User login
Two-drug combo deemed ‘very promising’ for PMBCL
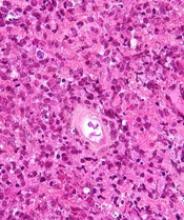
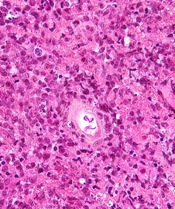
SAN DIEGO—Nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin may be a new treatment option for patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to investigators from the CheckMate 436 trial.
Interim results from this phase 1/2 trial revealed an overall response rate of 70%, including a complete response rate of 27%.
“It’s very promising . . . to see this level of activity in this advanced, relapsed/refractory population,” said Joseph E. Eid, MD, senior vice president and head of medical at Bristol-Myers Squibb, which is sponsoring CheckMate 436 in collaboration with Seattle Genetics.
Dr. Eid also noted that adverse events (AEs) observed with this regimen were consistent with the safety profiles of nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin alone.
These results were presented as a poster at the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 1691).
Rationale
Dr. Eid noted that patients with relapsed or refractory PMBCL have limited treatment options.
“The initial therapy works well in 70% to 80% of patients, but the patients who fail don’t have good options,” he said.
Prior research has shown that PMBCL is often characterized by overexpression of the PD-1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, and most PMBCL expresses CD30.
Dr. Eid said CheckMate 436 (NCT02581631) was designed to “take advantage” of these characteristics by employing the anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab and the anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate brentuximab vedotin.
Patients and treatment
The interim analysis of this trial included 30 patients with relapsed/refractory PMCBL. Their median age at enrollment was 35.5 (range, 19 to 83), and 57% of patients were female.
Sixty percent of patients had refractory disease, 23% had relapsed disease, and 17% had both.
The median number of prior therapies was 2 (range, 1-5). Thirteen percent of patients had prior autologous stem cell transplant.
The patients received nivolumab at 240 mg and brentuximab vedotin at 1.8 mg/kg every 3 weeks until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 6.1 months, 10 patients were still on treatment. Reasons for discontinuation included maximum clinical benefit (n=9), disease progression (n=7), AEs unrelated to treatment (n=2), patient request (n=1), and “other” reasons (n=1).
Safety
“There were no new safety signals,” Dr. Eid said. “The adverse events reflected the two agents’ profiles.”
The rate of treatment-related AEs was 83%. The most common of these were neutropenia (27%), peripheral neuropathy (20%), hyperthyroidism (13%), rash (10%), and thrombocytopenia (10%).
Grade 3-4 treatment-related AEs included neutropenia (27%), thrombocytopenia (7%), decreased neutrophil count (7%), hypersensitivity (3%), diarrhea (3%), and maculopapular rash (3%).
The rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 10%. This included grade 3-4 diarrhea and maculopapular rash and grade 5 acute kidney injury.
The acute kidney injury was the only fatal AE considered treatment-related. There were three other deaths in the trial, but they were considered unrelated to treatment.
Response
The complete response rate was 27% (n=8), and the partial response rate was 43% (n=13), for an overall response rate of 70% (n=21).
“The early indication is that 70% response is a pretty good outcome in a relapsed/refractory population that, otherwise, their outcome is pretty dismal,” Dr. Eid said.
Ten percent of patients (n=3) had stable disease, 13% (n=4) progressed, and investigators were unable to determine the status for 7% of patients (n=2).
The median time to response was 1.3 months, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. The median duration of response and complete response were not reached.
Overall and progression-free survival data are not yet mature.
Still, the investigators concluded that nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin “may provide a new treatment option” for patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL.
“The results are very, very promising,” Dr. Eid said.
This trial is supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb in collaboration with Seattle Genetics.
SAN DIEGO—Nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin may be a new treatment option for patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to investigators from the CheckMate 436 trial.
Interim results from this phase 1/2 trial revealed an overall response rate of 70%, including a complete response rate of 27%.
“It’s very promising . . . to see this level of activity in this advanced, relapsed/refractory population,” said Joseph E. Eid, MD, senior vice president and head of medical at Bristol-Myers Squibb, which is sponsoring CheckMate 436 in collaboration with Seattle Genetics.
Dr. Eid also noted that adverse events (AEs) observed with this regimen were consistent with the safety profiles of nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin alone.
These results were presented as a poster at the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 1691).
Rationale
Dr. Eid noted that patients with relapsed or refractory PMBCL have limited treatment options.
“The initial therapy works well in 70% to 80% of patients, but the patients who fail don’t have good options,” he said.
Prior research has shown that PMBCL is often characterized by overexpression of the PD-1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, and most PMBCL expresses CD30.
Dr. Eid said CheckMate 436 (NCT02581631) was designed to “take advantage” of these characteristics by employing the anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab and the anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate brentuximab vedotin.
Patients and treatment
The interim analysis of this trial included 30 patients with relapsed/refractory PMCBL. Their median age at enrollment was 35.5 (range, 19 to 83), and 57% of patients were female.
Sixty percent of patients had refractory disease, 23% had relapsed disease, and 17% had both.
The median number of prior therapies was 2 (range, 1-5). Thirteen percent of patients had prior autologous stem cell transplant.
The patients received nivolumab at 240 mg and brentuximab vedotin at 1.8 mg/kg every 3 weeks until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 6.1 months, 10 patients were still on treatment. Reasons for discontinuation included maximum clinical benefit (n=9), disease progression (n=7), AEs unrelated to treatment (n=2), patient request (n=1), and “other” reasons (n=1).
Safety
“There were no new safety signals,” Dr. Eid said. “The adverse events reflected the two agents’ profiles.”
The rate of treatment-related AEs was 83%. The most common of these were neutropenia (27%), peripheral neuropathy (20%), hyperthyroidism (13%), rash (10%), and thrombocytopenia (10%).
Grade 3-4 treatment-related AEs included neutropenia (27%), thrombocytopenia (7%), decreased neutrophil count (7%), hypersensitivity (3%), diarrhea (3%), and maculopapular rash (3%).
The rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 10%. This included grade 3-4 diarrhea and maculopapular rash and grade 5 acute kidney injury.
The acute kidney injury was the only fatal AE considered treatment-related. There were three other deaths in the trial, but they were considered unrelated to treatment.
Response
The complete response rate was 27% (n=8), and the partial response rate was 43% (n=13), for an overall response rate of 70% (n=21).
“The early indication is that 70% response is a pretty good outcome in a relapsed/refractory population that, otherwise, their outcome is pretty dismal,” Dr. Eid said.
Ten percent of patients (n=3) had stable disease, 13% (n=4) progressed, and investigators were unable to determine the status for 7% of patients (n=2).
The median time to response was 1.3 months, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. The median duration of response and complete response were not reached.
Overall and progression-free survival data are not yet mature.
Still, the investigators concluded that nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin “may provide a new treatment option” for patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL.
“The results are very, very promising,” Dr. Eid said.
This trial is supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb in collaboration with Seattle Genetics.
SAN DIEGO—Nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin may be a new treatment option for patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to investigators from the CheckMate 436 trial.
Interim results from this phase 1/2 trial revealed an overall response rate of 70%, including a complete response rate of 27%.
“It’s very promising . . . to see this level of activity in this advanced, relapsed/refractory population,” said Joseph E. Eid, MD, senior vice president and head of medical at Bristol-Myers Squibb, which is sponsoring CheckMate 436 in collaboration with Seattle Genetics.
Dr. Eid also noted that adverse events (AEs) observed with this regimen were consistent with the safety profiles of nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin alone.
These results were presented as a poster at the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 1691).
Rationale
Dr. Eid noted that patients with relapsed or refractory PMBCL have limited treatment options.
“The initial therapy works well in 70% to 80% of patients, but the patients who fail don’t have good options,” he said.
Prior research has shown that PMBCL is often characterized by overexpression of the PD-1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, and most PMBCL expresses CD30.
Dr. Eid said CheckMate 436 (NCT02581631) was designed to “take advantage” of these characteristics by employing the anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab and the anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate brentuximab vedotin.
Patients and treatment
The interim analysis of this trial included 30 patients with relapsed/refractory PMCBL. Their median age at enrollment was 35.5 (range, 19 to 83), and 57% of patients were female.
Sixty percent of patients had refractory disease, 23% had relapsed disease, and 17% had both.
The median number of prior therapies was 2 (range, 1-5). Thirteen percent of patients had prior autologous stem cell transplant.
The patients received nivolumab at 240 mg and brentuximab vedotin at 1.8 mg/kg every 3 weeks until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 6.1 months, 10 patients were still on treatment. Reasons for discontinuation included maximum clinical benefit (n=9), disease progression (n=7), AEs unrelated to treatment (n=2), patient request (n=1), and “other” reasons (n=1).
Safety
“There were no new safety signals,” Dr. Eid said. “The adverse events reflected the two agents’ profiles.”
The rate of treatment-related AEs was 83%. The most common of these were neutropenia (27%), peripheral neuropathy (20%), hyperthyroidism (13%), rash (10%), and thrombocytopenia (10%).
Grade 3-4 treatment-related AEs included neutropenia (27%), thrombocytopenia (7%), decreased neutrophil count (7%), hypersensitivity (3%), diarrhea (3%), and maculopapular rash (3%).
The rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 10%. This included grade 3-4 diarrhea and maculopapular rash and grade 5 acute kidney injury.
The acute kidney injury was the only fatal AE considered treatment-related. There were three other deaths in the trial, but they were considered unrelated to treatment.
Response
The complete response rate was 27% (n=8), and the partial response rate was 43% (n=13), for an overall response rate of 70% (n=21).
“The early indication is that 70% response is a pretty good outcome in a relapsed/refractory population that, otherwise, their outcome is pretty dismal,” Dr. Eid said.
Ten percent of patients (n=3) had stable disease, 13% (n=4) progressed, and investigators were unable to determine the status for 7% of patients (n=2).
The median time to response was 1.3 months, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. The median duration of response and complete response were not reached.
Overall and progression-free survival data are not yet mature.
Still, the investigators concluded that nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin “may provide a new treatment option” for patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL.
“The results are very, very promising,” Dr. Eid said.
This trial is supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb in collaboration with Seattle Genetics.
2018: A banner year for hematology drug approvals
SAN DIEGO – It was banner year for new hematology drug approvals, according to R. Angelo de Claro, MD, of the Food and Drug Administration.
, including 12 first-time approvals, 5 new biosimilars, and 15 new indications for previously approved drugs, Dr. de Claro, clinical team leader in the FDA’s division of hematology products in Silver Spring, Md., said during an overview of the approvals at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
These include six new approvals for first-line treatment, and eight for pediatric indications, he said.
Highlights were discussed at two ASH-FDA joint symposia at the meeting, including one focused on the malignant hematology approvals, and another on the nonmalignant hematology approvals. In a video interview, Dr. de Claro provides some additional insight into their importance and about what might lie ahead.
“I think what’s exciting is that you have drug development occurring in more common conditions such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia, as well as in rare conditions, including hairy cell leukemia – and the first-ever approval in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis,” he said. “It’s been very busy at the FDA; stay tuned ... the year’s not done yet. There could be more coming and we certainly anticipate more applications in the future.”
Dr. de Claro is an FDA employee. He reported having no other relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – It was banner year for new hematology drug approvals, according to R. Angelo de Claro, MD, of the Food and Drug Administration.
, including 12 first-time approvals, 5 new biosimilars, and 15 new indications for previously approved drugs, Dr. de Claro, clinical team leader in the FDA’s division of hematology products in Silver Spring, Md., said during an overview of the approvals at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
These include six new approvals for first-line treatment, and eight for pediatric indications, he said.
Highlights were discussed at two ASH-FDA joint symposia at the meeting, including one focused on the malignant hematology approvals, and another on the nonmalignant hematology approvals. In a video interview, Dr. de Claro provides some additional insight into their importance and about what might lie ahead.
“I think what’s exciting is that you have drug development occurring in more common conditions such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia, as well as in rare conditions, including hairy cell leukemia – and the first-ever approval in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis,” he said. “It’s been very busy at the FDA; stay tuned ... the year’s not done yet. There could be more coming and we certainly anticipate more applications in the future.”
Dr. de Claro is an FDA employee. He reported having no other relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – It was banner year for new hematology drug approvals, according to R. Angelo de Claro, MD, of the Food and Drug Administration.
, including 12 first-time approvals, 5 new biosimilars, and 15 new indications for previously approved drugs, Dr. de Claro, clinical team leader in the FDA’s division of hematology products in Silver Spring, Md., said during an overview of the approvals at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
These include six new approvals for first-line treatment, and eight for pediatric indications, he said.
Highlights were discussed at two ASH-FDA joint symposia at the meeting, including one focused on the malignant hematology approvals, and another on the nonmalignant hematology approvals. In a video interview, Dr. de Claro provides some additional insight into their importance and about what might lie ahead.
“I think what’s exciting is that you have drug development occurring in more common conditions such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia, as well as in rare conditions, including hairy cell leukemia – and the first-ever approval in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis,” he said. “It’s been very busy at the FDA; stay tuned ... the year’s not done yet. There could be more coming and we certainly anticipate more applications in the future.”
Dr. de Claro is an FDA employee. He reported having no other relevant disclosures.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Phase 3 study confirms biosimilarity of PF-05280586 with rituximab
SAN DIEGO – The potential rituximab biosimilar drug PF-05280586 showed efficacy, safety, immunogenicity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics similar to those of rituximab at up to 26 weeks in a randomized phase 3 study of treatment-naive patients with CD20-positive low tumor burden follicular lymphoma (LTB-FL).
The primary endpoint of overall response rate at 26 weeks was 75.5% in 196 patients randomized to receive PF-05280586, and 70.7% in 198 patients who received a rituximab reference product sourced from the European Union (MabThera; rituximab‑EU), Jeff Sharman, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“This resulted in a difference between the two arms of 4.66%,” said Dr. Sharman of Willamette Valley Cancer Institute and Research Center, Springfield, Ore.
The 95% confidence interval for this difference ... was entirely contained within the prespecified equivalence margin, he said.
“Depth of response was a key secondary endpoint, and rates of complete response were 29.3% and 30.4%, respectively,” he said, noting that rates of partial response, stable response, and progressive disease were also similar between the two study arms.
Estimated 1-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were also highly similar at 76.4% and 81.2% in the PF-05280586 and rituximab-EU arms.
Rapid depletion in CD19-positive B-cell counts was observed in both groups after initial dosing, with recovery by week 39 and a sustained increase until the end of week 52.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurred in 78.6% vs. 72.1% of patients in the PF‑05280586 vs. rituximab‑EU arms, respectively, and the rates of serious adverse events and grade 3 events were similar in the groups, as were rates of infusion interruptions or infusion-related reactions (IRRs), Dr. Sharman said.
IRRs occurred in about 25% of patients in each arm, and most were grade 1 or 2. Grade 3 IRRs occurred in 2.6% vs. 0.5% of patients in the groups, respectively, and no grade 4 IRRs occurred.
Rates of anti-drug antibodies were also similar in the two groups, as were serum drug concentrations – regardless of anti-drug antibody status, he noted.
Study subjects were adults with a mean age of 60 years and histologically confirmed CD20-positive grade 1-3a follicular lymphoma with no prior rituximab or system therapy for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). They had Ann Arbor disease stages II (26.9%), III (44.2%) or IV (28.9%), ECOG performance status of 0-1, and at least 1 measurable disease lesion identifiable on imaging.
Risk level as assessed by the Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index–2 was low in 28.4%, medium in 66%, and high in 5.6% of patients.
Treatment with each agent was given at intravenous doses of 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks at days 1, 8, 15, and 22.
PF-05280586 is being developed by Pfizer, and in this 52-week double-blind study – the largest study to date of the early use of the potential rituximab biosimilar in patients with previously untreated CD20-positive LTB-FL – the primary endpoint was met, demonstrating its therapeutic equivalence with rituximab-EU for overall response rate at week 26, Dr. Sharman said.
“These results therefore confirm the biosimilarity of PF-05280586 with rituximab-EU,” he concluded.
Of note, the reporting of these findings comes on the heels of the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a biosimilar rituximab product for the treatment of NHL; Celltrion’s product Truxima (formerly CT-P10), a biosimilar of Genentech’s Rituxan (rituximab), was approved Nov. 28 to treat adults with CD20-positive, B-cell NHL, either as a single agent or in combination with chemotherapy.
The PF-0528056 study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Sharman has been a consultant for, and/or received research funding and honoraria from Acerta, Pharmacyclics (an AbbVie Company), Pfizer, TG Therapeutics, Abbvie, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Sharman J et al. ASH 2018: Abstract 394.
SAN DIEGO – The potential rituximab biosimilar drug PF-05280586 showed efficacy, safety, immunogenicity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics similar to those of rituximab at up to 26 weeks in a randomized phase 3 study of treatment-naive patients with CD20-positive low tumor burden follicular lymphoma (LTB-FL).
The primary endpoint of overall response rate at 26 weeks was 75.5% in 196 patients randomized to receive PF-05280586, and 70.7% in 198 patients who received a rituximab reference product sourced from the European Union (MabThera; rituximab‑EU), Jeff Sharman, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“This resulted in a difference between the two arms of 4.66%,” said Dr. Sharman of Willamette Valley Cancer Institute and Research Center, Springfield, Ore.
The 95% confidence interval for this difference ... was entirely contained within the prespecified equivalence margin, he said.
“Depth of response was a key secondary endpoint, and rates of complete response were 29.3% and 30.4%, respectively,” he said, noting that rates of partial response, stable response, and progressive disease were also similar between the two study arms.
Estimated 1-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were also highly similar at 76.4% and 81.2% in the PF-05280586 and rituximab-EU arms.
Rapid depletion in CD19-positive B-cell counts was observed in both groups after initial dosing, with recovery by week 39 and a sustained increase until the end of week 52.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurred in 78.6% vs. 72.1% of patients in the PF‑05280586 vs. rituximab‑EU arms, respectively, and the rates of serious adverse events and grade 3 events were similar in the groups, as were rates of infusion interruptions or infusion-related reactions (IRRs), Dr. Sharman said.
IRRs occurred in about 25% of patients in each arm, and most were grade 1 or 2. Grade 3 IRRs occurred in 2.6% vs. 0.5% of patients in the groups, respectively, and no grade 4 IRRs occurred.
Rates of anti-drug antibodies were also similar in the two groups, as were serum drug concentrations – regardless of anti-drug antibody status, he noted.
Study subjects were adults with a mean age of 60 years and histologically confirmed CD20-positive grade 1-3a follicular lymphoma with no prior rituximab or system therapy for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). They had Ann Arbor disease stages II (26.9%), III (44.2%) or IV (28.9%), ECOG performance status of 0-1, and at least 1 measurable disease lesion identifiable on imaging.
Risk level as assessed by the Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index–2 was low in 28.4%, medium in 66%, and high in 5.6% of patients.
Treatment with each agent was given at intravenous doses of 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks at days 1, 8, 15, and 22.
PF-05280586 is being developed by Pfizer, and in this 52-week double-blind study – the largest study to date of the early use of the potential rituximab biosimilar in patients with previously untreated CD20-positive LTB-FL – the primary endpoint was met, demonstrating its therapeutic equivalence with rituximab-EU for overall response rate at week 26, Dr. Sharman said.
“These results therefore confirm the biosimilarity of PF-05280586 with rituximab-EU,” he concluded.
Of note, the reporting of these findings comes on the heels of the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a biosimilar rituximab product for the treatment of NHL; Celltrion’s product Truxima (formerly CT-P10), a biosimilar of Genentech’s Rituxan (rituximab), was approved Nov. 28 to treat adults with CD20-positive, B-cell NHL, either as a single agent or in combination with chemotherapy.
The PF-0528056 study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Sharman has been a consultant for, and/or received research funding and honoraria from Acerta, Pharmacyclics (an AbbVie Company), Pfizer, TG Therapeutics, Abbvie, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Sharman J et al. ASH 2018: Abstract 394.
SAN DIEGO – The potential rituximab biosimilar drug PF-05280586 showed efficacy, safety, immunogenicity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics similar to those of rituximab at up to 26 weeks in a randomized phase 3 study of treatment-naive patients with CD20-positive low tumor burden follicular lymphoma (LTB-FL).
The primary endpoint of overall response rate at 26 weeks was 75.5% in 196 patients randomized to receive PF-05280586, and 70.7% in 198 patients who received a rituximab reference product sourced from the European Union (MabThera; rituximab‑EU), Jeff Sharman, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“This resulted in a difference between the two arms of 4.66%,” said Dr. Sharman of Willamette Valley Cancer Institute and Research Center, Springfield, Ore.
The 95% confidence interval for this difference ... was entirely contained within the prespecified equivalence margin, he said.
“Depth of response was a key secondary endpoint, and rates of complete response were 29.3% and 30.4%, respectively,” he said, noting that rates of partial response, stable response, and progressive disease were also similar between the two study arms.
Estimated 1-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were also highly similar at 76.4% and 81.2% in the PF-05280586 and rituximab-EU arms.
Rapid depletion in CD19-positive B-cell counts was observed in both groups after initial dosing, with recovery by week 39 and a sustained increase until the end of week 52.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurred in 78.6% vs. 72.1% of patients in the PF‑05280586 vs. rituximab‑EU arms, respectively, and the rates of serious adverse events and grade 3 events were similar in the groups, as were rates of infusion interruptions or infusion-related reactions (IRRs), Dr. Sharman said.
IRRs occurred in about 25% of patients in each arm, and most were grade 1 or 2. Grade 3 IRRs occurred in 2.6% vs. 0.5% of patients in the groups, respectively, and no grade 4 IRRs occurred.
Rates of anti-drug antibodies were also similar in the two groups, as were serum drug concentrations – regardless of anti-drug antibody status, he noted.
Study subjects were adults with a mean age of 60 years and histologically confirmed CD20-positive grade 1-3a follicular lymphoma with no prior rituximab or system therapy for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). They had Ann Arbor disease stages II (26.9%), III (44.2%) or IV (28.9%), ECOG performance status of 0-1, and at least 1 measurable disease lesion identifiable on imaging.
Risk level as assessed by the Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index–2 was low in 28.4%, medium in 66%, and high in 5.6% of patients.
Treatment with each agent was given at intravenous doses of 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks at days 1, 8, 15, and 22.
PF-05280586 is being developed by Pfizer, and in this 52-week double-blind study – the largest study to date of the early use of the potential rituximab biosimilar in patients with previously untreated CD20-positive LTB-FL – the primary endpoint was met, demonstrating its therapeutic equivalence with rituximab-EU for overall response rate at week 26, Dr. Sharman said.
“These results therefore confirm the biosimilarity of PF-05280586 with rituximab-EU,” he concluded.
Of note, the reporting of these findings comes on the heels of the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a biosimilar rituximab product for the treatment of NHL; Celltrion’s product Truxima (formerly CT-P10), a biosimilar of Genentech’s Rituxan (rituximab), was approved Nov. 28 to treat adults with CD20-positive, B-cell NHL, either as a single agent or in combination with chemotherapy.
The PF-0528056 study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Sharman has been a consultant for, and/or received research funding and honoraria from Acerta, Pharmacyclics (an AbbVie Company), Pfizer, TG Therapeutics, Abbvie, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Sharman J et al. ASH 2018: Abstract 394.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point: PF-05280586 shows biosimilarity to rituximab at up to 26 weeks.
Major finding: ORR at 26 weeks was 75.5% vs. 70.7% with PF-05280586 vs. rituximab, respectively.
Study details: A phase 3 study of 394 patients.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Sharman has been a consultant for, and/or received research funding and honoraria from Acerta, Pharmacyclics (an AbbVie Company), Pfizer, TG Therapeutics, Abbvie, and Genentech.
Source: Sharman J et al. ASH 2018: Abstract 394.
CLL resistance mechanism to venetoclax identified
SAN DIEGO – A recurrent mutation in BCL2, the therapeutic target of venetoclax (Venclexta), appears to be a major contributor to drug resistance in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), investigators reported.
The mutation has been detected in some patients with CLL up to 2 years before resistance to venetoclax actually develops, said lead author Piers Blombery, MBBS, from the Peter MacCallum Cancer Center in Melbourne.
“We have identified the first acquired BCL2 mutation developed in patients clinically treated with venetoclax,” he said in a late-breaking oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The mutation, which the investigators have labeled BCL2 Gly101Val, “is a recurrent and frequent mediator of resistance and may be detected years before clinical relapse occurs,” he added.
The paper was published online in Cancer Discovery (2018 Dec 4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1119) to coincide with the presentation at ASH.
Despite the demonstrated efficacy of venetoclax as continuous therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL, the majority of patients experience disease progression, prompting the investigators to explore molecular mechanisms of secondary resistance.
To do this, they analyzed paired samples from 15 patients with CLL, enrolled in clinical trials of venetoclax, collected both before the start of venetoclax therapy and at the time of disease progression.
In seven of the patients, they identified a novel mutation that showed up at the time of progression, but was absent from the pre-venetoclax samples. The mutation first became detectable from about 19 to 42 months after the start of therapy and preceded clinical progression by as much as 25 months, the investigators found.
They pinned the mutation down to the BH3-binding groove on BCL2, the same molecular site targeted by venetoclax. They found that the mutation was not present in samples from 96 patients with venetoclax-naive CLL nor in any other B-cell malignancies. Searches for references to the mutation in both a cancer database (COSMIC) and a population database (gnomAD) came up empty.
In other experiments, they determined that cell lines overexpressing BCL2 Gly101Val are resistant to venetoclax, and that in the presence of venetoclax in vitro, BCL2 Gly101Val-expressing cells have a growth advantage, compared with wild type cells.
Additionally, they showed that the mutation results in impaired venetoclax binding in vitro.
“BCL2 Gly101Val is observed subclonally, implicating multiple mechanisms of venetoclax resistance in the same patient,” Dr. Blombery said.
In an interview, Dr. Blombery said that the identification of the resistance mutation is a strong rationale for using combination therapy to treat patients with relapsed or refractory CLL to help prevent or attenuate selection pressures that lead to resistance.
The investigators were supported by the Wilson Center for Lymphoma Genomics, Snowdome Foundation, National Health Medical Research Council, Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, Leukemia Foundation, Cancer Council of Victoria, and Australian Cancer Research Foundation. Dr. Blombery reported having no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Blombery P et al. ASH 2018, Abstract LBA-7.
SAN DIEGO – A recurrent mutation in BCL2, the therapeutic target of venetoclax (Venclexta), appears to be a major contributor to drug resistance in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), investigators reported.
The mutation has been detected in some patients with CLL up to 2 years before resistance to venetoclax actually develops, said lead author Piers Blombery, MBBS, from the Peter MacCallum Cancer Center in Melbourne.
“We have identified the first acquired BCL2 mutation developed in patients clinically treated with venetoclax,” he said in a late-breaking oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The mutation, which the investigators have labeled BCL2 Gly101Val, “is a recurrent and frequent mediator of resistance and may be detected years before clinical relapse occurs,” he added.
The paper was published online in Cancer Discovery (2018 Dec 4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1119) to coincide with the presentation at ASH.
Despite the demonstrated efficacy of venetoclax as continuous therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL, the majority of patients experience disease progression, prompting the investigators to explore molecular mechanisms of secondary resistance.
To do this, they analyzed paired samples from 15 patients with CLL, enrolled in clinical trials of venetoclax, collected both before the start of venetoclax therapy and at the time of disease progression.
In seven of the patients, they identified a novel mutation that showed up at the time of progression, but was absent from the pre-venetoclax samples. The mutation first became detectable from about 19 to 42 months after the start of therapy and preceded clinical progression by as much as 25 months, the investigators found.
They pinned the mutation down to the BH3-binding groove on BCL2, the same molecular site targeted by venetoclax. They found that the mutation was not present in samples from 96 patients with venetoclax-naive CLL nor in any other B-cell malignancies. Searches for references to the mutation in both a cancer database (COSMIC) and a population database (gnomAD) came up empty.
In other experiments, they determined that cell lines overexpressing BCL2 Gly101Val are resistant to venetoclax, and that in the presence of venetoclax in vitro, BCL2 Gly101Val-expressing cells have a growth advantage, compared with wild type cells.
Additionally, they showed that the mutation results in impaired venetoclax binding in vitro.
“BCL2 Gly101Val is observed subclonally, implicating multiple mechanisms of venetoclax resistance in the same patient,” Dr. Blombery said.
In an interview, Dr. Blombery said that the identification of the resistance mutation is a strong rationale for using combination therapy to treat patients with relapsed or refractory CLL to help prevent or attenuate selection pressures that lead to resistance.
The investigators were supported by the Wilson Center for Lymphoma Genomics, Snowdome Foundation, National Health Medical Research Council, Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, Leukemia Foundation, Cancer Council of Victoria, and Australian Cancer Research Foundation. Dr. Blombery reported having no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Blombery P et al. ASH 2018, Abstract LBA-7.
SAN DIEGO – A recurrent mutation in BCL2, the therapeutic target of venetoclax (Venclexta), appears to be a major contributor to drug resistance in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), investigators reported.
The mutation has been detected in some patients with CLL up to 2 years before resistance to venetoclax actually develops, said lead author Piers Blombery, MBBS, from the Peter MacCallum Cancer Center in Melbourne.
“We have identified the first acquired BCL2 mutation developed in patients clinically treated with venetoclax,” he said in a late-breaking oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The mutation, which the investigators have labeled BCL2 Gly101Val, “is a recurrent and frequent mediator of resistance and may be detected years before clinical relapse occurs,” he added.
The paper was published online in Cancer Discovery (2018 Dec 4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1119) to coincide with the presentation at ASH.
Despite the demonstrated efficacy of venetoclax as continuous therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL, the majority of patients experience disease progression, prompting the investigators to explore molecular mechanisms of secondary resistance.
To do this, they analyzed paired samples from 15 patients with CLL, enrolled in clinical trials of venetoclax, collected both before the start of venetoclax therapy and at the time of disease progression.
In seven of the patients, they identified a novel mutation that showed up at the time of progression, but was absent from the pre-venetoclax samples. The mutation first became detectable from about 19 to 42 months after the start of therapy and preceded clinical progression by as much as 25 months, the investigators found.
They pinned the mutation down to the BH3-binding groove on BCL2, the same molecular site targeted by venetoclax. They found that the mutation was not present in samples from 96 patients with venetoclax-naive CLL nor in any other B-cell malignancies. Searches for references to the mutation in both a cancer database (COSMIC) and a population database (gnomAD) came up empty.
In other experiments, they determined that cell lines overexpressing BCL2 Gly101Val are resistant to venetoclax, and that in the presence of venetoclax in vitro, BCL2 Gly101Val-expressing cells have a growth advantage, compared with wild type cells.
Additionally, they showed that the mutation results in impaired venetoclax binding in vitro.
“BCL2 Gly101Val is observed subclonally, implicating multiple mechanisms of venetoclax resistance in the same patient,” Dr. Blombery said.
In an interview, Dr. Blombery said that the identification of the resistance mutation is a strong rationale for using combination therapy to treat patients with relapsed or refractory CLL to help prevent or attenuate selection pressures that lead to resistance.
The investigators were supported by the Wilson Center for Lymphoma Genomics, Snowdome Foundation, National Health Medical Research Council, Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, Leukemia Foundation, Cancer Council of Victoria, and Australian Cancer Research Foundation. Dr. Blombery reported having no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Blombery P et al. ASH 2018, Abstract LBA-7.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The mutation was identified in samples from seven patients after venetoclax therapy, but not in any of the pretherapy samples.
Study details: Genetic analysis of CLL mutations in 15 patients enrolled in clinical trials of venetoclax.
Disclosures: The investigators were supported by the Wilson Center for Lymphoma Genomics, Snowdome Foundation, National Health Medical Research Council, Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, Leukemia Foundation, Cancer Council of Victoria, and Australian Cancer Research Foundation. Dr. Blombery reported having no relevant disclosures.
Source: Blombery P et al. ASH 2018, Abstract LBA-7.
Shorter R-CHOP regimen noninferior in certain DLBCL patients
SAN DIEGO—A shortened regimen of four cycles of rituximab (R) plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) chemotherapy was noninferior in efficacy to the standard six cycles of R-CHOP in younger patients with favorable-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to investigators of the FLYER trial.
In addition, the truncated regimen was associated with about a one-third reduction in non-hematologic adverse events.
Viola Poeschel, MD, of Saarland University Medical School in Homburg/Saar, Germany, reported results of this study on behalf of the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group/German Lymphoma Alliance at the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 781).
Among 588 evaluable patients younger than 60 with favorable-prognosis DLBCL, there were no significant differences in progression-free survival (PFS), event-free survival (EFS), or overall survival (OS) between patients who received four cycles of R-CHOP and those who received six cycles, Dr. Poeschel reported.
“Six cycles of R-CHOP led to a higher toxicity with respect to leukocytopenia and anemia, both of any grade and also of grades 3 to 4, compared to four cycles of R-CHOP,” she said.
The findings suggest that, for younger patients with favorable-prognosis DLBCL—defined as an age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score of 0 and low tumor burden (less than 7.5 cm)—four cycles of R-CHOP can be a new standard of care, Dr. Poeschel said.
The investigators were prompted to look at the question of a shorter R-CHOP regimen by results of the MInT trial, in which a subpopulation of favorable-prognosis DLBCL patients had a 3-year PFS rate of 89%.
The FLYER trial (NCT00278421) was designed as a non-inferiority study to see whether, in a similar group of patients, reducing the number of R-CHOP cycles could maintain efficacy while reducing toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 66 months, the PFS rate, the primary endpoint, was 94% in the six-cycle group and 96% for the four-cycle group.
“As the lower limit of the 95% confidence interval of our experimental arm was 94%, it is shown that it is definitely non-inferior to the standard arm, six cycles of R-CHOP,” Dr. Poeschel said.
Similarly, the rate of 3-year OS was 98% in the six-cycle group, compared with 99% in the four-cycle group, and the survival curves were virtually superimposable out to more than 10 years of follow-up.
Treatment with six cycles was associated with more frequent hematologic adverse events than four cycles. Leukopenia of any grade occurred in 237 and 171 patients, respectively. Grade 3-4 leukopenia occurred in 110 and 80 patients, respectively.
Any-grade anemia occurred in 172 patients assigned to six cycles and 107 assigned to four cycles. Rates of grade 3-4 anemia were similar between the groups, as were rates of thrombocytopenia of any grade or grade 3-4.
Non-hematologic adverse events of any grade or grade 3-4 that were more frequent with six cycles included parasthesia, nausea, infection, vomiting, and mucositis.
The total number of non-hematologic adverse events was reduced by about one-third.
“We are certainly always looking for ways to make treatments easier for our patients to reduce adverse effects, and, certainly, for this subgroup of patients, it appears that we can make their treatment shorter and have less burden but equivalent efficacy,” said David Steensma, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Cancer Center in Boston, Massachusetts.
Drs. Steensma and Poeschel both cautioned that the results of this study pertain only to those patients with DLBCL who are younger and have favorable-prognosis disease.
“We can’t extend it to other subtypes of large-cell lymphoma, but that’s always a laudable goal, so I think this will immediately influence clinical practice,” Dr. Steensma said.
The study was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe. Dr. Poeschel disclosed travel grants from Roche and Amgen. Dr. Steensma had no disclosures relevant to the study.
SAN DIEGO—A shortened regimen of four cycles of rituximab (R) plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) chemotherapy was noninferior in efficacy to the standard six cycles of R-CHOP in younger patients with favorable-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to investigators of the FLYER trial.
In addition, the truncated regimen was associated with about a one-third reduction in non-hematologic adverse events.
Viola Poeschel, MD, of Saarland University Medical School in Homburg/Saar, Germany, reported results of this study on behalf of the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group/German Lymphoma Alliance at the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 781).
Among 588 evaluable patients younger than 60 with favorable-prognosis DLBCL, there were no significant differences in progression-free survival (PFS), event-free survival (EFS), or overall survival (OS) between patients who received four cycles of R-CHOP and those who received six cycles, Dr. Poeschel reported.
“Six cycles of R-CHOP led to a higher toxicity with respect to leukocytopenia and anemia, both of any grade and also of grades 3 to 4, compared to four cycles of R-CHOP,” she said.
The findings suggest that, for younger patients with favorable-prognosis DLBCL—defined as an age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score of 0 and low tumor burden (less than 7.5 cm)—four cycles of R-CHOP can be a new standard of care, Dr. Poeschel said.
The investigators were prompted to look at the question of a shorter R-CHOP regimen by results of the MInT trial, in which a subpopulation of favorable-prognosis DLBCL patients had a 3-year PFS rate of 89%.
The FLYER trial (NCT00278421) was designed as a non-inferiority study to see whether, in a similar group of patients, reducing the number of R-CHOP cycles could maintain efficacy while reducing toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 66 months, the PFS rate, the primary endpoint, was 94% in the six-cycle group and 96% for the four-cycle group.
“As the lower limit of the 95% confidence interval of our experimental arm was 94%, it is shown that it is definitely non-inferior to the standard arm, six cycles of R-CHOP,” Dr. Poeschel said.
Similarly, the rate of 3-year OS was 98% in the six-cycle group, compared with 99% in the four-cycle group, and the survival curves were virtually superimposable out to more than 10 years of follow-up.
Treatment with six cycles was associated with more frequent hematologic adverse events than four cycles. Leukopenia of any grade occurred in 237 and 171 patients, respectively. Grade 3-4 leukopenia occurred in 110 and 80 patients, respectively.
Any-grade anemia occurred in 172 patients assigned to six cycles and 107 assigned to four cycles. Rates of grade 3-4 anemia were similar between the groups, as were rates of thrombocytopenia of any grade or grade 3-4.
Non-hematologic adverse events of any grade or grade 3-4 that were more frequent with six cycles included parasthesia, nausea, infection, vomiting, and mucositis.
The total number of non-hematologic adverse events was reduced by about one-third.
“We are certainly always looking for ways to make treatments easier for our patients to reduce adverse effects, and, certainly, for this subgroup of patients, it appears that we can make their treatment shorter and have less burden but equivalent efficacy,” said David Steensma, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Cancer Center in Boston, Massachusetts.
Drs. Steensma and Poeschel both cautioned that the results of this study pertain only to those patients with DLBCL who are younger and have favorable-prognosis disease.
“We can’t extend it to other subtypes of large-cell lymphoma, but that’s always a laudable goal, so I think this will immediately influence clinical practice,” Dr. Steensma said.
The study was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe. Dr. Poeschel disclosed travel grants from Roche and Amgen. Dr. Steensma had no disclosures relevant to the study.
SAN DIEGO—A shortened regimen of four cycles of rituximab (R) plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) chemotherapy was noninferior in efficacy to the standard six cycles of R-CHOP in younger patients with favorable-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to investigators of the FLYER trial.
In addition, the truncated regimen was associated with about a one-third reduction in non-hematologic adverse events.
Viola Poeschel, MD, of Saarland University Medical School in Homburg/Saar, Germany, reported results of this study on behalf of the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group/German Lymphoma Alliance at the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 781).
Among 588 evaluable patients younger than 60 with favorable-prognosis DLBCL, there were no significant differences in progression-free survival (PFS), event-free survival (EFS), or overall survival (OS) between patients who received four cycles of R-CHOP and those who received six cycles, Dr. Poeschel reported.
“Six cycles of R-CHOP led to a higher toxicity with respect to leukocytopenia and anemia, both of any grade and also of grades 3 to 4, compared to four cycles of R-CHOP,” she said.
The findings suggest that, for younger patients with favorable-prognosis DLBCL—defined as an age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score of 0 and low tumor burden (less than 7.5 cm)—four cycles of R-CHOP can be a new standard of care, Dr. Poeschel said.
The investigators were prompted to look at the question of a shorter R-CHOP regimen by results of the MInT trial, in which a subpopulation of favorable-prognosis DLBCL patients had a 3-year PFS rate of 89%.
The FLYER trial (NCT00278421) was designed as a non-inferiority study to see whether, in a similar group of patients, reducing the number of R-CHOP cycles could maintain efficacy while reducing toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 66 months, the PFS rate, the primary endpoint, was 94% in the six-cycle group and 96% for the four-cycle group.
“As the lower limit of the 95% confidence interval of our experimental arm was 94%, it is shown that it is definitely non-inferior to the standard arm, six cycles of R-CHOP,” Dr. Poeschel said.
Similarly, the rate of 3-year OS was 98% in the six-cycle group, compared with 99% in the four-cycle group, and the survival curves were virtually superimposable out to more than 10 years of follow-up.
Treatment with six cycles was associated with more frequent hematologic adverse events than four cycles. Leukopenia of any grade occurred in 237 and 171 patients, respectively. Grade 3-4 leukopenia occurred in 110 and 80 patients, respectively.
Any-grade anemia occurred in 172 patients assigned to six cycles and 107 assigned to four cycles. Rates of grade 3-4 anemia were similar between the groups, as were rates of thrombocytopenia of any grade or grade 3-4.
Non-hematologic adverse events of any grade or grade 3-4 that were more frequent with six cycles included parasthesia, nausea, infection, vomiting, and mucositis.
The total number of non-hematologic adverse events was reduced by about one-third.
“We are certainly always looking for ways to make treatments easier for our patients to reduce adverse effects, and, certainly, for this subgroup of patients, it appears that we can make their treatment shorter and have less burden but equivalent efficacy,” said David Steensma, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Cancer Center in Boston, Massachusetts.
Drs. Steensma and Poeschel both cautioned that the results of this study pertain only to those patients with DLBCL who are younger and have favorable-prognosis disease.
“We can’t extend it to other subtypes of large-cell lymphoma, but that’s always a laudable goal, so I think this will immediately influence clinical practice,” Dr. Steensma said.
The study was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe. Dr. Poeschel disclosed travel grants from Roche and Amgen. Dr. Steensma had no disclosures relevant to the study.
Update shows durable responses in rel/ref DLBCL
SAN DIEGO—An updated analysis of the JULIET trial showed that tisagenlecleucel produced a high rate of durable responses in adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
After a median follow-up of 19 months, two-thirds of adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who had early responses to the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy remained in remission with no evidence of minimal residual disease.
“Since the previous report, no new deaths have been reported due to any cause other than patient disease progression, no treatment-related mortality was seen throughout the study, and there were three early deaths, all related to lymphoma that progressed,” said study investigator Richard Thomas Maziarz, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University’s Knight Cancer Institute in Portland.
Dr. Maziarz and his colleagues reported the updated study results at the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 1684). Results were published simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine. Data reported here are based on the ASH data.
JULIET then
In the phase 2, single-arm trial, investigators enrolled adults with DLBCL who had relapsed or were refractory after two or more prior lines of therapy and who were either ineligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) or who experienced disease progression after HSCT.
Interim results of the study were previously reported at the 22nd Congress of the European Hematology Association in 2017.
At that meeting, Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, of the University of Lyon in France, presented results of an analysis of available efficacy data on 51 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up.
In this population, the best overall response rate (ORR) was 59%. Three-month ORR was 45%, consisting of 37% complete responses (CR) and 8% partial responses (PR).
Relapse-free survival at 6 months was 79%, and all patients who had responses at 3 months continued to have responses at the time of data cutoff.
JULIET now
The current analysis was completed after a median time from infusion to data cutoff of 19 months as of May 21, 2018. The analysis included 115 patients who received CAR T-cell infusions, 99 of whom were evaluable for efficacy.
As reported at ASH, the best ORR, the primary endpoint, was 54%, comprised of 40% CR and 13% PR.
Fifty-four percent of patients who had achieved PR converted to CR.
The response rates were consistent across all subgroups, regardless of age, sex, previous response status, International Prognostic Index score at enrollment, prior therapy, molecular subtype, and other factors.
Estimated relapse-free survival 12 months after documentation of an initial response was 64%.
The median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff, and the median overall survival had not been reached for patients with a CR.
Median overall survival in this heavily pretreated population as a whole (all patients who received CAR T-cell infusions) was 11.1 months and not reached for patients in CR.
Adverse events of special interest included grade 3 or 4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in 23% of patients, prolonged cytopenia in 34%, infections in 19%, neurologic events in 11%, febrile neutropenia in 15%, and tumor lysis syndrome in 2%.
There were no deaths attributable to the treatment, CRS, or to cerebral edema, a complication of CAR T-cell therapy that appears to be related to the costimulatory molecule used in various constructs.
The JULIET trial is supported by Novartis. Dr. Maziarz disclosed honoraria, consultancy fees, and/or research funding from Novartis, Incyte, Juno Therapeutics, and Kite Therapeutics as well as patents/royalties from Athersys, Inc.
SAN DIEGO—An updated analysis of the JULIET trial showed that tisagenlecleucel produced a high rate of durable responses in adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
After a median follow-up of 19 months, two-thirds of adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who had early responses to the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy remained in remission with no evidence of minimal residual disease.
“Since the previous report, no new deaths have been reported due to any cause other than patient disease progression, no treatment-related mortality was seen throughout the study, and there were three early deaths, all related to lymphoma that progressed,” said study investigator Richard Thomas Maziarz, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University’s Knight Cancer Institute in Portland.
Dr. Maziarz and his colleagues reported the updated study results at the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 1684). Results were published simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine. Data reported here are based on the ASH data.
JULIET then
In the phase 2, single-arm trial, investigators enrolled adults with DLBCL who had relapsed or were refractory after two or more prior lines of therapy and who were either ineligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) or who experienced disease progression after HSCT.
Interim results of the study were previously reported at the 22nd Congress of the European Hematology Association in 2017.
At that meeting, Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, of the University of Lyon in France, presented results of an analysis of available efficacy data on 51 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up.
In this population, the best overall response rate (ORR) was 59%. Three-month ORR was 45%, consisting of 37% complete responses (CR) and 8% partial responses (PR).
Relapse-free survival at 6 months was 79%, and all patients who had responses at 3 months continued to have responses at the time of data cutoff.
JULIET now
The current analysis was completed after a median time from infusion to data cutoff of 19 months as of May 21, 2018. The analysis included 115 patients who received CAR T-cell infusions, 99 of whom were evaluable for efficacy.
As reported at ASH, the best ORR, the primary endpoint, was 54%, comprised of 40% CR and 13% PR.
Fifty-four percent of patients who had achieved PR converted to CR.
The response rates were consistent across all subgroups, regardless of age, sex, previous response status, International Prognostic Index score at enrollment, prior therapy, molecular subtype, and other factors.
Estimated relapse-free survival 12 months after documentation of an initial response was 64%.
The median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff, and the median overall survival had not been reached for patients with a CR.
Median overall survival in this heavily pretreated population as a whole (all patients who received CAR T-cell infusions) was 11.1 months and not reached for patients in CR.
Adverse events of special interest included grade 3 or 4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in 23% of patients, prolonged cytopenia in 34%, infections in 19%, neurologic events in 11%, febrile neutropenia in 15%, and tumor lysis syndrome in 2%.
There were no deaths attributable to the treatment, CRS, or to cerebral edema, a complication of CAR T-cell therapy that appears to be related to the costimulatory molecule used in various constructs.
The JULIET trial is supported by Novartis. Dr. Maziarz disclosed honoraria, consultancy fees, and/or research funding from Novartis, Incyte, Juno Therapeutics, and Kite Therapeutics as well as patents/royalties from Athersys, Inc.
SAN DIEGO—An updated analysis of the JULIET trial showed that tisagenlecleucel produced a high rate of durable responses in adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
After a median follow-up of 19 months, two-thirds of adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who had early responses to the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy remained in remission with no evidence of minimal residual disease.
“Since the previous report, no new deaths have been reported due to any cause other than patient disease progression, no treatment-related mortality was seen throughout the study, and there were three early deaths, all related to lymphoma that progressed,” said study investigator Richard Thomas Maziarz, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University’s Knight Cancer Institute in Portland.
Dr. Maziarz and his colleagues reported the updated study results at the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 1684). Results were published simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine. Data reported here are based on the ASH data.
JULIET then
In the phase 2, single-arm trial, investigators enrolled adults with DLBCL who had relapsed or were refractory after two or more prior lines of therapy and who were either ineligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) or who experienced disease progression after HSCT.
Interim results of the study were previously reported at the 22nd Congress of the European Hematology Association in 2017.
At that meeting, Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, of the University of Lyon in France, presented results of an analysis of available efficacy data on 51 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up.
In this population, the best overall response rate (ORR) was 59%. Three-month ORR was 45%, consisting of 37% complete responses (CR) and 8% partial responses (PR).
Relapse-free survival at 6 months was 79%, and all patients who had responses at 3 months continued to have responses at the time of data cutoff.
JULIET now
The current analysis was completed after a median time from infusion to data cutoff of 19 months as of May 21, 2018. The analysis included 115 patients who received CAR T-cell infusions, 99 of whom were evaluable for efficacy.
As reported at ASH, the best ORR, the primary endpoint, was 54%, comprised of 40% CR and 13% PR.
Fifty-four percent of patients who had achieved PR converted to CR.
The response rates were consistent across all subgroups, regardless of age, sex, previous response status, International Prognostic Index score at enrollment, prior therapy, molecular subtype, and other factors.
Estimated relapse-free survival 12 months after documentation of an initial response was 64%.
The median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff, and the median overall survival had not been reached for patients with a CR.
Median overall survival in this heavily pretreated population as a whole (all patients who received CAR T-cell infusions) was 11.1 months and not reached for patients in CR.
Adverse events of special interest included grade 3 or 4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in 23% of patients, prolonged cytopenia in 34%, infections in 19%, neurologic events in 11%, febrile neutropenia in 15%, and tumor lysis syndrome in 2%.
There were no deaths attributable to the treatment, CRS, or to cerebral edema, a complication of CAR T-cell therapy that appears to be related to the costimulatory molecule used in various constructs.
The JULIET trial is supported by Novartis. Dr. Maziarz disclosed honoraria, consultancy fees, and/or research funding from Novartis, Incyte, Juno Therapeutics, and Kite Therapeutics as well as patents/royalties from Athersys, Inc.
JULIET: CAR T cells go the distance in r/r DLBCL
SAN DIEGO – Two-thirds of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who had early responses to chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) therapy with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) remain in remission with no evidence of minimal residual disease, according to an updated analysis of the JULIET trial.
In the single-arm, open-label trial, the overall response rate after 19 months of follow-up was 54%, including 40% complete remissions and 14% partial remissions. The median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff, and the median overall survival had not been reached for patients with a complete remission. Overall survival in this heavily pretreated population as a whole (all patients who received CAR T-cell infusions) was 11.1 months.
Adverse events were similar to those previously reported and were manageable, according to investigator Richard Thomas Maziarz, MD, from the Oregon Health & Science Knight Cancer Institute in Portland.
In this video interview at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Dr. Maziarz discusses the promising results using CAR T cells in this difficult to treat population.
SAN DIEGO – Two-thirds of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who had early responses to chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) therapy with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) remain in remission with no evidence of minimal residual disease, according to an updated analysis of the JULIET trial.
In the single-arm, open-label trial, the overall response rate after 19 months of follow-up was 54%, including 40% complete remissions and 14% partial remissions. The median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff, and the median overall survival had not been reached for patients with a complete remission. Overall survival in this heavily pretreated population as a whole (all patients who received CAR T-cell infusions) was 11.1 months.
Adverse events were similar to those previously reported and were manageable, according to investigator Richard Thomas Maziarz, MD, from the Oregon Health & Science Knight Cancer Institute in Portland.
In this video interview at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Dr. Maziarz discusses the promising results using CAR T cells in this difficult to treat population.
SAN DIEGO – Two-thirds of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who had early responses to chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) therapy with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) remain in remission with no evidence of minimal residual disease, according to an updated analysis of the JULIET trial.
In the single-arm, open-label trial, the overall response rate after 19 months of follow-up was 54%, including 40% complete remissions and 14% partial remissions. The median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff, and the median overall survival had not been reached for patients with a complete remission. Overall survival in this heavily pretreated population as a whole (all patients who received CAR T-cell infusions) was 11.1 months.
Adverse events were similar to those previously reported and were manageable, according to investigator Richard Thomas Maziarz, MD, from the Oregon Health & Science Knight Cancer Institute in Portland.
In this video interview at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Dr. Maziarz discusses the promising results using CAR T cells in this difficult to treat population.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
JULIET: CAR T cells keep trucking against DLBCL
SAN DIEGO – Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) is associated with a high rate of durable responses in adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, an updated analysis of the JULIET trial showed.
After a median follow-up of 19 months, two-thirds of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who had early responses to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel remained in remission with no evidence of minimal residual disease, reported Richard Thomas Maziarz, MD, from the Oregon Health & Science Knight Cancer Institute in Portland, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Since the previous report, no new deaths have been reported due to any cause other than patient disease progression. No treatment-related mortality was seen throughout the study, and there were three early deaths, all related to lymphoma that progressed,” he said in a briefing prior to presentation of the data in a scientific poster.
The updated study results were published simultaneously online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
JULIET then
In the phase 2, single-arm trial, investigators enrolled adults with DLBCL that had relapsed or was refractory after two or more prior lines of therapy and who were either ineligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant or who experienced disease progression after transplant.
Interim results of the study were previously reported at the European Hematology Association Congress in 2017.
At that meeting, Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, from the University of Lyon (France), presented results of an analysis of available efficacy data on 51 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up. In this population, the best overall response rate was 59%. The 3-month overall response rate was 45%, consisting of 37% complete responses and 8% partial responses. Relapse-free survival at 6 months was 79% and all patients who had responses at 3 months continued to have responses at the time of data cutoff.
JULIET now
In the most recent analysis, completed after a median time from infusion to data cutoff of 14 months, the investigators reported on efficacy in 93 patients who received CAR T-cell infusions.
The best overall response rate, the primary endpoint, was 52%, comprising 40% complete responses and 12% partial responses. The response rates were consistent across all prognostic subgroups, including age, sex, previous response status, International Prognostic Index score at enrollment, prior therapy, molecular subtype, and other factors.
Estimated relapse-free survival 12 months after documentation of an initial response was 65%, and was 79% among patients who had complete responses.
The median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff; the median overall survival had not been reached for patients with a complete remission. Overall survival in this heavily pretreated population as a whole (all patients who received CAR T-cell infusions) was 11.1 months.
Adverse events of special interest included grade 3 or 4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in 23% of patients, prolonged cytopenia in 34%, infections in 19%, neurologic events in 11%, febrile neutropenia in 15%, and tumor lysis syndrome in 2%.
There were no deaths attributable to CRS or to cerebral edema, a complication of CAR T-cell therapy that appears to be related to the costimulatory molecule used in various constructs.
“Patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who are not eligible for high-dose therapy and hematopoietic cell transplantation or for whom such therapy was not successful have very few treatment options. For these patients, tisagenlecleucel shows promise that will need to be confirmed through larger studies with longer follow-up,” the investigators wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The JULIET Trial is supported by Novartis. Dr. Maziar reported personal fees from Incyte, Kite Therapeutics, and Athersys.
SOURCE: Maziarz RT et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1804980.
SAN DIEGO – Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) is associated with a high rate of durable responses in adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, an updated analysis of the JULIET trial showed.
After a median follow-up of 19 months, two-thirds of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who had early responses to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel remained in remission with no evidence of minimal residual disease, reported Richard Thomas Maziarz, MD, from the Oregon Health & Science Knight Cancer Institute in Portland, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Since the previous report, no new deaths have been reported due to any cause other than patient disease progression. No treatment-related mortality was seen throughout the study, and there were three early deaths, all related to lymphoma that progressed,” he said in a briefing prior to presentation of the data in a scientific poster.
The updated study results were published simultaneously online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
JULIET then
In the phase 2, single-arm trial, investigators enrolled adults with DLBCL that had relapsed or was refractory after two or more prior lines of therapy and who were either ineligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant or who experienced disease progression after transplant.
Interim results of the study were previously reported at the European Hematology Association Congress in 2017.
At that meeting, Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, from the University of Lyon (France), presented results of an analysis of available efficacy data on 51 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up. In this population, the best overall response rate was 59%. The 3-month overall response rate was 45%, consisting of 37% complete responses and 8% partial responses. Relapse-free survival at 6 months was 79% and all patients who had responses at 3 months continued to have responses at the time of data cutoff.
JULIET now
In the most recent analysis, completed after a median time from infusion to data cutoff of 14 months, the investigators reported on efficacy in 93 patients who received CAR T-cell infusions.
The best overall response rate, the primary endpoint, was 52%, comprising 40% complete responses and 12% partial responses. The response rates were consistent across all prognostic subgroups, including age, sex, previous response status, International Prognostic Index score at enrollment, prior therapy, molecular subtype, and other factors.
Estimated relapse-free survival 12 months after documentation of an initial response was 65%, and was 79% among patients who had complete responses.
The median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff; the median overall survival had not been reached for patients with a complete remission. Overall survival in this heavily pretreated population as a whole (all patients who received CAR T-cell infusions) was 11.1 months.
Adverse events of special interest included grade 3 or 4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in 23% of patients, prolonged cytopenia in 34%, infections in 19%, neurologic events in 11%, febrile neutropenia in 15%, and tumor lysis syndrome in 2%.
There were no deaths attributable to CRS or to cerebral edema, a complication of CAR T-cell therapy that appears to be related to the costimulatory molecule used in various constructs.
“Patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who are not eligible for high-dose therapy and hematopoietic cell transplantation or for whom such therapy was not successful have very few treatment options. For these patients, tisagenlecleucel shows promise that will need to be confirmed through larger studies with longer follow-up,” the investigators wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The JULIET Trial is supported by Novartis. Dr. Maziar reported personal fees from Incyte, Kite Therapeutics, and Athersys.
SOURCE: Maziarz RT et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1804980.
SAN DIEGO – Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) is associated with a high rate of durable responses in adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, an updated analysis of the JULIET trial showed.
After a median follow-up of 19 months, two-thirds of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who had early responses to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel remained in remission with no evidence of minimal residual disease, reported Richard Thomas Maziarz, MD, from the Oregon Health & Science Knight Cancer Institute in Portland, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Since the previous report, no new deaths have been reported due to any cause other than patient disease progression. No treatment-related mortality was seen throughout the study, and there were three early deaths, all related to lymphoma that progressed,” he said in a briefing prior to presentation of the data in a scientific poster.
The updated study results were published simultaneously online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
JULIET then
In the phase 2, single-arm trial, investigators enrolled adults with DLBCL that had relapsed or was refractory after two or more prior lines of therapy and who were either ineligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant or who experienced disease progression after transplant.
Interim results of the study were previously reported at the European Hematology Association Congress in 2017.
At that meeting, Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, from the University of Lyon (France), presented results of an analysis of available efficacy data on 51 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up. In this population, the best overall response rate was 59%. The 3-month overall response rate was 45%, consisting of 37% complete responses and 8% partial responses. Relapse-free survival at 6 months was 79% and all patients who had responses at 3 months continued to have responses at the time of data cutoff.
JULIET now
In the most recent analysis, completed after a median time from infusion to data cutoff of 14 months, the investigators reported on efficacy in 93 patients who received CAR T-cell infusions.
The best overall response rate, the primary endpoint, was 52%, comprising 40% complete responses and 12% partial responses. The response rates were consistent across all prognostic subgroups, including age, sex, previous response status, International Prognostic Index score at enrollment, prior therapy, molecular subtype, and other factors.
Estimated relapse-free survival 12 months after documentation of an initial response was 65%, and was 79% among patients who had complete responses.
The median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff; the median overall survival had not been reached for patients with a complete remission. Overall survival in this heavily pretreated population as a whole (all patients who received CAR T-cell infusions) was 11.1 months.
Adverse events of special interest included grade 3 or 4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in 23% of patients, prolonged cytopenia in 34%, infections in 19%, neurologic events in 11%, febrile neutropenia in 15%, and tumor lysis syndrome in 2%.
There were no deaths attributable to CRS or to cerebral edema, a complication of CAR T-cell therapy that appears to be related to the costimulatory molecule used in various constructs.
“Patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who are not eligible for high-dose therapy and hematopoietic cell transplantation or for whom such therapy was not successful have very few treatment options. For these patients, tisagenlecleucel shows promise that will need to be confirmed through larger studies with longer follow-up,” the investigators wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The JULIET Trial is supported by Novartis. Dr. Maziar reported personal fees from Incyte, Kite Therapeutics, and Athersys.
SOURCE: Maziarz RT et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1804980.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point: Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy produced durable responses in patients with heavily pretreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Major finding: The best overall response rate, the primary endpoint, was 52%, comprising 40% complete responses and 12% partial responses.
Study details: A single-arm, open-label study of tisagenlecleucel in adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Disclosures: The JULIET trial is supported by Novartis. Dr. Maziarz reported personal fees from Incyte, Kite Therapeutics, and Athersys.
Source: Maziarz RT et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1804980.
New PCNSL guidelines emphasize importance of patient fitness
New guidelines on the diagnosis and management of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) emphasize prompt diagnosis, aggressive treatment whenever possible, and multidisciplinary team support.
A unique aspect for hematologic cancers, the guidelines note, is that appropriate treatment for PCNSL requires input from neurology specialists.
And the guidelines recommend methotrexate-based treatment only be administered at centers experienced in delivering intensive chemotherapy.
Christopher P. Fox, MD, of the Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust in Nottingham, U.K., and his colleagues on behalf of the British Society for Haematology published the guidelines in BJH.
The authors incorporated findings from studies published since the society’s last comprehensive PCNSL guidelines were issued more than a decade ago.
The new guidelines provide recommendations for diagnosis and imaging, primary treatment of PCNSL, consolidation chemotherapy, follow-up, management of relapsed/refractory disease, and neuropsychological assessments.
Highlights include:
- People with suspected PCNSL must receive quick and coordinated attention from a multidisciplinary team of neurologists, hematologist-oncologists, and ocular specialists
- Histological diagnoses in addition to imaging findings should be performed
- Corticosteroids should be avoided or discontinued before biopsy, as even a short course of steroids can impede diagnosis
- Aggressive induction treatment should be chosen based on the patient’s fitness
- Patients should be offered entry into clinical trials whenever possible
- Universal screening for eye involvement should be conducted.
Primary treatment
Dr. Fox and his colleagues say definitive treatment for PCNSL—induction of remission followed by consolidation—should start within 2 weeks of diagnosis, and a treatment regimen should be chosen according to a patient’s physiological fitness, not age.
The fittest patients, who have better organ function and fewer comorbidities, should be eligible for intensive combination immuno-chemotherapy incorporating high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX)—optimally, four cycles of HD-MTX, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab.
Those deemed unfit for this regimen should be offered induction treatment with HD-MTX, rituximab, and procarbazine, the guidelines say.
If patients cannot tolerate HD-MTX, oral chemotherapy, whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT), or corticosteroids may be used.
The authors do not recommend intrathecal chemotherapy alongside systemic CNS-directed therapy.
Response should be assessed with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) routinely after every two cycles of HD-MTX-based therapy and at the end of remission induction.
Consolidation chemotherapy
Consolidation therapy should be initiated after induction for all patients with non-progressive disease. High-dose thiotepa-based chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) is the recommended first-line option for consolidation.
Patients ineligible for high-dose therapy followed by ASCT who have residual disease after induction therapy should be considered for WBRT. This is also the case for patients with residual disease after thiotepa-based ASCT.
However, Dr. Fox and his colleagues say WBRT consolidation is “contentious” for patients in complete response after HD-MTX regimens but ineligible for ASCT. The authors suggest carefully balancing potential improvement in progression-free survival against risks of neurocognitive toxicity.
Response to consolidation, again measured with contrast-enhanced MRI, should be carried out between 1 and 2 months after therapy is completed, and patients should be referred for neuropsychological testing to assess cognitive function.
Patients with relapsed or refractory disease should be approached with maximum urgency—the guidelines offer an algorithm for retreatment options—and offered clinical trial entry wherever possible.
Some coauthors, including the lead author, disclosed receiving fees from pharmaceutical manufacturers Adienne and/or F. Hoffman-La Roche.
New guidelines on the diagnosis and management of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) emphasize prompt diagnosis, aggressive treatment whenever possible, and multidisciplinary team support.
A unique aspect for hematologic cancers, the guidelines note, is that appropriate treatment for PCNSL requires input from neurology specialists.
And the guidelines recommend methotrexate-based treatment only be administered at centers experienced in delivering intensive chemotherapy.
Christopher P. Fox, MD, of the Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust in Nottingham, U.K., and his colleagues on behalf of the British Society for Haematology published the guidelines in BJH.
The authors incorporated findings from studies published since the society’s last comprehensive PCNSL guidelines were issued more than a decade ago.
The new guidelines provide recommendations for diagnosis and imaging, primary treatment of PCNSL, consolidation chemotherapy, follow-up, management of relapsed/refractory disease, and neuropsychological assessments.
Highlights include:
- People with suspected PCNSL must receive quick and coordinated attention from a multidisciplinary team of neurologists, hematologist-oncologists, and ocular specialists
- Histological diagnoses in addition to imaging findings should be performed
- Corticosteroids should be avoided or discontinued before biopsy, as even a short course of steroids can impede diagnosis
- Aggressive induction treatment should be chosen based on the patient’s fitness
- Patients should be offered entry into clinical trials whenever possible
- Universal screening for eye involvement should be conducted.
Primary treatment
Dr. Fox and his colleagues say definitive treatment for PCNSL—induction of remission followed by consolidation—should start within 2 weeks of diagnosis, and a treatment regimen should be chosen according to a patient’s physiological fitness, not age.
The fittest patients, who have better organ function and fewer comorbidities, should be eligible for intensive combination immuno-chemotherapy incorporating high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX)—optimally, four cycles of HD-MTX, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab.
Those deemed unfit for this regimen should be offered induction treatment with HD-MTX, rituximab, and procarbazine, the guidelines say.
If patients cannot tolerate HD-MTX, oral chemotherapy, whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT), or corticosteroids may be used.
The authors do not recommend intrathecal chemotherapy alongside systemic CNS-directed therapy.
Response should be assessed with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) routinely after every two cycles of HD-MTX-based therapy and at the end of remission induction.
Consolidation chemotherapy
Consolidation therapy should be initiated after induction for all patients with non-progressive disease. High-dose thiotepa-based chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) is the recommended first-line option for consolidation.
Patients ineligible for high-dose therapy followed by ASCT who have residual disease after induction therapy should be considered for WBRT. This is also the case for patients with residual disease after thiotepa-based ASCT.
However, Dr. Fox and his colleagues say WBRT consolidation is “contentious” for patients in complete response after HD-MTX regimens but ineligible for ASCT. The authors suggest carefully balancing potential improvement in progression-free survival against risks of neurocognitive toxicity.
Response to consolidation, again measured with contrast-enhanced MRI, should be carried out between 1 and 2 months after therapy is completed, and patients should be referred for neuropsychological testing to assess cognitive function.
Patients with relapsed or refractory disease should be approached with maximum urgency—the guidelines offer an algorithm for retreatment options—and offered clinical trial entry wherever possible.
Some coauthors, including the lead author, disclosed receiving fees from pharmaceutical manufacturers Adienne and/or F. Hoffman-La Roche.
New guidelines on the diagnosis and management of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) emphasize prompt diagnosis, aggressive treatment whenever possible, and multidisciplinary team support.
A unique aspect for hematologic cancers, the guidelines note, is that appropriate treatment for PCNSL requires input from neurology specialists.
And the guidelines recommend methotrexate-based treatment only be administered at centers experienced in delivering intensive chemotherapy.
Christopher P. Fox, MD, of the Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust in Nottingham, U.K., and his colleagues on behalf of the British Society for Haematology published the guidelines in BJH.
The authors incorporated findings from studies published since the society’s last comprehensive PCNSL guidelines were issued more than a decade ago.
The new guidelines provide recommendations for diagnosis and imaging, primary treatment of PCNSL, consolidation chemotherapy, follow-up, management of relapsed/refractory disease, and neuropsychological assessments.
Highlights include:
- People with suspected PCNSL must receive quick and coordinated attention from a multidisciplinary team of neurologists, hematologist-oncologists, and ocular specialists
- Histological diagnoses in addition to imaging findings should be performed
- Corticosteroids should be avoided or discontinued before biopsy, as even a short course of steroids can impede diagnosis
- Aggressive induction treatment should be chosen based on the patient’s fitness
- Patients should be offered entry into clinical trials whenever possible
- Universal screening for eye involvement should be conducted.
Primary treatment
Dr. Fox and his colleagues say definitive treatment for PCNSL—induction of remission followed by consolidation—should start within 2 weeks of diagnosis, and a treatment regimen should be chosen according to a patient’s physiological fitness, not age.
The fittest patients, who have better organ function and fewer comorbidities, should be eligible for intensive combination immuno-chemotherapy incorporating high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX)—optimally, four cycles of HD-MTX, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab.
Those deemed unfit for this regimen should be offered induction treatment with HD-MTX, rituximab, and procarbazine, the guidelines say.
If patients cannot tolerate HD-MTX, oral chemotherapy, whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT), or corticosteroids may be used.
The authors do not recommend intrathecal chemotherapy alongside systemic CNS-directed therapy.
Response should be assessed with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) routinely after every two cycles of HD-MTX-based therapy and at the end of remission induction.
Consolidation chemotherapy
Consolidation therapy should be initiated after induction for all patients with non-progressive disease. High-dose thiotepa-based chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) is the recommended first-line option for consolidation.
Patients ineligible for high-dose therapy followed by ASCT who have residual disease after induction therapy should be considered for WBRT. This is also the case for patients with residual disease after thiotepa-based ASCT.
However, Dr. Fox and his colleagues say WBRT consolidation is “contentious” for patients in complete response after HD-MTX regimens but ineligible for ASCT. The authors suggest carefully balancing potential improvement in progression-free survival against risks of neurocognitive toxicity.
Response to consolidation, again measured with contrast-enhanced MRI, should be carried out between 1 and 2 months after therapy is completed, and patients should be referred for neuropsychological testing to assess cognitive function.
Patients with relapsed or refractory disease should be approached with maximum urgency—the guidelines offer an algorithm for retreatment options—and offered clinical trial entry wherever possible.
Some coauthors, including the lead author, disclosed receiving fees from pharmaceutical manufacturers Adienne and/or F. Hoffman-La Roche.
FLYER: Four cycles of R-CHOP as good as six in low-risk DLBCL
SAN DIEGO – A shortened regimen of four cycles of rituximab plus CHOP chemotherapy was noninferior in efficacy to the standard six cycles of R-CHOP in patients aged under age 60 years with favorable-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and the truncated regimen was associated with about a one-third reduction in nonhematologic adverse events, investigators in the FLYER trial reported.
Among 588 evaluable patients aged younger than 60 years with favorable-prognosis diffuse DLBCL, there were no significant differences in either progression-free survival (PFS), event-free survival, or overall survival (OS) between patients who were randomly assigned to therapy with four cycles of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), compared with patients assigned to six cycles, reported Viola Poeschel, MD, of Saarland University in Homburg, Germany.
“Six cycles of R-CHOP led to a higher toxicity with respect to leukocytopenia and anemia, both of any grades and also of grades 3 to 4, compared to four cycles of R-CHOP,” she said in a briefing at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
For younger patients with favorable-prognosis DLBCL – defined as an age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score of 0 and low tumor burden (less than 7.5 cm) – four cycles of R-CHOP can be a new standard of care, Dr. Poeschel said.
The investigators were prompted to look at the question of a shorter R-CHOP regimen by the results of the MInT trial, in which a subpopulation of favorable-prognosis DLBCL had a 3-year PFS rate of 89% (Lancet Oncol. 2006 May;7[5]379-91). The FLYER trial was designed as a noninferiority study to see whether in a similar group of patients reducing the number of R-CHOP cycles could maintain efficacy while reducing toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 66 months, the PFS rate, the primary endpoint, was 94% in the R-CHOP 6 group, compared with 96% for R-CHOP 4.
“As the lower limit of the 95% confidence interval of our experimental arm was 94%, it is shown that it is definitely noninferior to the standard arm, six cycles of R-CHOP,” Dr. Poeschel said.
Similarly, the rate of 3-year OS was 98% in the six-cycle group, compared with 99% in the four-cycle group, and the survival curves were virtually superimposable out to more than 10 years of follow-up.
R-CHOP 6 was associated with more frequent hematologic adverse events, compared with R-CHOP 4, with leukopenia of any grade occurring in 237 versus 171 patients, respectively, and grade 3 or 4 events occurring in 110 versus 80 patients, respectively.
Any grade anemia occurred in 172 patients assigned to six cycles versus 107 assigned to four cycles. Rates of grade 3-4 anemia and thrombocytopenia of any grade or of grade 3-4 were similar between the groups.
Nonhematologic adverse events of any grade or of grade 3 or 4 that were more frequent with R-CHOP 6 versus R-CHOP 4 included all events considered together, paresthesias, nausea, infection, vomiting, and mucositis.
As noted before, the total number of nonhematologic adverse events was reduced by about one-third.
“We are certainly always looking for ways to make treatments easier for our patients to reduce adverse effects, and certainly for this subgroup of patients it appears that we can make their treatment shorter and have less burden but equivalent efficacy,” commented David Steensma, MD, from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Cancer Center in Boston, who moderated the briefing.
Dr. Steensma and Dr. Poeschel both cautioned that the results of the study pertain only to those patients with DLBCL who are younger and have favorable-prognosis disease.
“We can’t extend it to other subtypes of large cell lymphoma, but that’s always a laudable goal, so I think this will immediately influence clinical practice,” Dr. Steensma said.
The study was sponsored by the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group. Dr. Poeschel reporteed travel grants from Roche and Amgen. Dr. Steensma reported no disclosures relevant to the study.
SOURCE: Poeschel V et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 781.
SAN DIEGO – A shortened regimen of four cycles of rituximab plus CHOP chemotherapy was noninferior in efficacy to the standard six cycles of R-CHOP in patients aged under age 60 years with favorable-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and the truncated regimen was associated with about a one-third reduction in nonhematologic adverse events, investigators in the FLYER trial reported.
Among 588 evaluable patients aged younger than 60 years with favorable-prognosis diffuse DLBCL, there were no significant differences in either progression-free survival (PFS), event-free survival, or overall survival (OS) between patients who were randomly assigned to therapy with four cycles of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), compared with patients assigned to six cycles, reported Viola Poeschel, MD, of Saarland University in Homburg, Germany.
“Six cycles of R-CHOP led to a higher toxicity with respect to leukocytopenia and anemia, both of any grades and also of grades 3 to 4, compared to four cycles of R-CHOP,” she said in a briefing at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
For younger patients with favorable-prognosis DLBCL – defined as an age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score of 0 and low tumor burden (less than 7.5 cm) – four cycles of R-CHOP can be a new standard of care, Dr. Poeschel said.
The investigators were prompted to look at the question of a shorter R-CHOP regimen by the results of the MInT trial, in which a subpopulation of favorable-prognosis DLBCL had a 3-year PFS rate of 89% (Lancet Oncol. 2006 May;7[5]379-91). The FLYER trial was designed as a noninferiority study to see whether in a similar group of patients reducing the number of R-CHOP cycles could maintain efficacy while reducing toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 66 months, the PFS rate, the primary endpoint, was 94% in the R-CHOP 6 group, compared with 96% for R-CHOP 4.
“As the lower limit of the 95% confidence interval of our experimental arm was 94%, it is shown that it is definitely noninferior to the standard arm, six cycles of R-CHOP,” Dr. Poeschel said.
Similarly, the rate of 3-year OS was 98% in the six-cycle group, compared with 99% in the four-cycle group, and the survival curves were virtually superimposable out to more than 10 years of follow-up.
R-CHOP 6 was associated with more frequent hematologic adverse events, compared with R-CHOP 4, with leukopenia of any grade occurring in 237 versus 171 patients, respectively, and grade 3 or 4 events occurring in 110 versus 80 patients, respectively.
Any grade anemia occurred in 172 patients assigned to six cycles versus 107 assigned to four cycles. Rates of grade 3-4 anemia and thrombocytopenia of any grade or of grade 3-4 were similar between the groups.
Nonhematologic adverse events of any grade or of grade 3 or 4 that were more frequent with R-CHOP 6 versus R-CHOP 4 included all events considered together, paresthesias, nausea, infection, vomiting, and mucositis.
As noted before, the total number of nonhematologic adverse events was reduced by about one-third.
“We are certainly always looking for ways to make treatments easier for our patients to reduce adverse effects, and certainly for this subgroup of patients it appears that we can make their treatment shorter and have less burden but equivalent efficacy,” commented David Steensma, MD, from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Cancer Center in Boston, who moderated the briefing.
Dr. Steensma and Dr. Poeschel both cautioned that the results of the study pertain only to those patients with DLBCL who are younger and have favorable-prognosis disease.
“We can’t extend it to other subtypes of large cell lymphoma, but that’s always a laudable goal, so I think this will immediately influence clinical practice,” Dr. Steensma said.
The study was sponsored by the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group. Dr. Poeschel reporteed travel grants from Roche and Amgen. Dr. Steensma reported no disclosures relevant to the study.
SOURCE: Poeschel V et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 781.
SAN DIEGO – A shortened regimen of four cycles of rituximab plus CHOP chemotherapy was noninferior in efficacy to the standard six cycles of R-CHOP in patients aged under age 60 years with favorable-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and the truncated regimen was associated with about a one-third reduction in nonhematologic adverse events, investigators in the FLYER trial reported.
Among 588 evaluable patients aged younger than 60 years with favorable-prognosis diffuse DLBCL, there were no significant differences in either progression-free survival (PFS), event-free survival, or overall survival (OS) between patients who were randomly assigned to therapy with four cycles of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), compared with patients assigned to six cycles, reported Viola Poeschel, MD, of Saarland University in Homburg, Germany.
“Six cycles of R-CHOP led to a higher toxicity with respect to leukocytopenia and anemia, both of any grades and also of grades 3 to 4, compared to four cycles of R-CHOP,” she said in a briefing at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
For younger patients with favorable-prognosis DLBCL – defined as an age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score of 0 and low tumor burden (less than 7.5 cm) – four cycles of R-CHOP can be a new standard of care, Dr. Poeschel said.
The investigators were prompted to look at the question of a shorter R-CHOP regimen by the results of the MInT trial, in which a subpopulation of favorable-prognosis DLBCL had a 3-year PFS rate of 89% (Lancet Oncol. 2006 May;7[5]379-91). The FLYER trial was designed as a noninferiority study to see whether in a similar group of patients reducing the number of R-CHOP cycles could maintain efficacy while reducing toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 66 months, the PFS rate, the primary endpoint, was 94% in the R-CHOP 6 group, compared with 96% for R-CHOP 4.
“As the lower limit of the 95% confidence interval of our experimental arm was 94%, it is shown that it is definitely noninferior to the standard arm, six cycles of R-CHOP,” Dr. Poeschel said.
Similarly, the rate of 3-year OS was 98% in the six-cycle group, compared with 99% in the four-cycle group, and the survival curves were virtually superimposable out to more than 10 years of follow-up.
R-CHOP 6 was associated with more frequent hematologic adverse events, compared with R-CHOP 4, with leukopenia of any grade occurring in 237 versus 171 patients, respectively, and grade 3 or 4 events occurring in 110 versus 80 patients, respectively.
Any grade anemia occurred in 172 patients assigned to six cycles versus 107 assigned to four cycles. Rates of grade 3-4 anemia and thrombocytopenia of any grade or of grade 3-4 were similar between the groups.
Nonhematologic adverse events of any grade or of grade 3 or 4 that were more frequent with R-CHOP 6 versus R-CHOP 4 included all events considered together, paresthesias, nausea, infection, vomiting, and mucositis.
As noted before, the total number of nonhematologic adverse events was reduced by about one-third.
“We are certainly always looking for ways to make treatments easier for our patients to reduce adverse effects, and certainly for this subgroup of patients it appears that we can make their treatment shorter and have less burden but equivalent efficacy,” commented David Steensma, MD, from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Cancer Center in Boston, who moderated the briefing.
Dr. Steensma and Dr. Poeschel both cautioned that the results of the study pertain only to those patients with DLBCL who are younger and have favorable-prognosis disease.
“We can’t extend it to other subtypes of large cell lymphoma, but that’s always a laudable goal, so I think this will immediately influence clinical practice,” Dr. Steensma said.
The study was sponsored by the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group. Dr. Poeschel reporteed travel grants from Roche and Amgen. Dr. Steensma reported no disclosures relevant to the study.
SOURCE: Poeschel V et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 781.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point: Four cycles of R-CHOP was noninferior to six cycles in younger patients with favorable-prognosis diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Major finding: R-CHOP 4 was noninferior to R-CHOP 6 for the primary progression-free survival endpoint.
Study details: A randomized trial in 588 patients with favorable-prognosis diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group. Dr. Poeschel reporteed travel grants from Roche and Amgen. Dr. Steensma reported no disclosures relevant to the study.
Source: Poeschel V et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 781.