User login
This patient's clinical presentation and laboratory findings are consistent with a diagnosis of Cushing syndrome (CS).
CS is a rare endocrine disease caused by prolonged exposure to high circulating cortisol levels. Exogenous hypercortisolism is the most common cause of CS. It is largely iatrogenic and results from the prolonged use of glucocorticoids. Less frequently, endogenous CS may occur as the result of excessive production of cortisol by adrenal glands. Endogenous CS can be ACTH-dependent or ACTH-independent. ACTH-dependent CS results from ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas (Cushing disease) and ectopic ACTH secretion by neoplasms, whereas adrenal hyperplasia, adenoma, and carcinoma are the primary causes of ACTH-independent CS.
The annual incidence and prevalence of CS are unknown; the reported incidence of newly diagnosed cases has ranged from 1.2 to 2.4 per million people per year. Women are affected more often than are men, with a peak of incidence in the third to fourth decade of life. CS is associated with various metabolic, psychiatric, musculoskeletal, and cardiovascular comorbidities. Untreated, it is associated with increased mortality, typically as the result of cardiovascular and infectious complications; however, even in appropriately treated patients, mortality is elevated.
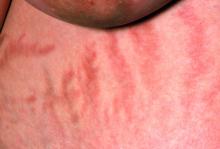
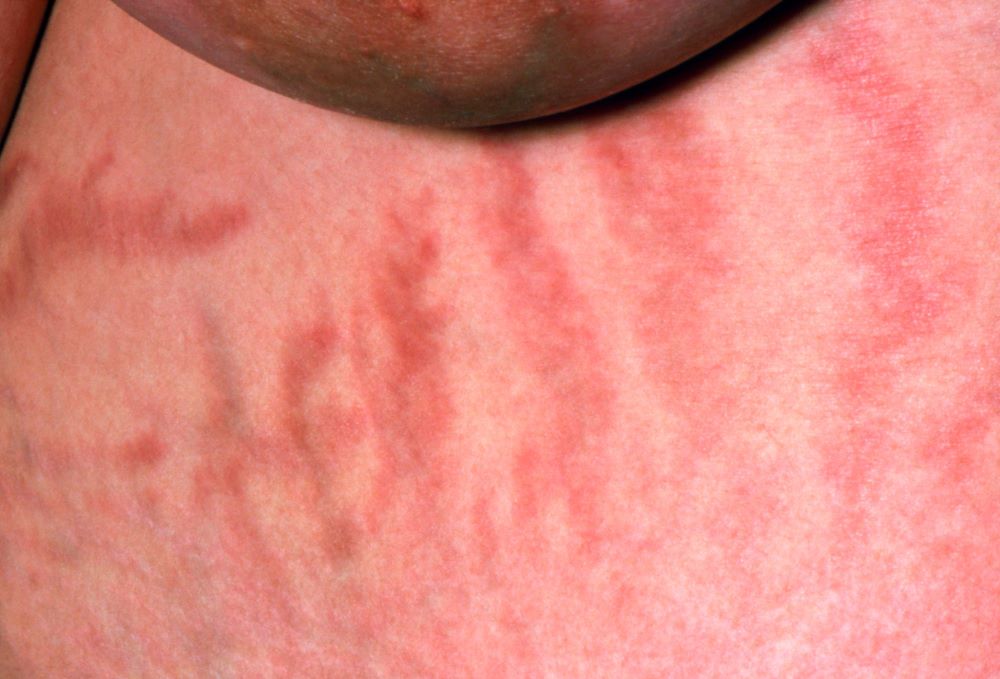
The chronic elevations of glucocorticoid concentrations in CS result in its characteristic phenotype, which includes weight gain, moon-shaped face, buffalo hump, muscle weakness, increased bruising, skin atrophy, red abdominal striae, menstrual irregularities, hirsutism, and acne. It is also associated with numerous comorbidities including diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and osteoporosis. Patients often experience mental health complications, such as depression, emotional lability, and cognitive dysfunction.
Given the rarity of CS and the fact that these symptoms overlap with other conditions, delayed diagnosis is common. The current obesity epidemic also poses diagnostic challenges because true CS can be difficult to differentiate from metabolic syndrome. The duration of hypercortisolism appears to be the most significant factor associated with the degree of morbidity and preterm mortality in CS; thus, an accurate diagnosis as early as possible is important.
Screening and diagnostic tests for CS evaluate cortisol secretion. Available options include late-night salivary cortisol (LNSC), impaired glucocorticoid feedback with overnight 1-mg DST or low-dose 2-day dexamethasone test (LDDT) and increased bioavailable cortisol with 24-hour UFC.
A 2021 consensus statement by Fleseriu and colleagues provides recommendations for the diagnosis of CS. If CS is suspected: begin with UFC, LNSC, or both; DST is an option if LNSC not feasible. If CS because of adrenal tumor is suspected: begin with DST because LNSC has lower specificity in these patients. To confirm CS, any of these tests can be used.
An individualized approach is recommended for the treatment of CS. The optimal approach for iatrogenic CS is to slowly taper exogenous steroids. Chronic exposure to steroids can suppress adrenal functioning; as such, recovery may take several months. Surgical resection is the first-line option for hypercortisolism because of Cushing disease, adrenal tumor, or ectopic tumor. Patients should be closely monitored after surgery to evaluate for possible recurrence. Radiotherapy may be recommended after failed transsphenoidal surgery or in Cushing disease with mass effect or invasion of surrounding structures. Medical therapy, such as pasireotide, cabergoline, and mifepristone, are also sometimes used. In addition, the treatment of comorbidities, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, hypertension, osteoporosis, psychiatric issues, and electrolyte disorders, is critical.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, Pediatric Lead, Obesity Champion, TSPMG, Weight A Minute Clinic, Atlanta, Georgia.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's clinical presentation and laboratory findings are consistent with a diagnosis of Cushing syndrome (CS).
CS is a rare endocrine disease caused by prolonged exposure to high circulating cortisol levels. Exogenous hypercortisolism is the most common cause of CS. It is largely iatrogenic and results from the prolonged use of glucocorticoids. Less frequently, endogenous CS may occur as the result of excessive production of cortisol by adrenal glands. Endogenous CS can be ACTH-dependent or ACTH-independent. ACTH-dependent CS results from ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas (Cushing disease) and ectopic ACTH secretion by neoplasms, whereas adrenal hyperplasia, adenoma, and carcinoma are the primary causes of ACTH-independent CS.
The annual incidence and prevalence of CS are unknown; the reported incidence of newly diagnosed cases has ranged from 1.2 to 2.4 per million people per year. Women are affected more often than are men, with a peak of incidence in the third to fourth decade of life. CS is associated with various metabolic, psychiatric, musculoskeletal, and cardiovascular comorbidities. Untreated, it is associated with increased mortality, typically as the result of cardiovascular and infectious complications; however, even in appropriately treated patients, mortality is elevated.
The chronic elevations of glucocorticoid concentrations in CS result in its characteristic phenotype, which includes weight gain, moon-shaped face, buffalo hump, muscle weakness, increased bruising, skin atrophy, red abdominal striae, menstrual irregularities, hirsutism, and acne. It is also associated with numerous comorbidities including diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and osteoporosis. Patients often experience mental health complications, such as depression, emotional lability, and cognitive dysfunction.
Given the rarity of CS and the fact that these symptoms overlap with other conditions, delayed diagnosis is common. The current obesity epidemic also poses diagnostic challenges because true CS can be difficult to differentiate from metabolic syndrome. The duration of hypercortisolism appears to be the most significant factor associated with the degree of morbidity and preterm mortality in CS; thus, an accurate diagnosis as early as possible is important.
Screening and diagnostic tests for CS evaluate cortisol secretion. Available options include late-night salivary cortisol (LNSC), impaired glucocorticoid feedback with overnight 1-mg DST or low-dose 2-day dexamethasone test (LDDT) and increased bioavailable cortisol with 24-hour UFC.
A 2021 consensus statement by Fleseriu and colleagues provides recommendations for the diagnosis of CS. If CS is suspected: begin with UFC, LNSC, or both; DST is an option if LNSC not feasible. If CS because of adrenal tumor is suspected: begin with DST because LNSC has lower specificity in these patients. To confirm CS, any of these tests can be used.
An individualized approach is recommended for the treatment of CS. The optimal approach for iatrogenic CS is to slowly taper exogenous steroids. Chronic exposure to steroids can suppress adrenal functioning; as such, recovery may take several months. Surgical resection is the first-line option for hypercortisolism because of Cushing disease, adrenal tumor, or ectopic tumor. Patients should be closely monitored after surgery to evaluate for possible recurrence. Radiotherapy may be recommended after failed transsphenoidal surgery or in Cushing disease with mass effect or invasion of surrounding structures. Medical therapy, such as pasireotide, cabergoline, and mifepristone, are also sometimes used. In addition, the treatment of comorbidities, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, hypertension, osteoporosis, psychiatric issues, and electrolyte disorders, is critical.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, Pediatric Lead, Obesity Champion, TSPMG, Weight A Minute Clinic, Atlanta, Georgia.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's clinical presentation and laboratory findings are consistent with a diagnosis of Cushing syndrome (CS).
CS is a rare endocrine disease caused by prolonged exposure to high circulating cortisol levels. Exogenous hypercortisolism is the most common cause of CS. It is largely iatrogenic and results from the prolonged use of glucocorticoids. Less frequently, endogenous CS may occur as the result of excessive production of cortisol by adrenal glands. Endogenous CS can be ACTH-dependent or ACTH-independent. ACTH-dependent CS results from ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas (Cushing disease) and ectopic ACTH secretion by neoplasms, whereas adrenal hyperplasia, adenoma, and carcinoma are the primary causes of ACTH-independent CS.
The annual incidence and prevalence of CS are unknown; the reported incidence of newly diagnosed cases has ranged from 1.2 to 2.4 per million people per year. Women are affected more often than are men, with a peak of incidence in the third to fourth decade of life. CS is associated with various metabolic, psychiatric, musculoskeletal, and cardiovascular comorbidities. Untreated, it is associated with increased mortality, typically as the result of cardiovascular and infectious complications; however, even in appropriately treated patients, mortality is elevated.
The chronic elevations of glucocorticoid concentrations in CS result in its characteristic phenotype, which includes weight gain, moon-shaped face, buffalo hump, muscle weakness, increased bruising, skin atrophy, red abdominal striae, menstrual irregularities, hirsutism, and acne. It is also associated with numerous comorbidities including diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and osteoporosis. Patients often experience mental health complications, such as depression, emotional lability, and cognitive dysfunction.
Given the rarity of CS and the fact that these symptoms overlap with other conditions, delayed diagnosis is common. The current obesity epidemic also poses diagnostic challenges because true CS can be difficult to differentiate from metabolic syndrome. The duration of hypercortisolism appears to be the most significant factor associated with the degree of morbidity and preterm mortality in CS; thus, an accurate diagnosis as early as possible is important.
Screening and diagnostic tests for CS evaluate cortisol secretion. Available options include late-night salivary cortisol (LNSC), impaired glucocorticoid feedback with overnight 1-mg DST or low-dose 2-day dexamethasone test (LDDT) and increased bioavailable cortisol with 24-hour UFC.
A 2021 consensus statement by Fleseriu and colleagues provides recommendations for the diagnosis of CS. If CS is suspected: begin with UFC, LNSC, or both; DST is an option if LNSC not feasible. If CS because of adrenal tumor is suspected: begin with DST because LNSC has lower specificity in these patients. To confirm CS, any of these tests can be used.
An individualized approach is recommended for the treatment of CS. The optimal approach for iatrogenic CS is to slowly taper exogenous steroids. Chronic exposure to steroids can suppress adrenal functioning; as such, recovery may take several months. Surgical resection is the first-line option for hypercortisolism because of Cushing disease, adrenal tumor, or ectopic tumor. Patients should be closely monitored after surgery to evaluate for possible recurrence. Radiotherapy may be recommended after failed transsphenoidal surgery or in Cushing disease with mass effect or invasion of surrounding structures. Medical therapy, such as pasireotide, cabergoline, and mifepristone, are also sometimes used. In addition, the treatment of comorbidities, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, hypertension, osteoporosis, psychiatric issues, and electrolyte disorders, is critical.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, Pediatric Lead, Obesity Champion, TSPMG, Weight A Minute Clinic, Atlanta, Georgia.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 37-year-old woman presents with reports of insomnia, weight gain (approximately 12 lb over the last 9 months), and excessive fatigue. The patient's medical history is significant for hypertension (diagnosed 4 years earlier) and depression (diagnosed 7 years earlier). Her current medications include lisinopril 10 mg/d, bupropion 75 mg/d, and venlafaxine 75 mg/d. There is no history of alcohol or drug abuse; family history is unremarkable. The patient's height and weight are 5 ft 5 in and 182 lb (body mass index of 30.3).
During physical examination, facial hirsutism is observed along with increased adipose tissue in the face (moon-shaped face), upper back at the base of the neck (buffalo hump), and abdomen. Vertical red abdominal striae are present. Several bruises are observed on the patient's thighs and arms; when questioned, she reports noting an increased tendency to bruise in recent months.
Pertinent laboratory findings include urinary free cortisol excretion (UFC) 324 mcg/24 h, 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test (DST) with a cortisol value of 3.64 mcg/dL (100.42 nmol/L), and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) level of 84.9 pg/mL.