, such as suturing mesh.”
Coauthor Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, FACS, disclosed he is a stockholder in Virtual Incision Corp. Dr. Armijo and other coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
HOUSTON – Subspecialties such as urology and gynecology have seen a steady increase in robot-assisted surgery and an offsetting decline in open procedures, but in general surgery, robot-assisted procedures seem to be making gains at the expense of laparoscopy, according to researchers from the University of Nebraska.
In two specific operations, ventral and inguinal hernia repairs (VHR and IHR), the percentage of open procedures has increased or held steady over the 7-year study period while the share of laparoscopic operations declined and robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) increased, Priscila Rodrigues Armijo, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons.
This shift to RAS rather than laparoscopy could have significant implications because RAS is significantly more costly than laparoscopy, Dr. Armijo said. “In our study, the open procedures were the most expensive, followed by the robot-assisted surgeries and then laparoscopy,” she said. Median direct costs were $14,364 for open procedures, $11,376 for RAS and $7,945 for laparoscopy.
The Nebraska study retrospectively analyzed five different general surgery procedures: colectomy, cholecystectomy, and bariatric procedures in addition to VHR and IHR. The researchers analyzed 857,468 operations entered into the University HealthSystem Consortium Clinical Database Resource Manager from October 2008 to September 2015.
Dr. Armijo explained that the goal was to study trends in general surgery because while several studies have examined trends in urologic and gynecologic surgery, few studies have done so in general surgery.

“There was a significant increase in minimally invasive utilizations over time, and robotic surgery increased disproportionately compared to the laparoscope counterpart,” Dr. Armijo said. “And although we cannot prove where those patients are coming from, we believe that, especially for inguinal and ventral hernia repairs, they are coming from laparoscopic surgeons who now are adopting robotic techniques and not from open surgeons switching to the robotic approach.”
In 7 years, the study showed a significant decrease in the share of open procedures in colectomy (from 71.8% to 61.9%), cholecystectomy (35.7% to 27.1%), and bariatric surgery (20.1% to 10.1%), but an increase in both laparoscopic and RAS approaches in these surgeries.
However, in IHR, open procedures held steady at around 84% through the study period, while laparoscopic procedures declined from 12.6% to 10.8% and RAS jumped 3.1% to 4.5%. For VHR, the share of open procedures actually jumped from 80.9% to 85.2%, while the proportion of laparoscopic procedures fell from 18.9% to 11.9% and RAS operations jumped more than tenfold, from 0.2% to 2.9%.
“For ventral hernia repair there was a significant decrease in the laparoscopic approach with a significant increase in both open and robotic procedures, which may be due to new open techniques, including component separation, that have been shown to be more durable as a repair,” Dr. Armijo said. “In addition, those repair techniques are more easily performed with the robotic approach. Laparoscopic surgeons are finding that robotic technology is enabling them to execute surgical tasks, such as suturing mesh.”
Coauthor Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, FACS, disclosed he is a stockholder in Virtual Incision Corp. Dr. Armijo and other coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
AT SAGES 2017
Key clinical point: In inguinal and ventral hernia repair, laparoscopic surgeons are more likely than are open surgery counterparts to move to surgical robot.
Major finding: Over the 7-year study period, the share of open ventral hernia repair procedures increased from 80.9% to 85.2%, while the proportion of laparoscopic procedures fell from 18.9% to 11.9% and RAS operations increased from 0.2% to 2.9%.
Data source: Multicenter, retrospective study of 857,468 general surgery procedures from 2008 to 2015 in the University HealthSystem Consortium Clinical Database Resource Manager.
Disclosures: Dr. Armijo reported having no financial disclosures. Coauthor Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, disclosed stock holding in Virtual Incision Corp.

