User login
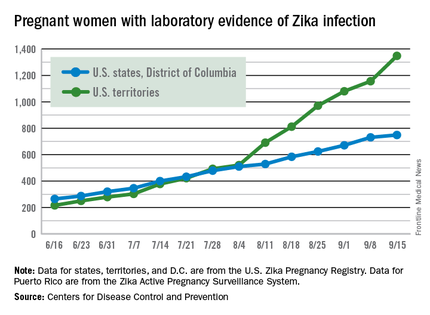
The weekly number of pregnant women in the United States with laboratory evidence of Zika virus infection topped 200 for the first time during the week ending Sept. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
With the 50 states and the District of Columbia reporting 18 new cases for the week and the U.S. territories reporting 192, there were 210 more pregnant women with Zika for the week ending Sept. 15, the CDC reported Sept. 22. The previous weekly high had been 199 for the week ending Aug. 25.
The CDC also reported two new cases of liveborn infants – both in the 50 states and D.C. – with Zika-related birth defects. No infants with Zika-related birth defects were reported in the territories for the week, and there were no new reports of pregnancy losses related to Zika. The number of pregnancy losses holds at six for the year so far, but the number of U.S. liveborn infants with Zika-related birth defects is now 21, with 20 cases in the states/D.C. and one in the territories, the CDC said. State- or territorial-level data are not being reported to protect the privacy of affected women and children.
There were 182 new cases of Zika infection reported among all Americans in the states/D.C. for the week ending Sept. 21, along with 2,083 new cases in the territories – almost all in Puerto Rico, which continues to retroactively report cases, the CDC noted Sept. 22. The U.S. total for 2015-2016 is 23,135 cases: 3,358 reported in the states/D.C. and 19,777 in the territories. Puerto Rico represents 98% of the territorial total, the CDC said.
Zika-related birth defects recorded by the CDC could include microcephaly, calcium deposits in the brain indicating possible brain damage, excess fluid in the brain cavities and surrounding the brain, absent or poorly formed brain structures, abnormal eye development, or other problems resulting from brain damage that affect nerves, muscles, and bones. The pregnancy losses encompass any miscarriage, stillbirth, and termination with evidence of birth defects.
The figures for states, territories, and D.C. reflect reporting to the U.S. Zika Pregnancy Registry; data for Puerto Rico are reported to the U.S. Zika Active Pregnancy Surveillance System.
The weekly number of pregnant women in the United States with laboratory evidence of Zika virus infection topped 200 for the first time during the week ending Sept. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
With the 50 states and the District of Columbia reporting 18 new cases for the week and the U.S. territories reporting 192, there were 210 more pregnant women with Zika for the week ending Sept. 15, the CDC reported Sept. 22. The previous weekly high had been 199 for the week ending Aug. 25.

The CDC also reported two new cases of liveborn infants – both in the 50 states and D.C. – with Zika-related birth defects. No infants with Zika-related birth defects were reported in the territories for the week, and there were no new reports of pregnancy losses related to Zika. The number of pregnancy losses holds at six for the year so far, but the number of U.S. liveborn infants with Zika-related birth defects is now 21, with 20 cases in the states/D.C. and one in the territories, the CDC said. State- or territorial-level data are not being reported to protect the privacy of affected women and children.
There were 182 new cases of Zika infection reported among all Americans in the states/D.C. for the week ending Sept. 21, along with 2,083 new cases in the territories – almost all in Puerto Rico, which continues to retroactively report cases, the CDC noted Sept. 22. The U.S. total for 2015-2016 is 23,135 cases: 3,358 reported in the states/D.C. and 19,777 in the territories. Puerto Rico represents 98% of the territorial total, the CDC said.
Zika-related birth defects recorded by the CDC could include microcephaly, calcium deposits in the brain indicating possible brain damage, excess fluid in the brain cavities and surrounding the brain, absent or poorly formed brain structures, abnormal eye development, or other problems resulting from brain damage that affect nerves, muscles, and bones. The pregnancy losses encompass any miscarriage, stillbirth, and termination with evidence of birth defects.
The figures for states, territories, and D.C. reflect reporting to the U.S. Zika Pregnancy Registry; data for Puerto Rico are reported to the U.S. Zika Active Pregnancy Surveillance System.
The weekly number of pregnant women in the United States with laboratory evidence of Zika virus infection topped 200 for the first time during the week ending Sept. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
With the 50 states and the District of Columbia reporting 18 new cases for the week and the U.S. territories reporting 192, there were 210 more pregnant women with Zika for the week ending Sept. 15, the CDC reported Sept. 22. The previous weekly high had been 199 for the week ending Aug. 25.

The CDC also reported two new cases of liveborn infants – both in the 50 states and D.C. – with Zika-related birth defects. No infants with Zika-related birth defects were reported in the territories for the week, and there were no new reports of pregnancy losses related to Zika. The number of pregnancy losses holds at six for the year so far, but the number of U.S. liveborn infants with Zika-related birth defects is now 21, with 20 cases in the states/D.C. and one in the territories, the CDC said. State- or territorial-level data are not being reported to protect the privacy of affected women and children.
There were 182 new cases of Zika infection reported among all Americans in the states/D.C. for the week ending Sept. 21, along with 2,083 new cases in the territories – almost all in Puerto Rico, which continues to retroactively report cases, the CDC noted Sept. 22. The U.S. total for 2015-2016 is 23,135 cases: 3,358 reported in the states/D.C. and 19,777 in the territories. Puerto Rico represents 98% of the territorial total, the CDC said.
Zika-related birth defects recorded by the CDC could include microcephaly, calcium deposits in the brain indicating possible brain damage, excess fluid in the brain cavities and surrounding the brain, absent or poorly formed brain structures, abnormal eye development, or other problems resulting from brain damage that affect nerves, muscles, and bones. The pregnancy losses encompass any miscarriage, stillbirth, and termination with evidence of birth defects.
The figures for states, territories, and D.C. reflect reporting to the U.S. Zika Pregnancy Registry; data for Puerto Rico are reported to the U.S. Zika Active Pregnancy Surveillance System.
