User login
SAN DIEGO – Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors improved the extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) among more than half of affected patients, according to a national cohort study.
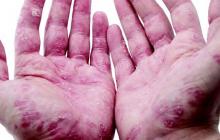
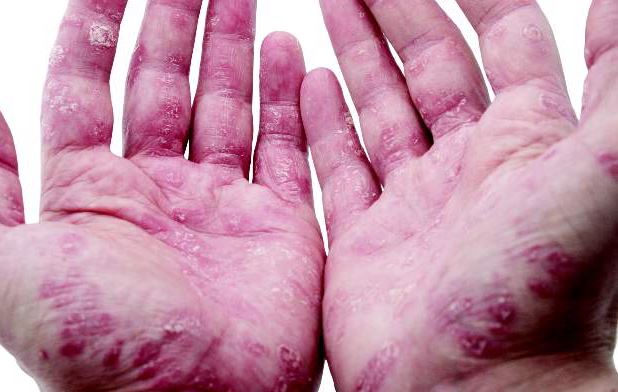
“The best response rates were for psoriasis, aphthous stomatitis, uveitis, and peripheral arthritis,” said Dr. Thomas Greuter of University Hospital in Zürich. Patients responded similarly whether they received oral infliximab or subcutaneous adalimumab or certolizumab, he noted.
IBD often is associated with debilitating disorders of the skin, joints, eyes, and hepatobiliary tract, but “due to the lack of randomized, controlled trials, the therapy of extraintestinal manifestations remains rather empirical,” Dr. Greuter said at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
To study the role of anti-TNF agents in treating these disorders, he and his associates analyzed data for 1,249 patients from the national Swiss IBD Cohort Study between 2006 and 2010. Patients were typically in their mid-30s and had lived with IBD for about 9 years, he said.
A total of 366 patients (29%) had at least one extraintestinal manifestation of IBD – most commonly peripheral arthritis (75%), followed by aphthous stomatitis (24%), and ankylosing spondylitis (22%). In all, 213 (58%) patients received at least one anti-TNF agent, and 40% received the prescription specifically for extraintestinal manifestations. Nearly two-thirds of the patients received infliximab, while 22% received adalimumab and 15% received certolizumab.
About 55% of patients improved on anti-TNF therapy over an average of 7 years of follow-up, Dr. Greuter and his associates reported. Among all three anti-TNF agents, response rates ranged from 100% for psoriasis, to 80% for erythema nodosum and stomatitis, to 73% for arthritis and uveitis, to 50% for pyoderma granulosum. Overall rates of improvement were slightly higher for infliximab than for the other two drugs, but “adalimumab and certolizumab were used mostly as a second or a third-line anti-TNF agent, and the response rate to a second or third-line treatment was lower than for the first one,” Dr. Greuter said. Some patients also received corticosteroids and immunomodulators, but excluding this subgroup had little effect on rates of response to anti-TNF therapy, he added.
Dr. Greuter also reported that 11 patients (about 5% of the cohort) developed 14 new extraintestinal manifestations after starting anti-TNF agents – usually peripheral arthritis, but also pyoderma granulosum, aphthous stomatitis, psoriasis, and uveitis. “We cannot say if this was primary, or a side effect of treatment,” he said. These disorders usually improved if patients stayed on their anti-TNF agent, he added.
About two-thirds of patients in the cohort were female, more than three-quarters had Crohn’s disease, 19% had ulcerative colitis, and 3% had indeterminate colitis, he noted.
A research grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation funded the study. Dr. Greuter had no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors improved the extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) among more than half of affected patients, according to a national cohort study.
“The best response rates were for psoriasis, aphthous stomatitis, uveitis, and peripheral arthritis,” said Dr. Thomas Greuter of University Hospital in Zürich. Patients responded similarly whether they received oral infliximab or subcutaneous adalimumab or certolizumab, he noted.
IBD often is associated with debilitating disorders of the skin, joints, eyes, and hepatobiliary tract, but “due to the lack of randomized, controlled trials, the therapy of extraintestinal manifestations remains rather empirical,” Dr. Greuter said at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
To study the role of anti-TNF agents in treating these disorders, he and his associates analyzed data for 1,249 patients from the national Swiss IBD Cohort Study between 2006 and 2010. Patients were typically in their mid-30s and had lived with IBD for about 9 years, he said.
A total of 366 patients (29%) had at least one extraintestinal manifestation of IBD – most commonly peripheral arthritis (75%), followed by aphthous stomatitis (24%), and ankylosing spondylitis (22%). In all, 213 (58%) patients received at least one anti-TNF agent, and 40% received the prescription specifically for extraintestinal manifestations. Nearly two-thirds of the patients received infliximab, while 22% received adalimumab and 15% received certolizumab.
About 55% of patients improved on anti-TNF therapy over an average of 7 years of follow-up, Dr. Greuter and his associates reported. Among all three anti-TNF agents, response rates ranged from 100% for psoriasis, to 80% for erythema nodosum and stomatitis, to 73% for arthritis and uveitis, to 50% for pyoderma granulosum. Overall rates of improvement were slightly higher for infliximab than for the other two drugs, but “adalimumab and certolizumab were used mostly as a second or a third-line anti-TNF agent, and the response rate to a second or third-line treatment was lower than for the first one,” Dr. Greuter said. Some patients also received corticosteroids and immunomodulators, but excluding this subgroup had little effect on rates of response to anti-TNF therapy, he added.
Dr. Greuter also reported that 11 patients (about 5% of the cohort) developed 14 new extraintestinal manifestations after starting anti-TNF agents – usually peripheral arthritis, but also pyoderma granulosum, aphthous stomatitis, psoriasis, and uveitis. “We cannot say if this was primary, or a side effect of treatment,” he said. These disorders usually improved if patients stayed on their anti-TNF agent, he added.
About two-thirds of patients in the cohort were female, more than three-quarters had Crohn’s disease, 19% had ulcerative colitis, and 3% had indeterminate colitis, he noted.
A research grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation funded the study. Dr. Greuter had no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors improved the extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) among more than half of affected patients, according to a national cohort study.
“The best response rates were for psoriasis, aphthous stomatitis, uveitis, and peripheral arthritis,” said Dr. Thomas Greuter of University Hospital in Zürich. Patients responded similarly whether they received oral infliximab or subcutaneous adalimumab or certolizumab, he noted.
IBD often is associated with debilitating disorders of the skin, joints, eyes, and hepatobiliary tract, but “due to the lack of randomized, controlled trials, the therapy of extraintestinal manifestations remains rather empirical,” Dr. Greuter said at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
To study the role of anti-TNF agents in treating these disorders, he and his associates analyzed data for 1,249 patients from the national Swiss IBD Cohort Study between 2006 and 2010. Patients were typically in their mid-30s and had lived with IBD for about 9 years, he said.
A total of 366 patients (29%) had at least one extraintestinal manifestation of IBD – most commonly peripheral arthritis (75%), followed by aphthous stomatitis (24%), and ankylosing spondylitis (22%). In all, 213 (58%) patients received at least one anti-TNF agent, and 40% received the prescription specifically for extraintestinal manifestations. Nearly two-thirds of the patients received infliximab, while 22% received adalimumab and 15% received certolizumab.
About 55% of patients improved on anti-TNF therapy over an average of 7 years of follow-up, Dr. Greuter and his associates reported. Among all three anti-TNF agents, response rates ranged from 100% for psoriasis, to 80% for erythema nodosum and stomatitis, to 73% for arthritis and uveitis, to 50% for pyoderma granulosum. Overall rates of improvement were slightly higher for infliximab than for the other two drugs, but “adalimumab and certolizumab were used mostly as a second or a third-line anti-TNF agent, and the response rate to a second or third-line treatment was lower than for the first one,” Dr. Greuter said. Some patients also received corticosteroids and immunomodulators, but excluding this subgroup had little effect on rates of response to anti-TNF therapy, he added.
Dr. Greuter also reported that 11 patients (about 5% of the cohort) developed 14 new extraintestinal manifestations after starting anti-TNF agents – usually peripheral arthritis, but also pyoderma granulosum, aphthous stomatitis, psoriasis, and uveitis. “We cannot say if this was primary, or a side effect of treatment,” he said. These disorders usually improved if patients stayed on their anti-TNF agent, he added.
About two-thirds of patients in the cohort were female, more than three-quarters had Crohn’s disease, 19% had ulcerative colitis, and 3% had indeterminate colitis, he noted.
A research grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation funded the study. Dr. Greuter had no disclosures.
AT DDW® 2016
Key clinical point: Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors improved the extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease among more than half of affected patients.
Major finding: About 55% of patients who received infliximab, adalimumab, or certolizumab had a clinical response.
Data source: A study of 1,249 patients with IBD from a national cohort.
Disclosures: A research grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation funded the study. Dr. Greuter had no disclosures.