User login
ORLANDO, FL—A recently conducted study confirms that survivors of hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have increased body fat mass and lower lean mass compared to normal controls. And this is despite having a comparable body mass index (BMI).
Researchers say the abnormalities in adipokine levels—leptin and adiponectin—could provide insight into the mechanisms that contribute to the metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular complications that often develop in HSCT survivors.
Leptin and adiponectin are associated with obesity, insulin secretion, insulin resistance, endothelial function, vascular homeostasis, and atherosclerosis.
“So knowing that there is a dynamic interplay between obesity and insulin resistance and cytokine and adipokine profiles and, ultimately, insulin-resistance syndrome, we sought to evaluate, as part of a larger study, how treatment effects, including high-dose chemotherapy and radiation, alter cytokine profiles as well as obesity and body composition,” said Tyler G. Ketterl, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington.
Dr Ketterl presented the findings at the 2017 BMT Tandem Meetings as abstract 52.*
Study design
The research team compared 151 HSCT recipients who had survived more than 2 years after transplant with 92 sibling controls.
HSCT survivors were randomly recruited from 2 centers—Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and University of Minnesota Masonic Children’s Hospital—and were younger than 21 years when diagnosed.
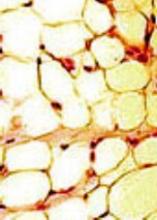
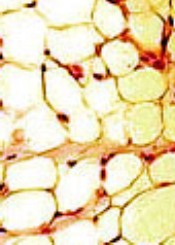
The researchers evaluated all participants for body composition, cardiovascular risk factors, and adipokines using anthropomorphic measurements, DXA scans for muscle and fat mass, and laboratory bloodwork.
The team stratified the HSCT survivors by the preparative regimen they had received—total body irradiation (TBI) alone, TBI plus cranial radiation (CRT), and chemotherapy alone.
Study population
Males comprised more than half the study population in each arm, 58% of HSCT survivors and 54% of siblings.
Nine percent and 8% in the HSCT and sibling arms, respectively, were non-white and/or Hispanic, and the mean current ages were 24.0 (range, 10-51) for HSCT survivors and 24.2 (range, 10-48) for siblings.
The survivors’ mean age at diagnosis was 9.1 years (range, 0.4–20.6), their mean age at transplant was 11.2 years (range, 0.6–32.6), and the mean time from transplant to study participation was 13.5 years (range, 2.6–32).
Most patients received a transplant for leukemia—54 (36%) for acute myeloid leukemia, 46 (31%) for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and 15 (10%) for chronic myeloid leukemia. Thirteen (9%) received transplants for myelodysplastic syndromes, 12 (8%) for Hodgkin lymphoma, and 10 (6%) for non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
A little more than half had TBI (85, 56%) as the preparative regimen, 31 (21%) had TBI plus CRT, and 35 (23%) had chemotherapy only.
About three-quarters (116, 77%) had an allogeneic transplant, and 35 (23%) had an autologous transplant.
Results
Overall, HSCT survivors had significantly lower adiponectin levels than siblings (P<0.001).
Survivors who received TBI with or without CRT had significantly lower adiponectin levels than siblings (P<0.001), while survivors who received chemotherapy alone did not (P=0.42).
Adiponectin is involved in insulin sensitization, hepatoprotective action, antiatherogenic action, protection against the development of diabetes, and regulation of lipid metabolism.
Overall, survivors had significantly higher leptin levels than siblings (P<0.001).
This held true regardless of conditioning regimen, although levels for patients who received chemotherapy only were not as significantly high (P=0.02) as for survivors who received TBI (P<0.001).
Leptin helps increase energy expenditure, decrease appetite and food uptake, modify insulin sensitivity on muscles and liver, prevent ectopic lipid deposition, and regulate immune function.
BMI adjusted for age, sex, and Tanner stage was not significantly different between survivors and siblings, but percent fat mass was significantly higher across all conditioning regimens for survivors compared to siblings (P<0.001).
“And this goes along with previous data,” Dr Ketterl said, “that shows sarcopenic obesity is common amongst transplant survivors.”
The researchers believe these significant differences may provide insight into the underlying risk of developing metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular complications in transplant survivors. ![]()
*Some details in the abstract differ from the presentation.
ORLANDO, FL—A recently conducted study confirms that survivors of hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have increased body fat mass and lower lean mass compared to normal controls. And this is despite having a comparable body mass index (BMI).
Researchers say the abnormalities in adipokine levels—leptin and adiponectin—could provide insight into the mechanisms that contribute to the metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular complications that often develop in HSCT survivors.
Leptin and adiponectin are associated with obesity, insulin secretion, insulin resistance, endothelial function, vascular homeostasis, and atherosclerosis.
“So knowing that there is a dynamic interplay between obesity and insulin resistance and cytokine and adipokine profiles and, ultimately, insulin-resistance syndrome, we sought to evaluate, as part of a larger study, how treatment effects, including high-dose chemotherapy and radiation, alter cytokine profiles as well as obesity and body composition,” said Tyler G. Ketterl, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington.
Dr Ketterl presented the findings at the 2017 BMT Tandem Meetings as abstract 52.*
Study design
The research team compared 151 HSCT recipients who had survived more than 2 years after transplant with 92 sibling controls.
HSCT survivors were randomly recruited from 2 centers—Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and University of Minnesota Masonic Children’s Hospital—and were younger than 21 years when diagnosed.
The researchers evaluated all participants for body composition, cardiovascular risk factors, and adipokines using anthropomorphic measurements, DXA scans for muscle and fat mass, and laboratory bloodwork.
The team stratified the HSCT survivors by the preparative regimen they had received—total body irradiation (TBI) alone, TBI plus cranial radiation (CRT), and chemotherapy alone.
Study population
Males comprised more than half the study population in each arm, 58% of HSCT survivors and 54% of siblings.
Nine percent and 8% in the HSCT and sibling arms, respectively, were non-white and/or Hispanic, and the mean current ages were 24.0 (range, 10-51) for HSCT survivors and 24.2 (range, 10-48) for siblings.
The survivors’ mean age at diagnosis was 9.1 years (range, 0.4–20.6), their mean age at transplant was 11.2 years (range, 0.6–32.6), and the mean time from transplant to study participation was 13.5 years (range, 2.6–32).
Most patients received a transplant for leukemia—54 (36%) for acute myeloid leukemia, 46 (31%) for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and 15 (10%) for chronic myeloid leukemia. Thirteen (9%) received transplants for myelodysplastic syndromes, 12 (8%) for Hodgkin lymphoma, and 10 (6%) for non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
A little more than half had TBI (85, 56%) as the preparative regimen, 31 (21%) had TBI plus CRT, and 35 (23%) had chemotherapy only.
About three-quarters (116, 77%) had an allogeneic transplant, and 35 (23%) had an autologous transplant.
Results
Overall, HSCT survivors had significantly lower adiponectin levels than siblings (P<0.001).
Survivors who received TBI with or without CRT had significantly lower adiponectin levels than siblings (P<0.001), while survivors who received chemotherapy alone did not (P=0.42).
Adiponectin is involved in insulin sensitization, hepatoprotective action, antiatherogenic action, protection against the development of diabetes, and regulation of lipid metabolism.
Overall, survivors had significantly higher leptin levels than siblings (P<0.001).
This held true regardless of conditioning regimen, although levels for patients who received chemotherapy only were not as significantly high (P=0.02) as for survivors who received TBI (P<0.001).
Leptin helps increase energy expenditure, decrease appetite and food uptake, modify insulin sensitivity on muscles and liver, prevent ectopic lipid deposition, and regulate immune function.
BMI adjusted for age, sex, and Tanner stage was not significantly different between survivors and siblings, but percent fat mass was significantly higher across all conditioning regimens for survivors compared to siblings (P<0.001).
“And this goes along with previous data,” Dr Ketterl said, “that shows sarcopenic obesity is common amongst transplant survivors.”
The researchers believe these significant differences may provide insight into the underlying risk of developing metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular complications in transplant survivors. ![]()
*Some details in the abstract differ from the presentation.
ORLANDO, FL—A recently conducted study confirms that survivors of hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have increased body fat mass and lower lean mass compared to normal controls. And this is despite having a comparable body mass index (BMI).
Researchers say the abnormalities in adipokine levels—leptin and adiponectin—could provide insight into the mechanisms that contribute to the metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular complications that often develop in HSCT survivors.
Leptin and adiponectin are associated with obesity, insulin secretion, insulin resistance, endothelial function, vascular homeostasis, and atherosclerosis.
“So knowing that there is a dynamic interplay between obesity and insulin resistance and cytokine and adipokine profiles and, ultimately, insulin-resistance syndrome, we sought to evaluate, as part of a larger study, how treatment effects, including high-dose chemotherapy and radiation, alter cytokine profiles as well as obesity and body composition,” said Tyler G. Ketterl, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington.
Dr Ketterl presented the findings at the 2017 BMT Tandem Meetings as abstract 52.*
Study design
The research team compared 151 HSCT recipients who had survived more than 2 years after transplant with 92 sibling controls.
HSCT survivors were randomly recruited from 2 centers—Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and University of Minnesota Masonic Children’s Hospital—and were younger than 21 years when diagnosed.
The researchers evaluated all participants for body composition, cardiovascular risk factors, and adipokines using anthropomorphic measurements, DXA scans for muscle and fat mass, and laboratory bloodwork.
The team stratified the HSCT survivors by the preparative regimen they had received—total body irradiation (TBI) alone, TBI plus cranial radiation (CRT), and chemotherapy alone.
Study population
Males comprised more than half the study population in each arm, 58% of HSCT survivors and 54% of siblings.
Nine percent and 8% in the HSCT and sibling arms, respectively, were non-white and/or Hispanic, and the mean current ages were 24.0 (range, 10-51) for HSCT survivors and 24.2 (range, 10-48) for siblings.
The survivors’ mean age at diagnosis was 9.1 years (range, 0.4–20.6), their mean age at transplant was 11.2 years (range, 0.6–32.6), and the mean time from transplant to study participation was 13.5 years (range, 2.6–32).
Most patients received a transplant for leukemia—54 (36%) for acute myeloid leukemia, 46 (31%) for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and 15 (10%) for chronic myeloid leukemia. Thirteen (9%) received transplants for myelodysplastic syndromes, 12 (8%) for Hodgkin lymphoma, and 10 (6%) for non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
A little more than half had TBI (85, 56%) as the preparative regimen, 31 (21%) had TBI plus CRT, and 35 (23%) had chemotherapy only.
About three-quarters (116, 77%) had an allogeneic transplant, and 35 (23%) had an autologous transplant.
Results
Overall, HSCT survivors had significantly lower adiponectin levels than siblings (P<0.001).
Survivors who received TBI with or without CRT had significantly lower adiponectin levels than siblings (P<0.001), while survivors who received chemotherapy alone did not (P=0.42).
Adiponectin is involved in insulin sensitization, hepatoprotective action, antiatherogenic action, protection against the development of diabetes, and regulation of lipid metabolism.
Overall, survivors had significantly higher leptin levels than siblings (P<0.001).
This held true regardless of conditioning regimen, although levels for patients who received chemotherapy only were not as significantly high (P=0.02) as for survivors who received TBI (P<0.001).
Leptin helps increase energy expenditure, decrease appetite and food uptake, modify insulin sensitivity on muscles and liver, prevent ectopic lipid deposition, and regulate immune function.
BMI adjusted for age, sex, and Tanner stage was not significantly different between survivors and siblings, but percent fat mass was significantly higher across all conditioning regimens for survivors compared to siblings (P<0.001).
“And this goes along with previous data,” Dr Ketterl said, “that shows sarcopenic obesity is common amongst transplant survivors.”
The researchers believe these significant differences may provide insight into the underlying risk of developing metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular complications in transplant survivors. ![]()
*Some details in the abstract differ from the presentation.