User login
Treatment with a novel myosin-inhibiting agent may improve symptoms and hemodynamics enough in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (OHCM) so that they can avoid or at least delay septal reduction therapy (SRT), suggests a randomized trial of modest size and duration.
Of 112 patients with OHCM who were sick enough while receiving standard medications to qualify for SRT, those assigned to take mavacamten (MyoKardia) instead of placebo were far less likely to still be eligible for SRT 16 weeks later.
In other words, their OHCM had improved enough during therapy with mavacamten such that SRT, either surgical septal myectomy or transcatheter alcohol septal ablation, could no longer be recommended per guidelines.
Mavacamten, which lessens myocardial contractility by selective inhibition of cardiac myosin, is the first agent tested in prospective trials to appear as a viable medical option in patients with severe, symptomatic OHCM, observed principal investigator Milind Y. Desai, MD, MBA, of the Cleveland Clinic.
“There’s clearly an unmet need for noninvasive therapies, medical therapies, that work in OHCM,” he said in an interview. Mavacamten “adds to the armamentarium” of OHCM management options and may give patients with symptoms despite conventional medications an alternative to SRT, which is considered definitive but has drawbacks.
The goal of SRT is to alleviate obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), but surgical SRT requires a sternotomy, with all the risks and recovery time that entails. Catheter-based alcohol septal ablation is a less common alternative for some patients with suitable anatomy, Dr. Desai noted.
But those procedures “are not uniformly available, and even when available, the outcomes are fairly heterogeneous,” he said. “The guidelines recommend that you should go to a center with a mortality rate of less than 1% with these procedures. Centers like that are very few across the world,” and procedural mortality can be much higher at centers with less SRT experience.
Dr. Desai presented the results of VALOR-HCM at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. Of the 56 patients assigned to mavacamten, 10 (17.9%) decided to undergo SRT by the end of the trial, or otherwise still met guideline-recommended criteria for receiving SRT, the primary endpoint. In comparison, 43 of the 56 patients (76.8%) in the control group (P < .0001) met that endpoint.
More patients receiving mavacamten improved by at least one New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class during the trial’s 16 weeks: 63% versus 21% for those assigned to placebo. And 27% and 2%, respectively, improved by at least two NYHA classes, Dr. Desai said.
Guidelines recommend that SRT be reserved for patients in NYHA class III or IV heart failure with a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg.
Of note, Desai said, only two patients in each group elected to undergo SRT during the study. “The primary endpoint was driven by reduction in guideline eligibility for SRT, but 95% of patients in the study chose to continue with medical therapy.”
Speaking as a panelist after Dr. Desai’s presentation, Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, lauded the phase 3 trial’s “brave design,” which featured a highly unusual subjective primary endpoint and framed it as an advantage.
That the trial showed a significant mavacamten effect for that endpoint “answered, in one step, the question of what does this actually mean to the patient – which often takes much longer,” observed Dr. Stevenson, from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
Even so, she added, whether patients still qualified for SRT in the trial at least had to be supported by objective measures of LVOT gradient and NT-proBNP levels.
“My perspective is that of a cardiac surgeon who performs septal myectomies,” said John Cleveland, MD, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who said he was impressed at how few patients receiving mavacamten went on to undergo SRT, while the rest were able to at least defer that decision.
Current recommendations are that patients who go to SRT “should be maximally medically treated and still symptomatic,” Dr. Cleveland observed at a press conference on VALOR-HCM. Should mavacamten be added to the list of agents to use before resorting to invasive therapy? “My answer would be yes,” he said, and patients who remain symptomatic even while receiving the myosin inhibitor and other medications should proceed to SRT.
The trial’s patients had documented OHCM, severe symptoms, and a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg despite maximally tolerated medications – which could include disopyramide, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers. About half the study population was female, and 89% were White. All had been referred for SRT.
Active therapy consisted of mavacamten initiated at 5 mg/day, with up-titrations at 8 and 12 weeks as tolerated, guided by echocardiographic left ventricular ejection fraction and LVOT gradient.
Most secondary endpoints improved significantly in patients receiving the drug, compared with placebo. They included measures of quality of life, symptom status, ventricular function, natriuretic peptides, and troponin I.
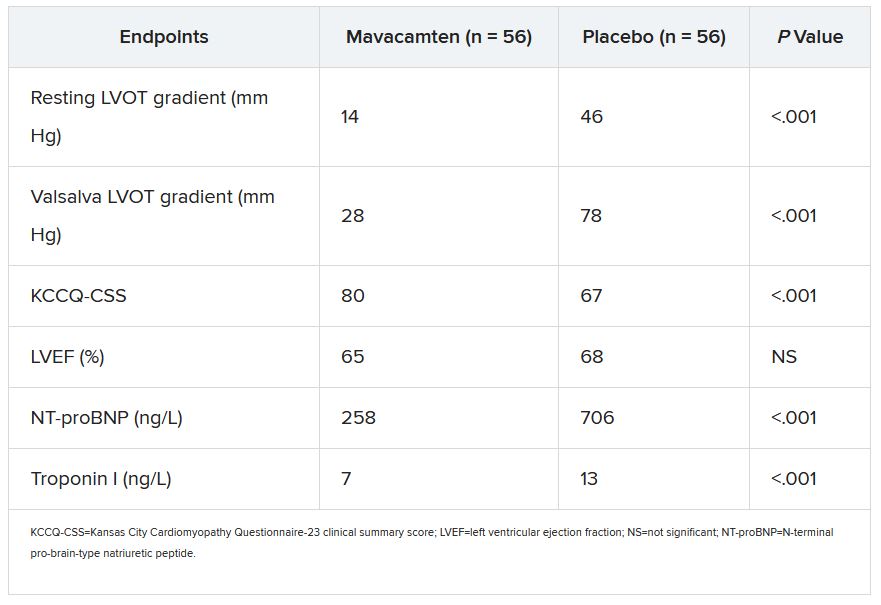
The secondary outcomes are consistent with what was observed in the EXPLORER-HCM trial, which in 2020 suggested that mavacamten could improve measures of quality of life, NYHA functional class, LVOT gradient, peak VO2, and other metrics in patients with OHCM.
Dr. Desai said mavacamten was well tolerated. “There were two patients who had a transient drop in ejection fraction to less than 50%, so the drug was temporarily discontinued, but resumed at a lower dose and they were able to complete the study.”
Dr. Stevenson commented on the “pretty quick” up-titration of mavacamten dosages in a study lasting only 4 months, which could have been a concern given the drug’s limited track record and its mechanism of action targeting contractility. “Fortunately, no serious safety signals” were observed.
Dr. Desai emphasized that mavacamten up-titrations were strictly guided by regular echocardiographic monitoring and assessment of LVOT gradients, in addition to clinical responses. And that, he said, is likely how up-titrations should be carried out if mavacamten is approved for OHCM.
VALOR-HCM was supported by MyoKardia. Dr. Desai disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Caristo Diagnostics, Medtronic, and MyoKardia. Dr. Stevenson disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Novartis; serving on a data safety monitoring board for Livanova; and other relationships with Abbott Medical, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Endotronic, Gore Medical, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Cleveland had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with a novel myosin-inhibiting agent may improve symptoms and hemodynamics enough in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (OHCM) so that they can avoid or at least delay septal reduction therapy (SRT), suggests a randomized trial of modest size and duration.
Of 112 patients with OHCM who were sick enough while receiving standard medications to qualify for SRT, those assigned to take mavacamten (MyoKardia) instead of placebo were far less likely to still be eligible for SRT 16 weeks later.
In other words, their OHCM had improved enough during therapy with mavacamten such that SRT, either surgical septal myectomy or transcatheter alcohol septal ablation, could no longer be recommended per guidelines.
Mavacamten, which lessens myocardial contractility by selective inhibition of cardiac myosin, is the first agent tested in prospective trials to appear as a viable medical option in patients with severe, symptomatic OHCM, observed principal investigator Milind Y. Desai, MD, MBA, of the Cleveland Clinic.
“There’s clearly an unmet need for noninvasive therapies, medical therapies, that work in OHCM,” he said in an interview. Mavacamten “adds to the armamentarium” of OHCM management options and may give patients with symptoms despite conventional medications an alternative to SRT, which is considered definitive but has drawbacks.
The goal of SRT is to alleviate obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), but surgical SRT requires a sternotomy, with all the risks and recovery time that entails. Catheter-based alcohol septal ablation is a less common alternative for some patients with suitable anatomy, Dr. Desai noted.
But those procedures “are not uniformly available, and even when available, the outcomes are fairly heterogeneous,” he said. “The guidelines recommend that you should go to a center with a mortality rate of less than 1% with these procedures. Centers like that are very few across the world,” and procedural mortality can be much higher at centers with less SRT experience.
Dr. Desai presented the results of VALOR-HCM at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. Of the 56 patients assigned to mavacamten, 10 (17.9%) decided to undergo SRT by the end of the trial, or otherwise still met guideline-recommended criteria for receiving SRT, the primary endpoint. In comparison, 43 of the 56 patients (76.8%) in the control group (P < .0001) met that endpoint.
More patients receiving mavacamten improved by at least one New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class during the trial’s 16 weeks: 63% versus 21% for those assigned to placebo. And 27% and 2%, respectively, improved by at least two NYHA classes, Dr. Desai said.
Guidelines recommend that SRT be reserved for patients in NYHA class III or IV heart failure with a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg.
Of note, Desai said, only two patients in each group elected to undergo SRT during the study. “The primary endpoint was driven by reduction in guideline eligibility for SRT, but 95% of patients in the study chose to continue with medical therapy.”
Speaking as a panelist after Dr. Desai’s presentation, Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, lauded the phase 3 trial’s “brave design,” which featured a highly unusual subjective primary endpoint and framed it as an advantage.
That the trial showed a significant mavacamten effect for that endpoint “answered, in one step, the question of what does this actually mean to the patient – which often takes much longer,” observed Dr. Stevenson, from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
Even so, she added, whether patients still qualified for SRT in the trial at least had to be supported by objective measures of LVOT gradient and NT-proBNP levels.
“My perspective is that of a cardiac surgeon who performs septal myectomies,” said John Cleveland, MD, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who said he was impressed at how few patients receiving mavacamten went on to undergo SRT, while the rest were able to at least defer that decision.
Current recommendations are that patients who go to SRT “should be maximally medically treated and still symptomatic,” Dr. Cleveland observed at a press conference on VALOR-HCM. Should mavacamten be added to the list of agents to use before resorting to invasive therapy? “My answer would be yes,” he said, and patients who remain symptomatic even while receiving the myosin inhibitor and other medications should proceed to SRT.
The trial’s patients had documented OHCM, severe symptoms, and a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg despite maximally tolerated medications – which could include disopyramide, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers. About half the study population was female, and 89% were White. All had been referred for SRT.
Active therapy consisted of mavacamten initiated at 5 mg/day, with up-titrations at 8 and 12 weeks as tolerated, guided by echocardiographic left ventricular ejection fraction and LVOT gradient.
Most secondary endpoints improved significantly in patients receiving the drug, compared with placebo. They included measures of quality of life, symptom status, ventricular function, natriuretic peptides, and troponin I.

The secondary outcomes are consistent with what was observed in the EXPLORER-HCM trial, which in 2020 suggested that mavacamten could improve measures of quality of life, NYHA functional class, LVOT gradient, peak VO2, and other metrics in patients with OHCM.
Dr. Desai said mavacamten was well tolerated. “There were two patients who had a transient drop in ejection fraction to less than 50%, so the drug was temporarily discontinued, but resumed at a lower dose and they were able to complete the study.”
Dr. Stevenson commented on the “pretty quick” up-titration of mavacamten dosages in a study lasting only 4 months, which could have been a concern given the drug’s limited track record and its mechanism of action targeting contractility. “Fortunately, no serious safety signals” were observed.
Dr. Desai emphasized that mavacamten up-titrations were strictly guided by regular echocardiographic monitoring and assessment of LVOT gradients, in addition to clinical responses. And that, he said, is likely how up-titrations should be carried out if mavacamten is approved for OHCM.
VALOR-HCM was supported by MyoKardia. Dr. Desai disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Caristo Diagnostics, Medtronic, and MyoKardia. Dr. Stevenson disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Novartis; serving on a data safety monitoring board for Livanova; and other relationships with Abbott Medical, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Endotronic, Gore Medical, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Cleveland had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with a novel myosin-inhibiting agent may improve symptoms and hemodynamics enough in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (OHCM) so that they can avoid or at least delay septal reduction therapy (SRT), suggests a randomized trial of modest size and duration.
Of 112 patients with OHCM who were sick enough while receiving standard medications to qualify for SRT, those assigned to take mavacamten (MyoKardia) instead of placebo were far less likely to still be eligible for SRT 16 weeks later.
In other words, their OHCM had improved enough during therapy with mavacamten such that SRT, either surgical septal myectomy or transcatheter alcohol septal ablation, could no longer be recommended per guidelines.
Mavacamten, which lessens myocardial contractility by selective inhibition of cardiac myosin, is the first agent tested in prospective trials to appear as a viable medical option in patients with severe, symptomatic OHCM, observed principal investigator Milind Y. Desai, MD, MBA, of the Cleveland Clinic.
“There’s clearly an unmet need for noninvasive therapies, medical therapies, that work in OHCM,” he said in an interview. Mavacamten “adds to the armamentarium” of OHCM management options and may give patients with symptoms despite conventional medications an alternative to SRT, which is considered definitive but has drawbacks.
The goal of SRT is to alleviate obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), but surgical SRT requires a sternotomy, with all the risks and recovery time that entails. Catheter-based alcohol septal ablation is a less common alternative for some patients with suitable anatomy, Dr. Desai noted.
But those procedures “are not uniformly available, and even when available, the outcomes are fairly heterogeneous,” he said. “The guidelines recommend that you should go to a center with a mortality rate of less than 1% with these procedures. Centers like that are very few across the world,” and procedural mortality can be much higher at centers with less SRT experience.
Dr. Desai presented the results of VALOR-HCM at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. Of the 56 patients assigned to mavacamten, 10 (17.9%) decided to undergo SRT by the end of the trial, or otherwise still met guideline-recommended criteria for receiving SRT, the primary endpoint. In comparison, 43 of the 56 patients (76.8%) in the control group (P < .0001) met that endpoint.
More patients receiving mavacamten improved by at least one New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class during the trial’s 16 weeks: 63% versus 21% for those assigned to placebo. And 27% and 2%, respectively, improved by at least two NYHA classes, Dr. Desai said.
Guidelines recommend that SRT be reserved for patients in NYHA class III or IV heart failure with a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg.
Of note, Desai said, only two patients in each group elected to undergo SRT during the study. “The primary endpoint was driven by reduction in guideline eligibility for SRT, but 95% of patients in the study chose to continue with medical therapy.”
Speaking as a panelist after Dr. Desai’s presentation, Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, lauded the phase 3 trial’s “brave design,” which featured a highly unusual subjective primary endpoint and framed it as an advantage.
That the trial showed a significant mavacamten effect for that endpoint “answered, in one step, the question of what does this actually mean to the patient – which often takes much longer,” observed Dr. Stevenson, from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
Even so, she added, whether patients still qualified for SRT in the trial at least had to be supported by objective measures of LVOT gradient and NT-proBNP levels.
“My perspective is that of a cardiac surgeon who performs septal myectomies,” said John Cleveland, MD, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who said he was impressed at how few patients receiving mavacamten went on to undergo SRT, while the rest were able to at least defer that decision.
Current recommendations are that patients who go to SRT “should be maximally medically treated and still symptomatic,” Dr. Cleveland observed at a press conference on VALOR-HCM. Should mavacamten be added to the list of agents to use before resorting to invasive therapy? “My answer would be yes,” he said, and patients who remain symptomatic even while receiving the myosin inhibitor and other medications should proceed to SRT.
The trial’s patients had documented OHCM, severe symptoms, and a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg despite maximally tolerated medications – which could include disopyramide, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers. About half the study population was female, and 89% were White. All had been referred for SRT.
Active therapy consisted of mavacamten initiated at 5 mg/day, with up-titrations at 8 and 12 weeks as tolerated, guided by echocardiographic left ventricular ejection fraction and LVOT gradient.
Most secondary endpoints improved significantly in patients receiving the drug, compared with placebo. They included measures of quality of life, symptom status, ventricular function, natriuretic peptides, and troponin I.

The secondary outcomes are consistent with what was observed in the EXPLORER-HCM trial, which in 2020 suggested that mavacamten could improve measures of quality of life, NYHA functional class, LVOT gradient, peak VO2, and other metrics in patients with OHCM.
Dr. Desai said mavacamten was well tolerated. “There were two patients who had a transient drop in ejection fraction to less than 50%, so the drug was temporarily discontinued, but resumed at a lower dose and they were able to complete the study.”
Dr. Stevenson commented on the “pretty quick” up-titration of mavacamten dosages in a study lasting only 4 months, which could have been a concern given the drug’s limited track record and its mechanism of action targeting contractility. “Fortunately, no serious safety signals” were observed.
Dr. Desai emphasized that mavacamten up-titrations were strictly guided by regular echocardiographic monitoring and assessment of LVOT gradients, in addition to clinical responses. And that, he said, is likely how up-titrations should be carried out if mavacamten is approved for OHCM.
VALOR-HCM was supported by MyoKardia. Dr. Desai disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Caristo Diagnostics, Medtronic, and MyoKardia. Dr. Stevenson disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Novartis; serving on a data safety monitoring board for Livanova; and other relationships with Abbott Medical, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Endotronic, Gore Medical, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Cleveland had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2022