User login
Obesity rates among “emerging adults” aged 18-25 have soared in the United States in recent decades with the mean body mass index (BMI) for these young adults now in the overweight category, according to research highlighting troubling trends in an often-overlooked age group.
While similar patterns have been observed in other age groups, including adolescents (ages 12-19) and young adults (ages 20-39) across recent decades, emerging adulthood tends to get less attention in the evaluation of obesity trends.
“Emerging adulthood may be a key period for preventing and treating obesity given that habits formed during this period often persist through the remainder of the life course,” write the authors of the study, which was published online Nov. 23 in JAMA.
“There is an urgent need for research on risk factors contributing to obesity during this developmental stage to inform the design of interventions as well as policies aimed at prevention,” they add.
They found that by 2018 a third of all young adults had obesity, compared with just 6% at the beginning of the study periods in 1976.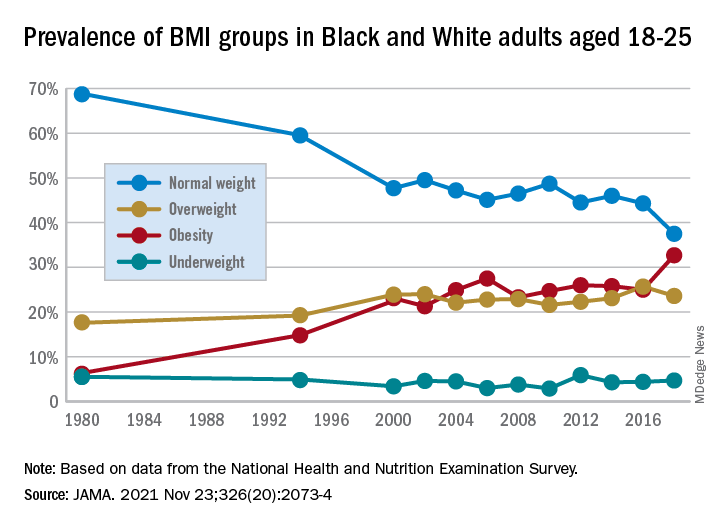
Studying the ages of transition
The findings are from an analysis of 8,015 emerging adults aged 18-25 in the cross-sectional National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), including NHANES II (1976-1980), NHANES III (1988-1994), and the continuous NHANES cycles from 1999 through 2018.
About half (3,965) of participants were female, 3,037 were non-Hispanic Black, and 2,386 met the criteria for household poverty.
The results showed substantial increases in mean BMI among emerging adults from a level in the normal range, at 23.1 kg/m2, in 1976-1980, increasing to 27.7 kg/m2 (overweight) in 2017-2018 (P = .006).
The prevalence of obesity (BMI 30.0 kg/m2 or higher) in the emerging adult age group soared from 6.2% between 1976-1980 to 32.7% in 2017-2018 (P = .007).
Meanwhile, the rate of those with normal/healthy weight (BMI 18.5-24.9 kg/m2) dropped from 68.7% to 37.5% (P = .005) over the same period.
Sensitivity analyses that were limited to continuous NHANES cycles showed similar results.
First author Alejandra Ellison-Barnes, MD, MPH, said the trends are consistent with rising obesity rates in the population as a whole – other studies have shown increases in obesity among children, adolescents, and adults over the same period – but are nevertheless striking, she stressed.
Young adults now fall into overweight category
“While we were not surprised by the general trend, given what is known about the increasing prevalence of obesity in both children and adults, we were surprised by the magnitude of the increase in prevalence and that the mean BMI in this age group now falls in the overweight range,” Dr. Ellison-Barnes, of the Division of General Internal Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
She said she is not aware of other studies that have looked at obesity trends specifically among emerging adults.
However, considering the substantial life changes and growing independence, the life stage is important to understand in terms of dietary/lifestyle patterns.
“We theorize that emerging adulthood is a critical period for obesity development given that it is a time when individuals are often undergoing major life transitions such as leaving home, attending higher education, entering the workforce, and developing new relationships,” she emphasized.
As far as causes are concerned, “societal and cultural trends in these areas over the past several decades may have played a role in the observed changes,” she speculated.
The study population was limited to non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic White individuals due to changes in how NHANES assessed race and ethnicity over time. Therefore, a study limitation is that the patterns observed may not be generalizable to other races and ethnicities, the authors note.
However, considering the influence lifestyle changes can have, early adulthood “may be an ideal time to intervene in the clinical setting to prevent, manage, or reverse obesity to prevent adverse health outcomes in the future,” Dr. Ellison-Barnes said.
Dr. Ellison-Barnes has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Obesity rates among “emerging adults” aged 18-25 have soared in the United States in recent decades with the mean body mass index (BMI) for these young adults now in the overweight category, according to research highlighting troubling trends in an often-overlooked age group.
While similar patterns have been observed in other age groups, including adolescents (ages 12-19) and young adults (ages 20-39) across recent decades, emerging adulthood tends to get less attention in the evaluation of obesity trends.
“Emerging adulthood may be a key period for preventing and treating obesity given that habits formed during this period often persist through the remainder of the life course,” write the authors of the study, which was published online Nov. 23 in JAMA.
“There is an urgent need for research on risk factors contributing to obesity during this developmental stage to inform the design of interventions as well as policies aimed at prevention,” they add.
They found that by 2018 a third of all young adults had obesity, compared with just 6% at the beginning of the study periods in 1976.
Studying the ages of transition
The findings are from an analysis of 8,015 emerging adults aged 18-25 in the cross-sectional National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), including NHANES II (1976-1980), NHANES III (1988-1994), and the continuous NHANES cycles from 1999 through 2018.
About half (3,965) of participants were female, 3,037 were non-Hispanic Black, and 2,386 met the criteria for household poverty.
The results showed substantial increases in mean BMI among emerging adults from a level in the normal range, at 23.1 kg/m2, in 1976-1980, increasing to 27.7 kg/m2 (overweight) in 2017-2018 (P = .006).
The prevalence of obesity (BMI 30.0 kg/m2 or higher) in the emerging adult age group soared from 6.2% between 1976-1980 to 32.7% in 2017-2018 (P = .007).
Meanwhile, the rate of those with normal/healthy weight (BMI 18.5-24.9 kg/m2) dropped from 68.7% to 37.5% (P = .005) over the same period.
Sensitivity analyses that were limited to continuous NHANES cycles showed similar results.
First author Alejandra Ellison-Barnes, MD, MPH, said the trends are consistent with rising obesity rates in the population as a whole – other studies have shown increases in obesity among children, adolescents, and adults over the same period – but are nevertheless striking, she stressed.
Young adults now fall into overweight category
“While we were not surprised by the general trend, given what is known about the increasing prevalence of obesity in both children and adults, we were surprised by the magnitude of the increase in prevalence and that the mean BMI in this age group now falls in the overweight range,” Dr. Ellison-Barnes, of the Division of General Internal Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
She said she is not aware of other studies that have looked at obesity trends specifically among emerging adults.
However, considering the substantial life changes and growing independence, the life stage is important to understand in terms of dietary/lifestyle patterns.
“We theorize that emerging adulthood is a critical period for obesity development given that it is a time when individuals are often undergoing major life transitions such as leaving home, attending higher education, entering the workforce, and developing new relationships,” she emphasized.
As far as causes are concerned, “societal and cultural trends in these areas over the past several decades may have played a role in the observed changes,” she speculated.
The study population was limited to non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic White individuals due to changes in how NHANES assessed race and ethnicity over time. Therefore, a study limitation is that the patterns observed may not be generalizable to other races and ethnicities, the authors note.
However, considering the influence lifestyle changes can have, early adulthood “may be an ideal time to intervene in the clinical setting to prevent, manage, or reverse obesity to prevent adverse health outcomes in the future,” Dr. Ellison-Barnes said.
Dr. Ellison-Barnes has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Obesity rates among “emerging adults” aged 18-25 have soared in the United States in recent decades with the mean body mass index (BMI) for these young adults now in the overweight category, according to research highlighting troubling trends in an often-overlooked age group.
While similar patterns have been observed in other age groups, including adolescents (ages 12-19) and young adults (ages 20-39) across recent decades, emerging adulthood tends to get less attention in the evaluation of obesity trends.
“Emerging adulthood may be a key period for preventing and treating obesity given that habits formed during this period often persist through the remainder of the life course,” write the authors of the study, which was published online Nov. 23 in JAMA.
“There is an urgent need for research on risk factors contributing to obesity during this developmental stage to inform the design of interventions as well as policies aimed at prevention,” they add.
They found that by 2018 a third of all young adults had obesity, compared with just 6% at the beginning of the study periods in 1976.
Studying the ages of transition
The findings are from an analysis of 8,015 emerging adults aged 18-25 in the cross-sectional National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), including NHANES II (1976-1980), NHANES III (1988-1994), and the continuous NHANES cycles from 1999 through 2018.
About half (3,965) of participants were female, 3,037 were non-Hispanic Black, and 2,386 met the criteria for household poverty.
The results showed substantial increases in mean BMI among emerging adults from a level in the normal range, at 23.1 kg/m2, in 1976-1980, increasing to 27.7 kg/m2 (overweight) in 2017-2018 (P = .006).
The prevalence of obesity (BMI 30.0 kg/m2 or higher) in the emerging adult age group soared from 6.2% between 1976-1980 to 32.7% in 2017-2018 (P = .007).
Meanwhile, the rate of those with normal/healthy weight (BMI 18.5-24.9 kg/m2) dropped from 68.7% to 37.5% (P = .005) over the same period.
Sensitivity analyses that were limited to continuous NHANES cycles showed similar results.
First author Alejandra Ellison-Barnes, MD, MPH, said the trends are consistent with rising obesity rates in the population as a whole – other studies have shown increases in obesity among children, adolescents, and adults over the same period – but are nevertheless striking, she stressed.
Young adults now fall into overweight category
“While we were not surprised by the general trend, given what is known about the increasing prevalence of obesity in both children and adults, we were surprised by the magnitude of the increase in prevalence and that the mean BMI in this age group now falls in the overweight range,” Dr. Ellison-Barnes, of the Division of General Internal Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
She said she is not aware of other studies that have looked at obesity trends specifically among emerging adults.
However, considering the substantial life changes and growing independence, the life stage is important to understand in terms of dietary/lifestyle patterns.
“We theorize that emerging adulthood is a critical period for obesity development given that it is a time when individuals are often undergoing major life transitions such as leaving home, attending higher education, entering the workforce, and developing new relationships,” she emphasized.
As far as causes are concerned, “societal and cultural trends in these areas over the past several decades may have played a role in the observed changes,” she speculated.
The study population was limited to non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic White individuals due to changes in how NHANES assessed race and ethnicity over time. Therefore, a study limitation is that the patterns observed may not be generalizable to other races and ethnicities, the authors note.
However, considering the influence lifestyle changes can have, early adulthood “may be an ideal time to intervene in the clinical setting to prevent, manage, or reverse obesity to prevent adverse health outcomes in the future,” Dr. Ellison-Barnes said.
Dr. Ellison-Barnes has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.