User login
Patients’ Out-of-Pocket Spending Increasing
Clinical Question: How much are insured nonelderly adult patients paying out of pocket for inpatient care, and does that amount vary over time or by patient characteristics, region, or type of insurance?
Background: Prior estimates have been based on patient-reported survey data. This is the first study to find nationwide out-of-pocket expenditure for inpatient hospitalizations.
Study Design: Retrospective analysis.
Setting: Medical claims data from Aetna, UnitedHealthcare, and Humana including 7.3 million hospitalizations from 2009 to 2013.
Synopsis: Authors used the Health Care Cost Institute (HCCI) database and studied inpatient hospitalization for ages 18–64. The adjusted total cost sharing per inpatient hospitalization increased by 37% (from $738 in 2009 to $1,013 in 2013). Both the mean amount of coinsurance and deductibles increased during this period by 33% (from $518 to $688) and 86% (from $145 to $270), respectively. The mean copayment decreased by 27% (from $75 to $55).
Increase in cost sharing was lowest in individual-market and consumer-directed health plans, although both had highest cost sharing.
Total cost sharing increased in every state. The largest increases were seen in Georgia, Louisiana, and Colorado. In 2013, the states with the highest cost sharing were Utah, Alaska, and Oregon.
Acute myocardial infarction and acute appendicitis saw maximum rise in out-of-pocket spending; both surpassed $1,500 in 2013. Cost sharing associated with procedures was lower.
Bottom Line: Even after adjusting for inflation and case-mix differences, the total cost sharing per inpatient hospitalization increased between 2009 and 2013. Policymakers and patients need to pay attention to these trends.
Citation: Adrion ER, Ryan AM, Seltzer AC, Chen LM, Ayanian JZ, Nallamothu BK. Out-of-pocket spending for hospitalizations among nonelderly adults. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(9)1325-1332.
Short Take
Aspirin Is Being Used Instead of Anticoagulation in Afib
Despite recommendations to anticoagulate patients with CHADS2 /CHA2DS2-VASc scores of ≥2, more than one-third of the patients in a large population of cardiology outpatients were treated with aspirin alone.
Citation: Hsu JC, Maddox TM, Kennedy K, et al. Aspirin instead of oral anticoagulant prescription in atrial fibrillation patients at risk for stroke. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(25):2913-2923.
Clinical Question: How much are insured nonelderly adult patients paying out of pocket for inpatient care, and does that amount vary over time or by patient characteristics, region, or type of insurance?
Background: Prior estimates have been based on patient-reported survey data. This is the first study to find nationwide out-of-pocket expenditure for inpatient hospitalizations.
Study Design: Retrospective analysis.
Setting: Medical claims data from Aetna, UnitedHealthcare, and Humana including 7.3 million hospitalizations from 2009 to 2013.
Synopsis: Authors used the Health Care Cost Institute (HCCI) database and studied inpatient hospitalization for ages 18–64. The adjusted total cost sharing per inpatient hospitalization increased by 37% (from $738 in 2009 to $1,013 in 2013). Both the mean amount of coinsurance and deductibles increased during this period by 33% (from $518 to $688) and 86% (from $145 to $270), respectively. The mean copayment decreased by 27% (from $75 to $55).
Increase in cost sharing was lowest in individual-market and consumer-directed health plans, although both had highest cost sharing.
Total cost sharing increased in every state. The largest increases were seen in Georgia, Louisiana, and Colorado. In 2013, the states with the highest cost sharing were Utah, Alaska, and Oregon.
Acute myocardial infarction and acute appendicitis saw maximum rise in out-of-pocket spending; both surpassed $1,500 in 2013. Cost sharing associated with procedures was lower.
Bottom Line: Even after adjusting for inflation and case-mix differences, the total cost sharing per inpatient hospitalization increased between 2009 and 2013. Policymakers and patients need to pay attention to these trends.
Citation: Adrion ER, Ryan AM, Seltzer AC, Chen LM, Ayanian JZ, Nallamothu BK. Out-of-pocket spending for hospitalizations among nonelderly adults. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(9)1325-1332.
Short Take
Aspirin Is Being Used Instead of Anticoagulation in Afib
Despite recommendations to anticoagulate patients with CHADS2 /CHA2DS2-VASc scores of ≥2, more than one-third of the patients in a large population of cardiology outpatients were treated with aspirin alone.
Citation: Hsu JC, Maddox TM, Kennedy K, et al. Aspirin instead of oral anticoagulant prescription in atrial fibrillation patients at risk for stroke. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(25):2913-2923.
Clinical Question: How much are insured nonelderly adult patients paying out of pocket for inpatient care, and does that amount vary over time or by patient characteristics, region, or type of insurance?
Background: Prior estimates have been based on patient-reported survey data. This is the first study to find nationwide out-of-pocket expenditure for inpatient hospitalizations.
Study Design: Retrospective analysis.
Setting: Medical claims data from Aetna, UnitedHealthcare, and Humana including 7.3 million hospitalizations from 2009 to 2013.
Synopsis: Authors used the Health Care Cost Institute (HCCI) database and studied inpatient hospitalization for ages 18–64. The adjusted total cost sharing per inpatient hospitalization increased by 37% (from $738 in 2009 to $1,013 in 2013). Both the mean amount of coinsurance and deductibles increased during this period by 33% (from $518 to $688) and 86% (from $145 to $270), respectively. The mean copayment decreased by 27% (from $75 to $55).
Increase in cost sharing was lowest in individual-market and consumer-directed health plans, although both had highest cost sharing.
Total cost sharing increased in every state. The largest increases were seen in Georgia, Louisiana, and Colorado. In 2013, the states with the highest cost sharing were Utah, Alaska, and Oregon.
Acute myocardial infarction and acute appendicitis saw maximum rise in out-of-pocket spending; both surpassed $1,500 in 2013. Cost sharing associated with procedures was lower.
Bottom Line: Even after adjusting for inflation and case-mix differences, the total cost sharing per inpatient hospitalization increased between 2009 and 2013. Policymakers and patients need to pay attention to these trends.
Citation: Adrion ER, Ryan AM, Seltzer AC, Chen LM, Ayanian JZ, Nallamothu BK. Out-of-pocket spending for hospitalizations among nonelderly adults. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(9)1325-1332.
Short Take
Aspirin Is Being Used Instead of Anticoagulation in Afib
Despite recommendations to anticoagulate patients with CHADS2 /CHA2DS2-VASc scores of ≥2, more than one-third of the patients in a large population of cardiology outpatients were treated with aspirin alone.
Citation: Hsu JC, Maddox TM, Kennedy K, et al. Aspirin instead of oral anticoagulant prescription in atrial fibrillation patients at risk for stroke. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(25):2913-2923.
What Hospitalists Can Really Learn from Aviation
The aviation safety model is often discussed in a healthcare context but in a way that may miss the most important points, a new article in BMJ Quality & Safety suggests.
The article, “Learning from Near Misses in Aviation: So Much More to It Than You Thought” by Robert Wears, MD, PhD, MS, of University of Florida’s Department of Emergency Medicine, suggests healthcare still has important lessons to learn from aviation. The article focuses on a book called Close Calls: Managing Risk and Resilience in Airline Flight Safety by Carl Macrae.
“Although the book itself is about airlines, it has important lessons for improving safety in healthcare, especially with respect to management of incidents or ‘near misses,’” Dr. Wears writes. “Its rich descriptions and detailed explanation of the practical, everyday work of flight safety investigators should be required reading for anyone interested in patient safety. It will destroy many of the myths and misconceptions about reporting systems and learning from incidents that have caused us to expend so much effort for such meager results; it will also overturn the normative model of safety prevalent in healthcare.”
Dr. Wears says he wanted to write the article for two reasons.
“First, the patient safety orthodoxy has been obsessed with systems for reporting incidents, accidents, hazards, general ‘hiccups’ in clinical work for years, but almost nothing of value has come from this effort despite frequent badgering of physicians to report more,” he says. “Second, mainstream patient safety has also been enamored of the aviation safety model, but its ideas about how aviation safety is actually accomplished are naive and simplistic.”
He emphasizes that patient safety efforts to date have focused on the wrong things: too much on acquiring and storing reports and too little on analyzing them to develop an understanding of the systems in which hazards to patients arise.
“Making sense of incidents is far more important than classifying, counting, or trending them,” Dr. Wears says.
Hospitalists are on the front line of these issues, of course.
“Hospitalists regularly encounter hazards to patients in their daily work and, for the most part, successfully manage to mitigate or work around them, but the hazards remain in the system, only to pop up again sometime later. … A rich description of how a successful and effective safety reporting and analysis effort really works—not how we imagine it to work—could help us exchange our current wasteful and ineffective approach for something better,” he says.
Reference
- Wears R. Learning from near misses in aviation: so much more to it than you thought [published online ahead of print September 1, 2016]. BMJ Qual Saf. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2016-005990.
The aviation safety model is often discussed in a healthcare context but in a way that may miss the most important points, a new article in BMJ Quality & Safety suggests.
The article, “Learning from Near Misses in Aviation: So Much More to It Than You Thought” by Robert Wears, MD, PhD, MS, of University of Florida’s Department of Emergency Medicine, suggests healthcare still has important lessons to learn from aviation. The article focuses on a book called Close Calls: Managing Risk and Resilience in Airline Flight Safety by Carl Macrae.
“Although the book itself is about airlines, it has important lessons for improving safety in healthcare, especially with respect to management of incidents or ‘near misses,’” Dr. Wears writes. “Its rich descriptions and detailed explanation of the practical, everyday work of flight safety investigators should be required reading for anyone interested in patient safety. It will destroy many of the myths and misconceptions about reporting systems and learning from incidents that have caused us to expend so much effort for such meager results; it will also overturn the normative model of safety prevalent in healthcare.”
Dr. Wears says he wanted to write the article for two reasons.
“First, the patient safety orthodoxy has been obsessed with systems for reporting incidents, accidents, hazards, general ‘hiccups’ in clinical work for years, but almost nothing of value has come from this effort despite frequent badgering of physicians to report more,” he says. “Second, mainstream patient safety has also been enamored of the aviation safety model, but its ideas about how aviation safety is actually accomplished are naive and simplistic.”
He emphasizes that patient safety efforts to date have focused on the wrong things: too much on acquiring and storing reports and too little on analyzing them to develop an understanding of the systems in which hazards to patients arise.
“Making sense of incidents is far more important than classifying, counting, or trending them,” Dr. Wears says.
Hospitalists are on the front line of these issues, of course.
“Hospitalists regularly encounter hazards to patients in their daily work and, for the most part, successfully manage to mitigate or work around them, but the hazards remain in the system, only to pop up again sometime later. … A rich description of how a successful and effective safety reporting and analysis effort really works—not how we imagine it to work—could help us exchange our current wasteful and ineffective approach for something better,” he says.
Reference
- Wears R. Learning from near misses in aviation: so much more to it than you thought [published online ahead of print September 1, 2016]. BMJ Qual Saf. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2016-005990.
The aviation safety model is often discussed in a healthcare context but in a way that may miss the most important points, a new article in BMJ Quality & Safety suggests.
The article, “Learning from Near Misses in Aviation: So Much More to It Than You Thought” by Robert Wears, MD, PhD, MS, of University of Florida’s Department of Emergency Medicine, suggests healthcare still has important lessons to learn from aviation. The article focuses on a book called Close Calls: Managing Risk and Resilience in Airline Flight Safety by Carl Macrae.
“Although the book itself is about airlines, it has important lessons for improving safety in healthcare, especially with respect to management of incidents or ‘near misses,’” Dr. Wears writes. “Its rich descriptions and detailed explanation of the practical, everyday work of flight safety investigators should be required reading for anyone interested in patient safety. It will destroy many of the myths and misconceptions about reporting systems and learning from incidents that have caused us to expend so much effort for such meager results; it will also overturn the normative model of safety prevalent in healthcare.”
Dr. Wears says he wanted to write the article for two reasons.
“First, the patient safety orthodoxy has been obsessed with systems for reporting incidents, accidents, hazards, general ‘hiccups’ in clinical work for years, but almost nothing of value has come from this effort despite frequent badgering of physicians to report more,” he says. “Second, mainstream patient safety has also been enamored of the aviation safety model, but its ideas about how aviation safety is actually accomplished are naive and simplistic.”
He emphasizes that patient safety efforts to date have focused on the wrong things: too much on acquiring and storing reports and too little on analyzing them to develop an understanding of the systems in which hazards to patients arise.
“Making sense of incidents is far more important than classifying, counting, or trending them,” Dr. Wears says.
Hospitalists are on the front line of these issues, of course.
“Hospitalists regularly encounter hazards to patients in their daily work and, for the most part, successfully manage to mitigate or work around them, but the hazards remain in the system, only to pop up again sometime later. … A rich description of how a successful and effective safety reporting and analysis effort really works—not how we imagine it to work—could help us exchange our current wasteful and ineffective approach for something better,” he says.
Reference
- Wears R. Learning from near misses in aviation: so much more to it than you thought [published online ahead of print September 1, 2016]. BMJ Qual Saf. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2016-005990.
Educating Patients about Sleep Tools
One of the biggest complaints of hospital patients today is poor sleep, which is not conducive to healing or good health in general.
“The reason I’m interested, as a cardiologist, is that sleep disorders are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality,” says Peter M. Farrehi, MD, assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Michigan and lead author of a recent sleep study published in The American Journal of Medicine.
Most information about sleeping in the hospital comes from ICU studies, he says.
Dr. Farrehi wanted to actually test an intervention rather than simply survey patients. All patients received an eye mask, ear plugs, and a white-noise machine, then were randomized to receive an education-based script on the importance of using these sleep-enhancing tools or a discussion about the general benefits of sleep.
“To avoid bias in the study both from the research staff and also hospital staff, I didn't want only the intervention to have the tools,” he says. “This was a double-blind, randomized control trial in the hospital, which is really unusual.”
Patients in the group that was taught about the sleep-enhancing tools had a statistically significant difference in their perceptions of fatigue and a trend toward improving their sleep and wake disturbances.
Dr. Farrehi suggests hospitalists talk to their patients complaining of poor sleep about these sleep tools. If they are not available in their hospital, hospitalists might refer their medical director to this paper to see if there is any interest in purchasing these sleep tools.
Reference
- 1. Farrehi PM, Clore KR, Scott JR, Vanini G, Clauw DJ. Efficacy of sleep tool education during hospitalization: a randomized controlled trial [published online ahead of print August 23, 2016]. Am J Med. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.08.001.
One of the biggest complaints of hospital patients today is poor sleep, which is not conducive to healing or good health in general.
“The reason I’m interested, as a cardiologist, is that sleep disorders are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality,” says Peter M. Farrehi, MD, assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Michigan and lead author of a recent sleep study published in The American Journal of Medicine.
Most information about sleeping in the hospital comes from ICU studies, he says.
Dr. Farrehi wanted to actually test an intervention rather than simply survey patients. All patients received an eye mask, ear plugs, and a white-noise machine, then were randomized to receive an education-based script on the importance of using these sleep-enhancing tools or a discussion about the general benefits of sleep.
“To avoid bias in the study both from the research staff and also hospital staff, I didn't want only the intervention to have the tools,” he says. “This was a double-blind, randomized control trial in the hospital, which is really unusual.”
Patients in the group that was taught about the sleep-enhancing tools had a statistically significant difference in their perceptions of fatigue and a trend toward improving their sleep and wake disturbances.
Dr. Farrehi suggests hospitalists talk to their patients complaining of poor sleep about these sleep tools. If they are not available in their hospital, hospitalists might refer their medical director to this paper to see if there is any interest in purchasing these sleep tools.
Reference
- 1. Farrehi PM, Clore KR, Scott JR, Vanini G, Clauw DJ. Efficacy of sleep tool education during hospitalization: a randomized controlled trial [published online ahead of print August 23, 2016]. Am J Med. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.08.001.
One of the biggest complaints of hospital patients today is poor sleep, which is not conducive to healing or good health in general.
“The reason I’m interested, as a cardiologist, is that sleep disorders are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality,” says Peter M. Farrehi, MD, assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Michigan and lead author of a recent sleep study published in The American Journal of Medicine.
Most information about sleeping in the hospital comes from ICU studies, he says.
Dr. Farrehi wanted to actually test an intervention rather than simply survey patients. All patients received an eye mask, ear plugs, and a white-noise machine, then were randomized to receive an education-based script on the importance of using these sleep-enhancing tools or a discussion about the general benefits of sleep.
“To avoid bias in the study both from the research staff and also hospital staff, I didn't want only the intervention to have the tools,” he says. “This was a double-blind, randomized control trial in the hospital, which is really unusual.”
Patients in the group that was taught about the sleep-enhancing tools had a statistically significant difference in their perceptions of fatigue and a trend toward improving their sleep and wake disturbances.
Dr. Farrehi suggests hospitalists talk to their patients complaining of poor sleep about these sleep tools. If they are not available in their hospital, hospitalists might refer their medical director to this paper to see if there is any interest in purchasing these sleep tools.
Reference
- 1. Farrehi PM, Clore KR, Scott JR, Vanini G, Clauw DJ. Efficacy of sleep tool education during hospitalization: a randomized controlled trial [published online ahead of print August 23, 2016]. Am J Med. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.08.001.
How to Better Connect with Patients
Editor’s note: “Everything We Say and Do” is an informational series developed by SHM’s Patient Experience Committee to provide readers with thoughtful and actionable communication tactics that have great potential to positively impact patients’ experience of care. Each article will focus on how the contributor applies one or more of the “key communication” tactics in practice to maintain provider accountability for “everything we say and do that affects our patients’ thoughts, feelings, and well-being.”
View a chart outlining key communication tactics
What I Say and Do
Before entering a patient’s room, I take a “mindful moment,” a brief mindfulness practice to boost empathy. This is a quick, simple, and effective way for me to rehab my empathy muscle.
Why I Do It
From empathy comes our desire to care about another human being, to connect with them, and to understand and be understood.
Many of the colleagues I talk to about patient experience echo the same sentiment: They feel powerless to change someone else’s experience, which is bundled with the immovable variables of their own perceptions and contexts.
While I believe there is truth to that, we can certainly change our experience, and that is what matters to patients. As my mentor and coach Anya Sophia Mann reminded me recently, “We are not responsible for the patient experience. We are responsible for our own experience, which we then bring to our patients. Your heart connection to your own empathic center is beautifully contagious and will spread to those around you throughout your day.”
How I Do It
We may think that empathy is an innate talent, but the literature supports that it is a skill like any other that can be taught, practiced, and deliberately and consciously turned up and down like the brightness on your smartphone.
A heartfelt patient experience starts with the feeling of connection to our own heart. But we can’t think our way into a feeling. If I let my head lead the way, I shield my heart from participating in true communication with the patient. We are both left without connection, without a sense of purpose, without fulfillment—empty and tired.
For the antidote, I choose to create an experience for my body to feel rather than an idea for my head to think about. Ironically, mindfulness starts not with the mind but with the body and, more precisely, with the breath.
Before entering the patient’s room, usually as I’m rubbing the hand sanitizer between my fingers, I take a deep breath that expands my belly instead of my chest, then I exhale, leaving plenty of time for the complete out breath. Next, I make the choice to be curious about the sensations in my body: “What have I carried with me from my interaction with the previous patient (or the nurse or the driver in front of me during my commute)? Does my jaw feel tight? Where do I feel stuck? Where exactly does that lump in my throat begin and end?”
The instruction here is just to notice without judgment. From that place of noticing, I have done a quick erasing of my emotional whiteboard to create space where I can respond rather than react to what is most important to my patient. I invite you to try these steps and notice what shifts happen for you and your patients. You won’t know it until you try it—and feel it—for yourself.
- Pause long enough to feel the ground supporting you under both feet.
- Take a deep, cleansing belly breath. Exhale fully without added effort.
- Notice, without judgment, the sensations in your body.
- Feel the space created by the melting and releasing of those feelings.
- Bring that feeling of space with you as you begin the conversation with the patient.
Michael Donlin, ACNP-BC, FHM, is an inpatient nurse practitioner for the Department of Medicine, VA Boston Healthcare System.
Editor’s note: “Everything We Say and Do” is an informational series developed by SHM’s Patient Experience Committee to provide readers with thoughtful and actionable communication tactics that have great potential to positively impact patients’ experience of care. Each article will focus on how the contributor applies one or more of the “key communication” tactics in practice to maintain provider accountability for “everything we say and do that affects our patients’ thoughts, feelings, and well-being.”
View a chart outlining key communication tactics
What I Say and Do
Before entering a patient’s room, I take a “mindful moment,” a brief mindfulness practice to boost empathy. This is a quick, simple, and effective way for me to rehab my empathy muscle.
Why I Do It
From empathy comes our desire to care about another human being, to connect with them, and to understand and be understood.
Many of the colleagues I talk to about patient experience echo the same sentiment: They feel powerless to change someone else’s experience, which is bundled with the immovable variables of their own perceptions and contexts.
While I believe there is truth to that, we can certainly change our experience, and that is what matters to patients. As my mentor and coach Anya Sophia Mann reminded me recently, “We are not responsible for the patient experience. We are responsible for our own experience, which we then bring to our patients. Your heart connection to your own empathic center is beautifully contagious and will spread to those around you throughout your day.”
How I Do It
We may think that empathy is an innate talent, but the literature supports that it is a skill like any other that can be taught, practiced, and deliberately and consciously turned up and down like the brightness on your smartphone.
A heartfelt patient experience starts with the feeling of connection to our own heart. But we can’t think our way into a feeling. If I let my head lead the way, I shield my heart from participating in true communication with the patient. We are both left without connection, without a sense of purpose, without fulfillment—empty and tired.
For the antidote, I choose to create an experience for my body to feel rather than an idea for my head to think about. Ironically, mindfulness starts not with the mind but with the body and, more precisely, with the breath.
Before entering the patient’s room, usually as I’m rubbing the hand sanitizer between my fingers, I take a deep breath that expands my belly instead of my chest, then I exhale, leaving plenty of time for the complete out breath. Next, I make the choice to be curious about the sensations in my body: “What have I carried with me from my interaction with the previous patient (or the nurse or the driver in front of me during my commute)? Does my jaw feel tight? Where do I feel stuck? Where exactly does that lump in my throat begin and end?”
The instruction here is just to notice without judgment. From that place of noticing, I have done a quick erasing of my emotional whiteboard to create space where I can respond rather than react to what is most important to my patient. I invite you to try these steps and notice what shifts happen for you and your patients. You won’t know it until you try it—and feel it—for yourself.
- Pause long enough to feel the ground supporting you under both feet.
- Take a deep, cleansing belly breath. Exhale fully without added effort.
- Notice, without judgment, the sensations in your body.
- Feel the space created by the melting and releasing of those feelings.
- Bring that feeling of space with you as you begin the conversation with the patient.
Michael Donlin, ACNP-BC, FHM, is an inpatient nurse practitioner for the Department of Medicine, VA Boston Healthcare System.
Editor’s note: “Everything We Say and Do” is an informational series developed by SHM’s Patient Experience Committee to provide readers with thoughtful and actionable communication tactics that have great potential to positively impact patients’ experience of care. Each article will focus on how the contributor applies one or more of the “key communication” tactics in practice to maintain provider accountability for “everything we say and do that affects our patients’ thoughts, feelings, and well-being.”
View a chart outlining key communication tactics
What I Say and Do
Before entering a patient’s room, I take a “mindful moment,” a brief mindfulness practice to boost empathy. This is a quick, simple, and effective way for me to rehab my empathy muscle.
Why I Do It
From empathy comes our desire to care about another human being, to connect with them, and to understand and be understood.
Many of the colleagues I talk to about patient experience echo the same sentiment: They feel powerless to change someone else’s experience, which is bundled with the immovable variables of their own perceptions and contexts.
While I believe there is truth to that, we can certainly change our experience, and that is what matters to patients. As my mentor and coach Anya Sophia Mann reminded me recently, “We are not responsible for the patient experience. We are responsible for our own experience, which we then bring to our patients. Your heart connection to your own empathic center is beautifully contagious and will spread to those around you throughout your day.”
How I Do It
We may think that empathy is an innate talent, but the literature supports that it is a skill like any other that can be taught, practiced, and deliberately and consciously turned up and down like the brightness on your smartphone.
A heartfelt patient experience starts with the feeling of connection to our own heart. But we can’t think our way into a feeling. If I let my head lead the way, I shield my heart from participating in true communication with the patient. We are both left without connection, without a sense of purpose, without fulfillment—empty and tired.
For the antidote, I choose to create an experience for my body to feel rather than an idea for my head to think about. Ironically, mindfulness starts not with the mind but with the body and, more precisely, with the breath.
Before entering the patient’s room, usually as I’m rubbing the hand sanitizer between my fingers, I take a deep breath that expands my belly instead of my chest, then I exhale, leaving plenty of time for the complete out breath. Next, I make the choice to be curious about the sensations in my body: “What have I carried with me from my interaction with the previous patient (or the nurse or the driver in front of me during my commute)? Does my jaw feel tight? Where do I feel stuck? Where exactly does that lump in my throat begin and end?”
The instruction here is just to notice without judgment. From that place of noticing, I have done a quick erasing of my emotional whiteboard to create space where I can respond rather than react to what is most important to my patient. I invite you to try these steps and notice what shifts happen for you and your patients. You won’t know it until you try it—and feel it—for yourself.
- Pause long enough to feel the ground supporting you under both feet.
- Take a deep, cleansing belly breath. Exhale fully without added effort.
- Notice, without judgment, the sensations in your body.
- Feel the space created by the melting and releasing of those feelings.
- Bring that feeling of space with you as you begin the conversation with the patient.
Michael Donlin, ACNP-BC, FHM, is an inpatient nurse practitioner for the Department of Medicine, VA Boston Healthcare System.
How Should Hospitalists Manage Elderly Patients with Dysphagia?
The Case
A 74-year-old man with Alzheimer’s dementia presents with urinary tract infection (UTI), hypovolemia, and hypernatremia. He also has chronic dysphagia with a history of aspiration pneumonia and has been on thickened liquids at home for the past five months. As his infection is treated, he improves and requests water to drink.
Background
The diagnosis of dysphagia is clinical, and assessments from patients and family are often sufficient. The optimal test to assess the severity of dysphagia is a bedside swallow evaluation using small amounts of water.1 Video-assisted fluoroscopic examinations can identify problem areas within the oropharynx and esophagus and may help determine the etiology of dysphagia.
What evidence supports various treatment options for dysphagia?
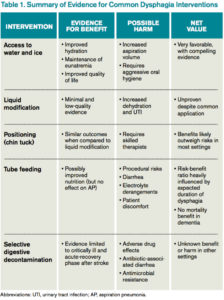
Access to Water
Water is a thin liquid with low viscosity, which allows for rapid transit through the oropharynx. In debilitated and elderly patients, thin liquids easily reach the epiglottis and enter the trachea before pharyngeal muscles compensate. As such, access to water and other thin liquids is often restricted in patients suspected to have dysphagia.4
However, allowing access to water improves patient satisfaction, reduces the development of dehydration, and does not increase the incidence of AP. Bedside therapy interventions such as correct positioning and chin-tuck and sipping technique as well as attention to oral hygiene are recommended prior to more noxious options such as thickened liquids.1 The Frazier water protocol may help provide logistical guidance for facilities interested in improving access to water for patients with dysphagia.
Liquid Modification
Many clinicians manage dysphagia through restricting access to all thin liquids. In the hospital setting where video fluoroscopy and speech therapy are readily available, clinicians frequently employ the use of modified diets with thickened liquids in order to minimize the risk of aspiration despite the lack of high-quality evidence supporting liquid modification.2 Patients associate thickened liquids and restricted diets with a reduction in quality of life. Compliance studies have shown that only a minority of patients are compliant with thickened liquids at five days. In addition, thickening liquids has not been shown to decrease the risk of AP nor improve nutritional status, and it may actually cause harm by increasing the risk of dehydration and UTI.4
Tube Feeding
In patients with severe dysphagia in whom conservative management is not feasible or has failed, maintaining adequate nutrition can be a challenge. There are encouraging data with nutritionally enriching and modifying the texture of solid foods.1 Alternative methods of enteral nutrition delivery are often also considered. The most common vehicles of delivery are nasogastric tubes, post-pyloric feeding tubes, and percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes. In theory, bypassing the pharynx and esophagus could result in fewer aspiration events and less AP.3 However, nasogastric, post-pyloric, or PEG feeding does not decrease the risk of AP. For patients with advanced dementia, there have been no randomized trials demonstrating an improvement in mortality with tube feeds.4 Tube feeding also carries with it a slight procedural risk and a high incidence of associated diarrhea, plus is associated with electrolyte derangements such as hypernatremia. The decision to pursue tube feeding should be weighed heavily in every patient and is highly influenced by the etiology and anticipated duration of dysphagia.
Selective Digestive Decontamination
Selective digestive decontamination (SDD) is a protocol-based treatment that aims to eradicate potentially pathogenic gut flora, particularly aerobic gram-negatives, in critically ill patients to reduce the impact of aspiration events. The utilization of SDD and the available literature center firmly on critically ill and ventilated patients. Subsequent studies have demonstrated recolonization after protocol cessation, and long-term effects are currently undefined.5 Until it can be studied in broader populations and proven to have clinical benefit, employing SSD in non-critically ill patients with dysphagia remains unsupported.
Multimodal Approach
Many rehabilitation centers incorporate a therapist-driven swallowing treatment program. Evidence suggests patient and family counseling alone may not be effective, so these programs variably incorporate diet/liquid modification, strengthening exercises, sensory processing techniques, and even neuromuscular electrical stimulation for muscle building.1 Accordingly, these programs are resource-intensive.
Management
Dysphagia remains a significant clinical problem for hospitalized patients. The existing literature and practice guidelines generally support a “less is more” approach. Though liquid/diet modification is common practice, it is not based in solid evidence and may contribute to unnecessary tube feeding. The best current evidence supports allowing access to water and ice chips. The ideal management plan for each patient will differ and should incorporate patient and family preferences in a multidisciplinary approach.
Back to the Case
Our patient requests water. He coughs after drinking during a bedside swallow evaluation. The risks of potential aspiration and AP are explained, and he expresses his understanding. He reiterates his choice to be allowed access to water as it is important to his quality of life. The speech therapy team is consulted and provides instruction on chin-tuck positioning, oral care, and timing water between meals rather than while eating food. He does well for the remainder of the hospital stay, and by time of discharge, his electrolytes are corrected, and he is much more comfortable being allowed to drink water. He is discharged home and encouraged to continue with these conservative measures.
Bottom Line
Evidence to support many common interventions for dysphagia is lacking; patients with dysphagia are best managed via a multidisciplinary, multimodal approach that provides access to water whenever possible. TH
Vijay G. Paryani, MD, is an internal medicine resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of Kentucky. Joseph R. Sweigart, MD, is a hospitalist and assistant professor of hospital medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky. Laura C. Fanucchi, MD, is a hospitalist and assistant professor of hospital medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky.
References
- Karagiannis MJ, Chivers L, Karagiannis TC. Effects of oral intake of water in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. BMC Geriatr. 2011;11(2):9.
- Foley N, Teasell R, Salter K, Kruger E, Martino R. Dysphagia treatment post stroke: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Age Ageing. 2008;37(3):258-264.
- Marik PE. Aspiration pneumonitis and aspiration pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(9):665-671.
- Loeb MB, Becker M, Eady A, Walker-Dilks C. Interventions to prevent aspiration pneumonia in older adults: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(7):1018-1022.
- Gosney M, Martin MV, Wright AE. The role of selective decontamination of the digestive tract in acute stroke. Age Ageing 2006;35(1):42-47.
The Case
A 74-year-old man with Alzheimer’s dementia presents with urinary tract infection (UTI), hypovolemia, and hypernatremia. He also has chronic dysphagia with a history of aspiration pneumonia and has been on thickened liquids at home for the past five months. As his infection is treated, he improves and requests water to drink.
Background
The diagnosis of dysphagia is clinical, and assessments from patients and family are often sufficient. The optimal test to assess the severity of dysphagia is a bedside swallow evaluation using small amounts of water.1 Video-assisted fluoroscopic examinations can identify problem areas within the oropharynx and esophagus and may help determine the etiology of dysphagia.
What evidence supports various treatment options for dysphagia?
Access to Water
Water is a thin liquid with low viscosity, which allows for rapid transit through the oropharynx. In debilitated and elderly patients, thin liquids easily reach the epiglottis and enter the trachea before pharyngeal muscles compensate. As such, access to water and other thin liquids is often restricted in patients suspected to have dysphagia.4
However, allowing access to water improves patient satisfaction, reduces the development of dehydration, and does not increase the incidence of AP. Bedside therapy interventions such as correct positioning and chin-tuck and sipping technique as well as attention to oral hygiene are recommended prior to more noxious options such as thickened liquids.1 The Frazier water protocol may help provide logistical guidance for facilities interested in improving access to water for patients with dysphagia.
Liquid Modification
Many clinicians manage dysphagia through restricting access to all thin liquids. In the hospital setting where video fluoroscopy and speech therapy are readily available, clinicians frequently employ the use of modified diets with thickened liquids in order to minimize the risk of aspiration despite the lack of high-quality evidence supporting liquid modification.2 Patients associate thickened liquids and restricted diets with a reduction in quality of life. Compliance studies have shown that only a minority of patients are compliant with thickened liquids at five days. In addition, thickening liquids has not been shown to decrease the risk of AP nor improve nutritional status, and it may actually cause harm by increasing the risk of dehydration and UTI.4
Tube Feeding
In patients with severe dysphagia in whom conservative management is not feasible or has failed, maintaining adequate nutrition can be a challenge. There are encouraging data with nutritionally enriching and modifying the texture of solid foods.1 Alternative methods of enteral nutrition delivery are often also considered. The most common vehicles of delivery are nasogastric tubes, post-pyloric feeding tubes, and percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes. In theory, bypassing the pharynx and esophagus could result in fewer aspiration events and less AP.3 However, nasogastric, post-pyloric, or PEG feeding does not decrease the risk of AP. For patients with advanced dementia, there have been no randomized trials demonstrating an improvement in mortality with tube feeds.4 Tube feeding also carries with it a slight procedural risk and a high incidence of associated diarrhea, plus is associated with electrolyte derangements such as hypernatremia. The decision to pursue tube feeding should be weighed heavily in every patient and is highly influenced by the etiology and anticipated duration of dysphagia.
Selective Digestive Decontamination
Selective digestive decontamination (SDD) is a protocol-based treatment that aims to eradicate potentially pathogenic gut flora, particularly aerobic gram-negatives, in critically ill patients to reduce the impact of aspiration events. The utilization of SDD and the available literature center firmly on critically ill and ventilated patients. Subsequent studies have demonstrated recolonization after protocol cessation, and long-term effects are currently undefined.5 Until it can be studied in broader populations and proven to have clinical benefit, employing SSD in non-critically ill patients with dysphagia remains unsupported.
Multimodal Approach
Many rehabilitation centers incorporate a therapist-driven swallowing treatment program. Evidence suggests patient and family counseling alone may not be effective, so these programs variably incorporate diet/liquid modification, strengthening exercises, sensory processing techniques, and even neuromuscular electrical stimulation for muscle building.1 Accordingly, these programs are resource-intensive.
Management
Dysphagia remains a significant clinical problem for hospitalized patients. The existing literature and practice guidelines generally support a “less is more” approach. Though liquid/diet modification is common practice, it is not based in solid evidence and may contribute to unnecessary tube feeding. The best current evidence supports allowing access to water and ice chips. The ideal management plan for each patient will differ and should incorporate patient and family preferences in a multidisciplinary approach.
Back to the Case
Our patient requests water. He coughs after drinking during a bedside swallow evaluation. The risks of potential aspiration and AP are explained, and he expresses his understanding. He reiterates his choice to be allowed access to water as it is important to his quality of life. The speech therapy team is consulted and provides instruction on chin-tuck positioning, oral care, and timing water between meals rather than while eating food. He does well for the remainder of the hospital stay, and by time of discharge, his electrolytes are corrected, and he is much more comfortable being allowed to drink water. He is discharged home and encouraged to continue with these conservative measures.
Bottom Line
Evidence to support many common interventions for dysphagia is lacking; patients with dysphagia are best managed via a multidisciplinary, multimodal approach that provides access to water whenever possible. TH
Vijay G. Paryani, MD, is an internal medicine resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of Kentucky. Joseph R. Sweigart, MD, is a hospitalist and assistant professor of hospital medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky. Laura C. Fanucchi, MD, is a hospitalist and assistant professor of hospital medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky.
References
- Karagiannis MJ, Chivers L, Karagiannis TC. Effects of oral intake of water in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. BMC Geriatr. 2011;11(2):9.
- Foley N, Teasell R, Salter K, Kruger E, Martino R. Dysphagia treatment post stroke: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Age Ageing. 2008;37(3):258-264.
- Marik PE. Aspiration pneumonitis and aspiration pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(9):665-671.
- Loeb MB, Becker M, Eady A, Walker-Dilks C. Interventions to prevent aspiration pneumonia in older adults: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(7):1018-1022.
- Gosney M, Martin MV, Wright AE. The role of selective decontamination of the digestive tract in acute stroke. Age Ageing 2006;35(1):42-47.
The Case
A 74-year-old man with Alzheimer’s dementia presents with urinary tract infection (UTI), hypovolemia, and hypernatremia. He also has chronic dysphagia with a history of aspiration pneumonia and has been on thickened liquids at home for the past five months. As his infection is treated, he improves and requests water to drink.
Background
The diagnosis of dysphagia is clinical, and assessments from patients and family are often sufficient. The optimal test to assess the severity of dysphagia is a bedside swallow evaluation using small amounts of water.1 Video-assisted fluoroscopic examinations can identify problem areas within the oropharynx and esophagus and may help determine the etiology of dysphagia.
What evidence supports various treatment options for dysphagia?
Access to Water
Water is a thin liquid with low viscosity, which allows for rapid transit through the oropharynx. In debilitated and elderly patients, thin liquids easily reach the epiglottis and enter the trachea before pharyngeal muscles compensate. As such, access to water and other thin liquids is often restricted in patients suspected to have dysphagia.4
However, allowing access to water improves patient satisfaction, reduces the development of dehydration, and does not increase the incidence of AP. Bedside therapy interventions such as correct positioning and chin-tuck and sipping technique as well as attention to oral hygiene are recommended prior to more noxious options such as thickened liquids.1 The Frazier water protocol may help provide logistical guidance for facilities interested in improving access to water for patients with dysphagia.
Liquid Modification
Many clinicians manage dysphagia through restricting access to all thin liquids. In the hospital setting where video fluoroscopy and speech therapy are readily available, clinicians frequently employ the use of modified diets with thickened liquids in order to minimize the risk of aspiration despite the lack of high-quality evidence supporting liquid modification.2 Patients associate thickened liquids and restricted diets with a reduction in quality of life. Compliance studies have shown that only a minority of patients are compliant with thickened liquids at five days. In addition, thickening liquids has not been shown to decrease the risk of AP nor improve nutritional status, and it may actually cause harm by increasing the risk of dehydration and UTI.4
Tube Feeding
In patients with severe dysphagia in whom conservative management is not feasible or has failed, maintaining adequate nutrition can be a challenge. There are encouraging data with nutritionally enriching and modifying the texture of solid foods.1 Alternative methods of enteral nutrition delivery are often also considered. The most common vehicles of delivery are nasogastric tubes, post-pyloric feeding tubes, and percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes. In theory, bypassing the pharynx and esophagus could result in fewer aspiration events and less AP.3 However, nasogastric, post-pyloric, or PEG feeding does not decrease the risk of AP. For patients with advanced dementia, there have been no randomized trials demonstrating an improvement in mortality with tube feeds.4 Tube feeding also carries with it a slight procedural risk and a high incidence of associated diarrhea, plus is associated with electrolyte derangements such as hypernatremia. The decision to pursue tube feeding should be weighed heavily in every patient and is highly influenced by the etiology and anticipated duration of dysphagia.
Selective Digestive Decontamination
Selective digestive decontamination (SDD) is a protocol-based treatment that aims to eradicate potentially pathogenic gut flora, particularly aerobic gram-negatives, in critically ill patients to reduce the impact of aspiration events. The utilization of SDD and the available literature center firmly on critically ill and ventilated patients. Subsequent studies have demonstrated recolonization after protocol cessation, and long-term effects are currently undefined.5 Until it can be studied in broader populations and proven to have clinical benefit, employing SSD in non-critically ill patients with dysphagia remains unsupported.
Multimodal Approach
Many rehabilitation centers incorporate a therapist-driven swallowing treatment program. Evidence suggests patient and family counseling alone may not be effective, so these programs variably incorporate diet/liquid modification, strengthening exercises, sensory processing techniques, and even neuromuscular electrical stimulation for muscle building.1 Accordingly, these programs are resource-intensive.
Management
Dysphagia remains a significant clinical problem for hospitalized patients. The existing literature and practice guidelines generally support a “less is more” approach. Though liquid/diet modification is common practice, it is not based in solid evidence and may contribute to unnecessary tube feeding. The best current evidence supports allowing access to water and ice chips. The ideal management plan for each patient will differ and should incorporate patient and family preferences in a multidisciplinary approach.
Back to the Case
Our patient requests water. He coughs after drinking during a bedside swallow evaluation. The risks of potential aspiration and AP are explained, and he expresses his understanding. He reiterates his choice to be allowed access to water as it is important to his quality of life. The speech therapy team is consulted and provides instruction on chin-tuck positioning, oral care, and timing water between meals rather than while eating food. He does well for the remainder of the hospital stay, and by time of discharge, his electrolytes are corrected, and he is much more comfortable being allowed to drink water. He is discharged home and encouraged to continue with these conservative measures.
Bottom Line
Evidence to support many common interventions for dysphagia is lacking; patients with dysphagia are best managed via a multidisciplinary, multimodal approach that provides access to water whenever possible. TH
Vijay G. Paryani, MD, is an internal medicine resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of Kentucky. Joseph R. Sweigart, MD, is a hospitalist and assistant professor of hospital medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky. Laura C. Fanucchi, MD, is a hospitalist and assistant professor of hospital medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky.
References
- Karagiannis MJ, Chivers L, Karagiannis TC. Effects of oral intake of water in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. BMC Geriatr. 2011;11(2):9.
- Foley N, Teasell R, Salter K, Kruger E, Martino R. Dysphagia treatment post stroke: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Age Ageing. 2008;37(3):258-264.
- Marik PE. Aspiration pneumonitis and aspiration pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(9):665-671.
- Loeb MB, Becker M, Eady A, Walker-Dilks C. Interventions to prevent aspiration pneumonia in older adults: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(7):1018-1022.
- Gosney M, Martin MV, Wright AE. The role of selective decontamination of the digestive tract in acute stroke. Age Ageing 2006;35(1):42-47.
Updated Guideline for Acute Diarrheal Infection
Clinical Question: What are current recommendations for diagnosis, management, and prevention of acute gastrointestinal infection in immune-competent adults?
Background: Acute diarrheal infection is a leading cause of healthcare visits and lost quality of life. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates there are 47.8 million cases annually, with a healthcare economy burden of $150 million.
Study Design: American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) practice guideline.
Setting: Expert panel.
Synopsis: Stool diagnostic studies may be used for dysentery with moderate-severe disease and symptoms lasting more than seven days (strong recommendation, low level of evidence). Traditional diagnostic methods in most cases fail to reveal etiology (strong recommendation, low level of evidence). Treatment with probiotics or prebiotics is not recommended (strong recommendation, moderate level of evidence). Bismuth subsalicylates may be considered for prophylaxis against traveler’s diarrhea (strong recommendation, high level of evidence). Short-term antibiotic chemoprophylaxis also may be considered for high-risk groups (strong recommendation, high level of evidence). Empiric antimicrobial therapy is not recommended except in cases of traveler’s diarrhea (strong recommendation, high level of evidence). Loperamide may be used as an adjunct to antibiotics for traveler’s diarrhea (strong recommendation, moderate level of evidence).
Bottom Line: ACG acute diarrheal illness guidelines have been updated. Few recommendations are strong, and very few have high levels of evidence.
Citation: Riddle MS, DuPont HL, Conner BA. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of acute diarrheal infections in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(5):602-622.
Clinical Question: What are current recommendations for diagnosis, management, and prevention of acute gastrointestinal infection in immune-competent adults?
Background: Acute diarrheal infection is a leading cause of healthcare visits and lost quality of life. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates there are 47.8 million cases annually, with a healthcare economy burden of $150 million.
Study Design: American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) practice guideline.
Setting: Expert panel.
Synopsis: Stool diagnostic studies may be used for dysentery with moderate-severe disease and symptoms lasting more than seven days (strong recommendation, low level of evidence). Traditional diagnostic methods in most cases fail to reveal etiology (strong recommendation, low level of evidence). Treatment with probiotics or prebiotics is not recommended (strong recommendation, moderate level of evidence). Bismuth subsalicylates may be considered for prophylaxis against traveler’s diarrhea (strong recommendation, high level of evidence). Short-term antibiotic chemoprophylaxis also may be considered for high-risk groups (strong recommendation, high level of evidence). Empiric antimicrobial therapy is not recommended except in cases of traveler’s diarrhea (strong recommendation, high level of evidence). Loperamide may be used as an adjunct to antibiotics for traveler’s diarrhea (strong recommendation, moderate level of evidence).
Bottom Line: ACG acute diarrheal illness guidelines have been updated. Few recommendations are strong, and very few have high levels of evidence.
Citation: Riddle MS, DuPont HL, Conner BA. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of acute diarrheal infections in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(5):602-622.
Clinical Question: What are current recommendations for diagnosis, management, and prevention of acute gastrointestinal infection in immune-competent adults?
Background: Acute diarrheal infection is a leading cause of healthcare visits and lost quality of life. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates there are 47.8 million cases annually, with a healthcare economy burden of $150 million.
Study Design: American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) practice guideline.
Setting: Expert panel.
Synopsis: Stool diagnostic studies may be used for dysentery with moderate-severe disease and symptoms lasting more than seven days (strong recommendation, low level of evidence). Traditional diagnostic methods in most cases fail to reveal etiology (strong recommendation, low level of evidence). Treatment with probiotics or prebiotics is not recommended (strong recommendation, moderate level of evidence). Bismuth subsalicylates may be considered for prophylaxis against traveler’s diarrhea (strong recommendation, high level of evidence). Short-term antibiotic chemoprophylaxis also may be considered for high-risk groups (strong recommendation, high level of evidence). Empiric antimicrobial therapy is not recommended except in cases of traveler’s diarrhea (strong recommendation, high level of evidence). Loperamide may be used as an adjunct to antibiotics for traveler’s diarrhea (strong recommendation, moderate level of evidence).
Bottom Line: ACG acute diarrheal illness guidelines have been updated. Few recommendations are strong, and very few have high levels of evidence.
Citation: Riddle MS, DuPont HL, Conner BA. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of acute diarrheal infections in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(5):602-622.
Risk-Assessment Models Are Unreliable Predictors of Venous Thromboembolism
Clinical Question: Do risk-assessment models (RAMs) accurately predict which hospitalized medical patients are at risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE)?
Background: Predicting which patients are at high risk for VTE is important. Several models exist, but limited data support their generalizability and accuracy in medical inpatients.
Study Design: Retrospective cohort.
Setting: Hospitals participating in the Michigan Hospital Medicine Safety Consortium (MHMSC).
Synopsis: Data collected through MHMSC for selected medical patients were used in the Kucher, Padua, predictive IMPROVE, and Intermountain DVT risk-assessment models. Patients were classified as “low risk” or “at risk” based on each RAM. Follow-up data came from chart extraction (100% of patients) and 90-day post-discharge telephone calls (58% of patients). The primary outcome was image-confirmed hospital associated VTE, including proximal upper- or proximal lower-extremity DVT or pulmonary embolism. These RAMs classified less than 20% of patients as “at risk.” The incidence of VTE was less than 1%. In this external validation study, the Kucher RAM was the least discriminate and the Intermountain was the best, but none yielded results equivalent to the original studies.
This study was limited by the retrospective design, subjectivity of some risk factors (such as immobility), and inability to obtain 90-day telephone follow-up in all patients. Lastly, the binary approach (“at risk” versus “low risk”) may not align with the original derivation studies in which each factor was evaluated independently.
Bottom Line: The incidence of VTE is low in medical inpatients, and current RAMs may not accurately identify at-risk patients.
Citation: Greene MT, Spyropoulos AC, Chopra V, et al. Validation of risk assessment models of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized medical patients. Am J Med. 2016;129(9):1001.e9-1001.e18. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.031.
Clinical Question: Do risk-assessment models (RAMs) accurately predict which hospitalized medical patients are at risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE)?
Background: Predicting which patients are at high risk for VTE is important. Several models exist, but limited data support their generalizability and accuracy in medical inpatients.
Study Design: Retrospective cohort.
Setting: Hospitals participating in the Michigan Hospital Medicine Safety Consortium (MHMSC).
Synopsis: Data collected through MHMSC for selected medical patients were used in the Kucher, Padua, predictive IMPROVE, and Intermountain DVT risk-assessment models. Patients were classified as “low risk” or “at risk” based on each RAM. Follow-up data came from chart extraction (100% of patients) and 90-day post-discharge telephone calls (58% of patients). The primary outcome was image-confirmed hospital associated VTE, including proximal upper- or proximal lower-extremity DVT or pulmonary embolism. These RAMs classified less than 20% of patients as “at risk.” The incidence of VTE was less than 1%. In this external validation study, the Kucher RAM was the least discriminate and the Intermountain was the best, but none yielded results equivalent to the original studies.
This study was limited by the retrospective design, subjectivity of some risk factors (such as immobility), and inability to obtain 90-day telephone follow-up in all patients. Lastly, the binary approach (“at risk” versus “low risk”) may not align with the original derivation studies in which each factor was evaluated independently.
Bottom Line: The incidence of VTE is low in medical inpatients, and current RAMs may not accurately identify at-risk patients.
Citation: Greene MT, Spyropoulos AC, Chopra V, et al. Validation of risk assessment models of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized medical patients. Am J Med. 2016;129(9):1001.e9-1001.e18. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.031.
Clinical Question: Do risk-assessment models (RAMs) accurately predict which hospitalized medical patients are at risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE)?
Background: Predicting which patients are at high risk for VTE is important. Several models exist, but limited data support their generalizability and accuracy in medical inpatients.
Study Design: Retrospective cohort.
Setting: Hospitals participating in the Michigan Hospital Medicine Safety Consortium (MHMSC).
Synopsis: Data collected through MHMSC for selected medical patients were used in the Kucher, Padua, predictive IMPROVE, and Intermountain DVT risk-assessment models. Patients were classified as “low risk” or “at risk” based on each RAM. Follow-up data came from chart extraction (100% of patients) and 90-day post-discharge telephone calls (58% of patients). The primary outcome was image-confirmed hospital associated VTE, including proximal upper- or proximal lower-extremity DVT or pulmonary embolism. These RAMs classified less than 20% of patients as “at risk.” The incidence of VTE was less than 1%. In this external validation study, the Kucher RAM was the least discriminate and the Intermountain was the best, but none yielded results equivalent to the original studies.
This study was limited by the retrospective design, subjectivity of some risk factors (such as immobility), and inability to obtain 90-day telephone follow-up in all patients. Lastly, the binary approach (“at risk” versus “low risk”) may not align with the original derivation studies in which each factor was evaluated independently.
Bottom Line: The incidence of VTE is low in medical inpatients, and current RAMs may not accurately identify at-risk patients.
Citation: Greene MT, Spyropoulos AC, Chopra V, et al. Validation of risk assessment models of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized medical patients. Am J Med. 2016;129(9):1001.e9-1001.e18. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.031.
Compete and Solve Clinical Cases with Human Diagnosis Project
SHM recently partnered with the Human Diagnosis Project. Human Dx is the world’s first open diagnostic system, which aims to understand the fundamental data structure of diagnosis and, in the future, considerably impact the cost of, access to, and effectiveness of healthcare globally.
Human Dx’s Global Morning Reports feature weekly case competitions of differential diagnoses and clinical reasoning skills. Each day, attendings, fellows, residents, and medical students have the opportunity to solve the best cases from around the world from the prior day and submit cases for the next day. This partnership with SHM provides a unique, interactive learning platform with cases tailored to hospitalists.
The rules are simple:
- Increase your “Impact” by creating and solving cases online.
- Creating cases creates more “Impact” than solving cases.
The team and individual with the most “Impact” each week win. Sign up today and test your skills in hospital medicine diagnostics at www.humandx.org/shm/.
SHM recently partnered with the Human Diagnosis Project. Human Dx is the world’s first open diagnostic system, which aims to understand the fundamental data structure of diagnosis and, in the future, considerably impact the cost of, access to, and effectiveness of healthcare globally.
Human Dx’s Global Morning Reports feature weekly case competitions of differential diagnoses and clinical reasoning skills. Each day, attendings, fellows, residents, and medical students have the opportunity to solve the best cases from around the world from the prior day and submit cases for the next day. This partnership with SHM provides a unique, interactive learning platform with cases tailored to hospitalists.
The rules are simple:
- Increase your “Impact” by creating and solving cases online.
- Creating cases creates more “Impact” than solving cases.
The team and individual with the most “Impact” each week win. Sign up today and test your skills in hospital medicine diagnostics at www.humandx.org/shm/.
SHM recently partnered with the Human Diagnosis Project. Human Dx is the world’s first open diagnostic system, which aims to understand the fundamental data structure of diagnosis and, in the future, considerably impact the cost of, access to, and effectiveness of healthcare globally.
Human Dx’s Global Morning Reports feature weekly case competitions of differential diagnoses and clinical reasoning skills. Each day, attendings, fellows, residents, and medical students have the opportunity to solve the best cases from around the world from the prior day and submit cases for the next day. This partnership with SHM provides a unique, interactive learning platform with cases tailored to hospitalists.
The rules are simple:
- Increase your “Impact” by creating and solving cases online.
- Creating cases creates more “Impact” than solving cases.
The team and individual with the most “Impact” each week win. Sign up today and test your skills in hospital medicine diagnostics at www.humandx.org/shm/.
2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report Now Available
- The percentage of the hospital’s total patient volume (for the population the group serves, i.e., adult versus children versus both) that the hospital medicine group (HMG) was responsible for caring for
- The presence of medical hospitalists within the HMG focusing their practice on a specific medical subspecialty, such as critical care, neurology, or oncology
- The value of CME allowances for hospitalists
- The utilization of prolonged service codes by hospitalists
- Charge capture methodologies being used by HMGs
- For academic HMGs, the dollar amount of financial support provided for non-clinical work
Order your copy now and improve your practice today at www.hospitalmedicine.org/survey.
- The percentage of the hospital’s total patient volume (for the population the group serves, i.e., adult versus children versus both) that the hospital medicine group (HMG) was responsible for caring for
- The presence of medical hospitalists within the HMG focusing their practice on a specific medical subspecialty, such as critical care, neurology, or oncology
- The value of CME allowances for hospitalists
- The utilization of prolonged service codes by hospitalists
- Charge capture methodologies being used by HMGs
- For academic HMGs, the dollar amount of financial support provided for non-clinical work
Order your copy now and improve your practice today at www.hospitalmedicine.org/survey.
- The percentage of the hospital’s total patient volume (for the population the group serves, i.e., adult versus children versus both) that the hospital medicine group (HMG) was responsible for caring for
- The presence of medical hospitalists within the HMG focusing their practice on a specific medical subspecialty, such as critical care, neurology, or oncology
- The value of CME allowances for hospitalists
- The utilization of prolonged service codes by hospitalists
- Charge capture methodologies being used by HMGs
- For academic HMGs, the dollar amount of financial support provided for non-clinical work
Order your copy now and improve your practice today at www.hospitalmedicine.org/survey.
Acute HIV Causes Transient Neurologic Findings
Clinical Question: How common are neurologic findings in acute HIV infection?
Background: The incidence of neurologic findings with acute HIV is unknown.
Study Design: Cohort study.
Setting: Bangkok, Thailand.
Synopsis: In this study, 134 patients were identified after presenting for voluntary HIV testing. Five others were enrolled through an ongoing local study. All 139 participants underwent structured neurologic evaluations at enrollment (median of 19 days after presumed exposure), then at four and 12 weeks. Combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) was initiated immediately after initial evaluation.
The cohort was 93% male. Mean age was younger than 30 years. Fifty-three percent of participants experienced some neurologic finding within 12 weeks of diagnosis. One-third (33%) were cognitive symptoms, predominantly problems of concentration (24% of patients) and memory (16% of patients). One-third (34%) were motor findings, and 11% were neuropathy. Forty-nine percent of the neurologic issues were present at diagnosis. Symptoms were mostly mild, although one patient developed fulminant Guillain-Barré syndrome. Patients with neurologic findings had higher viral loads at diagnosis (mean plasma log10 HIV RNA 5.9 versus 5.4; P = 0.006). Participants with and without neurologic findings had similar cerebral spinal fluid viral loads (mean log10 HIV RNA 3.7 versus 3.1, P = 0.14) and serum CD4 counts (339 versus 381 cells/mm3; P = 0.46). Neurologic findings resolved within one month of cART treatment in 90% of patients. Study limitations include lack of a control cohort and potential confounding from illicit drug use among participants.
Bottom Line: Acute HIV infection commonly causes mild neurologic problems, which remit with treatment.
Citation: Hellmuth J, Fletcher JL, Valcour V, et al. Neurologic signs and symptoms frequently manifest in acute HIV infection. Neurology. 2016;87(2):148-154.
Clinical Question: How common are neurologic findings in acute HIV infection?
Background: The incidence of neurologic findings with acute HIV is unknown.
Study Design: Cohort study.
Setting: Bangkok, Thailand.
Synopsis: In this study, 134 patients were identified after presenting for voluntary HIV testing. Five others were enrolled through an ongoing local study. All 139 participants underwent structured neurologic evaluations at enrollment (median of 19 days after presumed exposure), then at four and 12 weeks. Combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) was initiated immediately after initial evaluation.
The cohort was 93% male. Mean age was younger than 30 years. Fifty-three percent of participants experienced some neurologic finding within 12 weeks of diagnosis. One-third (33%) were cognitive symptoms, predominantly problems of concentration (24% of patients) and memory (16% of patients). One-third (34%) were motor findings, and 11% were neuropathy. Forty-nine percent of the neurologic issues were present at diagnosis. Symptoms were mostly mild, although one patient developed fulminant Guillain-Barré syndrome. Patients with neurologic findings had higher viral loads at diagnosis (mean plasma log10 HIV RNA 5.9 versus 5.4; P = 0.006). Participants with and without neurologic findings had similar cerebral spinal fluid viral loads (mean log10 HIV RNA 3.7 versus 3.1, P = 0.14) and serum CD4 counts (339 versus 381 cells/mm3; P = 0.46). Neurologic findings resolved within one month of cART treatment in 90% of patients. Study limitations include lack of a control cohort and potential confounding from illicit drug use among participants.
Bottom Line: Acute HIV infection commonly causes mild neurologic problems, which remit with treatment.
Citation: Hellmuth J, Fletcher JL, Valcour V, et al. Neurologic signs and symptoms frequently manifest in acute HIV infection. Neurology. 2016;87(2):148-154.
Clinical Question: How common are neurologic findings in acute HIV infection?
Background: The incidence of neurologic findings with acute HIV is unknown.
Study Design: Cohort study.
Setting: Bangkok, Thailand.
Synopsis: In this study, 134 patients were identified after presenting for voluntary HIV testing. Five others were enrolled through an ongoing local study. All 139 participants underwent structured neurologic evaluations at enrollment (median of 19 days after presumed exposure), then at four and 12 weeks. Combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) was initiated immediately after initial evaluation.
The cohort was 93% male. Mean age was younger than 30 years. Fifty-three percent of participants experienced some neurologic finding within 12 weeks of diagnosis. One-third (33%) were cognitive symptoms, predominantly problems of concentration (24% of patients) and memory (16% of patients). One-third (34%) were motor findings, and 11% were neuropathy. Forty-nine percent of the neurologic issues were present at diagnosis. Symptoms were mostly mild, although one patient developed fulminant Guillain-Barré syndrome. Patients with neurologic findings had higher viral loads at diagnosis (mean plasma log10 HIV RNA 5.9 versus 5.4; P = 0.006). Participants with and without neurologic findings had similar cerebral spinal fluid viral loads (mean log10 HIV RNA 3.7 versus 3.1, P = 0.14) and serum CD4 counts (339 versus 381 cells/mm3; P = 0.46). Neurologic findings resolved within one month of cART treatment in 90% of patients. Study limitations include lack of a control cohort and potential confounding from illicit drug use among participants.
Bottom Line: Acute HIV infection commonly causes mild neurologic problems, which remit with treatment.
Citation: Hellmuth J, Fletcher JL, Valcour V, et al. Neurologic signs and symptoms frequently manifest in acute HIV infection. Neurology. 2016;87(2):148-154.