User login
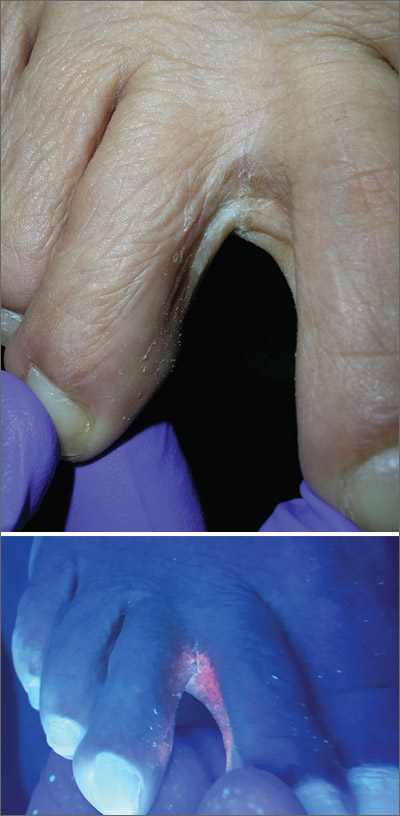
The Wood’s lamp revealed a coral-red fluorescence in the interdigital spaces, which led to a diagnosis of erythrasma.
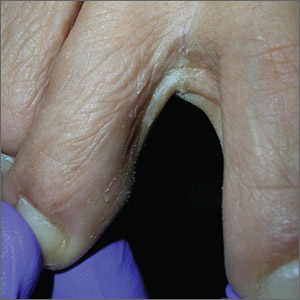
The coral-red fluorescence seen under the Wood’s lamp is due to porphyrins produced by Corynebacterium minutissimum. The organism invades the stratum corneum where it proliferates and causes erythrasma. Erythrasma typically appears as delineated, dry, red-brown patches in intertriginous areas, such as the axilla, groin, interdigital spaces, intergluteal cleft, perianal skin, and inframammary area.
Erythrasma affects 4% of the population; risk factors include poor hygiene, hyperhidrosis, obesity, warm climate, diabetes, and an immunocompromised state. The differential diagnosis for a pruritic rash between the toes includes tinea pedis and contact dermatitis.
First-line management of erythrasma includes both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic modalities. Good hygiene and, depending on the area affected, loose-fitting cotton undergarments can help treat and prevent erythrasma.
Topical 2% miconazole bid for 2 weeks has resulted in clearance rates as high as 88%. Its affordable price, over-the-counter availability, and lack of adverse effects make miconazole a reasonable choice. It is also a smart treatment choice when erythrasma is coexisting with tinea because it can treat both conditions.
Topical 1% clindamycin or 2% erythromycin solution or gel bid for 2 weeks also can be used to treat the condition. However, given that topical antibiotics are more expensive than single-dose oral treatment and are no better than the oral formulations of these antibiotics, clarithromycin 1 g taken once orally may be preferred. Our patient was treated with a single dose of clarithromycin 1 g. At follow-up, her erythrasma was clear.
This case was adapted from: Vo T, Usatine RP. Persistent rash on feet. J Fam Pract. 2018;67:107-109

The Wood’s lamp revealed a coral-red fluorescence in the interdigital spaces, which led to a diagnosis of erythrasma.
The coral-red fluorescence seen under the Wood’s lamp is due to porphyrins produced by Corynebacterium minutissimum. The organism invades the stratum corneum where it proliferates and causes erythrasma. Erythrasma typically appears as delineated, dry, red-brown patches in intertriginous areas, such as the axilla, groin, interdigital spaces, intergluteal cleft, perianal skin, and inframammary area.
Erythrasma affects 4% of the population; risk factors include poor hygiene, hyperhidrosis, obesity, warm climate, diabetes, and an immunocompromised state. The differential diagnosis for a pruritic rash between the toes includes tinea pedis and contact dermatitis.
First-line management of erythrasma includes both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic modalities. Good hygiene and, depending on the area affected, loose-fitting cotton undergarments can help treat and prevent erythrasma.
Topical 2% miconazole bid for 2 weeks has resulted in clearance rates as high as 88%. Its affordable price, over-the-counter availability, and lack of adverse effects make miconazole a reasonable choice. It is also a smart treatment choice when erythrasma is coexisting with tinea because it can treat both conditions.
Topical 1% clindamycin or 2% erythromycin solution or gel bid for 2 weeks also can be used to treat the condition. However, given that topical antibiotics are more expensive than single-dose oral treatment and are no better than the oral formulations of these antibiotics, clarithromycin 1 g taken once orally may be preferred. Our patient was treated with a single dose of clarithromycin 1 g. At follow-up, her erythrasma was clear.
This case was adapted from: Vo T, Usatine RP. Persistent rash on feet. J Fam Pract. 2018;67:107-109

The Wood’s lamp revealed a coral-red fluorescence in the interdigital spaces, which led to a diagnosis of erythrasma.
The coral-red fluorescence seen under the Wood’s lamp is due to porphyrins produced by Corynebacterium minutissimum. The organism invades the stratum corneum where it proliferates and causes erythrasma. Erythrasma typically appears as delineated, dry, red-brown patches in intertriginous areas, such as the axilla, groin, interdigital spaces, intergluteal cleft, perianal skin, and inframammary area.
Erythrasma affects 4% of the population; risk factors include poor hygiene, hyperhidrosis, obesity, warm climate, diabetes, and an immunocompromised state. The differential diagnosis for a pruritic rash between the toes includes tinea pedis and contact dermatitis.
First-line management of erythrasma includes both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic modalities. Good hygiene and, depending on the area affected, loose-fitting cotton undergarments can help treat and prevent erythrasma.
Topical 2% miconazole bid for 2 weeks has resulted in clearance rates as high as 88%. Its affordable price, over-the-counter availability, and lack of adverse effects make miconazole a reasonable choice. It is also a smart treatment choice when erythrasma is coexisting with tinea because it can treat both conditions.
Topical 1% clindamycin or 2% erythromycin solution or gel bid for 2 weeks also can be used to treat the condition. However, given that topical antibiotics are more expensive than single-dose oral treatment and are no better than the oral formulations of these antibiotics, clarithromycin 1 g taken once orally may be preferred. Our patient was treated with a single dose of clarithromycin 1 g. At follow-up, her erythrasma was clear.
This case was adapted from: Vo T, Usatine RP. Persistent rash on feet. J Fam Pract. 2018;67:107-109