User login
Children and COVID: Decline of summer surge continues
The continuing decline in COVID-19 incidence suggests the latest surge has peaked as new cases in children dropped for the 4th consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
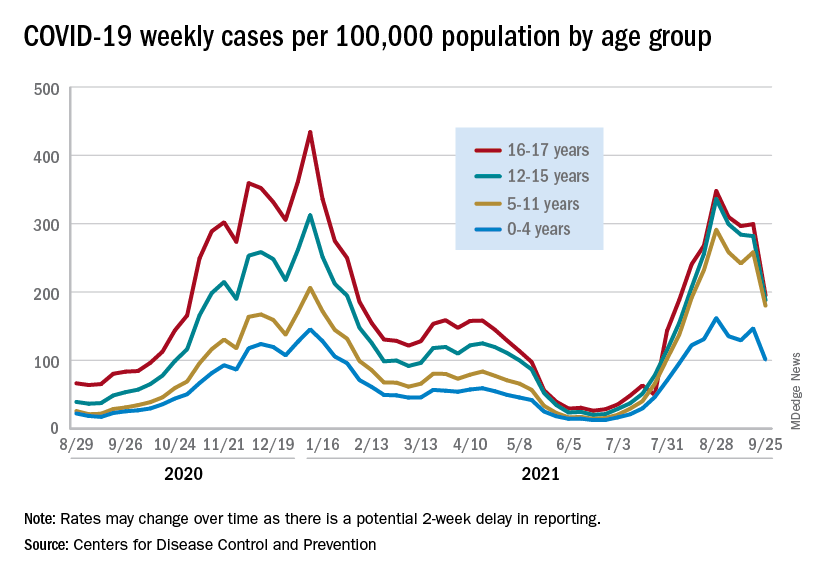
Preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, however, show an uptick in new cases in late September, largely among younger children, that may indicate otherwise. Those data have a potential 2-week reporting delay, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker, so the most recent points on the graph (see above) could still go up.
. Those new cases made up almost 27% of all cases for the week, and the nearly 5.9 million child cases that have been reported since the start of the pandemic represent 16.2% of cases among Americans of all ages, the two groups said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The CDC data on new cases by age group suggest that younger children have borne a heavier burden in the summer surge of COVID than they did last winter. The rate of new cases was not as high for 16- and 17-year-olds in the summer, but the other age groups all reached higher peaks than in the winter, including the 12- to 15-year-olds, who have been getting vaccinated since May, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
With vaccination approval getting closer for children under age 12 years, initiation in those already eligible continues to slide. Those aged 12-15 made up just 6.9% of new vaccinations during the 2 weeks from Sept. 21 to Oct. 4, and that figure has been dropping since July 13-26, when it was 14.1%. Vaccine initiation among 16- and 17-year-olds over that time has dropped by almost half, from 5.4% to 2.9%, the CDC data show.
All the vaccinations so far add up to this: Almost 55% of those aged 12-15 have gotten at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have over 62% of those aged 16-17, and 52% of the older group is fully vaccinated, as is 44% of the younger group. Altogether, 10.8 million children were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 4, including those under 12 who may be participating in clinical trials or had a birth date entered incorrectly, the CDC said.
The continuing decline in COVID-19 incidence suggests the latest surge has peaked as new cases in children dropped for the 4th consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, however, show an uptick in new cases in late September, largely among younger children, that may indicate otherwise. Those data have a potential 2-week reporting delay, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker, so the most recent points on the graph (see above) could still go up.
. Those new cases made up almost 27% of all cases for the week, and the nearly 5.9 million child cases that have been reported since the start of the pandemic represent 16.2% of cases among Americans of all ages, the two groups said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The CDC data on new cases by age group suggest that younger children have borne a heavier burden in the summer surge of COVID than they did last winter. The rate of new cases was not as high for 16- and 17-year-olds in the summer, but the other age groups all reached higher peaks than in the winter, including the 12- to 15-year-olds, who have been getting vaccinated since May, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
With vaccination approval getting closer for children under age 12 years, initiation in those already eligible continues to slide. Those aged 12-15 made up just 6.9% of new vaccinations during the 2 weeks from Sept. 21 to Oct. 4, and that figure has been dropping since July 13-26, when it was 14.1%. Vaccine initiation among 16- and 17-year-olds over that time has dropped by almost half, from 5.4% to 2.9%, the CDC data show.
All the vaccinations so far add up to this: Almost 55% of those aged 12-15 have gotten at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have over 62% of those aged 16-17, and 52% of the older group is fully vaccinated, as is 44% of the younger group. Altogether, 10.8 million children were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 4, including those under 12 who may be participating in clinical trials or had a birth date entered incorrectly, the CDC said.
The continuing decline in COVID-19 incidence suggests the latest surge has peaked as new cases in children dropped for the 4th consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, however, show an uptick in new cases in late September, largely among younger children, that may indicate otherwise. Those data have a potential 2-week reporting delay, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker, so the most recent points on the graph (see above) could still go up.
. Those new cases made up almost 27% of all cases for the week, and the nearly 5.9 million child cases that have been reported since the start of the pandemic represent 16.2% of cases among Americans of all ages, the two groups said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The CDC data on new cases by age group suggest that younger children have borne a heavier burden in the summer surge of COVID than they did last winter. The rate of new cases was not as high for 16- and 17-year-olds in the summer, but the other age groups all reached higher peaks than in the winter, including the 12- to 15-year-olds, who have been getting vaccinated since May, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
With vaccination approval getting closer for children under age 12 years, initiation in those already eligible continues to slide. Those aged 12-15 made up just 6.9% of new vaccinations during the 2 weeks from Sept. 21 to Oct. 4, and that figure has been dropping since July 13-26, when it was 14.1%. Vaccine initiation among 16- and 17-year-olds over that time has dropped by almost half, from 5.4% to 2.9%, the CDC data show.
All the vaccinations so far add up to this: Almost 55% of those aged 12-15 have gotten at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have over 62% of those aged 16-17, and 52% of the older group is fully vaccinated, as is 44% of the younger group. Altogether, 10.8 million children were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 4, including those under 12 who may be participating in clinical trials or had a birth date entered incorrectly, the CDC said.
Johnson & Johnson requests FDA approval for vaccine booster doses
The company said it filed a request for people ages 18 and older who have received the one-shot vaccine. Johnson & Johnson submitted data for several different booster intervals -- ranging from 2 months to 6 months -- but didn’t formally recommend one to the FDA, The Associated Press reported.
“We’re describing the data to them,” Mathai Mammen, MD, head of global research and development for Janssen, the company’s vaccine division, told CNN.
“The process is not that we asked for a very specific interval -- we’re providing them data and we’re going to be presenting to the committee,” he said. “They’ll take all that into consideration when they ultimately decide on an appropriate interval.”
The FDA’s independent vaccine advisory committee meets next week to review data on booster shots from both Johnson & Johnson and Moderna. It’s the first step in the review process, which then requires approval from leaders at the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If both agencies authorize the extra shots, Americans could receive boosters from Johnson & Johnson and Moderna later this month, the AP reported.
Johnson & Johnson previously released data that showed the vaccine remains highly effective against COVID-19 at least 5 months after vaccination, with 81% efficacy against hospitalizations in the United States.
Two weeks ago, the company reported that a booster dose at 2 months or 6 months further lifted immunity, with a booster at 2 months providing 94% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19. The company said the 6-month booster raised antibodies by 12 times but didn’t release additional data at that time.
In September, the FDA authorized booster shots of the Pfizer vaccine for ages 65 and older, those who live in long-term care facilities, and those with higher risks for contracting COVID-19. The Biden administration is supporting a booster campaign to address potential waning vaccine immunity and remaining surges of the more contagious Delta variant, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The company said it filed a request for people ages 18 and older who have received the one-shot vaccine. Johnson & Johnson submitted data for several different booster intervals -- ranging from 2 months to 6 months -- but didn’t formally recommend one to the FDA, The Associated Press reported.
“We’re describing the data to them,” Mathai Mammen, MD, head of global research and development for Janssen, the company’s vaccine division, told CNN.
“The process is not that we asked for a very specific interval -- we’re providing them data and we’re going to be presenting to the committee,” he said. “They’ll take all that into consideration when they ultimately decide on an appropriate interval.”
The FDA’s independent vaccine advisory committee meets next week to review data on booster shots from both Johnson & Johnson and Moderna. It’s the first step in the review process, which then requires approval from leaders at the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If both agencies authorize the extra shots, Americans could receive boosters from Johnson & Johnson and Moderna later this month, the AP reported.
Johnson & Johnson previously released data that showed the vaccine remains highly effective against COVID-19 at least 5 months after vaccination, with 81% efficacy against hospitalizations in the United States.
Two weeks ago, the company reported that a booster dose at 2 months or 6 months further lifted immunity, with a booster at 2 months providing 94% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19. The company said the 6-month booster raised antibodies by 12 times but didn’t release additional data at that time.
In September, the FDA authorized booster shots of the Pfizer vaccine for ages 65 and older, those who live in long-term care facilities, and those with higher risks for contracting COVID-19. The Biden administration is supporting a booster campaign to address potential waning vaccine immunity and remaining surges of the more contagious Delta variant, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The company said it filed a request for people ages 18 and older who have received the one-shot vaccine. Johnson & Johnson submitted data for several different booster intervals -- ranging from 2 months to 6 months -- but didn’t formally recommend one to the FDA, The Associated Press reported.
“We’re describing the data to them,” Mathai Mammen, MD, head of global research and development for Janssen, the company’s vaccine division, told CNN.
“The process is not that we asked for a very specific interval -- we’re providing them data and we’re going to be presenting to the committee,” he said. “They’ll take all that into consideration when they ultimately decide on an appropriate interval.”
The FDA’s independent vaccine advisory committee meets next week to review data on booster shots from both Johnson & Johnson and Moderna. It’s the first step in the review process, which then requires approval from leaders at the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If both agencies authorize the extra shots, Americans could receive boosters from Johnson & Johnson and Moderna later this month, the AP reported.
Johnson & Johnson previously released data that showed the vaccine remains highly effective against COVID-19 at least 5 months after vaccination, with 81% efficacy against hospitalizations in the United States.
Two weeks ago, the company reported that a booster dose at 2 months or 6 months further lifted immunity, with a booster at 2 months providing 94% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19. The company said the 6-month booster raised antibodies by 12 times but didn’t release additional data at that time.
In September, the FDA authorized booster shots of the Pfizer vaccine for ages 65 and older, those who live in long-term care facilities, and those with higher risks for contracting COVID-19. The Biden administration is supporting a booster campaign to address potential waning vaccine immunity and remaining surges of the more contagious Delta variant, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: New cases topped 200,000 after 3 weeks of declines
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
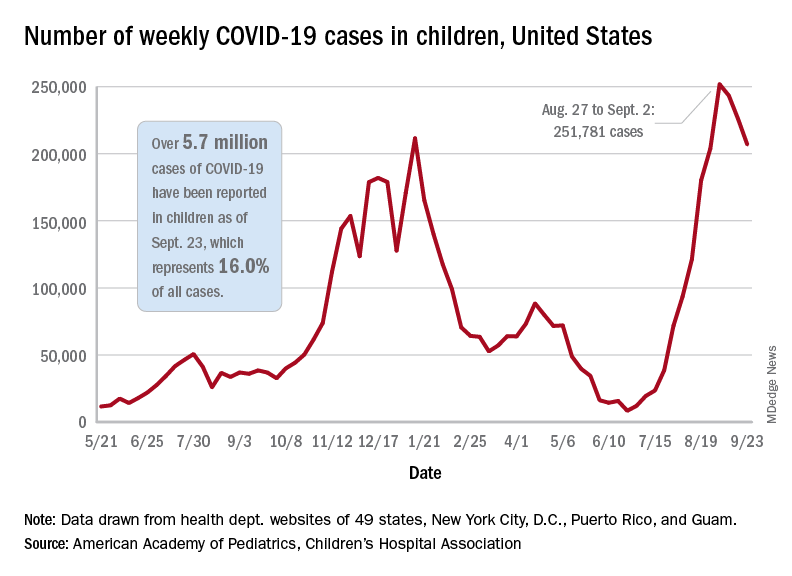
based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
One in three children fall short of sleep recommendations
Just over one-third of children in the United States get less sleep than recommended, with higher rates occurring among several racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
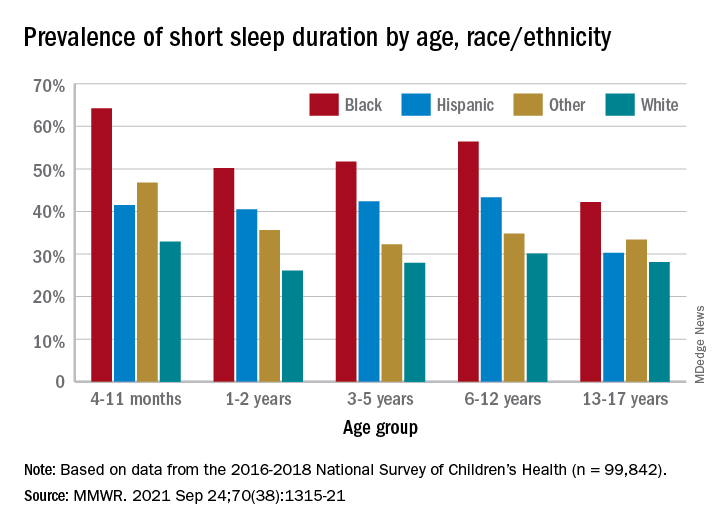
, Anne G. Wheaton, PhD, and Angelika H. Claussen, PhD, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Unlike previous reports, this analysis showed that adolescents were less likely than infants to have short sleep duration, 31.2% vs. 40.3%. These latest data are based on the 2016-2018 editions of the National Survey of Children’s Health, and the “difference might be explained by NSCH’s reliance on parent report rather than self-report with Youth Risk Behavior Surveys,” they suggested.
Black children had the highest prevalence of any group included in the study, as parents reported that 50.8% of all ages were not getting the recommended amount of sleep, compared with 39.1% among Hispanics, 34.6% for other races, and 28.8% for Whites. The figure for Black infants was 64.2%, almost double the prevalence for White infants (32.9%), said Dr. Wheaton and Dr. Claussen of the CDC.
Short sleep duration also was more common in children from lower-income families and among those with less educated parents. Geography had an effect as well, with prevalence “highest in the Southeast, similar to geographic variation in adequate sleep observed for adults,” they noted.
Previous research has shown that “sleep disparity was associated with various social determinants of health (e.g., poverty, food insecurity, and perceived racism), which can increase chronic and acute stress and result in environmental and psychological factors that negatively affect sleep duration and can compound long-term health risks,” the investigators wrote.
Short sleep duration by age group was defined as less the following amounts: Twelve hours for infants (4-11 months), 11 hours for children aged 1-2 years, 10 hours for children aged 3-5 years, 9 hours for children aged 6-12, and 8 hours for adolescents (13-17 years), they explained. Responses for the survey’s sleep-duration question totaled 99,842 for the 3 years included.
Just over one-third of children in the United States get less sleep than recommended, with higher rates occurring among several racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

, Anne G. Wheaton, PhD, and Angelika H. Claussen, PhD, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Unlike previous reports, this analysis showed that adolescents were less likely than infants to have short sleep duration, 31.2% vs. 40.3%. These latest data are based on the 2016-2018 editions of the National Survey of Children’s Health, and the “difference might be explained by NSCH’s reliance on parent report rather than self-report with Youth Risk Behavior Surveys,” they suggested.
Black children had the highest prevalence of any group included in the study, as parents reported that 50.8% of all ages were not getting the recommended amount of sleep, compared with 39.1% among Hispanics, 34.6% for other races, and 28.8% for Whites. The figure for Black infants was 64.2%, almost double the prevalence for White infants (32.9%), said Dr. Wheaton and Dr. Claussen of the CDC.
Short sleep duration also was more common in children from lower-income families and among those with less educated parents. Geography had an effect as well, with prevalence “highest in the Southeast, similar to geographic variation in adequate sleep observed for adults,” they noted.
Previous research has shown that “sleep disparity was associated with various social determinants of health (e.g., poverty, food insecurity, and perceived racism), which can increase chronic and acute stress and result in environmental and psychological factors that negatively affect sleep duration and can compound long-term health risks,” the investigators wrote.
Short sleep duration by age group was defined as less the following amounts: Twelve hours for infants (4-11 months), 11 hours for children aged 1-2 years, 10 hours for children aged 3-5 years, 9 hours for children aged 6-12, and 8 hours for adolescents (13-17 years), they explained. Responses for the survey’s sleep-duration question totaled 99,842 for the 3 years included.
Just over one-third of children in the United States get less sleep than recommended, with higher rates occurring among several racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

, Anne G. Wheaton, PhD, and Angelika H. Claussen, PhD, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Unlike previous reports, this analysis showed that adolescents were less likely than infants to have short sleep duration, 31.2% vs. 40.3%. These latest data are based on the 2016-2018 editions of the National Survey of Children’s Health, and the “difference might be explained by NSCH’s reliance on parent report rather than self-report with Youth Risk Behavior Surveys,” they suggested.
Black children had the highest prevalence of any group included in the study, as parents reported that 50.8% of all ages were not getting the recommended amount of sleep, compared with 39.1% among Hispanics, 34.6% for other races, and 28.8% for Whites. The figure for Black infants was 64.2%, almost double the prevalence for White infants (32.9%), said Dr. Wheaton and Dr. Claussen of the CDC.
Short sleep duration also was more common in children from lower-income families and among those with less educated parents. Geography had an effect as well, with prevalence “highest in the Southeast, similar to geographic variation in adequate sleep observed for adults,” they noted.
Previous research has shown that “sleep disparity was associated with various social determinants of health (e.g., poverty, food insecurity, and perceived racism), which can increase chronic and acute stress and result in environmental and psychological factors that negatively affect sleep duration and can compound long-term health risks,” the investigators wrote.
Short sleep duration by age group was defined as less the following amounts: Twelve hours for infants (4-11 months), 11 hours for children aged 1-2 years, 10 hours for children aged 3-5 years, 9 hours for children aged 6-12, and 8 hours for adolescents (13-17 years), they explained. Responses for the survey’s sleep-duration question totaled 99,842 for the 3 years included.
FROM MMWR
FDA issues proposed order for over-the-counter sunscreens
Federal efforts to improve the quality, safety, and efficacy of over-the-counter sunscreens took a step forward today with the release of two orders aimed at updating regulatory requirements for most sunscreen products in the United States.
“We see it as a key public health priority and our regulatory obligation to make sure that marketed sunscreen products offer protection from the sun’s effects and that they deliver on those promises to consumers,” Theresa Michele, MD, director of the office of nonprescription drugs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said during a media briefing.
When the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act was passed in 2020, the FDA was in the middle of amending a sunscreen monograph through the previous rule-making process, and the agency had issued a proposed rule for sunscreens in February of 2019. The CARES Act provided the FDA with new authority related to OTC drugs including sunscreens.
It also established a deemed final order for sunscreens, which set the current requirements for OTC sunscreen products marketed without an application. The deemed final order, released on Sept. 24, “essentially preserves the pre-CARES Act status quo marketing conditions for these sunscreens,” Dr. Michele explained. “Before the CARES Act was passed, sunscreens were marketed according to nearly identical terms that were described in an FDA enforcement discretion policy. For this reason, the agency believes that most sunscreens on the market today are already in compliance with this order.”
The CARES Act also required the FDA to issue a proposed order by Sept. 27 to amend and revise the deemed final order. Dr. Michele described the proposed order, which was released on Sept. 24, as “a vehicle to effectively transition our ongoing consideration of the appropriate requirements for OTC sunscreens marketed without approved applications from the previous rule-making process to this new order process. The provisions in today’s proposed order are therefore substantively the same as those described in the FDA’s 2019 proposed rule on sunscreens. With this proposed order, we’re proposing new requirements to improve the quality, safety, and efficacy of sunscreens that Americans use every day.”
The order proposes to update the generally recognized as safe (GRASE) status for the 16 active ingredients listed in the deemed final order. It also proposes that dosage forms that are GRASE for use as sunscreens include oils, lotions, creams, gels, butters, pastes, ointments, and sticks, and proposes GRASE status for spray sunscreens, subject to testing and labeling requirements.
Adam Friedman, MD, FAAD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, emphasized that photoprotection “is important for everyone, regardless of skin tone,” in an interview. “Broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 15 and higher play an important role in this. This should not be lost amidst the proposed order.”
Changes between the deemed and proposed order that he highlighted include a maximum SPF of 60+ (though up to 80 might be allowed) and that zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are GRASE. “The FDA did not say that nanoparticle formulations of these, which are easier to use, are not GRASE; they are asking for community input,” he said.
Other changes between the deemed and proposed order are that PABA and trolamine salicylate are not GRASE and that broad-spectrum testing will be mandatory. In addition, Dr. Friedman said, “sprays will be considered for GRASE so long as properly tested, labeling should be clearer (and a warning will be applied to those sunscreens not shown to prevent all the bad stuff with UVR [ultraviolet radiation]), and bug spray–sunscreen combos are a no-go.”
The FDA will consider comments on the proposed order submitted during a 45-day public comment period before issuing a revised final order. “As part of this process, we’ll consider all timely comments submitted both in response to the February 2019 proposed rule and to the current proposed order,” Dr. Michele said.
Dr. Friedman reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is also a speaker for Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Abbvie, LRP, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
Federal efforts to improve the quality, safety, and efficacy of over-the-counter sunscreens took a step forward today with the release of two orders aimed at updating regulatory requirements for most sunscreen products in the United States.
“We see it as a key public health priority and our regulatory obligation to make sure that marketed sunscreen products offer protection from the sun’s effects and that they deliver on those promises to consumers,” Theresa Michele, MD, director of the office of nonprescription drugs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said during a media briefing.
When the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act was passed in 2020, the FDA was in the middle of amending a sunscreen monograph through the previous rule-making process, and the agency had issued a proposed rule for sunscreens in February of 2019. The CARES Act provided the FDA with new authority related to OTC drugs including sunscreens.
It also established a deemed final order for sunscreens, which set the current requirements for OTC sunscreen products marketed without an application. The deemed final order, released on Sept. 24, “essentially preserves the pre-CARES Act status quo marketing conditions for these sunscreens,” Dr. Michele explained. “Before the CARES Act was passed, sunscreens were marketed according to nearly identical terms that were described in an FDA enforcement discretion policy. For this reason, the agency believes that most sunscreens on the market today are already in compliance with this order.”
The CARES Act also required the FDA to issue a proposed order by Sept. 27 to amend and revise the deemed final order. Dr. Michele described the proposed order, which was released on Sept. 24, as “a vehicle to effectively transition our ongoing consideration of the appropriate requirements for OTC sunscreens marketed without approved applications from the previous rule-making process to this new order process. The provisions in today’s proposed order are therefore substantively the same as those described in the FDA’s 2019 proposed rule on sunscreens. With this proposed order, we’re proposing new requirements to improve the quality, safety, and efficacy of sunscreens that Americans use every day.”
The order proposes to update the generally recognized as safe (GRASE) status for the 16 active ingredients listed in the deemed final order. It also proposes that dosage forms that are GRASE for use as sunscreens include oils, lotions, creams, gels, butters, pastes, ointments, and sticks, and proposes GRASE status for spray sunscreens, subject to testing and labeling requirements.
Adam Friedman, MD, FAAD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, emphasized that photoprotection “is important for everyone, regardless of skin tone,” in an interview. “Broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 15 and higher play an important role in this. This should not be lost amidst the proposed order.”
Changes between the deemed and proposed order that he highlighted include a maximum SPF of 60+ (though up to 80 might be allowed) and that zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are GRASE. “The FDA did not say that nanoparticle formulations of these, which are easier to use, are not GRASE; they are asking for community input,” he said.
Other changes between the deemed and proposed order are that PABA and trolamine salicylate are not GRASE and that broad-spectrum testing will be mandatory. In addition, Dr. Friedman said, “sprays will be considered for GRASE so long as properly tested, labeling should be clearer (and a warning will be applied to those sunscreens not shown to prevent all the bad stuff with UVR [ultraviolet radiation]), and bug spray–sunscreen combos are a no-go.”
The FDA will consider comments on the proposed order submitted during a 45-day public comment period before issuing a revised final order. “As part of this process, we’ll consider all timely comments submitted both in response to the February 2019 proposed rule and to the current proposed order,” Dr. Michele said.
Dr. Friedman reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is also a speaker for Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Abbvie, LRP, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
Federal efforts to improve the quality, safety, and efficacy of over-the-counter sunscreens took a step forward today with the release of two orders aimed at updating regulatory requirements for most sunscreen products in the United States.
“We see it as a key public health priority and our regulatory obligation to make sure that marketed sunscreen products offer protection from the sun’s effects and that they deliver on those promises to consumers,” Theresa Michele, MD, director of the office of nonprescription drugs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said during a media briefing.
When the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act was passed in 2020, the FDA was in the middle of amending a sunscreen monograph through the previous rule-making process, and the agency had issued a proposed rule for sunscreens in February of 2019. The CARES Act provided the FDA with new authority related to OTC drugs including sunscreens.
It also established a deemed final order for sunscreens, which set the current requirements for OTC sunscreen products marketed without an application. The deemed final order, released on Sept. 24, “essentially preserves the pre-CARES Act status quo marketing conditions for these sunscreens,” Dr. Michele explained. “Before the CARES Act was passed, sunscreens were marketed according to nearly identical terms that were described in an FDA enforcement discretion policy. For this reason, the agency believes that most sunscreens on the market today are already in compliance with this order.”
The CARES Act also required the FDA to issue a proposed order by Sept. 27 to amend and revise the deemed final order. Dr. Michele described the proposed order, which was released on Sept. 24, as “a vehicle to effectively transition our ongoing consideration of the appropriate requirements for OTC sunscreens marketed without approved applications from the previous rule-making process to this new order process. The provisions in today’s proposed order are therefore substantively the same as those described in the FDA’s 2019 proposed rule on sunscreens. With this proposed order, we’re proposing new requirements to improve the quality, safety, and efficacy of sunscreens that Americans use every day.”
The order proposes to update the generally recognized as safe (GRASE) status for the 16 active ingredients listed in the deemed final order. It also proposes that dosage forms that are GRASE for use as sunscreens include oils, lotions, creams, gels, butters, pastes, ointments, and sticks, and proposes GRASE status for spray sunscreens, subject to testing and labeling requirements.
Adam Friedman, MD, FAAD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, emphasized that photoprotection “is important for everyone, regardless of skin tone,” in an interview. “Broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 15 and higher play an important role in this. This should not be lost amidst the proposed order.”
Changes between the deemed and proposed order that he highlighted include a maximum SPF of 60+ (though up to 80 might be allowed) and that zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are GRASE. “The FDA did not say that nanoparticle formulations of these, which are easier to use, are not GRASE; they are asking for community input,” he said.
Other changes between the deemed and proposed order are that PABA and trolamine salicylate are not GRASE and that broad-spectrum testing will be mandatory. In addition, Dr. Friedman said, “sprays will be considered for GRASE so long as properly tested, labeling should be clearer (and a warning will be applied to those sunscreens not shown to prevent all the bad stuff with UVR [ultraviolet radiation]), and bug spray–sunscreen combos are a no-go.”
The FDA will consider comments on the proposed order submitted during a 45-day public comment period before issuing a revised final order. “As part of this process, we’ll consider all timely comments submitted both in response to the February 2019 proposed rule and to the current proposed order,” Dr. Michele said.
Dr. Friedman reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is also a speaker for Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Abbvie, LRP, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
CDC chief overrules panel, OKs boosters for health care workers
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices earlier Thursday voted to allow several groups of Americans to get a booster shot, but voted not to recommend it for adults age 18 to 64 who live or work in a place where the risk of COVID-19 is high. That would have included health care workers and other frontline employees.
But CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, decided to reverse that recommendation and include the 18-to-64-year-olds in her final decision.
“As CDC Director, it is my job to recognize where our actions can have the greatest impact,” Dr. Walensky said in a statement late Thursday night, according to published reports. “At CDC, we are tasked with analyzing complex, often imperfect data to make concrete recommendations that optimize health. In a pandemic, even with uncertainty, we must take actions that we anticipate will do the greatest good.”
Dr. Walensky agreed with the rest of the advisory committee's decisions, which included recommendations that the following groups also be eligible for a booster shot:
- Adults ages 65 and up and residents of long-term care facilities
- Adults ages 50 to 64 who have an underlying medical condition that may increase their risk from a COVID infection
- Adults ages 18 to 49 who may be at increased risk from a COVID-19 infection because of an underlying medical condition, if a person feels like they need one based on a consideration of their individual benefit and risks.
About 26 million Americans are at least 6 months past the last dose of the Pfizer vaccines, making them eligible to receive a third dose. About 13.6 million of them are over the age of 65. Another 5.3 million are ages 50 to 64.
In making the recommendations, the committee left out healthcare workers. This was a departure from the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization which included boosters for those 65 and over, and for people 18 through 64 years of age who are at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers – such as those in healthcare -- whose jobs increase their risk for infection.
This is the group Dr. Walensky added to the eligible list on her own.
Committee members “did not buy the need in occupational or institutional settings,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University in Nashville. Dr. Schaffner sits on the ACIP workgroup that considered the evidence behind boosters. He said that he would have voted yes to offer boosters to healthcare and other essential workers.
“There was a real split in the committee,” he said.
The vote on boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers was rejected 9 to 6.
“I think that there is ample evidence that people such as healthcare workers do not have repeated exposure in the workplace,” said Beth Bell, MD, a clinical professor at the University of Washington. “They’re using PPE as they should and they’re following the other policies within the healthcare setting. There’s lots of evidence that suggest that health care workers who become infected become infected because of exposures in the community.”
She was not alone in feeling cautious.
“I think this is an extremely slippery slope,” said Sarah Long, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Drexel University in Philadelphia, before her vote to reject boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers.
“We might as well just say, ‘Give it to everybody 18 and over.’ We have an extremely effective vaccine. It’s like saying it’s not working, and it is working.”
The committee saw data showing that all of the vaccines remain highly protective against hospitalization and death for all age groups, though protection against getting sick with COVID has waned slightly over time and with the dominance of the more contagious Delta variant. Those at highest risk for a severe breakthrough infection — those that cause hospitalization or death — are older adults.
How much will the U.S. benefit from boosters?
Some felt squeamish about broadly recommending boosters at all.
“We have too much hope on the line with these boosters,” said James Loehr, MD, who is a family physician in Ithaca, N.Y. Dr. Loehr said he felt the goal of giving boosters in the United States should be to decrease hospitalizations, and he felt they would, but that the impact would likely be smaller than appreciated.
Based on his calculations of the benefits of boosters for each age group, Dr. Loehr said if boosters were given to all 13 million seniors previously vaccinated with the Pfizer vaccine, we might prevent 200 hospitalizations a day, “which would be a lot,” he noted. But, he said, “considering that we have 10,000 hospitalizations a day now, it’s probably not that much.”
Others agreed.
“I really think this is a solution looking for a problem,” said Jason Goldman, MD, an associate professor at Florida Atlantic University who was representing the American College of Physicians. “You know, I don’t think it’s going to address the issue of the pandemic. I really think it’s just going to create more confusion on the provider from the position of implementation, and I really think it’s going really far afield of the data.”
ACIP Chair Grace Lee, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford, said she had cared for children who had died of COVID.
“I can tell you that their family members really wished they had extra protection for their kids, because they weren’t symptomatic. Nobody else was sick at home,” she said.
Dr. Lee said for her, access was paramount, and she was in favor of expanding access to boosters for as many people as possible.
Next steps
People who were initially vaccinated with either Moderna or Johnson & Johnson vaccines are excluded from booster recommendations, something many on the committee were uncomfortable with.
The FDA is still considering Moderna’s application to market booster doses. Johnson & Johnson hasn’t yet applied to the FDA for permission to offer second doses in the United States.
While the ACIP’s recommendations are important, in this case, they may not have a huge practical effect, said Schaffner. The CDC has already approved third shots for people who are immunocompromised, and no proof of a medical condition is required to get one.
More than 2 million people have already gotten a third dose, he noted, and not all of them are immunocompromised.
“They have heard the president say that, you know, everybody should get a booster, and they’ve taken that at face value,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices earlier Thursday voted to allow several groups of Americans to get a booster shot, but voted not to recommend it for adults age 18 to 64 who live or work in a place where the risk of COVID-19 is high. That would have included health care workers and other frontline employees.
But CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, decided to reverse that recommendation and include the 18-to-64-year-olds in her final decision.
“As CDC Director, it is my job to recognize where our actions can have the greatest impact,” Dr. Walensky said in a statement late Thursday night, according to published reports. “At CDC, we are tasked with analyzing complex, often imperfect data to make concrete recommendations that optimize health. In a pandemic, even with uncertainty, we must take actions that we anticipate will do the greatest good.”
Dr. Walensky agreed with the rest of the advisory committee's decisions, which included recommendations that the following groups also be eligible for a booster shot:
- Adults ages 65 and up and residents of long-term care facilities
- Adults ages 50 to 64 who have an underlying medical condition that may increase their risk from a COVID infection
- Adults ages 18 to 49 who may be at increased risk from a COVID-19 infection because of an underlying medical condition, if a person feels like they need one based on a consideration of their individual benefit and risks.
About 26 million Americans are at least 6 months past the last dose of the Pfizer vaccines, making them eligible to receive a third dose. About 13.6 million of them are over the age of 65. Another 5.3 million are ages 50 to 64.
In making the recommendations, the committee left out healthcare workers. This was a departure from the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization which included boosters for those 65 and over, and for people 18 through 64 years of age who are at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers – such as those in healthcare -- whose jobs increase their risk for infection.
This is the group Dr. Walensky added to the eligible list on her own.
Committee members “did not buy the need in occupational or institutional settings,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University in Nashville. Dr. Schaffner sits on the ACIP workgroup that considered the evidence behind boosters. He said that he would have voted yes to offer boosters to healthcare and other essential workers.
“There was a real split in the committee,” he said.
The vote on boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers was rejected 9 to 6.
“I think that there is ample evidence that people such as healthcare workers do not have repeated exposure in the workplace,” said Beth Bell, MD, a clinical professor at the University of Washington. “They’re using PPE as they should and they’re following the other policies within the healthcare setting. There’s lots of evidence that suggest that health care workers who become infected become infected because of exposures in the community.”
She was not alone in feeling cautious.
“I think this is an extremely slippery slope,” said Sarah Long, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Drexel University in Philadelphia, before her vote to reject boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers.
“We might as well just say, ‘Give it to everybody 18 and over.’ We have an extremely effective vaccine. It’s like saying it’s not working, and it is working.”
The committee saw data showing that all of the vaccines remain highly protective against hospitalization and death for all age groups, though protection against getting sick with COVID has waned slightly over time and with the dominance of the more contagious Delta variant. Those at highest risk for a severe breakthrough infection — those that cause hospitalization or death — are older adults.
How much will the U.S. benefit from boosters?
Some felt squeamish about broadly recommending boosters at all.
“We have too much hope on the line with these boosters,” said James Loehr, MD, who is a family physician in Ithaca, N.Y. Dr. Loehr said he felt the goal of giving boosters in the United States should be to decrease hospitalizations, and he felt they would, but that the impact would likely be smaller than appreciated.
Based on his calculations of the benefits of boosters for each age group, Dr. Loehr said if boosters were given to all 13 million seniors previously vaccinated with the Pfizer vaccine, we might prevent 200 hospitalizations a day, “which would be a lot,” he noted. But, he said, “considering that we have 10,000 hospitalizations a day now, it’s probably not that much.”
Others agreed.
“I really think this is a solution looking for a problem,” said Jason Goldman, MD, an associate professor at Florida Atlantic University who was representing the American College of Physicians. “You know, I don’t think it’s going to address the issue of the pandemic. I really think it’s just going to create more confusion on the provider from the position of implementation, and I really think it’s going really far afield of the data.”
ACIP Chair Grace Lee, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford, said she had cared for children who had died of COVID.
“I can tell you that their family members really wished they had extra protection for their kids, because they weren’t symptomatic. Nobody else was sick at home,” she said.
Dr. Lee said for her, access was paramount, and she was in favor of expanding access to boosters for as many people as possible.
Next steps
People who were initially vaccinated with either Moderna or Johnson & Johnson vaccines are excluded from booster recommendations, something many on the committee were uncomfortable with.
The FDA is still considering Moderna’s application to market booster doses. Johnson & Johnson hasn’t yet applied to the FDA for permission to offer second doses in the United States.
While the ACIP’s recommendations are important, in this case, they may not have a huge practical effect, said Schaffner. The CDC has already approved third shots for people who are immunocompromised, and no proof of a medical condition is required to get one.
More than 2 million people have already gotten a third dose, he noted, and not all of them are immunocompromised.
“They have heard the president say that, you know, everybody should get a booster, and they’ve taken that at face value,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices earlier Thursday voted to allow several groups of Americans to get a booster shot, but voted not to recommend it for adults age 18 to 64 who live or work in a place where the risk of COVID-19 is high. That would have included health care workers and other frontline employees.
But CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, decided to reverse that recommendation and include the 18-to-64-year-olds in her final decision.
“As CDC Director, it is my job to recognize where our actions can have the greatest impact,” Dr. Walensky said in a statement late Thursday night, according to published reports. “At CDC, we are tasked with analyzing complex, often imperfect data to make concrete recommendations that optimize health. In a pandemic, even with uncertainty, we must take actions that we anticipate will do the greatest good.”
Dr. Walensky agreed with the rest of the advisory committee's decisions, which included recommendations that the following groups also be eligible for a booster shot:
- Adults ages 65 and up and residents of long-term care facilities
- Adults ages 50 to 64 who have an underlying medical condition that may increase their risk from a COVID infection
- Adults ages 18 to 49 who may be at increased risk from a COVID-19 infection because of an underlying medical condition, if a person feels like they need one based on a consideration of their individual benefit and risks.
About 26 million Americans are at least 6 months past the last dose of the Pfizer vaccines, making them eligible to receive a third dose. About 13.6 million of them are over the age of 65. Another 5.3 million are ages 50 to 64.
In making the recommendations, the committee left out healthcare workers. This was a departure from the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization which included boosters for those 65 and over, and for people 18 through 64 years of age who are at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers – such as those in healthcare -- whose jobs increase their risk for infection.
This is the group Dr. Walensky added to the eligible list on her own.
Committee members “did not buy the need in occupational or institutional settings,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University in Nashville. Dr. Schaffner sits on the ACIP workgroup that considered the evidence behind boosters. He said that he would have voted yes to offer boosters to healthcare and other essential workers.
“There was a real split in the committee,” he said.
The vote on boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers was rejected 9 to 6.
“I think that there is ample evidence that people such as healthcare workers do not have repeated exposure in the workplace,” said Beth Bell, MD, a clinical professor at the University of Washington. “They’re using PPE as they should and they’re following the other policies within the healthcare setting. There’s lots of evidence that suggest that health care workers who become infected become infected because of exposures in the community.”
She was not alone in feeling cautious.
“I think this is an extremely slippery slope,” said Sarah Long, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Drexel University in Philadelphia, before her vote to reject boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers.
“We might as well just say, ‘Give it to everybody 18 and over.’ We have an extremely effective vaccine. It’s like saying it’s not working, and it is working.”
The committee saw data showing that all of the vaccines remain highly protective against hospitalization and death for all age groups, though protection against getting sick with COVID has waned slightly over time and with the dominance of the more contagious Delta variant. Those at highest risk for a severe breakthrough infection — those that cause hospitalization or death — are older adults.
How much will the U.S. benefit from boosters?
Some felt squeamish about broadly recommending boosters at all.
“We have too much hope on the line with these boosters,” said James Loehr, MD, who is a family physician in Ithaca, N.Y. Dr. Loehr said he felt the goal of giving boosters in the United States should be to decrease hospitalizations, and he felt they would, but that the impact would likely be smaller than appreciated.
Based on his calculations of the benefits of boosters for each age group, Dr. Loehr said if boosters were given to all 13 million seniors previously vaccinated with the Pfizer vaccine, we might prevent 200 hospitalizations a day, “which would be a lot,” he noted. But, he said, “considering that we have 10,000 hospitalizations a day now, it’s probably not that much.”
Others agreed.
“I really think this is a solution looking for a problem,” said Jason Goldman, MD, an associate professor at Florida Atlantic University who was representing the American College of Physicians. “You know, I don’t think it’s going to address the issue of the pandemic. I really think it’s just going to create more confusion on the provider from the position of implementation, and I really think it’s going really far afield of the data.”
ACIP Chair Grace Lee, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford, said she had cared for children who had died of COVID.
“I can tell you that their family members really wished they had extra protection for their kids, because they weren’t symptomatic. Nobody else was sick at home,” she said.
Dr. Lee said for her, access was paramount, and she was in favor of expanding access to boosters for as many people as possible.
Next steps
People who were initially vaccinated with either Moderna or Johnson & Johnson vaccines are excluded from booster recommendations, something many on the committee were uncomfortable with.
The FDA is still considering Moderna’s application to market booster doses. Johnson & Johnson hasn’t yet applied to the FDA for permission to offer second doses in the United States.
While the ACIP’s recommendations are important, in this case, they may not have a huge practical effect, said Schaffner. The CDC has already approved third shots for people who are immunocompromised, and no proof of a medical condition is required to get one.
More than 2 million people have already gotten a third dose, he noted, and not all of them are immunocompromised.
“They have heard the president say that, you know, everybody should get a booster, and they’ve taken that at face value,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA approves topical ruxolitinib for atopic dermatitis, first JAK inhibitor for this indication in the U.S.
The , making it the first topical JAK inhibitor approved for AD – and the first JAK inhibitor approved for this indication – in the United States.
The approval is limited to patients whose AD is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies, or when those therapies are not advisable.
“Approval of topical ruxolitinib fills a major gap in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a safe, effective, and tolerable non-steroidal topical therapy,” Eric L. Simpson, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the Oregon Health & Science University Dermatology Clinical Research Center, Portland, told this news organization. “This approval will allow for long-term treatment without the concern of steroid side effects. From earlier studies, ruxolitinib cream appears to be as effective as a medium-potency topical steroid. These efficacy levels and low incidence of burning will be a welcome addition to our current nonsteroidal therapies.”
The drug’s approval was based on results from two phase 3, randomized studies of identical design involving 1,249 patients aged 12 years and older with AD: TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2. In these studies, ruxolitinib cream demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity, with rapid and sustained antipruritic action, compared with vehicle. In the trials, patients with an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 2 or 3 and 3%-20% of affected body surface area (BSA) were randomized (2:2:1) to twice-daily 0.75% ruxolitinib cream, 1.5% ruxolitinib cream, or vehicle cream for 8 continuous weeks. The 1.5% concentration was approved by the FDA.
A study first published in May of 2021 found that significantly more patients in TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 achieved IGA treatment success with 0.75% (50% vs. 39%, respectively) and 1.5% ruxolitinib cream (53.8% vs. 51.3%), compared with vehicle (15.1% vs. 7.6%; P < .0001) at week 8. In addition, significant reductions in itch, compared with vehicle, were reported within 12 hours of first applying 1.5% ruxolitinib cream (P < .05).
More key findings from TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 are scheduled to be presented during the upcoming European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology meeting Sept. 29-Oct. 2, but during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis Symposium on June 13, Kim Papp, MD, PhD, presented long-term safety data of ruxolitinib cream in patients who were followed for an additional 44 weeks. Dr. Papp, a dermatologist and founder of Probity Medical Research, Waterloo, Ont., reported that 543 patients from TRuE-AD1 and 530 from TRuE-AD2 entered the long-term analysis and that about 78% of these patients completed the study. From weeks 12 to 52, the proportion of patients with an IGA score of 0 or 1 with 0.75% and 1.5% ruxolitinib cream ranged from 62%-77% and 67%-77%, respectively, in TRuE-AD1, to 60%-77% and 72%-80% in TRuE-AD2.
The measured mean total affected BSA was less than 3% throughout the follow-up period in the 1.5% ruxolitinib cream arm in TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 and was less than 3% in the 0.75% ruxolitinib cream arm during most of the study period.
In a pooled safety analysis, treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported in 60% and 54% of patients who applied 0.75% and 1.5% ruxolitinib cream, respectively, over 44 weeks. The frequency of application-site reactions remained low. Specifically, treatment-related adverse events were reported in 5% of patients who applied 0.75% ruxolitinib cream and in 3% of patients who applied 1.5% ruxolitinib cream; none were serious. TEAEs led to discontinuation in 2% of patients in the 0.75% ruxolitinib cream group, and no patients in the 1.5% ruxolitinib cream group.
Dr. Papp and his colleagues observed that the most common treatment adverse events were upper respiratory tract infections and nasopharyngitis. According to Incyte’s press release, the most common treatment-emergent adverse reactions in patients treated with ruxolitinib during clinical trials were nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, bronchitis, ear infection, eosinophil count increases, urticaria, folliculitis, tonsillitis, and rhinorrhea. The labeling includes boxed warnings for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis, seen with oral JAK inhibitors for inflammatory conditions.
Incyte will market ruxolitinib under the trade name Opzelura.
Dr. Simpson disclosed that he is a consultant to and/or an investigator for several pharmaceutical companies, including Incyte, Regeneron/Sanofi, Eli Lilly and Company, AbbVie, and Pfizer.
Dr. Papp disclosed that he has received honoraria or clinical research grants as a consultant, speaker, scientific officer, advisory board member, and/or steering committee member for several pharmaceutical companies, including Incyte.
Commentary by Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH
Another nonsteroidal topical medication approved for atopic dermatitis (AD)? Thank goodness. Topical ruxolitinib 1.5% cream twice daily for mild to moderate AD demonstrated excellent efficacy vs. placebo in duplicative trials (53.8/51.3% vs. 15.1%/7.6%; P < .001), with a reassuring safety profile. Application site reactions were uncommon, though past experience with other new nonsteroidal agents suggests judgment be reserved on that score. More compelling was the fact that no patients discontinued therapy in the 1.5% arm, and adverse events were mild and self-limited such as nasopharyngitis and diarrhea. This stands in contradistinction to the boxed warning attached to JAK inhibitors (topical and systemic) against a daunting list of destructive possibilities: malignancy, infection, cardiovascular disease, and blood clots. None of these things was seen in these topical ruxolitinib trials.
Dr. Sidbury is chief of dermatology at Seattle Children's Hospital and professor, department of pediatrics, University of Washington, Seattle. He is a site principal investigator for dupilumab trials, for which the hospital has a contract with Regeneron.
This article was updated 6/16/22.
The , making it the first topical JAK inhibitor approved for AD – and the first JAK inhibitor approved for this indication – in the United States.
The approval is limited to patients whose AD is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies, or when those therapies are not advisable.
“Approval of topical ruxolitinib fills a major gap in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a safe, effective, and tolerable non-steroidal topical therapy,” Eric L. Simpson, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the Oregon Health & Science University Dermatology Clinical Research Center, Portland, told this news organization. “This approval will allow for long-term treatment without the concern of steroid side effects. From earlier studies, ruxolitinib cream appears to be as effective as a medium-potency topical steroid. These efficacy levels and low incidence of burning will be a welcome addition to our current nonsteroidal therapies.”
The drug’s approval was based on results from two phase 3, randomized studies of identical design involving 1,249 patients aged 12 years and older with AD: TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2. In these studies, ruxolitinib cream demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity, with rapid and sustained antipruritic action, compared with vehicle. In the trials, patients with an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 2 or 3 and 3%-20% of affected body surface area (BSA) were randomized (2:2:1) to twice-daily 0.75% ruxolitinib cream, 1.5% ruxolitinib cream, or vehicle cream for 8 continuous weeks. The 1.5% concentration was approved by the FDA.
A study first published in May of 2021 found that significantly more patients in TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 achieved IGA treatment success with 0.75% (50% vs. 39%, respectively) and 1.5% ruxolitinib cream (53.8% vs. 51.3%), compared with vehicle (15.1% vs. 7.6%; P < .0001) at week 8. In addition, significant reductions in itch, compared with vehicle, were reported within 12 hours of first applying 1.5% ruxolitinib cream (P < .05).
More key findings from TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 are scheduled to be presented during the upcoming European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology meeting Sept. 29-Oct. 2, but during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis Symposium on June 13, Kim Papp, MD, PhD, presented long-term safety data of ruxolitinib cream in patients who were followed for an additional 44 weeks. Dr. Papp, a dermatologist and founder of Probity Medical Research, Waterloo, Ont., reported that 543 patients from TRuE-AD1 and 530 from TRuE-AD2 entered the long-term analysis and that about 78% of these patients completed the study. From weeks 12 to 52, the proportion of patients with an IGA score of 0 or 1 with 0.75% and 1.5% ruxolitinib cream ranged from 62%-77% and 67%-77%, respectively, in TRuE-AD1, to 60%-77% and 72%-80% in TRuE-AD2.
The measured mean total affected BSA was less than 3% throughout the follow-up period in the 1.5% ruxolitinib cream arm in TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 and was less than 3% in the 0.75% ruxolitinib cream arm during most of the study period.
In a pooled safety analysis, treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported in 60% and 54% of patients who applied 0.75% and 1.5% ruxolitinib cream, respectively, over 44 weeks. The frequency of application-site reactions remained low. Specifically, treatment-related adverse events were reported in 5% of patients who applied 0.75% ruxolitinib cream and in 3% of patients who applied 1.5% ruxolitinib cream; none were serious. TEAEs led to discontinuation in 2% of patients in the 0.75% ruxolitinib cream group, and no patients in the 1.5% ruxolitinib cream group.
Dr. Papp and his colleagues observed that the most common treatment adverse events were upper respiratory tract infections and nasopharyngitis. According to Incyte’s press release, the most common treatment-emergent adverse reactions in patients treated with ruxolitinib during clinical trials were nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, bronchitis, ear infection, eosinophil count increases, urticaria, folliculitis, tonsillitis, and rhinorrhea. The labeling includes boxed warnings for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis, seen with oral JAK inhibitors for inflammatory conditions.
Incyte will market ruxolitinib under the trade name Opzelura.
Dr. Simpson disclosed that he is a consultant to and/or an investigator for several pharmaceutical companies, including Incyte, Regeneron/Sanofi, Eli Lilly and Company, AbbVie, and Pfizer.
Dr. Papp disclosed that he has received honoraria or clinical research grants as a consultant, speaker, scientific officer, advisory board member, and/or steering committee member for several pharmaceutical companies, including Incyte.
Commentary by Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH
Another nonsteroidal topical medication approved for atopic dermatitis (AD)? Thank goodness. Topical ruxolitinib 1.5% cream twice daily for mild to moderate AD demonstrated excellent efficacy vs. placebo in duplicative trials (53.8/51.3% vs. 15.1%/7.6%; P < .001), with a reassuring safety profile. Application site reactions were uncommon, though past experience with other new nonsteroidal agents suggests judgment be reserved on that score. More compelling was the fact that no patients discontinued therapy in the 1.5% arm, and adverse events were mild and self-limited such as nasopharyngitis and diarrhea. This stands in contradistinction to the boxed warning attached to JAK inhibitors (topical and systemic) against a daunting list of destructive possibilities: malignancy, infection, cardiovascular disease, and blood clots. None of these things was seen in these topical ruxolitinib trials.
Dr. Sidbury is chief of dermatology at Seattle Children's Hospital and professor, department of pediatrics, University of Washington, Seattle. He is a site principal investigator for dupilumab trials, for which the hospital has a contract with Regeneron.
This article was updated 6/16/22.
The , making it the first topical JAK inhibitor approved for AD – and the first JAK inhibitor approved for this indication – in the United States.
The approval is limited to patients whose AD is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies, or when those therapies are not advisable.
“Approval of topical ruxolitinib fills a major gap in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a safe, effective, and tolerable non-steroidal topical therapy,” Eric L. Simpson, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the Oregon Health & Science University Dermatology Clinical Research Center, Portland, told this news organization. “This approval will allow for long-term treatment without the concern of steroid side effects. From earlier studies, ruxolitinib cream appears to be as effective as a medium-potency topical steroid. These efficacy levels and low incidence of burning will be a welcome addition to our current nonsteroidal therapies.”
The drug’s approval was based on results from two phase 3, randomized studies of identical design involving 1,249 patients aged 12 years and older with AD: TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2. In these studies, ruxolitinib cream demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity, with rapid and sustained antipruritic action, compared with vehicle. In the trials, patients with an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 2 or 3 and 3%-20% of affected body surface area (BSA) were randomized (2:2:1) to twice-daily 0.75% ruxolitinib cream, 1.5% ruxolitinib cream, or vehicle cream for 8 continuous weeks. The 1.5% concentration was approved by the FDA.
A study first published in May of 2021 found that significantly more patients in TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 achieved IGA treatment success with 0.75% (50% vs. 39%, respectively) and 1.5% ruxolitinib cream (53.8% vs. 51.3%), compared with vehicle (15.1% vs. 7.6%; P < .0001) at week 8. In addition, significant reductions in itch, compared with vehicle, were reported within 12 hours of first applying 1.5% ruxolitinib cream (P < .05).
More key findings from TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 are scheduled to be presented during the upcoming European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology meeting Sept. 29-Oct. 2, but during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis Symposium on June 13, Kim Papp, MD, PhD, presented long-term safety data of ruxolitinib cream in patients who were followed for an additional 44 weeks. Dr. Papp, a dermatologist and founder of Probity Medical Research, Waterloo, Ont., reported that 543 patients from TRuE-AD1 and 530 from TRuE-AD2 entered the long-term analysis and that about 78% of these patients completed the study. From weeks 12 to 52, the proportion of patients with an IGA score of 0 or 1 with 0.75% and 1.5% ruxolitinib cream ranged from 62%-77% and 67%-77%, respectively, in TRuE-AD1, to 60%-77% and 72%-80% in TRuE-AD2.
The measured mean total affected BSA was less than 3% throughout the follow-up period in the 1.5% ruxolitinib cream arm in TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 and was less than 3% in the 0.75% ruxolitinib cream arm during most of the study period.
In a pooled safety analysis, treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported in 60% and 54% of patients who applied 0.75% and 1.5% ruxolitinib cream, respectively, over 44 weeks. The frequency of application-site reactions remained low. Specifically, treatment-related adverse events were reported in 5% of patients who applied 0.75% ruxolitinib cream and in 3% of patients who applied 1.5% ruxolitinib cream; none were serious. TEAEs led to discontinuation in 2% of patients in the 0.75% ruxolitinib cream group, and no patients in the 1.5% ruxolitinib cream group.
Dr. Papp and his colleagues observed that the most common treatment adverse events were upper respiratory tract infections and nasopharyngitis. According to Incyte’s press release, the most common treatment-emergent adverse reactions in patients treated with ruxolitinib during clinical trials were nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, bronchitis, ear infection, eosinophil count increases, urticaria, folliculitis, tonsillitis, and rhinorrhea. The labeling includes boxed warnings for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis, seen with oral JAK inhibitors for inflammatory conditions.
Incyte will market ruxolitinib under the trade name Opzelura.
Dr. Simpson disclosed that he is a consultant to and/or an investigator for several pharmaceutical companies, including Incyte, Regeneron/Sanofi, Eli Lilly and Company, AbbVie, and Pfizer.
Dr. Papp disclosed that he has received honoraria or clinical research grants as a consultant, speaker, scientific officer, advisory board member, and/or steering committee member for several pharmaceutical companies, including Incyte.
Commentary by Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH
Another nonsteroidal topical medication approved for atopic dermatitis (AD)? Thank goodness. Topical ruxolitinib 1.5% cream twice daily for mild to moderate AD demonstrated excellent efficacy vs. placebo in duplicative trials (53.8/51.3% vs. 15.1%/7.6%; P < .001), with a reassuring safety profile. Application site reactions were uncommon, though past experience with other new nonsteroidal agents suggests judgment be reserved on that score. More compelling was the fact that no patients discontinued therapy in the 1.5% arm, and adverse events were mild and self-limited such as nasopharyngitis and diarrhea. This stands in contradistinction to the boxed warning attached to JAK inhibitors (topical and systemic) against a daunting list of destructive possibilities: malignancy, infection, cardiovascular disease, and blood clots. None of these things was seen in these topical ruxolitinib trials.
Dr. Sidbury is chief of dermatology at Seattle Children's Hospital and professor, department of pediatrics, University of Washington, Seattle. He is a site principal investigator for dupilumab trials, for which the hospital has a contract with Regeneron.
This article was updated 6/16/22.
Decline in child COVID may signal end of latest surge
A second consecutive week of falling COVID-19 cases in children, along with continued declines in new admissions, may indicate that the latest surge has peaked.
Children made up over 25% of all new cases each week over that 3-week period covering the end of August and the first half of September, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.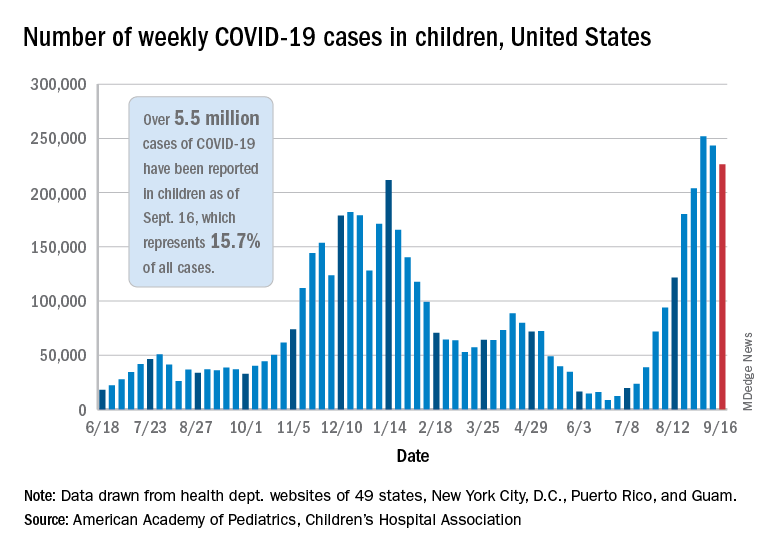
New hospitalizations in children aged 0-17 years peaked on Sept. 4 – when the rate reached 0.51 per 100,000 population – and were down to 0.47 as of Sept. 11, the latest date for which data should be considered reliable, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
The CDC’s data largely agree with the AAP/CHA report, showing that cases peaked during the week of Aug. 22-28. Cases per 100,000 for children that week looked like this: 154.7 (age 0-4 years), 276.6 (5-11 years), 320.0 (12-15), and 334.1 (16-17). The highest rates that week among adults were 288.6 per 100,000 in 30- to 39-year-olds and 286.5 for those aged 18-29, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
By the week of Sept. 5-11 – reporting delays can affect more recent data – the rates in children were down more than 20% in each of the four age groups, according to the CDC.
Vaccinations among children, unfortunately, continue to decline. Vaccine initiations for 12- to 15-year-olds slipped from 199,000 (Sept. 7-13) to 179,000 during the week of Sept. 14-20, while the 16- to 17-year-olds went from almost 83,000 down to 75,000. Initiations have dropped for 6 straight weeks in both age groups, based on the CDC data.
Despite those declines, however, the 16- and 17-year-olds just passed a couple of vaccination milestones. More than 60% – 60.9%, to be exact – have now received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, and 50.3% can be considered fully vaccinated. For those aged 12-15, the corresponding figures are 53.1% and 42.0%, the CDC reported.
When children under age 12 years are included – through clinical trial involvement or incorrect birth dates – the CDC data put the total count of Americans under age 18 who have received at least one dose of vaccine at almost 12.8 million, with vaccination complete in 10.3 million.
Total cases, as calculated by the APA and CHA, are now over 5.5 million, although that figure includes cases in individuals as old as 20 years, since many states differ from the CDC on the age range for a child. The CDC’s COVID Data Tracker put the total for children aged 0-17 at nearly 4.6 million.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 480 as of Sept. 16, the AAP and CHA said, based on data from 45 states, New York, City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, but the CDC provides a higher number, 548, since the pandemic began. Children aged 0-4 years represent the largest share (32.3%) of those 548 deaths, followed by the 12- to 15-year-olds (26.5%), based on the CDC data.
A second consecutive week of falling COVID-19 cases in children, along with continued declines in new admissions, may indicate that the latest surge has peaked.
Children made up over 25% of all new cases each week over that 3-week period covering the end of August and the first half of September, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New hospitalizations in children aged 0-17 years peaked on Sept. 4 – when the rate reached 0.51 per 100,000 population – and were down to 0.47 as of Sept. 11, the latest date for which data should be considered reliable, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
The CDC’s data largely agree with the AAP/CHA report, showing that cases peaked during the week of Aug. 22-28. Cases per 100,000 for children that week looked like this: 154.7 (age 0-4 years), 276.6 (5-11 years), 320.0 (12-15), and 334.1 (16-17). The highest rates that week among adults were 288.6 per 100,000 in 30- to 39-year-olds and 286.5 for those aged 18-29, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
By the week of Sept. 5-11 – reporting delays can affect more recent data – the rates in children were down more than 20% in each of the four age groups, according to the CDC.
Vaccinations among children, unfortunately, continue to decline. Vaccine initiations for 12- to 15-year-olds slipped from 199,000 (Sept. 7-13) to 179,000 during the week of Sept. 14-20, while the 16- to 17-year-olds went from almost 83,000 down to 75,000. Initiations have dropped for 6 straight weeks in both age groups, based on the CDC data.
Despite those declines, however, the 16- and 17-year-olds just passed a couple of vaccination milestones. More than 60% – 60.9%, to be exact – have now received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, and 50.3% can be considered fully vaccinated. For those aged 12-15, the corresponding figures are 53.1% and 42.0%, the CDC reported.
When children under age 12 years are included – through clinical trial involvement or incorrect birth dates – the CDC data put the total count of Americans under age 18 who have received at least one dose of vaccine at almost 12.8 million, with vaccination complete in 10.3 million.
Total cases, as calculated by the APA and CHA, are now over 5.5 million, although that figure includes cases in individuals as old as 20 years, since many states differ from the CDC on the age range for a child. The CDC’s COVID Data Tracker put the total for children aged 0-17 at nearly 4.6 million.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 480 as of Sept. 16, the AAP and CHA said, based on data from 45 states, New York, City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, but the CDC provides a higher number, 548, since the pandemic began. Children aged 0-4 years represent the largest share (32.3%) of those 548 deaths, followed by the 12- to 15-year-olds (26.5%), based on the CDC data.
A second consecutive week of falling COVID-19 cases in children, along with continued declines in new admissions, may indicate that the latest surge has peaked.
Children made up over 25% of all new cases each week over that 3-week period covering the end of August and the first half of September, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New hospitalizations in children aged 0-17 years peaked on Sept. 4 – when the rate reached 0.51 per 100,000 population – and were down to 0.47 as of Sept. 11, the latest date for which data should be considered reliable, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
The CDC’s data largely agree with the AAP/CHA report, showing that cases peaked during the week of Aug. 22-28. Cases per 100,000 for children that week looked like this: 154.7 (age 0-4 years), 276.6 (5-11 years), 320.0 (12-15), and 334.1 (16-17). The highest rates that week among adults were 288.6 per 100,000 in 30- to 39-year-olds and 286.5 for those aged 18-29, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
By the week of Sept. 5-11 – reporting delays can affect more recent data – the rates in children were down more than 20% in each of the four age groups, according to the CDC.
Vaccinations among children, unfortunately, continue to decline. Vaccine initiations for 12- to 15-year-olds slipped from 199,000 (Sept. 7-13) to 179,000 during the week of Sept. 14-20, while the 16- to 17-year-olds went from almost 83,000 down to 75,000. Initiations have dropped for 6 straight weeks in both age groups, based on the CDC data.
Despite those declines, however, the 16- and 17-year-olds just passed a couple of vaccination milestones. More than 60% – 60.9%, to be exact – have now received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, and 50.3% can be considered fully vaccinated. For those aged 12-15, the corresponding figures are 53.1% and 42.0%, the CDC reported.
When children under age 12 years are included – through clinical trial involvement or incorrect birth dates – the CDC data put the total count of Americans under age 18 who have received at least one dose of vaccine at almost 12.8 million, with vaccination complete in 10.3 million.
Total cases, as calculated by the APA and CHA, are now over 5.5 million, although that figure includes cases in individuals as old as 20 years, since many states differ from the CDC on the age range for a child. The CDC’s COVID Data Tracker put the total for children aged 0-17 at nearly 4.6 million.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 480 as of Sept. 16, the AAP and CHA said, based on data from 45 states, New York, City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, but the CDC provides a higher number, 548, since the pandemic began. Children aged 0-4 years represent the largest share (32.3%) of those 548 deaths, followed by the 12- to 15-year-olds (26.5%), based on the CDC data.
COVID-19 claims more than 675,000 U.S. lives, surpassing the 1918 flu
, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University.
Although the raw numbers match, epidemiologists point out that 675,000 deaths in 1918 was a much greater proportion of the population. In 1918, the U.S. population was 105 million, less than one third of what it is today.
The AIDS pandemic of the 1980s remains the deadliest of the 20th Century, claiming the lives of 700,000 Americans. But at our current pace of 2,000 COVID deaths a day, we could quickly eclipse that death toll, too.
Even though the 1918 epidemic is often called the “Spanish Flu,” there is no universal consensus regarding where the virus originated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Still, the almost incomprehensible loss harkens back to a time when medicine and technology were far less advanced than they are today.
In 1918, the United States didn’t have access to a vaccine, or near real-time tools to trace the spread and communicate the threat.
In some ways, the United States has failed to learn from the mistakes of the past.
There are many similarities between the two pandemics. In the spring of 1918, when the first wave of influenza hit, the United States and its allies were nearing victory in Europe in World War I. Just this summer the United States has ended its longest war, the conflict in Afghanistan, as COVID cases surge.
In both pandemics, hospitals and funeral homes were overrun and makeshift clinics were opened where space was available. Mask mandates were installed; schools, churches, and theaters closed; and social distancing was encouraged.
As is the case today, different jurisdictions took different steps to fight the pandemic and some were more successful than others.
According to History.com, in 1918, Philadelphia’s mayor said a popular annual parade could be held, and an estimated 200,000 people attended. In less than 2 weeks, more than 1,000 local residents were dead. But in St. Louis, public gatherings were banned, schools and theaters closed, and the death toll there was one eighth of Philadelphia’s.
Just as in 1918, America has at times continued to fan the flames of the epidemic by relaxing restrictions too quickly and relying on unproven treatments. Poor communication allowed younger people to feel that they wouldn’t necessarily face the worst consequences of the virus, contributing to a false sense of security in the age group that was fueling the spread.
“A lot of the mistakes that we definitely fell into in 1918, we hoped we wouldn’t fall into in 2020,” epidemiologist Stephen Kissler, PhD, of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, told CNN. “We did.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University.
Although the raw numbers match, epidemiologists point out that 675,000 deaths in 1918 was a much greater proportion of the population. In 1918, the U.S. population was 105 million, less than one third of what it is today.
The AIDS pandemic of the 1980s remains the deadliest of the 20th Century, claiming the lives of 700,000 Americans. But at our current pace of 2,000 COVID deaths a day, we could quickly eclipse that death toll, too.
Even though the 1918 epidemic is often called the “Spanish Flu,” there is no universal consensus regarding where the virus originated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Still, the almost incomprehensible loss harkens back to a time when medicine and technology were far less advanced than they are today.
In 1918, the United States didn’t have access to a vaccine, or near real-time tools to trace the spread and communicate the threat.
In some ways, the United States has failed to learn from the mistakes of the past.
There are many similarities between the two pandemics. In the spring of 1918, when the first wave of influenza hit, the United States and its allies were nearing victory in Europe in World War I. Just this summer the United States has ended its longest war, the conflict in Afghanistan, as COVID cases surge.
In both pandemics, hospitals and funeral homes were overrun and makeshift clinics were opened where space was available. Mask mandates were installed; schools, churches, and theaters closed; and social distancing was encouraged.
As is the case today, different jurisdictions took different steps to fight the pandemic and some were more successful than others.
According to History.com, in 1918, Philadelphia’s mayor said a popular annual parade could be held, and an estimated 200,000 people attended. In less than 2 weeks, more than 1,000 local residents were dead. But in St. Louis, public gatherings were banned, schools and theaters closed, and the death toll there was one eighth of Philadelphia’s.
Just as in 1918, America has at times continued to fan the flames of the epidemic by relaxing restrictions too quickly and relying on unproven treatments. Poor communication allowed younger people to feel that they wouldn’t necessarily face the worst consequences of the virus, contributing to a false sense of security in the age group that was fueling the spread.
“A lot of the mistakes that we definitely fell into in 1918, we hoped we wouldn’t fall into in 2020,” epidemiologist Stephen Kissler, PhD, of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, told CNN. “We did.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University.
Although the raw numbers match, epidemiologists point out that 675,000 deaths in 1918 was a much greater proportion of the population. In 1918, the U.S. population was 105 million, less than one third of what it is today.
The AIDS pandemic of the 1980s remains the deadliest of the 20th Century, claiming the lives of 700,000 Americans. But at our current pace of 2,000 COVID deaths a day, we could quickly eclipse that death toll, too.
Even though the 1918 epidemic is often called the “Spanish Flu,” there is no universal consensus regarding where the virus originated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Still, the almost incomprehensible loss harkens back to a time when medicine and technology were far less advanced than they are today.
In 1918, the United States didn’t have access to a vaccine, or near real-time tools to trace the spread and communicate the threat.
In some ways, the United States has failed to learn from the mistakes of the past.
There are many similarities between the two pandemics. In the spring of 1918, when the first wave of influenza hit, the United States and its allies were nearing victory in Europe in World War I. Just this summer the United States has ended its longest war, the conflict in Afghanistan, as COVID cases surge.
In both pandemics, hospitals and funeral homes were overrun and makeshift clinics were opened where space was available. Mask mandates were installed; schools, churches, and theaters closed; and social distancing was encouraged.
As is the case today, different jurisdictions took different steps to fight the pandemic and some were more successful than others.
According to History.com, in 1918, Philadelphia’s mayor said a popular annual parade could be held, and an estimated 200,000 people attended. In less than 2 weeks, more than 1,000 local residents were dead. But in St. Louis, public gatherings were banned, schools and theaters closed, and the death toll there was one eighth of Philadelphia’s.
Just as in 1918, America has at times continued to fan the flames of the epidemic by relaxing restrictions too quickly and relying on unproven treatments. Poor communication allowed younger people to feel that they wouldn’t necessarily face the worst consequences of the virus, contributing to a false sense of security in the age group that was fueling the spread.
“A lot of the mistakes that we definitely fell into in 1918, we hoped we wouldn’t fall into in 2020,” epidemiologist Stephen Kissler, PhD, of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, told CNN. “We did.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HPV vaccine safety concerns up 80% from 2015 to 2018
Despite a decrease in reported adverse events after receiving the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, among parents of unvaccinated adolescents, concerns about the vaccine’s safety rose 80% from 2015 to 2018, according to research published September 17 in JAMA Network Open.
Since its approval in 2006 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, uptake of the HPV vaccine has consistently lagged behind that of other routine vaccinations. According to the most recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, released September 3, 58.6% of adolescents were considered up to date with their HPV vaccinations in 2020.
Trials prior to the vaccine’s FDA approval as well as an abundance of clinical and observational evidence after it hit the market demonstrate the vaccine’s efficacy and safety, said lead author Kalyani Sonawane, PhD, an assistant professor of management, policy, and community health at the UTHealth School of Public Health, in Houston, Texas, in an interview. Still, recent research suggests that safety concerns are a main reason why parents are hesitant to have their children vaccinated, she noted.
In the study, Dr. Sonawane and colleagues analyzed data from National Immunization Survey-Teen (NIS-Teen) from 2015 through 2018. NIS-Teen is a random-digit-dialed telephone survey conducted annually by the CDC to monitor routine vaccination coverage among adolescents aged 13 to 17. The researchers identified 39,364 adolescents who had not received any HPV shots and reviewed the caregivers’ reasons for vaccine hesitancy. The research team also reviewed the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). They identified 16,621 reports that listed the HPV vaccine from 2015 through 2018.
The top five reasons caregivers cited for avoiding the HPV vaccine were the following:
- not needed or necessary
- safety concerns
- not recommended
- lack of knowledge
- not sexually active
Of these, safety concerns were the only factor that increased during the study period. They increased from 13.0% in 2015 to 23.4% in 2018. Concerns over vaccine safety rose in 30 states, with increases of over 200% in California, Hawaii, South Dakota, and Mississippi.
The proportion of unvaccinated adolescents whose caregivers thought the HPV vaccine was not needed or necessary remained steady at around 25%. Those whose caregivers listed “not recommended,” “lack of knowledge,” and “not sexually active” as reasons for avoiding vaccination decreased over the study period.
The reporting rate for adverse events following HPV vaccination decreased from 44.7 per 100,000 doses in 2015 to 29.4 per 100,000 doses in 2018. Of the reported 16,621 adverse events following HPV vaccination that occurred over the study period, 4.6% were serious, resulting in hospitalizations, disability, life-threatening events, or death. From 2015 through 2018, reporting rates for serious adverse events remained level at around 0.3 events per 100,000 doses.
This mismatch between increasing vaccine safety concerns and decreasing adverse events suggests that disinformation may be driving these concerns more than scientific fact, Nosayaba Osazuwa-Peters, PhD, MPH, an assistant professor in head and neck surgery and communication sciences at the Duke University School of Medicine, in Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization. He co-wrote an invited commentary on the study and was not involved with the research. Although there have always been people who are hesitant to receive vaccinations, he said, social media and the internet have undoubtedly played a role in spreading concern.
Dr. Sonawane agreed. Online, “there are a lot of antivaccine groups that are making unwarranted claims about the vaccine’s safety,” such as that the HPV vaccine causes autism or fertility problems in women, she said. “We believe that this growing antivaccine movement in the U.S. and across the globe – which the World Health Organization has declared as one of the biggest threats right now – is also contributing to safety concerns among U.S. parents, particularly HPV vaccine safety.”
Although the study did not address strategies to combat this misinformation, Dr. Osazuwa-Peters said clinicians need to improve their communication with parents and patients. One way to do that, he said, is by bolstering an online presence and by countering vaccine disinformation with evidence-based responses on the internet. Most people get their medical information online. “Many people are just afraid because they don’t trust the messages coming from health care,” he said. “So, we need to a better job of not just providing the facts but providing the facts in a way that the end users can understand and appreciate.”
Dr. Sonawane and Dr. Osazuwa-Peters report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite a decrease in reported adverse events after receiving the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, among parents of unvaccinated adolescents, concerns about the vaccine’s safety rose 80% from 2015 to 2018, according to research published September 17 in JAMA Network Open.
Since its approval in 2006 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, uptake of the HPV vaccine has consistently lagged behind that of other routine vaccinations. According to the most recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, released September 3, 58.6% of adolescents were considered up to date with their HPV vaccinations in 2020.
Trials prior to the vaccine’s FDA approval as well as an abundance of clinical and observational evidence after it hit the market demonstrate the vaccine’s efficacy and safety, said lead author Kalyani Sonawane, PhD, an assistant professor of management, policy, and community health at the UTHealth School of Public Health, in Houston, Texas, in an interview. Still, recent research suggests that safety concerns are a main reason why parents are hesitant to have their children vaccinated, she noted.
In the study, Dr. Sonawane and colleagues analyzed data from National Immunization Survey-Teen (NIS-Teen) from 2015 through 2018. NIS-Teen is a random-digit-dialed telephone survey conducted annually by the CDC to monitor routine vaccination coverage among adolescents aged 13 to 17. The researchers identified 39,364 adolescents who had not received any HPV shots and reviewed the caregivers’ reasons for vaccine hesitancy. The research team also reviewed the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). They identified 16,621 reports that listed the HPV vaccine from 2015 through 2018.
The top five reasons caregivers cited for avoiding the HPV vaccine were the following:
- not needed or necessary
- safety concerns
- not recommended
- lack of knowledge
- not sexually active
Of these, safety concerns were the only factor that increased during the study period. They increased from 13.0% in 2015 to 23.4% in 2018. Concerns over vaccine safety rose in 30 states, with increases of over 200% in California, Hawaii, South Dakota, and Mississippi.
The proportion of unvaccinated adolescents whose caregivers thought the HPV vaccine was not needed or necessary remained steady at around 25%. Those whose caregivers listed “not recommended,” “lack of knowledge,” and “not sexually active” as reasons for avoiding vaccination decreased over the study period.
The reporting rate for adverse events following HPV vaccination decreased from 44.7 per 100,000 doses in 2015 to 29.4 per 100,000 doses in 2018. Of the reported 16,621 adverse events following HPV vaccination that occurred over the study period, 4.6% were serious, resulting in hospitalizations, disability, life-threatening events, or death. From 2015 through 2018, reporting rates for serious adverse events remained level at around 0.3 events per 100,000 doses.
This mismatch between increasing vaccine safety concerns and decreasing adverse events suggests that disinformation may be driving these concerns more than scientific fact, Nosayaba Osazuwa-Peters, PhD, MPH, an assistant professor in head and neck surgery and communication sciences at the Duke University School of Medicine, in Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization. He co-wrote an invited commentary on the study and was not involved with the research. Although there have always been people who are hesitant to receive vaccinations, he said, social media and the internet have undoubtedly played a role in spreading concern.
Dr. Sonawane agreed. Online, “there are a lot of antivaccine groups that are making unwarranted claims about the vaccine’s safety,” such as that the HPV vaccine causes autism or fertility problems in women, she said. “We believe that this growing antivaccine movement in the U.S. and across the globe – which the World Health Organization has declared as one of the biggest threats right now – is also contributing to safety concerns among U.S. parents, particularly HPV vaccine safety.”
Although the study did not address strategies to combat this misinformation, Dr. Osazuwa-Peters said clinicians need to improve their communication with parents and patients. One way to do that, he said, is by bolstering an online presence and by countering vaccine disinformation with evidence-based responses on the internet. Most people get their medical information online. “Many people are just afraid because they don’t trust the messages coming from health care,” he said. “So, we need to a better job of not just providing the facts but providing the facts in a way that the end users can understand and appreciate.”
Dr. Sonawane and Dr. Osazuwa-Peters report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite a decrease in reported adverse events after receiving the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, among parents of unvaccinated adolescents, concerns about the vaccine’s safety rose 80% from 2015 to 2018, according to research published September 17 in JAMA Network Open.
Since its approval in 2006 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, uptake of the HPV vaccine has consistently lagged behind that of other routine vaccinations. According to the most recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, released September 3, 58.6% of adolescents were considered up to date with their HPV vaccinations in 2020.
Trials prior to the vaccine’s FDA approval as well as an abundance of clinical and observational evidence after it hit the market demonstrate the vaccine’s efficacy and safety, said lead author Kalyani Sonawane, PhD, an assistant professor of management, policy, and community health at the UTHealth School of Public Health, in Houston, Texas, in an interview. Still, recent research suggests that safety concerns are a main reason why parents are hesitant to have their children vaccinated, she noted.
In the study, Dr. Sonawane and colleagues analyzed data from National Immunization Survey-Teen (NIS-Teen) from 2015 through 2018. NIS-Teen is a random-digit-dialed telephone survey conducted annually by the CDC to monitor routine vaccination coverage among adolescents aged 13 to 17. The researchers identified 39,364 adolescents who had not received any HPV shots and reviewed the caregivers’ reasons for vaccine hesitancy. The research team also reviewed the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). They identified 16,621 reports that listed the HPV vaccine from 2015 through 2018.
The top five reasons caregivers cited for avoiding the HPV vaccine were the following:
- not needed or necessary
- safety concerns
- not recommended
- lack of knowledge
- not sexually active
Of these, safety concerns were the only factor that increased during the study period. They increased from 13.0% in 2015 to 23.4% in 2018. Concerns over vaccine safety rose in 30 states, with increases of over 200% in California, Hawaii, South Dakota, and Mississippi.
The proportion of unvaccinated adolescents whose caregivers thought the HPV vaccine was not needed or necessary remained steady at around 25%. Those whose caregivers listed “not recommended,” “lack of knowledge,” and “not sexually active” as reasons for avoiding vaccination decreased over the study period.
The reporting rate for adverse events following HPV vaccination decreased from 44.7 per 100,000 doses in 2015 to 29.4 per 100,000 doses in 2018. Of the reported 16,621 adverse events following HPV vaccination that occurred over the study period, 4.6% were serious, resulting in hospitalizations, disability, life-threatening events, or death. From 2015 through 2018, reporting rates for serious adverse events remained level at around 0.3 events per 100,000 doses.
This mismatch between increasing vaccine safety concerns and decreasing adverse events suggests that disinformation may be driving these concerns more than scientific fact, Nosayaba Osazuwa-Peters, PhD, MPH, an assistant professor in head and neck surgery and communication sciences at the Duke University School of Medicine, in Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization. He co-wrote an invited commentary on the study and was not involved with the research. Although there have always been people who are hesitant to receive vaccinations, he said, social media and the internet have undoubtedly played a role in spreading concern.
Dr. Sonawane agreed. Online, “there are a lot of antivaccine groups that are making unwarranted claims about the vaccine’s safety,” such as that the HPV vaccine causes autism or fertility problems in women, she said. “We believe that this growing antivaccine movement in the U.S. and across the globe – which the World Health Organization has declared as one of the biggest threats right now – is also contributing to safety concerns among U.S. parents, particularly HPV vaccine safety.”
Although the study did not address strategies to combat this misinformation, Dr. Osazuwa-Peters said clinicians need to improve their communication with parents and patients. One way to do that, he said, is by bolstering an online presence and by countering vaccine disinformation with evidence-based responses on the internet. Most people get their medical information online. “Many people are just afraid because they don’t trust the messages coming from health care,” he said. “So, we need to a better job of not just providing the facts but providing the facts in a way that the end users can understand and appreciate.”
Dr. Sonawane and Dr. Osazuwa-Peters report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

