User login
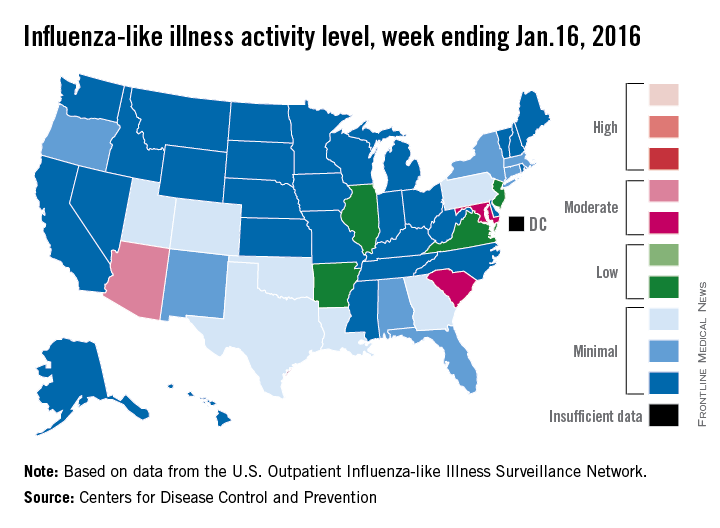
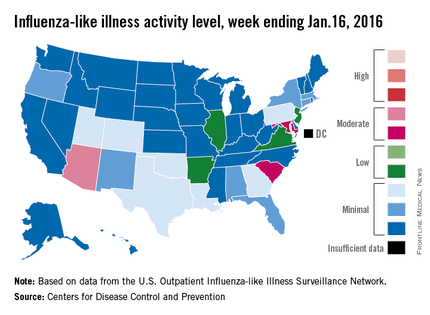
There were no states in the “high” range of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity during week 14 of the 2015-2016 flu season, but there were more states with elevated levels, compared with the previous week, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
Arizona had the highest activity (level 7) for the week ending Jan. 16, with Maryland and South Carolina (level 6) the only other states in the “moderate” range of ILI activity. There were 21 states at level 2 or higher, up from 18 the week before, but still below the peak of 24 that was seen 2 weeks ago. The overall proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 2.1% for week 14, which was up from 2% for week 13 but was right at the national baseline, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
There were no influenza-related pediatric deaths reported for week 14, so the number of total deaths remains at seven for the season, which is well below the week-14 totals for each of the previous three seasons. There have been 494 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations reported in the 13 states of the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network through week 14, for an overall hospitalization rate of 1.8/100,000 population, the CDC said.
Among all hospitalizations, 65.4% were associated with influenza A, 28.7% with influenza B, 3.2% with influenza A and B coinfection, and 2.6% had no virus type information, the CDC report noted.
There were no states in the “high” range of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity during week 14 of the 2015-2016 flu season, but there were more states with elevated levels, compared with the previous week, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
Arizona had the highest activity (level 7) for the week ending Jan. 16, with Maryland and South Carolina (level 6) the only other states in the “moderate” range of ILI activity. There were 21 states at level 2 or higher, up from 18 the week before, but still below the peak of 24 that was seen 2 weeks ago. The overall proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 2.1% for week 14, which was up from 2% for week 13 but was right at the national baseline, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.

There were no influenza-related pediatric deaths reported for week 14, so the number of total deaths remains at seven for the season, which is well below the week-14 totals for each of the previous three seasons. There have been 494 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations reported in the 13 states of the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network through week 14, for an overall hospitalization rate of 1.8/100,000 population, the CDC said.
Among all hospitalizations, 65.4% were associated with influenza A, 28.7% with influenza B, 3.2% with influenza A and B coinfection, and 2.6% had no virus type information, the CDC report noted.
There were no states in the “high” range of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity during week 14 of the 2015-2016 flu season, but there were more states with elevated levels, compared with the previous week, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
Arizona had the highest activity (level 7) for the week ending Jan. 16, with Maryland and South Carolina (level 6) the only other states in the “moderate” range of ILI activity. There were 21 states at level 2 or higher, up from 18 the week before, but still below the peak of 24 that was seen 2 weeks ago. The overall proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 2.1% for week 14, which was up from 2% for week 13 but was right at the national baseline, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.

There were no influenza-related pediatric deaths reported for week 14, so the number of total deaths remains at seven for the season, which is well below the week-14 totals for each of the previous three seasons. There have been 494 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations reported in the 13 states of the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network through week 14, for an overall hospitalization rate of 1.8/100,000 population, the CDC said.
Among all hospitalizations, 65.4% were associated with influenza A, 28.7% with influenza B, 3.2% with influenza A and B coinfection, and 2.6% had no virus type information, the CDC report noted.