User login
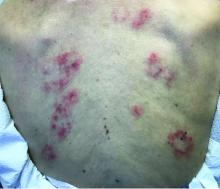
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) is a type of cutaneous lupus erythematosus that may occur independently of or in combination with systemic lupus erythematosus. About 10%-15% of patients with SCLE will develop systemic lupus erythematosus. White females are more typically affected.
SCLE lesions often present as scaly, annular, or polycyclic scaly patches and plaques with central clearing. They may appear psoriasiform. They heal without atrophy or scarring but may leave dyspigmentation. Follicular plugging is absent. Lesions generally occur on sun exposed areas such as the neck, V of the chest, and upper extremities. Up to 75% of patients may exhibit associated symptoms such as photosensitivity, oral ulcers, and arthritis. Less than 20% of patients will develop internal disease, including nephritis and pulmonary disease. Symptoms of Sjögren’s syndrome and SCLE may overlap in some patients, and will portend higher risk for internal disease.
The differential diagnosis includes eczema, psoriasis, dermatophytosis, granuloma annulare, and erythema annulare centrifugum. Histology reveals epidermal atrophy and keratinocyte apoptosis, with a superficial and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the upper dermis. Interface changes at the dermal-epidermal junction can be seen. Direct immunofluorescence of lesional skin is positive in one-third of cases, often revealing granular deposits of IgG and IgM at the dermal-epidermal junction and around hair follicles (called the lupus-band test). Serology in SCLE may reveal a positive antinuclear antigen test, as well as positive Ro/SSA antigen. Other lupus serologies such as La/SSB, dsDNA, antihistone, and Sm antibodies may be positive, but are less commonly seen.
Several drugs may cause SCLE, such as hydrochlorothiazide, terbinafine, ACE inhibitors, NSAIDs, calcium-channel blockers, interferons, anticonvulsants, griseofulvin, penicillamine, spironolactone, tumor necrosis factor–alpha inhibitors, and statins. Discontinuing the offending medications may clear the lesions, but not always.
Treatment includes sunscreen and avoidance of sun exposure. Potent topical corticosteroids are helpful. If systemic treatment is indicated, antimalarials are first line.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
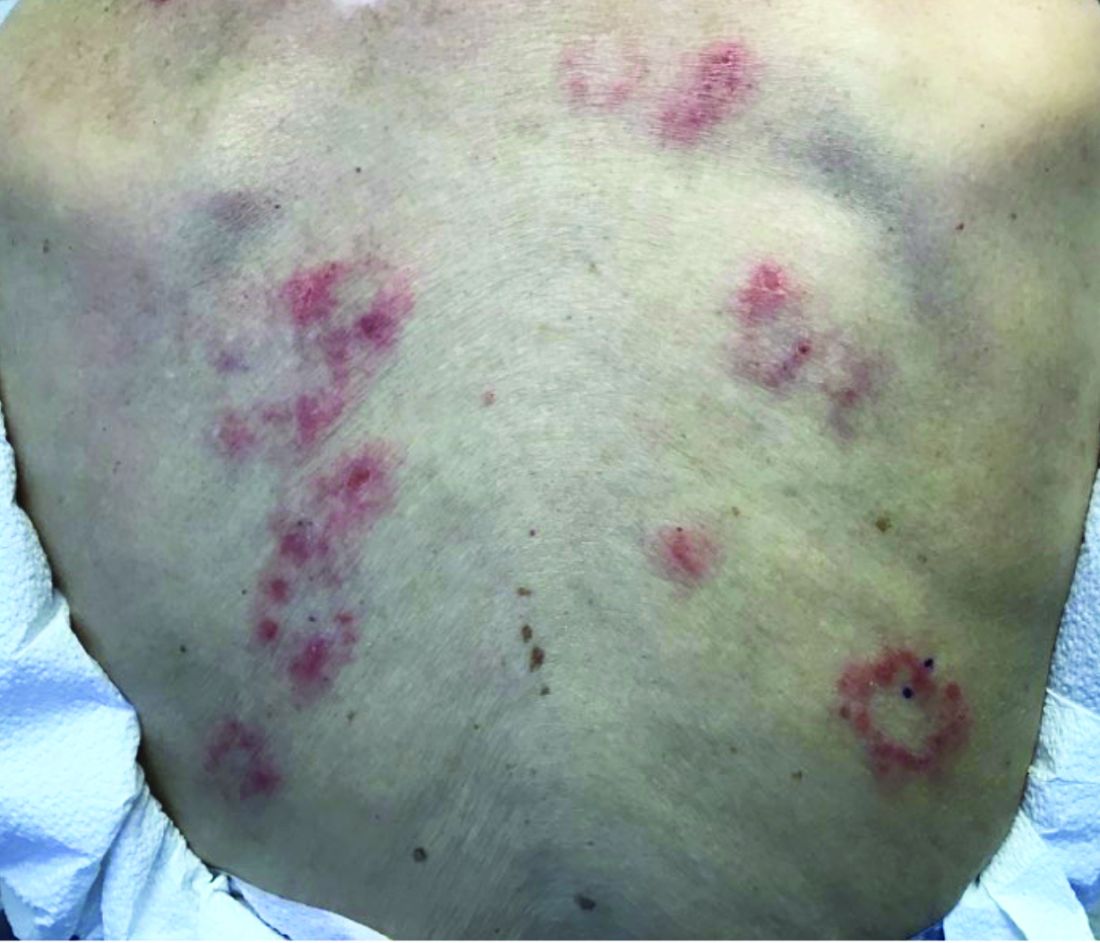
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) is a type of cutaneous lupus erythematosus that may occur independently of or in combination with systemic lupus erythematosus. About 10%-15% of patients with SCLE will develop systemic lupus erythematosus. White females are more typically affected.
SCLE lesions often present as scaly, annular, or polycyclic scaly patches and plaques with central clearing. They may appear psoriasiform. They heal without atrophy or scarring but may leave dyspigmentation. Follicular plugging is absent. Lesions generally occur on sun exposed areas such as the neck, V of the chest, and upper extremities. Up to 75% of patients may exhibit associated symptoms such as photosensitivity, oral ulcers, and arthritis. Less than 20% of patients will develop internal disease, including nephritis and pulmonary disease. Symptoms of Sjögren’s syndrome and SCLE may overlap in some patients, and will portend higher risk for internal disease.
The differential diagnosis includes eczema, psoriasis, dermatophytosis, granuloma annulare, and erythema annulare centrifugum. Histology reveals epidermal atrophy and keratinocyte apoptosis, with a superficial and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the upper dermis. Interface changes at the dermal-epidermal junction can be seen. Direct immunofluorescence of lesional skin is positive in one-third of cases, often revealing granular deposits of IgG and IgM at the dermal-epidermal junction and around hair follicles (called the lupus-band test). Serology in SCLE may reveal a positive antinuclear antigen test, as well as positive Ro/SSA antigen. Other lupus serologies such as La/SSB, dsDNA, antihistone, and Sm antibodies may be positive, but are less commonly seen.
Several drugs may cause SCLE, such as hydrochlorothiazide, terbinafine, ACE inhibitors, NSAIDs, calcium-channel blockers, interferons, anticonvulsants, griseofulvin, penicillamine, spironolactone, tumor necrosis factor–alpha inhibitors, and statins. Discontinuing the offending medications may clear the lesions, but not always.
Treatment includes sunscreen and avoidance of sun exposure. Potent topical corticosteroids are helpful. If systemic treatment is indicated, antimalarials are first line.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) is a type of cutaneous lupus erythematosus that may occur independently of or in combination with systemic lupus erythematosus. About 10%-15% of patients with SCLE will develop systemic lupus erythematosus. White females are more typically affected.
SCLE lesions often present as scaly, annular, or polycyclic scaly patches and plaques with central clearing. They may appear psoriasiform. They heal without atrophy or scarring but may leave dyspigmentation. Follicular plugging is absent. Lesions generally occur on sun exposed areas such as the neck, V of the chest, and upper extremities. Up to 75% of patients may exhibit associated symptoms such as photosensitivity, oral ulcers, and arthritis. Less than 20% of patients will develop internal disease, including nephritis and pulmonary disease. Symptoms of Sjögren’s syndrome and SCLE may overlap in some patients, and will portend higher risk for internal disease.
The differential diagnosis includes eczema, psoriasis, dermatophytosis, granuloma annulare, and erythema annulare centrifugum. Histology reveals epidermal atrophy and keratinocyte apoptosis, with a superficial and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the upper dermis. Interface changes at the dermal-epidermal junction can be seen. Direct immunofluorescence of lesional skin is positive in one-third of cases, often revealing granular deposits of IgG and IgM at the dermal-epidermal junction and around hair follicles (called the lupus-band test). Serology in SCLE may reveal a positive antinuclear antigen test, as well as positive Ro/SSA antigen. Other lupus serologies such as La/SSB, dsDNA, antihistone, and Sm antibodies may be positive, but are less commonly seen.
Several drugs may cause SCLE, such as hydrochlorothiazide, terbinafine, ACE inhibitors, NSAIDs, calcium-channel blockers, interferons, anticonvulsants, griseofulvin, penicillamine, spironolactone, tumor necrosis factor–alpha inhibitors, and statins. Discontinuing the offending medications may clear the lesions, but not always.
Treatment includes sunscreen and avoidance of sun exposure. Potent topical corticosteroids are helpful. If systemic treatment is indicated, antimalarials are first line.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].