User login
Sonja E. van Roeden, MD, and colleagues from Utrecht University, the Netherlands, performed a retrospective, population-based analysis of the entire general population of the Netherlands from 2002 to 2013, encompassing the 3-year period of a large Q fever epidemic in the country.
In total, there were 48,760 cases of NHL diagnosed between Jan. 1, 2002 and Dec. 31, 2013, with the annual incidence ranging from 21.4 cases per 100,000 population in 2002 to 26.7 in 2010. While researchers found a significant association between NHL incidence and areas of high endemicity of Q fever in 2009 (relative risk 1.16; P = .029), there were no other associations.
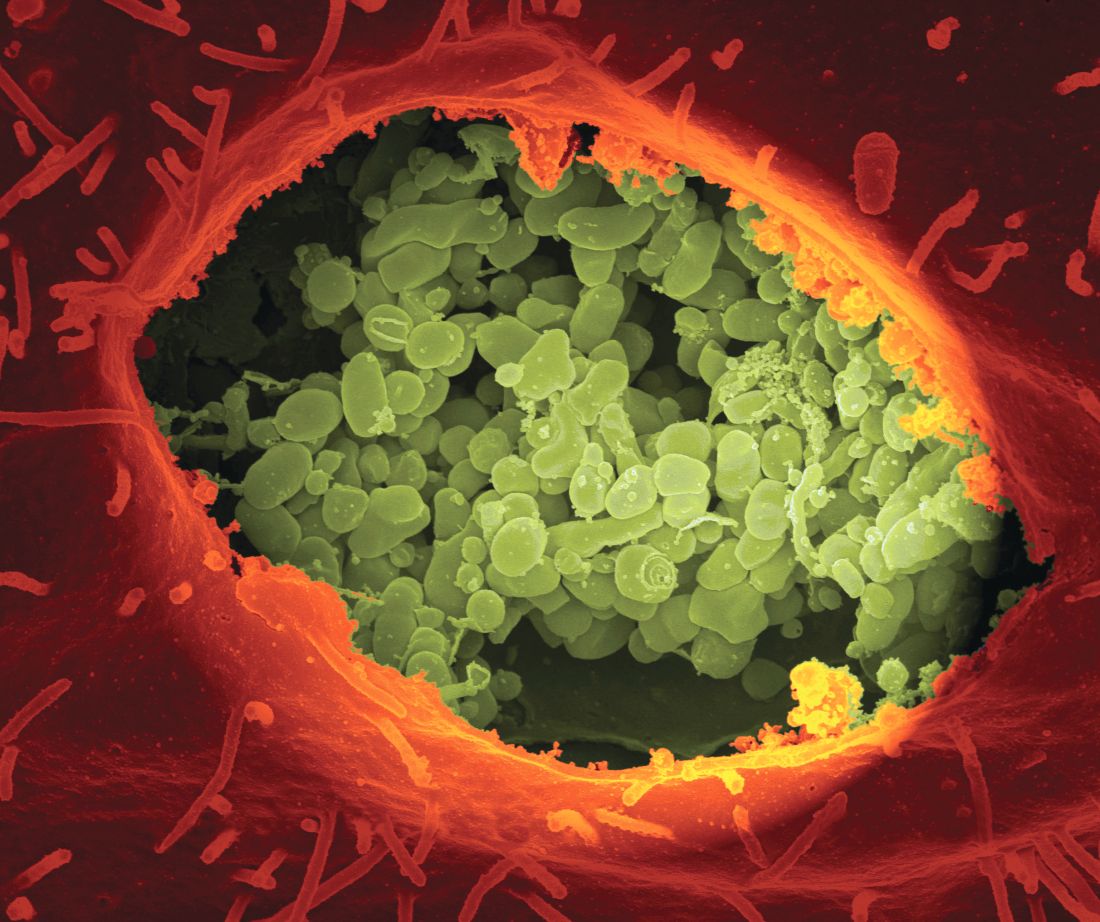
Among the 439 people with chronic Q fever, 5 went on to develop NHL, resulting in a relative risk of 4.99 (P = .0003), compared with the general population of the Netherlands.
“The absence of an exposure-response relation between the intensity of exposure and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, based on reported incidence of acute Q fever, does not imply a causal relation,” the researchers wrote. “However, one could consider exposure to C. burnetii in people with chronic Q fever as more intense than in acute Q fever because of the ongoing character and duration of exposure, and assume an exposure-response relation on the basis of the higher risk for non-Hodgkin lymphoma in patients with chronic Q fever.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: van Roeden SE et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 May;5:e211-9.
Sonja E. van Roeden, MD, and colleagues from Utrecht University, the Netherlands, performed a retrospective, population-based analysis of the entire general population of the Netherlands from 2002 to 2013, encompassing the 3-year period of a large Q fever epidemic in the country.
In total, there were 48,760 cases of NHL diagnosed between Jan. 1, 2002 and Dec. 31, 2013, with the annual incidence ranging from 21.4 cases per 100,000 population in 2002 to 26.7 in 2010. While researchers found a significant association between NHL incidence and areas of high endemicity of Q fever in 2009 (relative risk 1.16; P = .029), there were no other associations.
Among the 439 people with chronic Q fever, 5 went on to develop NHL, resulting in a relative risk of 4.99 (P = .0003), compared with the general population of the Netherlands.
“The absence of an exposure-response relation between the intensity of exposure and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, based on reported incidence of acute Q fever, does not imply a causal relation,” the researchers wrote. “However, one could consider exposure to C. burnetii in people with chronic Q fever as more intense than in acute Q fever because of the ongoing character and duration of exposure, and assume an exposure-response relation on the basis of the higher risk for non-Hodgkin lymphoma in patients with chronic Q fever.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: van Roeden SE et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 May;5:e211-9.
Sonja E. van Roeden, MD, and colleagues from Utrecht University, the Netherlands, performed a retrospective, population-based analysis of the entire general population of the Netherlands from 2002 to 2013, encompassing the 3-year period of a large Q fever epidemic in the country.
In total, there were 48,760 cases of NHL diagnosed between Jan. 1, 2002 and Dec. 31, 2013, with the annual incidence ranging from 21.4 cases per 100,000 population in 2002 to 26.7 in 2010. While researchers found a significant association between NHL incidence and areas of high endemicity of Q fever in 2009 (relative risk 1.16; P = .029), there were no other associations.
Among the 439 people with chronic Q fever, 5 went on to develop NHL, resulting in a relative risk of 4.99 (P = .0003), compared with the general population of the Netherlands.
“The absence of an exposure-response relation between the intensity of exposure and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, based on reported incidence of acute Q fever, does not imply a causal relation,” the researchers wrote. “However, one could consider exposure to C. burnetii in people with chronic Q fever as more intense than in acute Q fever because of the ongoing character and duration of exposure, and assume an exposure-response relation on the basis of the higher risk for non-Hodgkin lymphoma in patients with chronic Q fever.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: van Roeden SE et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 May;5:e211-9.
FROM LANCET HAEMATOLOGY