User login
The development of vitiligo or alopecia areata is not common in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease, but it is significantly more likely to occur when the donor was female, especially when the recipient was male, according to a report published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Dermatology.
Fifteen case reports and small series in the literature have reported the development of vitiligo or alopecia areata after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, most often among patients who first developed chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after the procedure. To further explore the frequency of these two skin autoimmune manifestations in GVHD and to identify associated risk factors, researchers performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adult and pediatric patients referred to the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center for GVHD in 2004-2013.
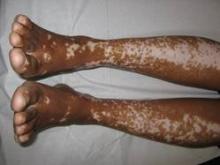
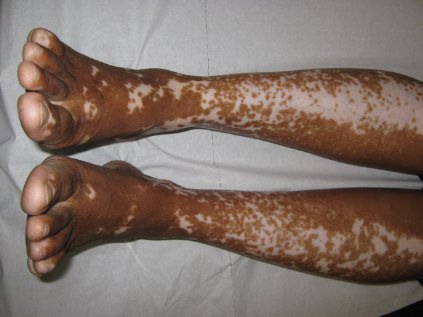
They identified 15 GVHD patients with vitiligo (4.9%) and 2 with alopecia areata (0.7%); one of these patients had both skin disorders. Most of the 15 patients had undergone stem-cell transplantation to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (5 patients) or acute leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (5 patients), and most had had a human leukocyte antigen–identical donor. Twelve of the 15 developed the skin disorder after having GVHD for more than 1 year, said Rena C. Zuo of the National Cancer Institute’s dermatology branch and her associates.
"Notably, CML accounts for only about 300 of 7,892 (3.8%) allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantations per year in the United States, a relative minority among indicated diseases," they said.
In what they described as the first study to identify an association between donor/recipient sex mismatch and the development of concomitant autoimmunity in patients with chronic GVHD, the investigators found that 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors, 2 of whom had previously given birth; the gender of the donor in the 15th case was unknown. Nine of these 14 recipients were male, "resulting in a female-to-male sex mismatch in [at least] 64% of cases," Ms. Zuo and her colleagues said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 Sept. 10 [doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1550]).
Both parous female donors and donor-recipient sex mismatch are known risk factors for GVHD. The risk of autoimmunity in female-to-male transplants "may reflect the activity of skin-homing donor T cells specific for recipient minor histocompatibility antigens encoded by Y-chromosome genes, a mechanism previously implicated in both GVHD and graft-versus-tumor responses," the investigators added.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
The development of vitiligo or alopecia areata is not common in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease, but it is significantly more likely to occur when the donor was female, especially when the recipient was male, according to a report published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Dermatology.
Fifteen case reports and small series in the literature have reported the development of vitiligo or alopecia areata after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, most often among patients who first developed chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after the procedure. To further explore the frequency of these two skin autoimmune manifestations in GVHD and to identify associated risk factors, researchers performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adult and pediatric patients referred to the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center for GVHD in 2004-2013.
They identified 15 GVHD patients with vitiligo (4.9%) and 2 with alopecia areata (0.7%); one of these patients had both skin disorders. Most of the 15 patients had undergone stem-cell transplantation to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (5 patients) or acute leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (5 patients), and most had had a human leukocyte antigen–identical donor. Twelve of the 15 developed the skin disorder after having GVHD for more than 1 year, said Rena C. Zuo of the National Cancer Institute’s dermatology branch and her associates.
"Notably, CML accounts for only about 300 of 7,892 (3.8%) allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantations per year in the United States, a relative minority among indicated diseases," they said.
In what they described as the first study to identify an association between donor/recipient sex mismatch and the development of concomitant autoimmunity in patients with chronic GVHD, the investigators found that 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors, 2 of whom had previously given birth; the gender of the donor in the 15th case was unknown. Nine of these 14 recipients were male, "resulting in a female-to-male sex mismatch in [at least] 64% of cases," Ms. Zuo and her colleagues said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 Sept. 10 [doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1550]).
Both parous female donors and donor-recipient sex mismatch are known risk factors for GVHD. The risk of autoimmunity in female-to-male transplants "may reflect the activity of skin-homing donor T cells specific for recipient minor histocompatibility antigens encoded by Y-chromosome genes, a mechanism previously implicated in both GVHD and graft-versus-tumor responses," the investigators added.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
The development of vitiligo or alopecia areata is not common in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease, but it is significantly more likely to occur when the donor was female, especially when the recipient was male, according to a report published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Dermatology.
Fifteen case reports and small series in the literature have reported the development of vitiligo or alopecia areata after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, most often among patients who first developed chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after the procedure. To further explore the frequency of these two skin autoimmune manifestations in GVHD and to identify associated risk factors, researchers performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adult and pediatric patients referred to the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center for GVHD in 2004-2013.
They identified 15 GVHD patients with vitiligo (4.9%) and 2 with alopecia areata (0.7%); one of these patients had both skin disorders. Most of the 15 patients had undergone stem-cell transplantation to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (5 patients) or acute leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (5 patients), and most had had a human leukocyte antigen–identical donor. Twelve of the 15 developed the skin disorder after having GVHD for more than 1 year, said Rena C. Zuo of the National Cancer Institute’s dermatology branch and her associates.
"Notably, CML accounts for only about 300 of 7,892 (3.8%) allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantations per year in the United States, a relative minority among indicated diseases," they said.
In what they described as the first study to identify an association between donor/recipient sex mismatch and the development of concomitant autoimmunity in patients with chronic GVHD, the investigators found that 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors, 2 of whom had previously given birth; the gender of the donor in the 15th case was unknown. Nine of these 14 recipients were male, "resulting in a female-to-male sex mismatch in [at least] 64% of cases," Ms. Zuo and her colleagues said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 Sept. 10 [doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1550]).
Both parous female donors and donor-recipient sex mismatch are known risk factors for GVHD. The risk of autoimmunity in female-to-male transplants "may reflect the activity of skin-homing donor T cells specific for recipient minor histocompatibility antigens encoded by Y-chromosome genes, a mechanism previously implicated in both GVHD and graft-versus-tumor responses," the investigators added.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Female-to-male stem cell donation ups the risk for vitiligo in GVHD.
Major finding: 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors (the gender of the 15th donor was unknown), and 9 of these 14 recipients were male.
Data source: A retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adults and children with chronic GVHD, 15 of whom developed vitiligo or alopecia areata.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.