User login
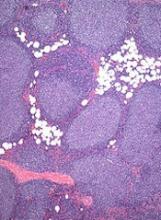
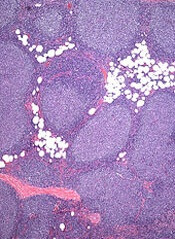
Treatment improves PFS in early stage FL
A multidrug regimen can improve upon involved-field radiotherapy (IFRT) in patients with early stage follicular lymphoma (FL), according to research published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
FL patients who received IFRT plus cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisolone (CVP)—with or without rituximab—had a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) compared to patients who received standard treatment with IFRT alone.
However, there was no significant difference in overall survival (OS) between the treatment arms.
“This is the first successful randomized study ever to be conducted in early stage follicular lymphoma comparing standard therapy to standard therapy plus effective chemotherapy or immunochemotherapy,” said Michael MacManus, MBBCh, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
“It shows that the initial treatment received by patients can significantly affect their long-term chance of staying free from disease. Moving forward, we are interested in determining whether there is a benefit in overall long-term survival for patients treated with the combination with further follow-up, and if there is any way to predict if a person will benefit from combined treatment based on analyses of blood or biopsy specimens.”
Dr MacManus and his colleagues studied 150 patients with stage I to II, low-grade FL who were enrolled in this trial between 2000 and 2012.
At randomization, the patients’ median age was 57, 52% were male, 75% had stage I disease, and 48% had PET staging.
Half of patients (n=75) were randomized to receive IFRT (30-36 Gy) alone, and half were randomized to IFRT (30-36 Gy) plus 6 cycles of CVP. From 2006 on, patients in the CVP arm received rituximab (R) as well (n=31).
Baseline characteristics were well-balanced between the treatment arms.
Efficacy
The median follow-up was 9.6 years (range, 3.1 to 15.8 years).
PFS was significantly better among patients randomized to receive CVP±R (hazard ratio [HR]=0.57; P=0.033). The estimated 10-year PFS rate was 41% in the IFRT arm and 59% in the CVP±R arm.
Patients randomized to receive CVP plus R (n=31) had significantly better PFS than patients randomized to receive IFRT alone (n=31) over the same time period (HR=0.26; P=0.045).
There were 10 deaths in the IRFT arm and 5 in the CVP±R arm, but there was no significant difference in OS between the arms (HR=0.62; P=0.40). The 10-year OS rate was 86% in the IFRT arm and 95% in the CVP±R arm.
There was no significant between-arm difference in transformation to aggressive lymphoma (P=0.1). Transformation occurred in 10 patients in the IFRT arm and 4 in the CVP±R arm.
Safety
There were 148 patients from both arms who ultimately received IFRT, and 69 patients who received CVP±R.
Grade 2 toxicities occurring in more than 10% of IFRT recipients included upper gastrointestinal (n=27; 18%), skin (n=21; 14%), and mucous membrane (n=19; 12%) toxicity. One IFRT recipient had grade 3 mucositis, and 1 had grade 4 esophageal/pharyngeal mucosal toxicity.
Grade 3 toxicities occurring in at least 2 patients in the CVP±R arm included neutropenia (n=10; 14%), infection (n=8; 12%), diarrhea (n=3; 4%), elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase (n=3; 4%), fatigue (n=3; 4%), and febrile neutropenia (n=3; 4%).
Three patients (4%) in the CVP±R arm had acute grade 3 neuropathy related to vincristine. Ten patients (14%) had grade 4 neutropenia.
The most common late toxicities for the entire patient cohort were salivary gland (n=8; 5%) and skin (n=4; 3%) toxicities.
Grade 3 lung and menopausal toxicities occurred in 1 patient each. Two patients had late grade 3 vincristine neuropathy. One patient who had grade 3 neuropathy during chemotherapy progressed to grade 4.
A multidrug regimen can improve upon involved-field radiotherapy (IFRT) in patients with early stage follicular lymphoma (FL), according to research published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
FL patients who received IFRT plus cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisolone (CVP)—with or without rituximab—had a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) compared to patients who received standard treatment with IFRT alone.
However, there was no significant difference in overall survival (OS) between the treatment arms.
“This is the first successful randomized study ever to be conducted in early stage follicular lymphoma comparing standard therapy to standard therapy plus effective chemotherapy or immunochemotherapy,” said Michael MacManus, MBBCh, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
“It shows that the initial treatment received by patients can significantly affect their long-term chance of staying free from disease. Moving forward, we are interested in determining whether there is a benefit in overall long-term survival for patients treated with the combination with further follow-up, and if there is any way to predict if a person will benefit from combined treatment based on analyses of blood or biopsy specimens.”
Dr MacManus and his colleagues studied 150 patients with stage I to II, low-grade FL who were enrolled in this trial between 2000 and 2012.
At randomization, the patients’ median age was 57, 52% were male, 75% had stage I disease, and 48% had PET staging.
Half of patients (n=75) were randomized to receive IFRT (30-36 Gy) alone, and half were randomized to IFRT (30-36 Gy) plus 6 cycles of CVP. From 2006 on, patients in the CVP arm received rituximab (R) as well (n=31).
Baseline characteristics were well-balanced between the treatment arms.
Efficacy
The median follow-up was 9.6 years (range, 3.1 to 15.8 years).
PFS was significantly better among patients randomized to receive CVP±R (hazard ratio [HR]=0.57; P=0.033). The estimated 10-year PFS rate was 41% in the IFRT arm and 59% in the CVP±R arm.
Patients randomized to receive CVP plus R (n=31) had significantly better PFS than patients randomized to receive IFRT alone (n=31) over the same time period (HR=0.26; P=0.045).
There were 10 deaths in the IRFT arm and 5 in the CVP±R arm, but there was no significant difference in OS between the arms (HR=0.62; P=0.40). The 10-year OS rate was 86% in the IFRT arm and 95% in the CVP±R arm.
There was no significant between-arm difference in transformation to aggressive lymphoma (P=0.1). Transformation occurred in 10 patients in the IFRT arm and 4 in the CVP±R arm.
Safety
There were 148 patients from both arms who ultimately received IFRT, and 69 patients who received CVP±R.
Grade 2 toxicities occurring in more than 10% of IFRT recipients included upper gastrointestinal (n=27; 18%), skin (n=21; 14%), and mucous membrane (n=19; 12%) toxicity. One IFRT recipient had grade 3 mucositis, and 1 had grade 4 esophageal/pharyngeal mucosal toxicity.
Grade 3 toxicities occurring in at least 2 patients in the CVP±R arm included neutropenia (n=10; 14%), infection (n=8; 12%), diarrhea (n=3; 4%), elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase (n=3; 4%), fatigue (n=3; 4%), and febrile neutropenia (n=3; 4%).
Three patients (4%) in the CVP±R arm had acute grade 3 neuropathy related to vincristine. Ten patients (14%) had grade 4 neutropenia.
The most common late toxicities for the entire patient cohort were salivary gland (n=8; 5%) and skin (n=4; 3%) toxicities.
Grade 3 lung and menopausal toxicities occurred in 1 patient each. Two patients had late grade 3 vincristine neuropathy. One patient who had grade 3 neuropathy during chemotherapy progressed to grade 4.
A multidrug regimen can improve upon involved-field radiotherapy (IFRT) in patients with early stage follicular lymphoma (FL), according to research published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
FL patients who received IFRT plus cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisolone (CVP)—with or without rituximab—had a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) compared to patients who received standard treatment with IFRT alone.
However, there was no significant difference in overall survival (OS) between the treatment arms.
“This is the first successful randomized study ever to be conducted in early stage follicular lymphoma comparing standard therapy to standard therapy plus effective chemotherapy or immunochemotherapy,” said Michael MacManus, MBBCh, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
“It shows that the initial treatment received by patients can significantly affect their long-term chance of staying free from disease. Moving forward, we are interested in determining whether there is a benefit in overall long-term survival for patients treated with the combination with further follow-up, and if there is any way to predict if a person will benefit from combined treatment based on analyses of blood or biopsy specimens.”
Dr MacManus and his colleagues studied 150 patients with stage I to II, low-grade FL who were enrolled in this trial between 2000 and 2012.
At randomization, the patients’ median age was 57, 52% were male, 75% had stage I disease, and 48% had PET staging.
Half of patients (n=75) were randomized to receive IFRT (30-36 Gy) alone, and half were randomized to IFRT (30-36 Gy) plus 6 cycles of CVP. From 2006 on, patients in the CVP arm received rituximab (R) as well (n=31).
Baseline characteristics were well-balanced between the treatment arms.
Efficacy
The median follow-up was 9.6 years (range, 3.1 to 15.8 years).
PFS was significantly better among patients randomized to receive CVP±R (hazard ratio [HR]=0.57; P=0.033). The estimated 10-year PFS rate was 41% in the IFRT arm and 59% in the CVP±R arm.
Patients randomized to receive CVP plus R (n=31) had significantly better PFS than patients randomized to receive IFRT alone (n=31) over the same time period (HR=0.26; P=0.045).
There were 10 deaths in the IRFT arm and 5 in the CVP±R arm, but there was no significant difference in OS between the arms (HR=0.62; P=0.40). The 10-year OS rate was 86% in the IFRT arm and 95% in the CVP±R arm.
There was no significant between-arm difference in transformation to aggressive lymphoma (P=0.1). Transformation occurred in 10 patients in the IFRT arm and 4 in the CVP±R arm.
Safety
There were 148 patients from both arms who ultimately received IFRT, and 69 patients who received CVP±R.
Grade 2 toxicities occurring in more than 10% of IFRT recipients included upper gastrointestinal (n=27; 18%), skin (n=21; 14%), and mucous membrane (n=19; 12%) toxicity. One IFRT recipient had grade 3 mucositis, and 1 had grade 4 esophageal/pharyngeal mucosal toxicity.
Grade 3 toxicities occurring in at least 2 patients in the CVP±R arm included neutropenia (n=10; 14%), infection (n=8; 12%), diarrhea (n=3; 4%), elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase (n=3; 4%), fatigue (n=3; 4%), and febrile neutropenia (n=3; 4%).
Three patients (4%) in the CVP±R arm had acute grade 3 neuropathy related to vincristine. Ten patients (14%) had grade 4 neutropenia.
The most common late toxicities for the entire patient cohort were salivary gland (n=8; 5%) and skin (n=4; 3%) toxicities.
Grade 3 lung and menopausal toxicities occurred in 1 patient each. Two patients had late grade 3 vincristine neuropathy. One patient who had grade 3 neuropathy during chemotherapy progressed to grade 4.
Adult CCSs report financial hardships
Health-related financial hardship is common among adult survivors of childhood cancer, according to a study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Researchers analyzed more than 2800 long-term childhood cancer survivors (CCSs) and found that 65% had financial challenges related to their cancer diagnosis.
“These findings suggest primary care doctors and oncologists should routinely screen childhood cancer survivors for possible financial hardship,” said I-Chan Huang, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
Specifically, Dr Huang recommends that healthcare providers routinely ask CCSs if they are unable to purchase medications, ever skip appointments for economic reasons, or worry about how to pay their medical bills.
For this study, Dr Huang and his colleagues analyzed data from 2811 CCSs. The subjects had a mean age of 31.8 (range, 18 to 65) and were a mean of 23.6 years from cancer diagnosis. Most (57.8%) had been diagnosed with hematologic malignancies, 32.0% with solid tumors, and 10.1% with central nervous system malignancies.
All subjects had been treated at St. Jude and enrolled in the St. Jude LIFE study. Participants return to St. Jude periodically for several days of clinical and functional assessments. Data for this study were collected during the CCSs’ first St. Jude LIFE evaluations.
Assessing hardship
The researchers measured 3 types of financial hardship—material, psychological, and coping/behavioral.
About 1 in 5 CCSs (22.4%) reported material financial hardship. In other words, their cancer had an impact on their financial situation.
More than half of CCSs (51.1%) reported psychological hardship—concern about their ability to pay for medical expenses.
And 33% of CCSs reported coping/behavioral hardship—an inability to see a doctor or go to the hospital due to finances.
Roughly 65% of CCSs reported at least 1 type of financial hardship.
All 3 types of hardship were significantly associated with somatization (all P<0.001), anxiety (all P<0.001), depression (all P<0.001), suicidal thoughts (all P<0.05), and difficulty in retirement planning (all P<0.001).
Furthermore, CCSs who reported financial hardship had significantly lower health-related quality of life (P<0.001 for all 3 domains), sensation abnormality (all P<0.001), pulmonary symptoms (all P<0.05), and cardiac symptoms (all P<0.05).
Predicting hardship
Intensive cancer treatment, chronic health conditions, second cancers, age at the time of study evaluation, education level, and annual household income were all significantly associated with a greater risk of financial hardship.
CCSs age 40 and older had an increased risk of psychological and coping/behavioral hardship (P<0.001 for both domains).
CCSs with an annual household income of less than $40,000 had an increased risk of material, psychological, and coping/behavioral hardship, compared to CCSs with an income of $80,000 or more (P<0.001 for all domains).
CCSs who did not obtain a high school diploma had an increased risk of material (P<0.001), psychological (P<0.01), and coping/behavioral hardship (P<0.001) compared to college graduates.
CCSs who received cancer treatments associated with a high-risk disease burden (vs low-risk) had an increased risk of material (P=0.01) and psychological (P=0.004) hardship.
Health conditions associated with material financial hardship included grade 2-4 myocardial infarction (P<0.001), peripheral neuropathy (P<0.001), subsequent neoplasm (P<0.001), seizure (P=0.007), reproductive disorders (P=0.01), stroke (P=0.02), amputation (P=0.02), upper gastrointestinal disease (P=0.04), and hearing loss (P=0.05).
Grade 2-4 myocardial infarction and reproductive disorders were significantly associated with psychological financial hardship (P=0.02 for both).
“Severe late effects that emerge early in life and disrupt education and training opportunities are a double hit for survivors,” Dr Huang said. “These health problems decrease the survivors’ earning mobility and financial security later in life. The phenomenon leaves them at risk for poor health and psychological outcomes compared to healthier survivors.”
Health-related financial hardship is common among adult survivors of childhood cancer, according to a study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Researchers analyzed more than 2800 long-term childhood cancer survivors (CCSs) and found that 65% had financial challenges related to their cancer diagnosis.
“These findings suggest primary care doctors and oncologists should routinely screen childhood cancer survivors for possible financial hardship,” said I-Chan Huang, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
Specifically, Dr Huang recommends that healthcare providers routinely ask CCSs if they are unable to purchase medications, ever skip appointments for economic reasons, or worry about how to pay their medical bills.
For this study, Dr Huang and his colleagues analyzed data from 2811 CCSs. The subjects had a mean age of 31.8 (range, 18 to 65) and were a mean of 23.6 years from cancer diagnosis. Most (57.8%) had been diagnosed with hematologic malignancies, 32.0% with solid tumors, and 10.1% with central nervous system malignancies.
All subjects had been treated at St. Jude and enrolled in the St. Jude LIFE study. Participants return to St. Jude periodically for several days of clinical and functional assessments. Data for this study were collected during the CCSs’ first St. Jude LIFE evaluations.
Assessing hardship
The researchers measured 3 types of financial hardship—material, psychological, and coping/behavioral.
About 1 in 5 CCSs (22.4%) reported material financial hardship. In other words, their cancer had an impact on their financial situation.
More than half of CCSs (51.1%) reported psychological hardship—concern about their ability to pay for medical expenses.
And 33% of CCSs reported coping/behavioral hardship—an inability to see a doctor or go to the hospital due to finances.
Roughly 65% of CCSs reported at least 1 type of financial hardship.
All 3 types of hardship were significantly associated with somatization (all P<0.001), anxiety (all P<0.001), depression (all P<0.001), suicidal thoughts (all P<0.05), and difficulty in retirement planning (all P<0.001).
Furthermore, CCSs who reported financial hardship had significantly lower health-related quality of life (P<0.001 for all 3 domains), sensation abnormality (all P<0.001), pulmonary symptoms (all P<0.05), and cardiac symptoms (all P<0.05).
Predicting hardship
Intensive cancer treatment, chronic health conditions, second cancers, age at the time of study evaluation, education level, and annual household income were all significantly associated with a greater risk of financial hardship.
CCSs age 40 and older had an increased risk of psychological and coping/behavioral hardship (P<0.001 for both domains).
CCSs with an annual household income of less than $40,000 had an increased risk of material, psychological, and coping/behavioral hardship, compared to CCSs with an income of $80,000 or more (P<0.001 for all domains).
CCSs who did not obtain a high school diploma had an increased risk of material (P<0.001), psychological (P<0.01), and coping/behavioral hardship (P<0.001) compared to college graduates.
CCSs who received cancer treatments associated with a high-risk disease burden (vs low-risk) had an increased risk of material (P=0.01) and psychological (P=0.004) hardship.
Health conditions associated with material financial hardship included grade 2-4 myocardial infarction (P<0.001), peripheral neuropathy (P<0.001), subsequent neoplasm (P<0.001), seizure (P=0.007), reproductive disorders (P=0.01), stroke (P=0.02), amputation (P=0.02), upper gastrointestinal disease (P=0.04), and hearing loss (P=0.05).
Grade 2-4 myocardial infarction and reproductive disorders were significantly associated with psychological financial hardship (P=0.02 for both).
“Severe late effects that emerge early in life and disrupt education and training opportunities are a double hit for survivors,” Dr Huang said. “These health problems decrease the survivors’ earning mobility and financial security later in life. The phenomenon leaves them at risk for poor health and psychological outcomes compared to healthier survivors.”
Health-related financial hardship is common among adult survivors of childhood cancer, according to a study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Researchers analyzed more than 2800 long-term childhood cancer survivors (CCSs) and found that 65% had financial challenges related to their cancer diagnosis.
“These findings suggest primary care doctors and oncologists should routinely screen childhood cancer survivors for possible financial hardship,” said I-Chan Huang, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
Specifically, Dr Huang recommends that healthcare providers routinely ask CCSs if they are unable to purchase medications, ever skip appointments for economic reasons, or worry about how to pay their medical bills.
For this study, Dr Huang and his colleagues analyzed data from 2811 CCSs. The subjects had a mean age of 31.8 (range, 18 to 65) and were a mean of 23.6 years from cancer diagnosis. Most (57.8%) had been diagnosed with hematologic malignancies, 32.0% with solid tumors, and 10.1% with central nervous system malignancies.
All subjects had been treated at St. Jude and enrolled in the St. Jude LIFE study. Participants return to St. Jude periodically for several days of clinical and functional assessments. Data for this study were collected during the CCSs’ first St. Jude LIFE evaluations.
Assessing hardship
The researchers measured 3 types of financial hardship—material, psychological, and coping/behavioral.
About 1 in 5 CCSs (22.4%) reported material financial hardship. In other words, their cancer had an impact on their financial situation.
More than half of CCSs (51.1%) reported psychological hardship—concern about their ability to pay for medical expenses.
And 33% of CCSs reported coping/behavioral hardship—an inability to see a doctor or go to the hospital due to finances.
Roughly 65% of CCSs reported at least 1 type of financial hardship.
All 3 types of hardship were significantly associated with somatization (all P<0.001), anxiety (all P<0.001), depression (all P<0.001), suicidal thoughts (all P<0.05), and difficulty in retirement planning (all P<0.001).
Furthermore, CCSs who reported financial hardship had significantly lower health-related quality of life (P<0.001 for all 3 domains), sensation abnormality (all P<0.001), pulmonary symptoms (all P<0.05), and cardiac symptoms (all P<0.05).
Predicting hardship
Intensive cancer treatment, chronic health conditions, second cancers, age at the time of study evaluation, education level, and annual household income were all significantly associated with a greater risk of financial hardship.
CCSs age 40 and older had an increased risk of psychological and coping/behavioral hardship (P<0.001 for both domains).
CCSs with an annual household income of less than $40,000 had an increased risk of material, psychological, and coping/behavioral hardship, compared to CCSs with an income of $80,000 or more (P<0.001 for all domains).
CCSs who did not obtain a high school diploma had an increased risk of material (P<0.001), psychological (P<0.01), and coping/behavioral hardship (P<0.001) compared to college graduates.
CCSs who received cancer treatments associated with a high-risk disease burden (vs low-risk) had an increased risk of material (P=0.01) and psychological (P=0.004) hardship.
Health conditions associated with material financial hardship included grade 2-4 myocardial infarction (P<0.001), peripheral neuropathy (P<0.001), subsequent neoplasm (P<0.001), seizure (P=0.007), reproductive disorders (P=0.01), stroke (P=0.02), amputation (P=0.02), upper gastrointestinal disease (P=0.04), and hearing loss (P=0.05).
Grade 2-4 myocardial infarction and reproductive disorders were significantly associated with psychological financial hardship (P=0.02 for both).
“Severe late effects that emerge early in life and disrupt education and training opportunities are a double hit for survivors,” Dr Huang said. “These health problems decrease the survivors’ earning mobility and financial security later in life. The phenomenon leaves them at risk for poor health and psychological outcomes compared to healthier survivors.”
Isavuconazole resolved invasive fungal disease in patients on ibrutinib
Treatment with isavuconazole resolved or substantially improved invasive fungal disease among seven of eight patients receiving concomitant ibrutinib, according to the results of a small two-center study.
The combination “was well-tolerated overall,” wrote Kaelyn C. Cummins of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, together with her associates there and at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston. Their letter to the editor was published in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
Although ibrutinib is considered less immunosuppressive than conventional chemotherapy, it has been tied to invasive fungal infections, even in seemingly low-risk patients. The preferred treatment, voriconazole, is a very strong inhibitor of cytochrome P450 systems, of which ibrutinib is a substrate. For this study, the researchers queried the pharmacy databases of their institutions to identify adults who received concomitant isavuconazole (200 mg per day) and ibrutinib between 2015 and 2018. Drug exposures were confirmed by medical record review.
Four patients experienced clinical and radiologic resolution of invasive aspergillosis, fusariosis, mucormycosis, or phaeohyphomycosis. Another three had clinical and radiologic improvement of confirmed or probable aspergillosis or histoplasmosis. One of these patients underwent five debridements for central nervous system invasive aspergillosis but had 8 months of clinical improvement between debridements. This patient’s fungal isolate remained susceptible to isavuconazole throughout treatment. The patient who did not respond at all to isavuconazole had invasive aspergillosis with recurrent brain abscesses. The fungal isolate remained susceptible to isavuconazole, and the patient switched to long-term voriconazole therapy after stopping ibrutinib.
Several adverse events occurred while patients were on concomitant therapy. One patient developed paroxysmal atrial fibrillation that persisted after stopping ibrutinib. Another had worsening of preexisting thrombocytopenia. Among four patients with electrocardiogram data, two had transient QTc prolongation. No patient died within 12 weeks of starting concomitant therapy. Two patients eventually died after their cancer progressed.
The median age of the patients was 60 years (range, 38-76 years). Five were men. Six had chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and two had marginal zone lymphoma. Two CLL patients were on ibrutinib monotherapy, two also received rituximab, one also received umbralisib, and one also received obinutuzumab. One patient with marginal zone lymphoma was on ibrutinib monotherapy, and the other received concomitant rituximab, gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin.
Researchers should study the mechanisms by which [Bruton’s tyrosine kinase] inhibitors might increase susceptibility to fungal infections among patients with lymphoma or CLL, said Ms. Cummins and her associates. Because the CYP3A enzyme system also metabolizes PI3K and BCL-2 inhibitors, their results “could be more broadly applicable.”
Ms. Cummins had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Cummins KC et al. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018 Jul 24. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1485913.
Treatment with isavuconazole resolved or substantially improved invasive fungal disease among seven of eight patients receiving concomitant ibrutinib, according to the results of a small two-center study.
The combination “was well-tolerated overall,” wrote Kaelyn C. Cummins of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, together with her associates there and at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston. Their letter to the editor was published in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
Although ibrutinib is considered less immunosuppressive than conventional chemotherapy, it has been tied to invasive fungal infections, even in seemingly low-risk patients. The preferred treatment, voriconazole, is a very strong inhibitor of cytochrome P450 systems, of which ibrutinib is a substrate. For this study, the researchers queried the pharmacy databases of their institutions to identify adults who received concomitant isavuconazole (200 mg per day) and ibrutinib between 2015 and 2018. Drug exposures were confirmed by medical record review.
Four patients experienced clinical and radiologic resolution of invasive aspergillosis, fusariosis, mucormycosis, or phaeohyphomycosis. Another three had clinical and radiologic improvement of confirmed or probable aspergillosis or histoplasmosis. One of these patients underwent five debridements for central nervous system invasive aspergillosis but had 8 months of clinical improvement between debridements. This patient’s fungal isolate remained susceptible to isavuconazole throughout treatment. The patient who did not respond at all to isavuconazole had invasive aspergillosis with recurrent brain abscesses. The fungal isolate remained susceptible to isavuconazole, and the patient switched to long-term voriconazole therapy after stopping ibrutinib.
Several adverse events occurred while patients were on concomitant therapy. One patient developed paroxysmal atrial fibrillation that persisted after stopping ibrutinib. Another had worsening of preexisting thrombocytopenia. Among four patients with electrocardiogram data, two had transient QTc prolongation. No patient died within 12 weeks of starting concomitant therapy. Two patients eventually died after their cancer progressed.
The median age of the patients was 60 years (range, 38-76 years). Five were men. Six had chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and two had marginal zone lymphoma. Two CLL patients were on ibrutinib monotherapy, two also received rituximab, one also received umbralisib, and one also received obinutuzumab. One patient with marginal zone lymphoma was on ibrutinib monotherapy, and the other received concomitant rituximab, gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin.
Researchers should study the mechanisms by which [Bruton’s tyrosine kinase] inhibitors might increase susceptibility to fungal infections among patients with lymphoma or CLL, said Ms. Cummins and her associates. Because the CYP3A enzyme system also metabolizes PI3K and BCL-2 inhibitors, their results “could be more broadly applicable.”
Ms. Cummins had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Cummins KC et al. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018 Jul 24. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1485913.
Treatment with isavuconazole resolved or substantially improved invasive fungal disease among seven of eight patients receiving concomitant ibrutinib, according to the results of a small two-center study.
The combination “was well-tolerated overall,” wrote Kaelyn C. Cummins of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, together with her associates there and at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston. Their letter to the editor was published in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
Although ibrutinib is considered less immunosuppressive than conventional chemotherapy, it has been tied to invasive fungal infections, even in seemingly low-risk patients. The preferred treatment, voriconazole, is a very strong inhibitor of cytochrome P450 systems, of which ibrutinib is a substrate. For this study, the researchers queried the pharmacy databases of their institutions to identify adults who received concomitant isavuconazole (200 mg per day) and ibrutinib between 2015 and 2018. Drug exposures were confirmed by medical record review.
Four patients experienced clinical and radiologic resolution of invasive aspergillosis, fusariosis, mucormycosis, or phaeohyphomycosis. Another three had clinical and radiologic improvement of confirmed or probable aspergillosis or histoplasmosis. One of these patients underwent five debridements for central nervous system invasive aspergillosis but had 8 months of clinical improvement between debridements. This patient’s fungal isolate remained susceptible to isavuconazole throughout treatment. The patient who did not respond at all to isavuconazole had invasive aspergillosis with recurrent brain abscesses. The fungal isolate remained susceptible to isavuconazole, and the patient switched to long-term voriconazole therapy after stopping ibrutinib.
Several adverse events occurred while patients were on concomitant therapy. One patient developed paroxysmal atrial fibrillation that persisted after stopping ibrutinib. Another had worsening of preexisting thrombocytopenia. Among four patients with electrocardiogram data, two had transient QTc prolongation. No patient died within 12 weeks of starting concomitant therapy. Two patients eventually died after their cancer progressed.
The median age of the patients was 60 years (range, 38-76 years). Five were men. Six had chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and two had marginal zone lymphoma. Two CLL patients were on ibrutinib monotherapy, two also received rituximab, one also received umbralisib, and one also received obinutuzumab. One patient with marginal zone lymphoma was on ibrutinib monotherapy, and the other received concomitant rituximab, gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin.
Researchers should study the mechanisms by which [Bruton’s tyrosine kinase] inhibitors might increase susceptibility to fungal infections among patients with lymphoma or CLL, said Ms. Cummins and her associates. Because the CYP3A enzyme system also metabolizes PI3K and BCL-2 inhibitors, their results “could be more broadly applicable.”
Ms. Cummins had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Cummins KC et al. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018 Jul 24. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1485913.
FROM LEUKEMIA & LYMPHOMA
Key clinical point: Treatment with isavuconazole resolved or substantially improved invasive fungal disease in patients receiving concomitant ibrutinib.
Major finding: Seven of eight patients experienced clinical and radiographic resolution or improvement. Adverse events of concomitant treatment included paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, worsening of baseline thrombocytopenia, and QTc interval prolongation.
Study details: Retrospective study at two centers.
Disclosures: The article did not include information on funding sources or conflicts of interests.
Source: Cummins KC. et al. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018 Jul 24. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1485913.
Global burden of hematologic malignancies
Research has shown an increase in the global incidence of leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in recent years.
The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study showed that, from 2006 to 2016, the incidence of NHL increased 45%, and the incidence of leukemia increased 26%.
These increases were largely due to population growth and aging.
Results from the GDB study were published in JAMA Oncology.
The study indicated that, in 2016, there were 17.2 million cases of cancer worldwide and 8.9 million cancer deaths.
One in 3 men were likely to get cancer during their lifetime, as were 1 in 5 women. Cancer was associated with 213.2 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
The following table lists the 2016 global incidence and mortality figures for all cancers combined and for individual hematologic malignancies.
| Cancer type | Cases, thousands | Deaths, thousands |
| All cancers | 17,228 | 8927 |
| Leukemias | 467 | 310 |
| Acute lymphoid leukemia | 76 | 51 |
| Chronic lymphoid leukemia | 105 | 35 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 103 | 85 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 32 | 22 |
| Other leukemias | 150 | 117 |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 73 | 29 |
| NHL | 461 | 240 |
| Multiple myeloma | 139 | 98 |
Leukemia
In 2016, there were 467,000 new cases of leukemia and 310,000 leukemia deaths. Leukemia was responsible for 10.2 million DALYs. Leukemia developed in 1 in 118 men and 1 in 194 women worldwide.
Between 2006 and 2016, the global leukemia incidence increased by 26%—from 370,482 to 466,802 cases.
The researchers said the factors contributing to this increase were population growth (12%), population aging (10%), and an increase in age-specific incidence rates (3%).
NHL
In 2016, there were 461,000 new cases of NHL and 240,000 NHL deaths. NHL was responsible for 6.8 million DALYs. NHL developed in 1 in 110 men and 1 in 161 women worldwide.
Between 2006 and 2016, NHL increased by 45%, from 319,078 to 461,164 cases.
The factors contributing to this increase were increasing age-specific incidence rates (17%), changing population age structure (15%), and population growth (12%).
“A large proportion of the increase in cancer incidence can be explained by improving life expectancy and population growth—a development that can at least partially be attributed to a reduced burden from other common diseases,” the study authors wrote.
The authors also pointed out that prevention efforts are less effective for hematologic malignancies than for other cancers.
Research has shown an increase in the global incidence of leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in recent years.
The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study showed that, from 2006 to 2016, the incidence of NHL increased 45%, and the incidence of leukemia increased 26%.
These increases were largely due to population growth and aging.
Results from the GDB study were published in JAMA Oncology.
The study indicated that, in 2016, there were 17.2 million cases of cancer worldwide and 8.9 million cancer deaths.
One in 3 men were likely to get cancer during their lifetime, as were 1 in 5 women. Cancer was associated with 213.2 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
The following table lists the 2016 global incidence and mortality figures for all cancers combined and for individual hematologic malignancies.
| Cancer type | Cases, thousands | Deaths, thousands |
| All cancers | 17,228 | 8927 |
| Leukemias | 467 | 310 |
| Acute lymphoid leukemia | 76 | 51 |
| Chronic lymphoid leukemia | 105 | 35 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 103 | 85 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 32 | 22 |
| Other leukemias | 150 | 117 |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 73 | 29 |
| NHL | 461 | 240 |
| Multiple myeloma | 139 | 98 |
Leukemia
In 2016, there were 467,000 new cases of leukemia and 310,000 leukemia deaths. Leukemia was responsible for 10.2 million DALYs. Leukemia developed in 1 in 118 men and 1 in 194 women worldwide.
Between 2006 and 2016, the global leukemia incidence increased by 26%—from 370,482 to 466,802 cases.
The researchers said the factors contributing to this increase were population growth (12%), population aging (10%), and an increase in age-specific incidence rates (3%).
NHL
In 2016, there were 461,000 new cases of NHL and 240,000 NHL deaths. NHL was responsible for 6.8 million DALYs. NHL developed in 1 in 110 men and 1 in 161 women worldwide.
Between 2006 and 2016, NHL increased by 45%, from 319,078 to 461,164 cases.
The factors contributing to this increase were increasing age-specific incidence rates (17%), changing population age structure (15%), and population growth (12%).
“A large proportion of the increase in cancer incidence can be explained by improving life expectancy and population growth—a development that can at least partially be attributed to a reduced burden from other common diseases,” the study authors wrote.
The authors also pointed out that prevention efforts are less effective for hematologic malignancies than for other cancers.
Research has shown an increase in the global incidence of leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in recent years.
The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study showed that, from 2006 to 2016, the incidence of NHL increased 45%, and the incidence of leukemia increased 26%.
These increases were largely due to population growth and aging.
Results from the GDB study were published in JAMA Oncology.
The study indicated that, in 2016, there were 17.2 million cases of cancer worldwide and 8.9 million cancer deaths.
One in 3 men were likely to get cancer during their lifetime, as were 1 in 5 women. Cancer was associated with 213.2 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
The following table lists the 2016 global incidence and mortality figures for all cancers combined and for individual hematologic malignancies.
| Cancer type | Cases, thousands | Deaths, thousands |
| All cancers | 17,228 | 8927 |
| Leukemias | 467 | 310 |
| Acute lymphoid leukemia | 76 | 51 |
| Chronic lymphoid leukemia | 105 | 35 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 103 | 85 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 32 | 22 |
| Other leukemias | 150 | 117 |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 73 | 29 |
| NHL | 461 | 240 |
| Multiple myeloma | 139 | 98 |
Leukemia
In 2016, there were 467,000 new cases of leukemia and 310,000 leukemia deaths. Leukemia was responsible for 10.2 million DALYs. Leukemia developed in 1 in 118 men and 1 in 194 women worldwide.
Between 2006 and 2016, the global leukemia incidence increased by 26%—from 370,482 to 466,802 cases.
The researchers said the factors contributing to this increase were population growth (12%), population aging (10%), and an increase in age-specific incidence rates (3%).
NHL
In 2016, there were 461,000 new cases of NHL and 240,000 NHL deaths. NHL was responsible for 6.8 million DALYs. NHL developed in 1 in 110 men and 1 in 161 women worldwide.
Between 2006 and 2016, NHL increased by 45%, from 319,078 to 461,164 cases.
The factors contributing to this increase were increasing age-specific incidence rates (17%), changing population age structure (15%), and population growth (12%).
“A large proportion of the increase in cancer incidence can be explained by improving life expectancy and population growth—a development that can at least partially be attributed to a reduced burden from other common diseases,” the study authors wrote.
The authors also pointed out that prevention efforts are less effective for hematologic malignancies than for other cancers.
Drug receives fast track designation for WM
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted fast track designation to zanubrutinib for the treatment of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a BTK inhibitor being developed by BeiGene to treat various B-cell malignancies.
BeiGene is preparing to submit to the FDA, in the first half of 2019, a new drug application seeking accelerated approval of zanubrutinib for patients with WM.
The application will be supported by results from a phase 1 study. Results from this trial were presented at the 14th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (14-ICML) last year.
Researchers are also evaluating zanubrutinib in phase 2 (NCT03332173) and phase 3 (NCT03053440) trials of WM patients. In the phase 3 trial, researchers are comparing zanubrutinib to the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib.
Phase 1 results
As of March 31, 2017, 48 WM patients were enrolled in the phase 1 study. Thirty-eight patients had relapsed/refractory disease, and 10 patients were treatment-naïve.
There was a dose-escalation phase and a dose-expansion phase. The dose-expansion phase included doses of 160 mg twice a day or 320 mg once a day.
The most common (>10%) adverse events, (AEs) of any attribution were petechiae/purpura/contusion (35%), upper respiratory tract infection (31%), constipation (25%), diarrhea (19%), epistaxis (19%), nausea (17%), cough (15%), anemia (15%), headache (15%), neutropenia (13%), and rash (13%).
Most of these events were grade 1 or 2 in severity. The exceptions were grade 3/4 anemia and neutropenia (8% each) as well as grade 3/4 diarrhea and headache (2% each).
Five serious AEs were considered possibly related to zanubrutinib—1 case each of hemothorax, atrial fibrillation, colitis, febrile neutropenia, and headache. Three AEs led to treatment discontinuation—1 case each of bronchiectasis, prostate adenocarcinoma, and adenocarcinoma of pylorus.
At the time of the data cutoff, 42 patients were evaluable for response. At a median follow-up of 12.3 months (range, 4.4 to 30.5 months), the overall response rate was 90% (38/42).
The major response rate was 76% (32/42), with very good partial responses in 43% (18/42) of patients and partial responses in 33% (14/42) of patients. There were no complete responses and 2 cases of disease progression.
About fast track designation
The FDA’s fast track development program is designed to expedite clinical development and submission of applications for products with the potential to treat serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical needs.
Fast track designation facilitates frequent interactions with the FDA review team, including meetings to discuss the product’s development plan and written communications about issues such as trial design and use of biomarkers.
Products that receive fast track designation may be eligible for accelerated approval and priority review if relevant criteria are met. Such products may also be eligible for rolling review, which allows a developer to submit individual sections of a product’s application for review as they are ready, rather than waiting until all sections are complete.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted fast track designation to zanubrutinib for the treatment of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a BTK inhibitor being developed by BeiGene to treat various B-cell malignancies.
BeiGene is preparing to submit to the FDA, in the first half of 2019, a new drug application seeking accelerated approval of zanubrutinib for patients with WM.
The application will be supported by results from a phase 1 study. Results from this trial were presented at the 14th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (14-ICML) last year.
Researchers are also evaluating zanubrutinib in phase 2 (NCT03332173) and phase 3 (NCT03053440) trials of WM patients. In the phase 3 trial, researchers are comparing zanubrutinib to the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib.
Phase 1 results
As of March 31, 2017, 48 WM patients were enrolled in the phase 1 study. Thirty-eight patients had relapsed/refractory disease, and 10 patients were treatment-naïve.
There was a dose-escalation phase and a dose-expansion phase. The dose-expansion phase included doses of 160 mg twice a day or 320 mg once a day.
The most common (>10%) adverse events, (AEs) of any attribution were petechiae/purpura/contusion (35%), upper respiratory tract infection (31%), constipation (25%), diarrhea (19%), epistaxis (19%), nausea (17%), cough (15%), anemia (15%), headache (15%), neutropenia (13%), and rash (13%).
Most of these events were grade 1 or 2 in severity. The exceptions were grade 3/4 anemia and neutropenia (8% each) as well as grade 3/4 diarrhea and headache (2% each).
Five serious AEs were considered possibly related to zanubrutinib—1 case each of hemothorax, atrial fibrillation, colitis, febrile neutropenia, and headache. Three AEs led to treatment discontinuation—1 case each of bronchiectasis, prostate adenocarcinoma, and adenocarcinoma of pylorus.
At the time of the data cutoff, 42 patients were evaluable for response. At a median follow-up of 12.3 months (range, 4.4 to 30.5 months), the overall response rate was 90% (38/42).
The major response rate was 76% (32/42), with very good partial responses in 43% (18/42) of patients and partial responses in 33% (14/42) of patients. There were no complete responses and 2 cases of disease progression.
About fast track designation
The FDA’s fast track development program is designed to expedite clinical development and submission of applications for products with the potential to treat serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical needs.
Fast track designation facilitates frequent interactions with the FDA review team, including meetings to discuss the product’s development plan and written communications about issues such as trial design and use of biomarkers.
Products that receive fast track designation may be eligible for accelerated approval and priority review if relevant criteria are met. Such products may also be eligible for rolling review, which allows a developer to submit individual sections of a product’s application for review as they are ready, rather than waiting until all sections are complete.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted fast track designation to zanubrutinib for the treatment of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a BTK inhibitor being developed by BeiGene to treat various B-cell malignancies.
BeiGene is preparing to submit to the FDA, in the first half of 2019, a new drug application seeking accelerated approval of zanubrutinib for patients with WM.
The application will be supported by results from a phase 1 study. Results from this trial were presented at the 14th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (14-ICML) last year.
Researchers are also evaluating zanubrutinib in phase 2 (NCT03332173) and phase 3 (NCT03053440) trials of WM patients. In the phase 3 trial, researchers are comparing zanubrutinib to the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib.
Phase 1 results
As of March 31, 2017, 48 WM patients were enrolled in the phase 1 study. Thirty-eight patients had relapsed/refractory disease, and 10 patients were treatment-naïve.
There was a dose-escalation phase and a dose-expansion phase. The dose-expansion phase included doses of 160 mg twice a day or 320 mg once a day.
The most common (>10%) adverse events, (AEs) of any attribution were petechiae/purpura/contusion (35%), upper respiratory tract infection (31%), constipation (25%), diarrhea (19%), epistaxis (19%), nausea (17%), cough (15%), anemia (15%), headache (15%), neutropenia (13%), and rash (13%).
Most of these events were grade 1 or 2 in severity. The exceptions were grade 3/4 anemia and neutropenia (8% each) as well as grade 3/4 diarrhea and headache (2% each).
Five serious AEs were considered possibly related to zanubrutinib—1 case each of hemothorax, atrial fibrillation, colitis, febrile neutropenia, and headache. Three AEs led to treatment discontinuation—1 case each of bronchiectasis, prostate adenocarcinoma, and adenocarcinoma of pylorus.
At the time of the data cutoff, 42 patients were evaluable for response. At a median follow-up of 12.3 months (range, 4.4 to 30.5 months), the overall response rate was 90% (38/42).
The major response rate was 76% (32/42), with very good partial responses in 43% (18/42) of patients and partial responses in 33% (14/42) of patients. There were no complete responses and 2 cases of disease progression.
About fast track designation
The FDA’s fast track development program is designed to expedite clinical development and submission of applications for products with the potential to treat serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical needs.
Fast track designation facilitates frequent interactions with the FDA review team, including meetings to discuss the product’s development plan and written communications about issues such as trial design and use of biomarkers.
Products that receive fast track designation may be eligible for accelerated approval and priority review if relevant criteria are met. Such products may also be eligible for rolling review, which allows a developer to submit individual sections of a product’s application for review as they are ready, rather than waiting until all sections are complete.
FDA approves biosimilar filgrastim
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the leukocyte growth factor Nivestym™ (filgrastim-aafi), a biosimilar to Neupogen (filgrastim).
Nivestym is approved to treat patients with nonmyeloid malignancies who are receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy or undergoing bone marrow transplant, acute myeloid leukemia patients receiving induction or consolidation chemotherapy, patients undergoing autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell collection, and patients with severe chronic neutropenia.
The FDA’s approval of Nivestym was based on a review of evidence suggesting the drug is highly similar to Neupogen, according to Pfizer, the company developing Nivestym.
The full approved indication for Nivestym is as follows:
- To decrease the incidence of infection, as manifested by febrile neutropenia, in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anticancer drugs associated with a significant incidence of severe neutropenia with fever
- To reduce the time to neutrophil recovery and the duration of fever following induction or consolidation chemotherapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia
- To reduce the duration of neutropenia and neutropenia-related clinical sequelae (eg, febrile neutropenia) in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies undergoing myeloablative chemotherapy followed by bone marrow transplant
- For the mobilization of autologous hematopoietic progenitor cells into the peripheral blood for collection by leukapheresis
- For chronic administration to reduce the incidence and duration of sequelae of severe neutropenia (eg, fever, infections, oropharyngeal ulcers) in symptomatic patients with congenital neutropenia, cyclic neutropenia, or idiopathic neutropenia.
For more details on Nivestym, see the full prescribing information.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the leukocyte growth factor Nivestym™ (filgrastim-aafi), a biosimilar to Neupogen (filgrastim).
Nivestym is approved to treat patients with nonmyeloid malignancies who are receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy or undergoing bone marrow transplant, acute myeloid leukemia patients receiving induction or consolidation chemotherapy, patients undergoing autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell collection, and patients with severe chronic neutropenia.
The FDA’s approval of Nivestym was based on a review of evidence suggesting the drug is highly similar to Neupogen, according to Pfizer, the company developing Nivestym.
The full approved indication for Nivestym is as follows:
- To decrease the incidence of infection, as manifested by febrile neutropenia, in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anticancer drugs associated with a significant incidence of severe neutropenia with fever
- To reduce the time to neutrophil recovery and the duration of fever following induction or consolidation chemotherapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia
- To reduce the duration of neutropenia and neutropenia-related clinical sequelae (eg, febrile neutropenia) in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies undergoing myeloablative chemotherapy followed by bone marrow transplant
- For the mobilization of autologous hematopoietic progenitor cells into the peripheral blood for collection by leukapheresis
- For chronic administration to reduce the incidence and duration of sequelae of severe neutropenia (eg, fever, infections, oropharyngeal ulcers) in symptomatic patients with congenital neutropenia, cyclic neutropenia, or idiopathic neutropenia.
For more details on Nivestym, see the full prescribing information.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the leukocyte growth factor Nivestym™ (filgrastim-aafi), a biosimilar to Neupogen (filgrastim).
Nivestym is approved to treat patients with nonmyeloid malignancies who are receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy or undergoing bone marrow transplant, acute myeloid leukemia patients receiving induction or consolidation chemotherapy, patients undergoing autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell collection, and patients with severe chronic neutropenia.
The FDA’s approval of Nivestym was based on a review of evidence suggesting the drug is highly similar to Neupogen, according to Pfizer, the company developing Nivestym.
The full approved indication for Nivestym is as follows:
- To decrease the incidence of infection, as manifested by febrile neutropenia, in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anticancer drugs associated with a significant incidence of severe neutropenia with fever
- To reduce the time to neutrophil recovery and the duration of fever following induction or consolidation chemotherapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia
- To reduce the duration of neutropenia and neutropenia-related clinical sequelae (eg, febrile neutropenia) in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies undergoing myeloablative chemotherapy followed by bone marrow transplant
- For the mobilization of autologous hematopoietic progenitor cells into the peripheral blood for collection by leukapheresis
- For chronic administration to reduce the incidence and duration of sequelae of severe neutropenia (eg, fever, infections, oropharyngeal ulcers) in symptomatic patients with congenital neutropenia, cyclic neutropenia, or idiopathic neutropenia.
For more details on Nivestym, see the full prescribing information.
Diabetics have higher risk of hematologic, other cancers
A review of data from more than 19 million people indicates that diabetes significantly raises a person’s risk of developing cancer.
When researchers compared patients with diabetes and without, both male and female diabetics had an increased risk of leukemias and lymphomas as well as certain solid tumors.
Researchers also found that diabetes conferred a higher cancer risk for women than men, both for all cancers combined and for some specific cancers, including leukemia.
“The link between diabetes and the risk of developing cancer is now firmly established,” said Toshiaki Ohkuma, PhD, of The George Institute for Global Health at the University of New South Wales in Australia.
“We have also demonstrated, for the first time, that women with diabetes are more likely to develop any form of cancer and have a significantly higher chance of developing kidney, oral, and stomach cancers and leukemia.”
Dr Ohkuma and his colleagues reported these findings in Diabetologia.
The researchers conducted a systematic search in PubMed MEDLINE to identify reports on the links between diabetes and cancer. Additional reports were identified from the reference lists of the relevant studies.
Only those cohort studies providing relative risks (RRs) for the association between diabetes and cancer for both women and men were included. In total, 107 relevant articles were identified, along with 36 cohorts of individual participant data.
RRs for cancer were obtained for patients with diabetes (types 1 and 2 combined) versus those without diabetes, for both men and women. The women-to-men ratios of these relative risk ratios (RRRs) were then calculated to determine the excess risk in women if present.
Data on all-site cancer was available from 47 studies, involving 121 cohorts and 19,239,302 individuals.
Diabetics vs non-diabetics
Women with diabetes had a 27% higher risk of all-site cancer compared to women without diabetes (RR=1.27; 95% CI 1.21, 1.32; P<0.001).
For men, the risk of all-site cancer was 19% higher among those with diabetes than those without (RR=1.19; 95% CI 1.13, 1.25; P<0.001).
There were several hematologic malignancies for which diabetics had an increased risk, as shown in the following table.
| Cancer type | RR for women (99% CI) | RR for men (99% CI) |
| Lymphatic and hematopoietic tissue | 1.24 (1.05, 1.46)* | 1.21 (0.98, 1.48) |
| Leukemia | 1.53 (1.00, 2.33) | 1.22 (0.80, 1.85) |
| Myeloid leukemia | 0.83 (0.39, 1.76) | 1.12 (0.77, 1.62) |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 1.33 (1.12, 1.57)* | 1.14 (0.56, 2.33) |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 1.67 (1.27, 2.20)* | 1.62 (1.32, 1.98)* |
| Lymphoid leukemia | 1.74 (0.31, 9.79) | 1.20 (0.86, 1.68) |
| Lymphoma | 2.31 (0.57, 9.30) | 1.80 (0.68, 4.75) |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 1.16 (1.02, 1.32)* | 1.20 (1.08, 1.34)* |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 1.20 (0.61, 2.38) | 1.36 (1.05, 1.77)* |
| Multiple myeloma | 1.19 (0.97, 1.47) | 1.12 (0.90, 1.41) |
| *denotes statistical significance with a P value < 0.01 | ||
Sex comparison
Calculation of the women-to-men ratio revealed that women with diabetes had a 6% greater excess risk of all-site cancer compared to men with diabetes (RRR=1.06; 95% CI 1.03, 1.09; P<0.001).
The women-to-men ratios also showed significantly higher risks for female diabetics for:
- Kidney cancer—RRR=1.11 (99% CI 1.04, 1.18; P<0.001)
- Oral cancer—RRR=1.13 (99% CI 1.00, 1.28; P=0.009)
- Stomach cancer—RRR=1.14 (99% CI 1.07, 1.22; P<0.001)
- Leukemia—RRR=1.15 (99% CI 1.02, 1.28; P=0.002).
However, women had a significantly lower risk of liver cancer (RRR=0.88; 99% CI 0.79, 0.99; P=0.005).
There are several possible reasons for the excess cancer risk observed in women, according to study author Sanne Peters, PhD, of The George Institute for Global Health at the University of Oxford in the UK.
For example, on average, women are in the pre-diabetic state of impaired glucose tolerance 2 years longer than men.
“Historically, we know that women are often under-treated when they first present with symptoms of diabetes, are less likely to receive intensive care, and are not taking the same levels of medications as men,” Dr Peters said. “All of these could go some way into explaining why women are at greater risk of developing cancer, but, without more research, we can’t be certain.”
A review of data from more than 19 million people indicates that diabetes significantly raises a person’s risk of developing cancer.
When researchers compared patients with diabetes and without, both male and female diabetics had an increased risk of leukemias and lymphomas as well as certain solid tumors.
Researchers also found that diabetes conferred a higher cancer risk for women than men, both for all cancers combined and for some specific cancers, including leukemia.
“The link between diabetes and the risk of developing cancer is now firmly established,” said Toshiaki Ohkuma, PhD, of The George Institute for Global Health at the University of New South Wales in Australia.
“We have also demonstrated, for the first time, that women with diabetes are more likely to develop any form of cancer and have a significantly higher chance of developing kidney, oral, and stomach cancers and leukemia.”
Dr Ohkuma and his colleagues reported these findings in Diabetologia.
The researchers conducted a systematic search in PubMed MEDLINE to identify reports on the links between diabetes and cancer. Additional reports were identified from the reference lists of the relevant studies.
Only those cohort studies providing relative risks (RRs) for the association between diabetes and cancer for both women and men were included. In total, 107 relevant articles were identified, along with 36 cohorts of individual participant data.
RRs for cancer were obtained for patients with diabetes (types 1 and 2 combined) versus those without diabetes, for both men and women. The women-to-men ratios of these relative risk ratios (RRRs) were then calculated to determine the excess risk in women if present.
Data on all-site cancer was available from 47 studies, involving 121 cohorts and 19,239,302 individuals.
Diabetics vs non-diabetics
Women with diabetes had a 27% higher risk of all-site cancer compared to women without diabetes (RR=1.27; 95% CI 1.21, 1.32; P<0.001).
For men, the risk of all-site cancer was 19% higher among those with diabetes than those without (RR=1.19; 95% CI 1.13, 1.25; P<0.001).
There were several hematologic malignancies for which diabetics had an increased risk, as shown in the following table.
| Cancer type | RR for women (99% CI) | RR for men (99% CI) |
| Lymphatic and hematopoietic tissue | 1.24 (1.05, 1.46)* | 1.21 (0.98, 1.48) |
| Leukemia | 1.53 (1.00, 2.33) | 1.22 (0.80, 1.85) |
| Myeloid leukemia | 0.83 (0.39, 1.76) | 1.12 (0.77, 1.62) |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 1.33 (1.12, 1.57)* | 1.14 (0.56, 2.33) |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 1.67 (1.27, 2.20)* | 1.62 (1.32, 1.98)* |
| Lymphoid leukemia | 1.74 (0.31, 9.79) | 1.20 (0.86, 1.68) |
| Lymphoma | 2.31 (0.57, 9.30) | 1.80 (0.68, 4.75) |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 1.16 (1.02, 1.32)* | 1.20 (1.08, 1.34)* |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 1.20 (0.61, 2.38) | 1.36 (1.05, 1.77)* |
| Multiple myeloma | 1.19 (0.97, 1.47) | 1.12 (0.90, 1.41) |
| *denotes statistical significance with a P value < 0.01 | ||
Sex comparison
Calculation of the women-to-men ratio revealed that women with diabetes had a 6% greater excess risk of all-site cancer compared to men with diabetes (RRR=1.06; 95% CI 1.03, 1.09; P<0.001).
The women-to-men ratios also showed significantly higher risks for female diabetics for:
- Kidney cancer—RRR=1.11 (99% CI 1.04, 1.18; P<0.001)
- Oral cancer—RRR=1.13 (99% CI 1.00, 1.28; P=0.009)
- Stomach cancer—RRR=1.14 (99% CI 1.07, 1.22; P<0.001)
- Leukemia—RRR=1.15 (99% CI 1.02, 1.28; P=0.002).
However, women had a significantly lower risk of liver cancer (RRR=0.88; 99% CI 0.79, 0.99; P=0.005).
There are several possible reasons for the excess cancer risk observed in women, according to study author Sanne Peters, PhD, of The George Institute for Global Health at the University of Oxford in the UK.
For example, on average, women are in the pre-diabetic state of impaired glucose tolerance 2 years longer than men.
“Historically, we know that women are often under-treated when they first present with symptoms of diabetes, are less likely to receive intensive care, and are not taking the same levels of medications as men,” Dr Peters said. “All of these could go some way into explaining why women are at greater risk of developing cancer, but, without more research, we can’t be certain.”
A review of data from more than 19 million people indicates that diabetes significantly raises a person’s risk of developing cancer.
When researchers compared patients with diabetes and without, both male and female diabetics had an increased risk of leukemias and lymphomas as well as certain solid tumors.
Researchers also found that diabetes conferred a higher cancer risk for women than men, both for all cancers combined and for some specific cancers, including leukemia.
“The link between diabetes and the risk of developing cancer is now firmly established,” said Toshiaki Ohkuma, PhD, of The George Institute for Global Health at the University of New South Wales in Australia.
“We have also demonstrated, for the first time, that women with diabetes are more likely to develop any form of cancer and have a significantly higher chance of developing kidney, oral, and stomach cancers and leukemia.”
Dr Ohkuma and his colleagues reported these findings in Diabetologia.
The researchers conducted a systematic search in PubMed MEDLINE to identify reports on the links between diabetes and cancer. Additional reports were identified from the reference lists of the relevant studies.
Only those cohort studies providing relative risks (RRs) for the association between diabetes and cancer for both women and men were included. In total, 107 relevant articles were identified, along with 36 cohorts of individual participant data.
RRs for cancer were obtained for patients with diabetes (types 1 and 2 combined) versus those without diabetes, for both men and women. The women-to-men ratios of these relative risk ratios (RRRs) were then calculated to determine the excess risk in women if present.
Data on all-site cancer was available from 47 studies, involving 121 cohorts and 19,239,302 individuals.
Diabetics vs non-diabetics
Women with diabetes had a 27% higher risk of all-site cancer compared to women without diabetes (RR=1.27; 95% CI 1.21, 1.32; P<0.001).
For men, the risk of all-site cancer was 19% higher among those with diabetes than those without (RR=1.19; 95% CI 1.13, 1.25; P<0.001).
There were several hematologic malignancies for which diabetics had an increased risk, as shown in the following table.
| Cancer type | RR for women (99% CI) | RR for men (99% CI) |
| Lymphatic and hematopoietic tissue | 1.24 (1.05, 1.46)* | 1.21 (0.98, 1.48) |
| Leukemia | 1.53 (1.00, 2.33) | 1.22 (0.80, 1.85) |
| Myeloid leukemia | 0.83 (0.39, 1.76) | 1.12 (0.77, 1.62) |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 1.33 (1.12, 1.57)* | 1.14 (0.56, 2.33) |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 1.67 (1.27, 2.20)* | 1.62 (1.32, 1.98)* |
| Lymphoid leukemia | 1.74 (0.31, 9.79) | 1.20 (0.86, 1.68) |
| Lymphoma | 2.31 (0.57, 9.30) | 1.80 (0.68, 4.75) |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 1.16 (1.02, 1.32)* | 1.20 (1.08, 1.34)* |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 1.20 (0.61, 2.38) | 1.36 (1.05, 1.77)* |
| Multiple myeloma | 1.19 (0.97, 1.47) | 1.12 (0.90, 1.41) |
| *denotes statistical significance with a P value < 0.01 | ||
Sex comparison
Calculation of the women-to-men ratio revealed that women with diabetes had a 6% greater excess risk of all-site cancer compared to men with diabetes (RRR=1.06; 95% CI 1.03, 1.09; P<0.001).
The women-to-men ratios also showed significantly higher risks for female diabetics for:
- Kidney cancer—RRR=1.11 (99% CI 1.04, 1.18; P<0.001)
- Oral cancer—RRR=1.13 (99% CI 1.00, 1.28; P=0.009)
- Stomach cancer—RRR=1.14 (99% CI 1.07, 1.22; P<0.001)
- Leukemia—RRR=1.15 (99% CI 1.02, 1.28; P=0.002).
However, women had a significantly lower risk of liver cancer (RRR=0.88; 99% CI 0.79, 0.99; P=0.005).
There are several possible reasons for the excess cancer risk observed in women, according to study author Sanne Peters, PhD, of The George Institute for Global Health at the University of Oxford in the UK.
For example, on average, women are in the pre-diabetic state of impaired glucose tolerance 2 years longer than men.
“Historically, we know that women are often under-treated when they first present with symptoms of diabetes, are less likely to receive intensive care, and are not taking the same levels of medications as men,” Dr Peters said. “All of these could go some way into explaining why women are at greater risk of developing cancer, but, without more research, we can’t be certain.”
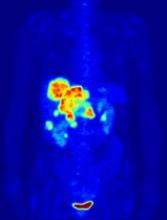
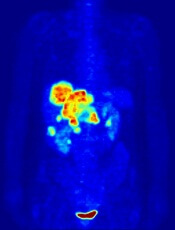
PET-guided treatment didn’t improve outcomes
In the PETAL trial, treatment intensification based on results of an interim positron emission tomography (PET) scan did not improve survival outcomes for patients with aggressive lymphomas.
PET-positive patients did not benefit by switching from R-CHOP to a more intensive chemotherapy regimen.
PET-negative patients did not benefit from 2 additional cycles of rituximab after R-CHOP.
These results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
PETAL was a randomized trial of patients with newly diagnosed T- or B-cell lymphomas.
Patients received 2 cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone)—plus rituximab (R-CHOP) in CD20-positive lymphomas—followed by a PET scan.
PET-positive patients were randomized to receive 6 additional cycles of R-CHOP or 6 blocks of an intensive protocol used to treat Burkitt lymphoma. This protocol consisted of high-dose methotrexate, cytarabine, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide, split-dose doxorubicin and etoposide, vincristine, vindesine, and dexamethasone.
PET-negative patients with CD20-positive lymphomas were randomized to receive 4 additional cycles of R-CHOP or 4 additional cycles of R-CHOP followed by 2 more doses of rituximab.
Among patients with T-cell lymphomas, only PET-positive individuals underwent randomization. PET-negative patients received CHOP. Patients with CD20-positive T-cell lymphomas also received rituximab.
PET-positive results
Of the PET-positive patients (108/862), 52 were randomized to receive 6 additional cycles of R-CHOP, and 56 were randomized to 6 cycles of the Burkitt protocol.
In general, survival rates were similar regardless of treatment. The 2-year overall survival (OS) rate was 63.6% for patients who received R-CHOP and 55.4% for those who received the more intensive protocol.
Two-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 49.4% and 43.1%, respectively. Two-year event-free survival (EFS) rates were 42.0% and 31.6%, respectively.
Among patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the OS rate was 64.8% for patients who received R-CHOP and 47.1% for those on the Burkitt protocol. PFS rates were 55.5% and 41.4%, respectively.
There was a significant difference in EFS rates among the DLBCL patients—52.4% in the R-CHOP arm and 28.3% in the intensive arm (P=0.0186).
Among T-cell lymphoma patients, the OS rate was 22.2% in the R-CHOP arm and 30.0% in the intensive arm. The PFS rates were 12.7% and 30%, respectively. The EFS rates were the same as the PFS rates.
Overall, patients who received the Burkitt protocol had significantly higher rates of grade 3/4 hematologic toxicities, infection, and mucositis.
PET-negative results
Of 754 PET-negative patients, 697 had CD20-positive lymphomas, and 255 of those patients (all with B-cell lymphomas) underwent randomization.
There were 129 patients who were randomized to receive 6 cycles of R-CHOP (2 before and 4 after randomization) and 126 who were randomized to receive 6 cycles of R-CHOP plus 2 additional cycles of rituximab.
Again, survival rates were similar regardless of treatment.
The 2-year OS was 88.2% for patients who received only R-CHOP and 87.2% for those with additional rituximab exposure. PFS rates were 82.0% and 77.5%, respectively. EFS rates were 76.4% and 73.5%, respectively.
In the DLBCL patients, the OS rate was 88.5% in the R-CHOP arm and 85.8% in the intensive arm. PFS rates were 82.3% and 77.7%, respectively. EFS rates were 72.6% and 78.9%, respectively.
As increasing the dose of rituximab did not improve outcomes, the investigators concluded that 6 cycles of R-CHOP should be the standard of care for these patients.
The team also said interim PET scanning is “a powerful tool” for identifying chemotherapy-resistant lymphomas, and PET-positive patients may be candidates for immunologic treatment approaches.
In the PETAL trial, treatment intensification based on results of an interim positron emission tomography (PET) scan did not improve survival outcomes for patients with aggressive lymphomas.
PET-positive patients did not benefit by switching from R-CHOP to a more intensive chemotherapy regimen.
PET-negative patients did not benefit from 2 additional cycles of rituximab after R-CHOP.
These results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
PETAL was a randomized trial of patients with newly diagnosed T- or B-cell lymphomas.
Patients received 2 cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone)—plus rituximab (R-CHOP) in CD20-positive lymphomas—followed by a PET scan.
PET-positive patients were randomized to receive 6 additional cycles of R-CHOP or 6 blocks of an intensive protocol used to treat Burkitt lymphoma. This protocol consisted of high-dose methotrexate, cytarabine, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide, split-dose doxorubicin and etoposide, vincristine, vindesine, and dexamethasone.
PET-negative patients with CD20-positive lymphomas were randomized to receive 4 additional cycles of R-CHOP or 4 additional cycles of R-CHOP followed by 2 more doses of rituximab.
Among patients with T-cell lymphomas, only PET-positive individuals underwent randomization. PET-negative patients received CHOP. Patients with CD20-positive T-cell lymphomas also received rituximab.
PET-positive results
Of the PET-positive patients (108/862), 52 were randomized to receive 6 additional cycles of R-CHOP, and 56 were randomized to 6 cycles of the Burkitt protocol.
In general, survival rates were similar regardless of treatment. The 2-year overall survival (OS) rate was 63.6% for patients who received R-CHOP and 55.4% for those who received the more intensive protocol.
Two-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 49.4% and 43.1%, respectively. Two-year event-free survival (EFS) rates were 42.0% and 31.6%, respectively.
Among patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the OS rate was 64.8% for patients who received R-CHOP and 47.1% for those on the Burkitt protocol. PFS rates were 55.5% and 41.4%, respectively.
There was a significant difference in EFS rates among the DLBCL patients—52.4% in the R-CHOP arm and 28.3% in the intensive arm (P=0.0186).
Among T-cell lymphoma patients, the OS rate was 22.2% in the R-CHOP arm and 30.0% in the intensive arm. The PFS rates were 12.7% and 30%, respectively. The EFS rates were the same as the PFS rates.
Overall, patients who received the Burkitt protocol had significantly higher rates of grade 3/4 hematologic toxicities, infection, and mucositis.
PET-negative results
Of 754 PET-negative patients, 697 had CD20-positive lymphomas, and 255 of those patients (all with B-cell lymphomas) underwent randomization.
There were 129 patients who were randomized to receive 6 cycles of R-CHOP (2 before and 4 after randomization) and 126 who were randomized to receive 6 cycles of R-CHOP plus 2 additional cycles of rituximab.
Again, survival rates were similar regardless of treatment.
The 2-year OS was 88.2% for patients who received only R-CHOP and 87.2% for those with additional rituximab exposure. PFS rates were 82.0% and 77.5%, respectively. EFS rates were 76.4% and 73.5%, respectively.
In the DLBCL patients, the OS rate was 88.5% in the R-CHOP arm and 85.8% in the intensive arm. PFS rates were 82.3% and 77.7%, respectively. EFS rates were 72.6% and 78.9%, respectively.
As increasing the dose of rituximab did not improve outcomes, the investigators concluded that 6 cycles of R-CHOP should be the standard of care for these patients.
The team also said interim PET scanning is “a powerful tool” for identifying chemotherapy-resistant lymphomas, and PET-positive patients may be candidates for immunologic treatment approaches.
In the PETAL trial, treatment intensification based on results of an interim positron emission tomography (PET) scan did not improve survival outcomes for patients with aggressive lymphomas.
PET-positive patients did not benefit by switching from R-CHOP to a more intensive chemotherapy regimen.
PET-negative patients did not benefit from 2 additional cycles of rituximab after R-CHOP.
These results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
PETAL was a randomized trial of patients with newly diagnosed T- or B-cell lymphomas.
Patients received 2 cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone)—plus rituximab (R-CHOP) in CD20-positive lymphomas—followed by a PET scan.
PET-positive patients were randomized to receive 6 additional cycles of R-CHOP or 6 blocks of an intensive protocol used to treat Burkitt lymphoma. This protocol consisted of high-dose methotrexate, cytarabine, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide, split-dose doxorubicin and etoposide, vincristine, vindesine, and dexamethasone.
PET-negative patients with CD20-positive lymphomas were randomized to receive 4 additional cycles of R-CHOP or 4 additional cycles of R-CHOP followed by 2 more doses of rituximab.
Among patients with T-cell lymphomas, only PET-positive individuals underwent randomization. PET-negative patients received CHOP. Patients with CD20-positive T-cell lymphomas also received rituximab.
PET-positive results
Of the PET-positive patients (108/862), 52 were randomized to receive 6 additional cycles of R-CHOP, and 56 were randomized to 6 cycles of the Burkitt protocol.
In general, survival rates were similar regardless of treatment. The 2-year overall survival (OS) rate was 63.6% for patients who received R-CHOP and 55.4% for those who received the more intensive protocol.
Two-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 49.4% and 43.1%, respectively. Two-year event-free survival (EFS) rates were 42.0% and 31.6%, respectively.
Among patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the OS rate was 64.8% for patients who received R-CHOP and 47.1% for those on the Burkitt protocol. PFS rates were 55.5% and 41.4%, respectively.
There was a significant difference in EFS rates among the DLBCL patients—52.4% in the R-CHOP arm and 28.3% in the intensive arm (P=0.0186).
Among T-cell lymphoma patients, the OS rate was 22.2% in the R-CHOP arm and 30.0% in the intensive arm. The PFS rates were 12.7% and 30%, respectively. The EFS rates were the same as the PFS rates.
Overall, patients who received the Burkitt protocol had significantly higher rates of grade 3/4 hematologic toxicities, infection, and mucositis.
PET-negative results
Of 754 PET-negative patients, 697 had CD20-positive lymphomas, and 255 of those patients (all with B-cell lymphomas) underwent randomization.
There were 129 patients who were randomized to receive 6 cycles of R-CHOP (2 before and 4 after randomization) and 126 who were randomized to receive 6 cycles of R-CHOP plus 2 additional cycles of rituximab.
Again, survival rates were similar regardless of treatment.
The 2-year OS was 88.2% for patients who received only R-CHOP and 87.2% for those with additional rituximab exposure. PFS rates were 82.0% and 77.5%, respectively. EFS rates were 76.4% and 73.5%, respectively.
In the DLBCL patients, the OS rate was 88.5% in the R-CHOP arm and 85.8% in the intensive arm. PFS rates were 82.3% and 77.7%, respectively. EFS rates were 72.6% and 78.9%, respectively.
As increasing the dose of rituximab did not improve outcomes, the investigators concluded that 6 cycles of R-CHOP should be the standard of care for these patients.
The team also said interim PET scanning is “a powerful tool” for identifying chemotherapy-resistant lymphomas, and PET-positive patients may be candidates for immunologic treatment approaches.
New guideline for managing MCL
Rituximab should be included in first-line chemotherapy when treating mantle cell lymphoma, according to a new management guideline from the British Society for Haematology.
The best outcome data is for the R-CHOP regimen (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) followed by maintenance treatment with rituximab, wrote Pamela McKay, MD, of Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre in Glasgow, and her colleagues. The report was published in the British Journal of Haematology. But the combination of rituximab and bendamustine is also effective and a more favorable safety profile, according to the guideline. Single agent rituximab is not recommended.
At relapse, the guideline calls on physicians to take an individualized approach based on age, comorbidities, performance status, and response to prior therapy. Some options to consider include ibrutinib as a single agent or rituximab plus chemotherapy. The authors cautioned that there is little evidence to support maintenance rituximab after relapse treatment.
The guideline also explores the role of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and allogeneic SCT (alloSCT). The authors recommend that ASCT be considered as consolidation of first-line therapy for patients who are fit for intensive therapy. AlloSCT is a viable option in second remission among fit patients who have an appropriate donor and it may also be effective as a rescue therapy for patients who relapse after ASCT. But alloSCT is appropriate only as a first-line therapy for high-risk patients and is best used as part of a clinical trial, according to the recommendations.
The British Society of Haematology previously issued guidance on mantle cell lymphoma in 2012, but the updated document includes new drug therapeutic options and transplant data. The guideline includes a therapeutic algorithm to assist physicians in choosing first-line therapy, options after first relapse, and management in the case of higher relapse.
The guideline authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: McKay P et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul;182(1):46-62.
Rituximab should be included in first-line chemotherapy when treating mantle cell lymphoma, according to a new management guideline from the British Society for Haematology.
The best outcome data is for the R-CHOP regimen (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) followed by maintenance treatment with rituximab, wrote Pamela McKay, MD, of Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre in Glasgow, and her colleagues. The report was published in the British Journal of Haematology. But the combination of rituximab and bendamustine is also effective and a more favorable safety profile, according to the guideline. Single agent rituximab is not recommended.
At relapse, the guideline calls on physicians to take an individualized approach based on age, comorbidities, performance status, and response to prior therapy. Some options to consider include ibrutinib as a single agent or rituximab plus chemotherapy. The authors cautioned that there is little evidence to support maintenance rituximab after relapse treatment.
The guideline also explores the role of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and allogeneic SCT (alloSCT). The authors recommend that ASCT be considered as consolidation of first-line therapy for patients who are fit for intensive therapy. AlloSCT is a viable option in second remission among fit patients who have an appropriate donor and it may also be effective as a rescue therapy for patients who relapse after ASCT. But alloSCT is appropriate only as a first-line therapy for high-risk patients and is best used as part of a clinical trial, according to the recommendations.
The British Society of Haematology previously issued guidance on mantle cell lymphoma in 2012, but the updated document includes new drug therapeutic options and transplant data. The guideline includes a therapeutic algorithm to assist physicians in choosing first-line therapy, options after first relapse, and management in the case of higher relapse.
The guideline authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: McKay P et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul;182(1):46-62.
Rituximab should be included in first-line chemotherapy when treating mantle cell lymphoma, according to a new management guideline from the British Society for Haematology.
The best outcome data is for the R-CHOP regimen (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) followed by maintenance treatment with rituximab, wrote Pamela McKay, MD, of Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre in Glasgow, and her colleagues. The report was published in the British Journal of Haematology. But the combination of rituximab and bendamustine is also effective and a more favorable safety profile, according to the guideline. Single agent rituximab is not recommended.
At relapse, the guideline calls on physicians to take an individualized approach based on age, comorbidities, performance status, and response to prior therapy. Some options to consider include ibrutinib as a single agent or rituximab plus chemotherapy. The authors cautioned that there is little evidence to support maintenance rituximab after relapse treatment.
The guideline also explores the role of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and allogeneic SCT (alloSCT). The authors recommend that ASCT be considered as consolidation of first-line therapy for patients who are fit for intensive therapy. AlloSCT is a viable option in second remission among fit patients who have an appropriate donor and it may also be effective as a rescue therapy for patients who relapse after ASCT. But alloSCT is appropriate only as a first-line therapy for high-risk patients and is best used as part of a clinical trial, according to the recommendations.
The British Society of Haematology previously issued guidance on mantle cell lymphoma in 2012, but the updated document includes new drug therapeutic options and transplant data. The guideline includes a therapeutic algorithm to assist physicians in choosing first-line therapy, options after first relapse, and management in the case of higher relapse.
The guideline authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: McKay P et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul;182(1):46-62.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF HAEMATOLOGY
Ibrutinib/venetoclax shows early promise in relapsed CLL
STOCKHOLM – A chemotherapy-free regimen of ibrutinib plus venetoclax was generally safe and showed promising early efficacy in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia, investigators reported.
A planned interim analysis performed after the first 15 patients who had received two cycles of ibrutinib plus one of ibrutinib and venetoclax showed no treatment-related deaths or treatment interruptions, and all patients had clinical responses, including 8 with complete clinical remission (CR), reported Carsten U. Niemann, MD, PhD, from Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen, and his colleagues.
The goal of the ongoing VISION/HOVEN 141 study is to evaluate whether minimal residual disease (MRD)–guided therapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax could lead to MRD negativity and allow select patients to stop treatment, Dr. Niemann said in an interview at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“It’s a 100% clinical response rate and 53% CR. Obviously these are clinical responses, so we don’t have the CT scans, we don’t have the bone marrow biopsies, but we’re very happy to see even in the relapsed/refractory setting such good response rates,” he said.
The investigators are enrolling patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic leukemia requiring treatment and starting all patients on ibrutinib 420 mg daily for the first 2 cycles, with venetoclax added in a 5-week ramp-up from 20 mg beginning with cycle 3 to a final dose of 400 mg daily for 15 total treatment cycles.
At the end of the induction phase, patients who are determined to be MRD-negative by flow cytometry at cycles 12 and 15, and by bone marrow at cycle 15, are randomized on a 1:2 basis to ibrutinib maintenance until disease progression or intolerable toxicity, or to observation until progression or loss of MRD negativity, at which time they start maintenance with ibrutinib until progression or toxicity, plus 12 months of venetoclax.
All 15 patients who were followed for 3 months had clinical responses, including 8 CRs (53%), 6 partial remissions (40%), and 1 partial remission with lymphocytosis (7%).
Three patients had ibrutinib dose reductions and two had venetoclax dose reductions, but no patients stopped treatment. Three patients had grade 2 adverse events (AEs), three had grade 3 AEs, and two had grade 4 AEs. There were no grade 5 AEs.
Two patients had serious AEs during the first two cycles with ibrutinib alone, one of which was a case of febrile neutropenia and one which was an adenocarcinoma of the lung. There were no serious AEs reported during venetoclax ramp-up. To date, there have been no cases of tumor lysis syndrome, atrial fibrillation, or bleeding events reported.
The results suggest that treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax ramp-up is manageable in this patient population, and the study is ongoing, with further results expected to be reported at either the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology or the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Dr. Niemann said.
The study is supported by AbbVie and Janssen, which supplied the drugs and had the right to comment on the presentation. Dr. Niemann has previously disclosed consultancy fees from those companies and others.
SOURCE: Niemann CU et al. EHA Congress, Abstract PF346.
STOCKHOLM – A chemotherapy-free regimen of ibrutinib plus venetoclax was generally safe and showed promising early efficacy in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia, investigators reported.
A planned interim analysis performed after the first 15 patients who had received two cycles of ibrutinib plus one of ibrutinib and venetoclax showed no treatment-related deaths or treatment interruptions, and all patients had clinical responses, including 8 with complete clinical remission (CR), reported Carsten U. Niemann, MD, PhD, from Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen, and his colleagues.
The goal of the ongoing VISION/HOVEN 141 study is to evaluate whether minimal residual disease (MRD)–guided therapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax could lead to MRD negativity and allow select patients to stop treatment, Dr. Niemann said in an interview at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“It’s a 100% clinical response rate and 53% CR. Obviously these are clinical responses, so we don’t have the CT scans, we don’t have the bone marrow biopsies, but we’re very happy to see even in the relapsed/refractory setting such good response rates,” he said.
The investigators are enrolling patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic leukemia requiring treatment and starting all patients on ibrutinib 420 mg daily for the first 2 cycles, with venetoclax added in a 5-week ramp-up from 20 mg beginning with cycle 3 to a final dose of 400 mg daily for 15 total treatment cycles.
At the end of the induction phase, patients who are determined to be MRD-negative by flow cytometry at cycles 12 and 15, and by bone marrow at cycle 15, are randomized on a 1:2 basis to ibrutinib maintenance until disease progression or intolerable toxicity, or to observation until progression or loss of MRD negativity, at which time they start maintenance with ibrutinib until progression or toxicity, plus 12 months of venetoclax.
All 15 patients who were followed for 3 months had clinical responses, including 8 CRs (53%), 6 partial remissions (40%), and 1 partial remission with lymphocytosis (7%).
Three patients had ibrutinib dose reductions and two had venetoclax dose reductions, but no patients stopped treatment. Three patients had grade 2 adverse events (AEs), three had grade 3 AEs, and two had grade 4 AEs. There were no grade 5 AEs.
Two patients had serious AEs during the first two cycles with ibrutinib alone, one of which was a case of febrile neutropenia and one which was an adenocarcinoma of the lung. There were no serious AEs reported during venetoclax ramp-up. To date, there have been no cases of tumor lysis syndrome, atrial fibrillation, or bleeding events reported.
The results suggest that treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax ramp-up is manageable in this patient population, and the study is ongoing, with further results expected to be reported at either the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology or the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Dr. Niemann said.
The study is supported by AbbVie and Janssen, which supplied the drugs and had the right to comment on the presentation. Dr. Niemann has previously disclosed consultancy fees from those companies and others.
SOURCE: Niemann CU et al. EHA Congress, Abstract PF346.
STOCKHOLM – A chemotherapy-free regimen of ibrutinib plus venetoclax was generally safe and showed promising early efficacy in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia, investigators reported.
A planned interim analysis performed after the first 15 patients who had received two cycles of ibrutinib plus one of ibrutinib and venetoclax showed no treatment-related deaths or treatment interruptions, and all patients had clinical responses, including 8 with complete clinical remission (CR), reported Carsten U. Niemann, MD, PhD, from Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen, and his colleagues.
The goal of the ongoing VISION/HOVEN 141 study is to evaluate whether minimal residual disease (MRD)–guided therapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax could lead to MRD negativity and allow select patients to stop treatment, Dr. Niemann said in an interview at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“It’s a 100% clinical response rate and 53% CR. Obviously these are clinical responses, so we don’t have the CT scans, we don’t have the bone marrow biopsies, but we’re very happy to see even in the relapsed/refractory setting such good response rates,” he said.
The investigators are enrolling patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic leukemia requiring treatment and starting all patients on ibrutinib 420 mg daily for the first 2 cycles, with venetoclax added in a 5-week ramp-up from 20 mg beginning with cycle 3 to a final dose of 400 mg daily for 15 total treatment cycles.
At the end of the induction phase, patients who are determined to be MRD-negative by flow cytometry at cycles 12 and 15, and by bone marrow at cycle 15, are randomized on a 1:2 basis to ibrutinib maintenance until disease progression or intolerable toxicity, or to observation until progression or loss of MRD negativity, at which time they start maintenance with ibrutinib until progression or toxicity, plus 12 months of venetoclax.
All 15 patients who were followed for 3 months had clinical responses, including 8 CRs (53%), 6 partial remissions (40%), and 1 partial remission with lymphocytosis (7%).
Three patients had ibrutinib dose reductions and two had venetoclax dose reductions, but no patients stopped treatment. Three patients had grade 2 adverse events (AEs), three had grade 3 AEs, and two had grade 4 AEs. There were no grade 5 AEs.
Two patients had serious AEs during the first two cycles with ibrutinib alone, one of which was a case of febrile neutropenia and one which was an adenocarcinoma of the lung. There were no serious AEs reported during venetoclax ramp-up. To date, there have been no cases of tumor lysis syndrome, atrial fibrillation, or bleeding events reported.
The results suggest that treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax ramp-up is manageable in this patient population, and the study is ongoing, with further results expected to be reported at either the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology or the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Dr. Niemann said.
The study is supported by AbbVie and Janssen, which supplied the drugs and had the right to comment on the presentation. Dr. Niemann has previously disclosed consultancy fees from those companies and others.
SOURCE: Niemann CU et al. EHA Congress, Abstract PF346.
REPORTING FROM THE EHA CONGRESS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: All of the 15 patients analyzed to date had clinical responses to the combination, including 8 complete clinical remissions.
Study details: An ongoing, open-label, phase 2, randomized trial in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic leukemia.
Disclosures: The study is supported by AbbVie and Janssen, which supplied the drugs and had the right to comment on the presentation. Dr. Niemann has previously disclosed consultancy fees from those companies and others.
Source: Niemann CU et al. EHA Congress, Abstract PF346