User login
DANA POINT, CALIF. – Scar formation and fibrosis can be reduced by altering the mechanical environment of wounds, results from a phase I study found.
At the Summit in Aesthetic Medicine, sponsored by Skin Disease Education Foundation (SDEF), Dr. Geoffrey C. Gurtner presented findings from a study in which nine patients undergoing elective abdominal surgery were treated postoperatively with a stress-shielding polymer on one side while the other side was treated with standard wound care.
The device, manufactured by Neodyne Biosciences, looks like a Band-Aid strip and is stretched over the incision after sutures are removed. It conforms to the wound and adheres to skin, creating "a compressive region that has no level of mechanical stimulation or distractive strain," said Dr. Gurtner, professor of surgery at Stanford (Calif.) University. "Essentially, you create stress risers in the unwounded skin and a mechanically privileged environment in the wounded skin."
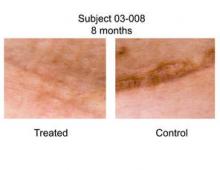
A panel of three independent plastic surgeons reviewed 18 photos of the scars (nine treated, nine control) taken 6-12 months after surgery (Ann. Surg. 2011 May 19 [doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318220b159]). They used a visual analog scale (VAS) that ranged from 0 (very good scar) to 100 (very poor hypertrophic scar).
Dr. Gurtner reported that the average VAS score in the treated group was 18.6, while the average VAS score in the control group was 50.5, a difference that was statistically significant (P = .0039). "In none of the cases was the treated scar worse than the control scar, which I think is different than some of the biologic agents we’ve seen over the last few years," he said.*
A panel of lay persons who reviewed the photos reported similar results that favored the treated group (P = .004).
In earlier mouse studies of wound environment manipulation, Dr. Gurtner and his associates found that focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a critical regulator in the formation of hypertrophic scars. He described FAK as "a molecule that exists on the inner surface of cell membranes and transmits forces that are set in the external extracellular matrix to the inside of the cell. FAK transmits those forces into biological or biochemical cues that then turn on genes in the nucleus and make the cells do different things. This seems to be a very important molecule in the ability of us to produce hypertrophic scars in mice. If you take out FAK, you can prevent hypertrophic scar formation."
FAK is a target that has been examined extensively in cancer, Dr. Gurtner said, suggesting that in the next few years, "We should have products that will not only be able to treat incision wounds but will also be able to treat large burn injuries. You need to fool the cells into thinking they’re in a different mechanical environment, either by using small molecule or pharmacologic blocking therapies such as fat inhibitors, or by using biomaterials that provide cues in a controlled way that minimize the amount of mechanical stimulation that the fibroblasts feel in the healing wound so as to mitigate the inflammation and subsequent fibrosis."
The study was supported by a Wallace H. Coulter Translational Partners Grant; the Armed Forces Institute of Regenerative Medicine; the Hagey Family Endowed Fund in Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine; and the Oak Foundation. Neodyne Biosciences supplied the surgical dressings used in the study. Dr. Gurtner disclosed that he holds an equity interest in Neodyne.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by Elsevier.
*Correction 8/22/11: An earlier version of this story misstated the VAS scores for the two groups of patients.
DANA POINT, CALIF. – Scar formation and fibrosis can be reduced by altering the mechanical environment of wounds, results from a phase I study found.
At the Summit in Aesthetic Medicine, sponsored by Skin Disease Education Foundation (SDEF), Dr. Geoffrey C. Gurtner presented findings from a study in which nine patients undergoing elective abdominal surgery were treated postoperatively with a stress-shielding polymer on one side while the other side was treated with standard wound care.
The device, manufactured by Neodyne Biosciences, looks like a Band-Aid strip and is stretched over the incision after sutures are removed. It conforms to the wound and adheres to skin, creating "a compressive region that has no level of mechanical stimulation or distractive strain," said Dr. Gurtner, professor of surgery at Stanford (Calif.) University. "Essentially, you create stress risers in the unwounded skin and a mechanically privileged environment in the wounded skin."
A panel of three independent plastic surgeons reviewed 18 photos of the scars (nine treated, nine control) taken 6-12 months after surgery (Ann. Surg. 2011 May 19 [doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318220b159]). They used a visual analog scale (VAS) that ranged from 0 (very good scar) to 100 (very poor hypertrophic scar).
Dr. Gurtner reported that the average VAS score in the treated group was 18.6, while the average VAS score in the control group was 50.5, a difference that was statistically significant (P = .0039). "In none of the cases was the treated scar worse than the control scar, which I think is different than some of the biologic agents we’ve seen over the last few years," he said.*
A panel of lay persons who reviewed the photos reported similar results that favored the treated group (P = .004).
In earlier mouse studies of wound environment manipulation, Dr. Gurtner and his associates found that focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a critical regulator in the formation of hypertrophic scars. He described FAK as "a molecule that exists on the inner surface of cell membranes and transmits forces that are set in the external extracellular matrix to the inside of the cell. FAK transmits those forces into biological or biochemical cues that then turn on genes in the nucleus and make the cells do different things. This seems to be a very important molecule in the ability of us to produce hypertrophic scars in mice. If you take out FAK, you can prevent hypertrophic scar formation."
FAK is a target that has been examined extensively in cancer, Dr. Gurtner said, suggesting that in the next few years, "We should have products that will not only be able to treat incision wounds but will also be able to treat large burn injuries. You need to fool the cells into thinking they’re in a different mechanical environment, either by using small molecule or pharmacologic blocking therapies such as fat inhibitors, or by using biomaterials that provide cues in a controlled way that minimize the amount of mechanical stimulation that the fibroblasts feel in the healing wound so as to mitigate the inflammation and subsequent fibrosis."
The study was supported by a Wallace H. Coulter Translational Partners Grant; the Armed Forces Institute of Regenerative Medicine; the Hagey Family Endowed Fund in Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine; and the Oak Foundation. Neodyne Biosciences supplied the surgical dressings used in the study. Dr. Gurtner disclosed that he holds an equity interest in Neodyne.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by Elsevier.
*Correction 8/22/11: An earlier version of this story misstated the VAS scores for the two groups of patients.
DANA POINT, CALIF. – Scar formation and fibrosis can be reduced by altering the mechanical environment of wounds, results from a phase I study found.
At the Summit in Aesthetic Medicine, sponsored by Skin Disease Education Foundation (SDEF), Dr. Geoffrey C. Gurtner presented findings from a study in which nine patients undergoing elective abdominal surgery were treated postoperatively with a stress-shielding polymer on one side while the other side was treated with standard wound care.
The device, manufactured by Neodyne Biosciences, looks like a Band-Aid strip and is stretched over the incision after sutures are removed. It conforms to the wound and adheres to skin, creating "a compressive region that has no level of mechanical stimulation or distractive strain," said Dr. Gurtner, professor of surgery at Stanford (Calif.) University. "Essentially, you create stress risers in the unwounded skin and a mechanically privileged environment in the wounded skin."
A panel of three independent plastic surgeons reviewed 18 photos of the scars (nine treated, nine control) taken 6-12 months after surgery (Ann. Surg. 2011 May 19 [doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318220b159]). They used a visual analog scale (VAS) that ranged from 0 (very good scar) to 100 (very poor hypertrophic scar).
Dr. Gurtner reported that the average VAS score in the treated group was 18.6, while the average VAS score in the control group was 50.5, a difference that was statistically significant (P = .0039). "In none of the cases was the treated scar worse than the control scar, which I think is different than some of the biologic agents we’ve seen over the last few years," he said.*
A panel of lay persons who reviewed the photos reported similar results that favored the treated group (P = .004).
In earlier mouse studies of wound environment manipulation, Dr. Gurtner and his associates found that focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a critical regulator in the formation of hypertrophic scars. He described FAK as "a molecule that exists on the inner surface of cell membranes and transmits forces that are set in the external extracellular matrix to the inside of the cell. FAK transmits those forces into biological or biochemical cues that then turn on genes in the nucleus and make the cells do different things. This seems to be a very important molecule in the ability of us to produce hypertrophic scars in mice. If you take out FAK, you can prevent hypertrophic scar formation."
FAK is a target that has been examined extensively in cancer, Dr. Gurtner said, suggesting that in the next few years, "We should have products that will not only be able to treat incision wounds but will also be able to treat large burn injuries. You need to fool the cells into thinking they’re in a different mechanical environment, either by using small molecule or pharmacologic blocking therapies such as fat inhibitors, or by using biomaterials that provide cues in a controlled way that minimize the amount of mechanical stimulation that the fibroblasts feel in the healing wound so as to mitigate the inflammation and subsequent fibrosis."
The study was supported by a Wallace H. Coulter Translational Partners Grant; the Armed Forces Institute of Regenerative Medicine; the Hagey Family Endowed Fund in Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine; and the Oak Foundation. Neodyne Biosciences supplied the surgical dressings used in the study. Dr. Gurtner disclosed that he holds an equity interest in Neodyne.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by Elsevier.
*Correction 8/22/11: An earlier version of this story misstated the VAS scores for the two groups of patients.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE SDEF SUMMIT IN AESTHETIC MEDICINE
Major Finding: The average VAS score in the treated group was 50.5, while the average VAS score in the control group was 18.6, a statistically significant difference (P = .004).
Data Source: Nine patients undergoing elective abdominal surgery who were treated postoperatively with a stress-shielding polymer on one side while the other side was treated with standard wound care.
Disclosures: The study was supported by a Wallace H. Coulter Translational Partners Grant; the Armed Forces Institute of Regenerative Medicine; the Hagey Family Endowed Fund in Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine; and the Oak Foundation. Neodyne Biosciences supplied the surgical dressings used in the study. Dr. Gurtner disclosed that he holds an equity interest in Neodyne. SDEF and this news organization are owned by Elsevier.