User login
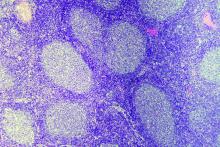
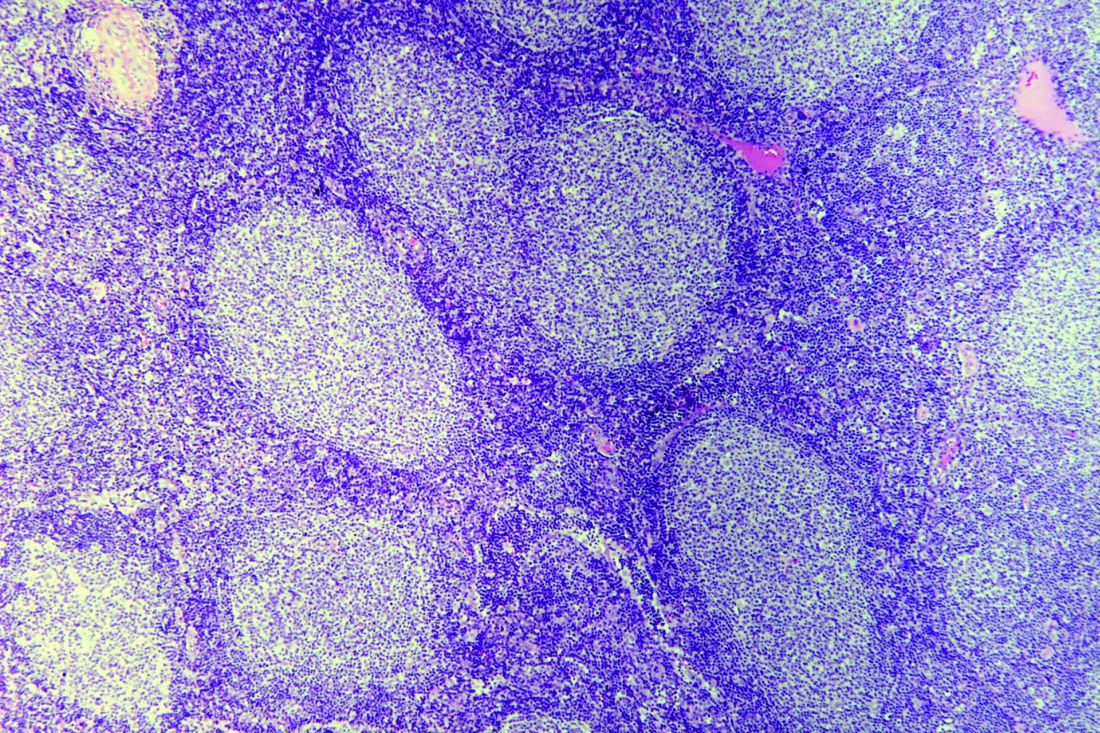
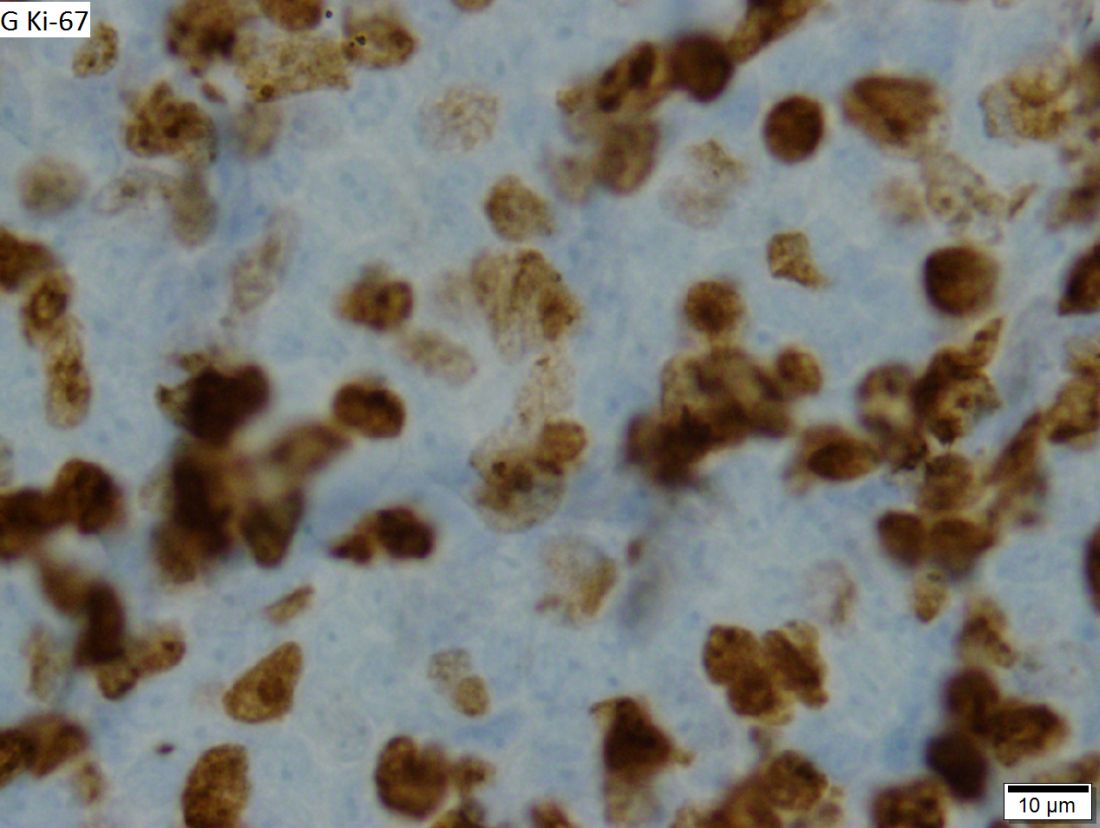
High survival in relapsed FL after primary radiotherapy
The prognosis post relapse following primary radiotherapy was found to be excellent for patients with localized follicular lymphoma (FL), according to a retrospective analysis.
But patients who experienced early relapse – at 1 year or less after diagnosis – had significantly worse survival.
While primary radiotherapy may be curative for localized FL, about 30%-50% of patients will relapse and optimal salvage therapy is not well defined, Michael S. Binkley, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and his colleagues wrote in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
The researchers retrospectively studied 512 patients with localized FL using data from multiple centers under the direction of the International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group (ILROG). Clinical information was collected, including method of detection, age at relapse, location of recurrence, and response to salvage therapy.
The team defined disease recurrence as lymphoma nonresponsive to primary radiotherapy inside of the prescribed dose volume, which included having no radiographic or clinical response within 6 months of initial radiotherapy treatment.
With a median follow-up of 52 months, Dr. Binkley and his colleagues found that 29.1% of patients developed relapsed lymphoma at a median 23 months (range, 1-143 months) following primary radiotherapy.
The team reported that the 3-year overall survival rate was 91.4% for patients with lymphoma recurrence after primary radiotherapy. In total, 16 deaths occurred during follow-up: eight were lymphoma specific deaths, three were from other causes, and in five patients the cause was unknown.
Of the 149 cases of relapsed lymphoma, 93 were indolent. There were also three cases of FL grade 3B/not otherwise specified and 18 cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. In 35 patients who relapsed, biopsies were not performed.
“The excellent prognosis observed for this relapse cohort emphasizes that primary radiation for localized follicular lymphoma is an excellent treatment option,” the researchers wrote.
When the researchers examined survival based on the time of relapse, they found that overall survival was “significantly worse” for patients who had relapsed 12 months or less after the date of diagnosis, at 88.7%, compared with all others at 95.8% (P = .01).
They found no difference in overall survival between patients who received immediate salvage treatment, compared with observation after relapse (P = .28). There was also no significant difference in survival between patients who relapsed in 1 year or less but underwent immediate treatment, compared to early relapsed patients who were observed (log-rank P = .34).
“[A]ny decision to offer treatment at time of relapse must be weighed with the risk of acute and late adverse effects. Greater than 60% of patients in our cohort with indolent recurrence who underwent salvage treatment received rituximab, likely contributing to the excellent outcomes,” the researchers wrote. “However, nearly 60% of patients with indolent recurrence who were observed did not have disease progression nor [did they] receive treatment within 3 years.”
The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Binkley MS et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Mar 8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.004.
The prognosis post relapse following primary radiotherapy was found to be excellent for patients with localized follicular lymphoma (FL), according to a retrospective analysis.
But patients who experienced early relapse – at 1 year or less after diagnosis – had significantly worse survival.
While primary radiotherapy may be curative for localized FL, about 30%-50% of patients will relapse and optimal salvage therapy is not well defined, Michael S. Binkley, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and his colleagues wrote in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
The researchers retrospectively studied 512 patients with localized FL using data from multiple centers under the direction of the International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group (ILROG). Clinical information was collected, including method of detection, age at relapse, location of recurrence, and response to salvage therapy.
The team defined disease recurrence as lymphoma nonresponsive to primary radiotherapy inside of the prescribed dose volume, which included having no radiographic or clinical response within 6 months of initial radiotherapy treatment.
With a median follow-up of 52 months, Dr. Binkley and his colleagues found that 29.1% of patients developed relapsed lymphoma at a median 23 months (range, 1-143 months) following primary radiotherapy.
The team reported that the 3-year overall survival rate was 91.4% for patients with lymphoma recurrence after primary radiotherapy. In total, 16 deaths occurred during follow-up: eight were lymphoma specific deaths, three were from other causes, and in five patients the cause was unknown.
Of the 149 cases of relapsed lymphoma, 93 were indolent. There were also three cases of FL grade 3B/not otherwise specified and 18 cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. In 35 patients who relapsed, biopsies were not performed.
“The excellent prognosis observed for this relapse cohort emphasizes that primary radiation for localized follicular lymphoma is an excellent treatment option,” the researchers wrote.
When the researchers examined survival based on the time of relapse, they found that overall survival was “significantly worse” for patients who had relapsed 12 months or less after the date of diagnosis, at 88.7%, compared with all others at 95.8% (P = .01).
They found no difference in overall survival between patients who received immediate salvage treatment, compared with observation after relapse (P = .28). There was also no significant difference in survival between patients who relapsed in 1 year or less but underwent immediate treatment, compared to early relapsed patients who were observed (log-rank P = .34).
“[A]ny decision to offer treatment at time of relapse must be weighed with the risk of acute and late adverse effects. Greater than 60% of patients in our cohort with indolent recurrence who underwent salvage treatment received rituximab, likely contributing to the excellent outcomes,” the researchers wrote. “However, nearly 60% of patients with indolent recurrence who were observed did not have disease progression nor [did they] receive treatment within 3 years.”
The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Binkley MS et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Mar 8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.004.
The prognosis post relapse following primary radiotherapy was found to be excellent for patients with localized follicular lymphoma (FL), according to a retrospective analysis.
But patients who experienced early relapse – at 1 year or less after diagnosis – had significantly worse survival.
While primary radiotherapy may be curative for localized FL, about 30%-50% of patients will relapse and optimal salvage therapy is not well defined, Michael S. Binkley, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and his colleagues wrote in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
The researchers retrospectively studied 512 patients with localized FL using data from multiple centers under the direction of the International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group (ILROG). Clinical information was collected, including method of detection, age at relapse, location of recurrence, and response to salvage therapy.
The team defined disease recurrence as lymphoma nonresponsive to primary radiotherapy inside of the prescribed dose volume, which included having no radiographic or clinical response within 6 months of initial radiotherapy treatment.
With a median follow-up of 52 months, Dr. Binkley and his colleagues found that 29.1% of patients developed relapsed lymphoma at a median 23 months (range, 1-143 months) following primary radiotherapy.
The team reported that the 3-year overall survival rate was 91.4% for patients with lymphoma recurrence after primary radiotherapy. In total, 16 deaths occurred during follow-up: eight were lymphoma specific deaths, three were from other causes, and in five patients the cause was unknown.
Of the 149 cases of relapsed lymphoma, 93 were indolent. There were also three cases of FL grade 3B/not otherwise specified and 18 cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. In 35 patients who relapsed, biopsies were not performed.
“The excellent prognosis observed for this relapse cohort emphasizes that primary radiation for localized follicular lymphoma is an excellent treatment option,” the researchers wrote.
When the researchers examined survival based on the time of relapse, they found that overall survival was “significantly worse” for patients who had relapsed 12 months or less after the date of diagnosis, at 88.7%, compared with all others at 95.8% (P = .01).
They found no difference in overall survival between patients who received immediate salvage treatment, compared with observation after relapse (P = .28). There was also no significant difference in survival between patients who relapsed in 1 year or less but underwent immediate treatment, compared to early relapsed patients who were observed (log-rank P = .34).
“[A]ny decision to offer treatment at time of relapse must be weighed with the risk of acute and late adverse effects. Greater than 60% of patients in our cohort with indolent recurrence who underwent salvage treatment received rituximab, likely contributing to the excellent outcomes,” the researchers wrote. “However, nearly 60% of patients with indolent recurrence who were observed did not have disease progression nor [did they] receive treatment within 3 years.”
The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Binkley MS et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Mar 8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.004.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY, BIOLOGY, PHYSICS
MCL survival rates improve with novel agents
Survival outcomes for patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) substantially improved from 1995 to 2013, particularly for those with advanced-stage tumors, according to a retrospective analysis.
The median overall survival for the study period was 52 months and 57 months in two cancer databases.
“Over the past 20 years, many novel agents and treatment regimens have been developed to treat MCL,” Shuangshuang Fu, PhD, of the University of Texas, Houston, and her colleagues wrote in Cancer Epidemiology.
The researchers retrospectively studied population-based data from two separate databases: the national Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database and the Texas Cancer Registry (TCR). They identified all adult patients who received a new diagnosis of MCL between Jan. 1, 1995, and Dec. 31, 2013.
A total of 9,610 patients were included in the study: 7,555 patients from SEER and 2,055 from the TCR. The team collected data related to MCL diagnosis, mortality, and other variables, including age at diagnosis, marital status, sex, and tumor stage.
In total, 76.2% and 61.6% of patients from the SEER and TCR databases, respectively, had an advanced-stage tumor.
Dr. Fu and her colleagues found that all-cause mortality rates in both groups were significantly reduced from 1995 to 2013 (SEER, P less than .001; TCR, P = .03).
In addition, the team reported that the median overall survival time for all patients in the SEER database was 52 months, and it was 57 months for the TCR database.
“MCL patients with [an] advanced stage tumor benefitted most from the introduction of newly developed regimens,” they added.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the inability to assess treatment regimen–specific survival, which could only be estimated with these data.
“The findings of our study further confirmed the impact of novel agents on improved survival over time that was shown in other studies,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grant funding from the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas and the National Institutes of Health. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Fu S et al. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019 Feb;58:89-97.
Survival outcomes for patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) substantially improved from 1995 to 2013, particularly for those with advanced-stage tumors, according to a retrospective analysis.
The median overall survival for the study period was 52 months and 57 months in two cancer databases.
“Over the past 20 years, many novel agents and treatment regimens have been developed to treat MCL,” Shuangshuang Fu, PhD, of the University of Texas, Houston, and her colleagues wrote in Cancer Epidemiology.
The researchers retrospectively studied population-based data from two separate databases: the national Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database and the Texas Cancer Registry (TCR). They identified all adult patients who received a new diagnosis of MCL between Jan. 1, 1995, and Dec. 31, 2013.
A total of 9,610 patients were included in the study: 7,555 patients from SEER and 2,055 from the TCR. The team collected data related to MCL diagnosis, mortality, and other variables, including age at diagnosis, marital status, sex, and tumor stage.
In total, 76.2% and 61.6% of patients from the SEER and TCR databases, respectively, had an advanced-stage tumor.
Dr. Fu and her colleagues found that all-cause mortality rates in both groups were significantly reduced from 1995 to 2013 (SEER, P less than .001; TCR, P = .03).
In addition, the team reported that the median overall survival time for all patients in the SEER database was 52 months, and it was 57 months for the TCR database.
“MCL patients with [an] advanced stage tumor benefitted most from the introduction of newly developed regimens,” they added.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the inability to assess treatment regimen–specific survival, which could only be estimated with these data.
“The findings of our study further confirmed the impact of novel agents on improved survival over time that was shown in other studies,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grant funding from the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas and the National Institutes of Health. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Fu S et al. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019 Feb;58:89-97.
Survival outcomes for patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) substantially improved from 1995 to 2013, particularly for those with advanced-stage tumors, according to a retrospective analysis.
The median overall survival for the study period was 52 months and 57 months in two cancer databases.
“Over the past 20 years, many novel agents and treatment regimens have been developed to treat MCL,” Shuangshuang Fu, PhD, of the University of Texas, Houston, and her colleagues wrote in Cancer Epidemiology.
The researchers retrospectively studied population-based data from two separate databases: the national Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database and the Texas Cancer Registry (TCR). They identified all adult patients who received a new diagnosis of MCL between Jan. 1, 1995, and Dec. 31, 2013.
A total of 9,610 patients were included in the study: 7,555 patients from SEER and 2,055 from the TCR. The team collected data related to MCL diagnosis, mortality, and other variables, including age at diagnosis, marital status, sex, and tumor stage.
In total, 76.2% and 61.6% of patients from the SEER and TCR databases, respectively, had an advanced-stage tumor.
Dr. Fu and her colleagues found that all-cause mortality rates in both groups were significantly reduced from 1995 to 2013 (SEER, P less than .001; TCR, P = .03).
In addition, the team reported that the median overall survival time for all patients in the SEER database was 52 months, and it was 57 months for the TCR database.
“MCL patients with [an] advanced stage tumor benefitted most from the introduction of newly developed regimens,” they added.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the inability to assess treatment regimen–specific survival, which could only be estimated with these data.
“The findings of our study further confirmed the impact of novel agents on improved survival over time that was shown in other studies,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grant funding from the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas and the National Institutes of Health. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Fu S et al. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019 Feb;58:89-97.
FROM CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY
Worse survival seen among black patients with MCL
Black non-Hispanic patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) have a lower rate of 5-year overall survival, compared with white non-Hispanic and Hispanic patients, according to a retrospective analysis of more than 18,000 cases.
However, black patients were also most likely to receive treatment at an academic center, which was an independent predictor of better survival, reported Nikesh N. Shah, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and his colleagues. This finding suggests that even academic centers still need to focus on overcoming demographic disparities.
“Racial and socioeconomic differences have been reported in many malignancies and certain lymphomas; however, few studies report on disparities in MCL,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia. “To our knowledge this is the first such study to assess racial and socioeconomic disparities in this disease.”
The investigators reviewed 18,120 patients with MCL diagnosed between 2004 and 2013; data were drawn from the National Cancer Database. The primary endpoint was overall survival from the time of diagnosis, with analyses conducted to assess various associations with race/ethnicity, facility type, clinical/tumor characteristics, cancer stage, insurance type, and other factors.
Results showed that Hispanic patients had the highest rate of overall survival, at 55.8%, followed by white patients, at 50.1%. Trailing behind these groups were black patients (46.8%) and patients of other races/ethnicities (46.0%).
Along with survival disparities, race/ethnicity was tied to certain clinical and treatment characteristics. Compared with white patients, black patients were more likely to experience B symptoms (28% vs. 25%) and have Medicaid or lack insurance (15% vs. 5%). Black and Hispanic patients were also less likely than white non-Hispanic patients to receive stem cell transplant (13% vs. 10% vs. 10%).
Although black patients were more likely than white patients to receive treatment at an academic center (51% vs. 38%), a factor independently associated with best survival among center types, whatever advantage provided apparently did not exceed disadvantages associated with race.
“We report inferior overall survival in black patients after accounting for socioeconomic status, as seen in other malignancies,” the investigators wrote. “Surprisingly, these patients were more likely to be treated at academic centers, which independently showed improved overall survival in multivariable analysis that controlled for age, disease stage, insurance status, and other socioeconomic factors.”
The researchers cited a number of steps that could help close the survival gap, including providing more comprehensive supportive care between physician visits and enrollment of patients from diverse racial background on clinical trials.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Shah NN et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Mar 11. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.03.006.
Black non-Hispanic patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) have a lower rate of 5-year overall survival, compared with white non-Hispanic and Hispanic patients, according to a retrospective analysis of more than 18,000 cases.
However, black patients were also most likely to receive treatment at an academic center, which was an independent predictor of better survival, reported Nikesh N. Shah, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and his colleagues. This finding suggests that even academic centers still need to focus on overcoming demographic disparities.
“Racial and socioeconomic differences have been reported in many malignancies and certain lymphomas; however, few studies report on disparities in MCL,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia. “To our knowledge this is the first such study to assess racial and socioeconomic disparities in this disease.”
The investigators reviewed 18,120 patients with MCL diagnosed between 2004 and 2013; data were drawn from the National Cancer Database. The primary endpoint was overall survival from the time of diagnosis, with analyses conducted to assess various associations with race/ethnicity, facility type, clinical/tumor characteristics, cancer stage, insurance type, and other factors.
Results showed that Hispanic patients had the highest rate of overall survival, at 55.8%, followed by white patients, at 50.1%. Trailing behind these groups were black patients (46.8%) and patients of other races/ethnicities (46.0%).
Along with survival disparities, race/ethnicity was tied to certain clinical and treatment characteristics. Compared with white patients, black patients were more likely to experience B symptoms (28% vs. 25%) and have Medicaid or lack insurance (15% vs. 5%). Black and Hispanic patients were also less likely than white non-Hispanic patients to receive stem cell transplant (13% vs. 10% vs. 10%).
Although black patients were more likely than white patients to receive treatment at an academic center (51% vs. 38%), a factor independently associated with best survival among center types, whatever advantage provided apparently did not exceed disadvantages associated with race.
“We report inferior overall survival in black patients after accounting for socioeconomic status, as seen in other malignancies,” the investigators wrote. “Surprisingly, these patients were more likely to be treated at academic centers, which independently showed improved overall survival in multivariable analysis that controlled for age, disease stage, insurance status, and other socioeconomic factors.”
The researchers cited a number of steps that could help close the survival gap, including providing more comprehensive supportive care between physician visits and enrollment of patients from diverse racial background on clinical trials.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Shah NN et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Mar 11. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.03.006.
Black non-Hispanic patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) have a lower rate of 5-year overall survival, compared with white non-Hispanic and Hispanic patients, according to a retrospective analysis of more than 18,000 cases.
However, black patients were also most likely to receive treatment at an academic center, which was an independent predictor of better survival, reported Nikesh N. Shah, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and his colleagues. This finding suggests that even academic centers still need to focus on overcoming demographic disparities.
“Racial and socioeconomic differences have been reported in many malignancies and certain lymphomas; however, few studies report on disparities in MCL,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia. “To our knowledge this is the first such study to assess racial and socioeconomic disparities in this disease.”
The investigators reviewed 18,120 patients with MCL diagnosed between 2004 and 2013; data were drawn from the National Cancer Database. The primary endpoint was overall survival from the time of diagnosis, with analyses conducted to assess various associations with race/ethnicity, facility type, clinical/tumor characteristics, cancer stage, insurance type, and other factors.
Results showed that Hispanic patients had the highest rate of overall survival, at 55.8%, followed by white patients, at 50.1%. Trailing behind these groups were black patients (46.8%) and patients of other races/ethnicities (46.0%).
Along with survival disparities, race/ethnicity was tied to certain clinical and treatment characteristics. Compared with white patients, black patients were more likely to experience B symptoms (28% vs. 25%) and have Medicaid or lack insurance (15% vs. 5%). Black and Hispanic patients were also less likely than white non-Hispanic patients to receive stem cell transplant (13% vs. 10% vs. 10%).
Although black patients were more likely than white patients to receive treatment at an academic center (51% vs. 38%), a factor independently associated with best survival among center types, whatever advantage provided apparently did not exceed disadvantages associated with race.
“We report inferior overall survival in black patients after accounting for socioeconomic status, as seen in other malignancies,” the investigators wrote. “Surprisingly, these patients were more likely to be treated at academic centers, which independently showed improved overall survival in multivariable analysis that controlled for age, disease stage, insurance status, and other socioeconomic factors.”
The researchers cited a number of steps that could help close the survival gap, including providing more comprehensive supportive care between physician visits and enrollment of patients from diverse racial background on clinical trials.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Shah NN et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Mar 11. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.03.006.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Venetoclax and obinutuzumab induces deep responses in CLL
The combination of venetoclax and obinutuzumab provided high response rates and deep remissions regardless of cytogenetic risk factors in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to recently reported results of a phase 1b study.
The regimen elicited high rates of undetectable minimal residual disease in peripheral blood and had an acceptable safety profile with manageable toxicities in the study reported in Blood, which included patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
“The deep remission rates we observed with venetoclax-obinutuzumab have not been reported with previously available CLL treatments, including FCR [fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab], which is currently considered the most efficacious regimen with limited-duration therapy,” wrote the investigators, led by Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute/Tennessee Oncology, Nashville.
Venetoclax-obinutuzumab combinations are meanwhile being tested in other studies – including the phase 3 CLL13 and CLL14 studies – which have enrolled previously untreated fit or unfit CLL patients, respectively.
“If the primary endpoints of these large-scale trials are met, venetoclax-obinutuzumab may become a new standard treatment option in [first-line] CLL, irrespective of clinical fitness,” Dr. Flinn and his colleagues wrote in their report.
The present phase 1b, dose-escalation study enrolled 32 patients who were previously untreated (median age, 63 years) and 46 patients who were relapsed or refractory to previous treatments (median age, 61 years).
Doses of venetoclax were escalated from 100 mg to 400 mg to determine its maximum tolerated dose when combined with obinutuzumab, the investigators wrote. Some patients received venetoclax first, while others received obinutuzumab first, for a total of 1 year of treatment.
The study confirmed favorable risk-benefit treatment used a dose of 400 mg venetoclax plus the standard dose of obinutuzumab, according to the researchers.
The overall best response rate was 95% for relapsed/refractory patients, including a 37% rate of complete response or complete response with incomplete marrow recovery. In previously untreated patients, the overall best response rate was 100%, including a 78% rate of complete responses by those criteria.
Undetectable minimal residual disease was observed in 64% of relapsed/refractory patients and 91% of previously untreated patients at 3 months after the last obinutuzumab dose, the investigators reported.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities in the study, no clinical tumor lysis syndrome, and no differences between the two schedules (venetoclax first or obinutuzumab first) in terms of adverse events, the investigators wrote.
Neutropenia was the most common serious (grade 3-4) adverse event, occurring in 58% of relapsed/refractory patients and 53% of patients treated in the first line. Grade 3-4 infections were seen in 29% and 13% of the relapsed/refractory and previously untreated patients, respectively.
There were no fatal infections among previously untreated patients, while three relapsed/refractory patients (7%) had fatal adverse events, including one case of acute respiratory failure in a patient with suspected Richter’s transformation, pneumonia in a patient with metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma, and another case of pneumonia occurring about 3 months after the last dose of venetoclax.
Genentech and AbbVie provided financial support for the study. Dr. Flinn reported receiving research funding for his institution from Genentech, AbbVie, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. Blood. 2019 Mar 12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-01-896290.
The combination of venetoclax and obinutuzumab provided high response rates and deep remissions regardless of cytogenetic risk factors in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to recently reported results of a phase 1b study.
The regimen elicited high rates of undetectable minimal residual disease in peripheral blood and had an acceptable safety profile with manageable toxicities in the study reported in Blood, which included patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
“The deep remission rates we observed with venetoclax-obinutuzumab have not been reported with previously available CLL treatments, including FCR [fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab], which is currently considered the most efficacious regimen with limited-duration therapy,” wrote the investigators, led by Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute/Tennessee Oncology, Nashville.
Venetoclax-obinutuzumab combinations are meanwhile being tested in other studies – including the phase 3 CLL13 and CLL14 studies – which have enrolled previously untreated fit or unfit CLL patients, respectively.
“If the primary endpoints of these large-scale trials are met, venetoclax-obinutuzumab may become a new standard treatment option in [first-line] CLL, irrespective of clinical fitness,” Dr. Flinn and his colleagues wrote in their report.
The present phase 1b, dose-escalation study enrolled 32 patients who were previously untreated (median age, 63 years) and 46 patients who were relapsed or refractory to previous treatments (median age, 61 years).
Doses of venetoclax were escalated from 100 mg to 400 mg to determine its maximum tolerated dose when combined with obinutuzumab, the investigators wrote. Some patients received venetoclax first, while others received obinutuzumab first, for a total of 1 year of treatment.
The study confirmed favorable risk-benefit treatment used a dose of 400 mg venetoclax plus the standard dose of obinutuzumab, according to the researchers.
The overall best response rate was 95% for relapsed/refractory patients, including a 37% rate of complete response or complete response with incomplete marrow recovery. In previously untreated patients, the overall best response rate was 100%, including a 78% rate of complete responses by those criteria.
Undetectable minimal residual disease was observed in 64% of relapsed/refractory patients and 91% of previously untreated patients at 3 months after the last obinutuzumab dose, the investigators reported.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities in the study, no clinical tumor lysis syndrome, and no differences between the two schedules (venetoclax first or obinutuzumab first) in terms of adverse events, the investigators wrote.
Neutropenia was the most common serious (grade 3-4) adverse event, occurring in 58% of relapsed/refractory patients and 53% of patients treated in the first line. Grade 3-4 infections were seen in 29% and 13% of the relapsed/refractory and previously untreated patients, respectively.
There were no fatal infections among previously untreated patients, while three relapsed/refractory patients (7%) had fatal adverse events, including one case of acute respiratory failure in a patient with suspected Richter’s transformation, pneumonia in a patient with metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma, and another case of pneumonia occurring about 3 months after the last dose of venetoclax.
Genentech and AbbVie provided financial support for the study. Dr. Flinn reported receiving research funding for his institution from Genentech, AbbVie, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. Blood. 2019 Mar 12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-01-896290.
The combination of venetoclax and obinutuzumab provided high response rates and deep remissions regardless of cytogenetic risk factors in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to recently reported results of a phase 1b study.
The regimen elicited high rates of undetectable minimal residual disease in peripheral blood and had an acceptable safety profile with manageable toxicities in the study reported in Blood, which included patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
“The deep remission rates we observed with venetoclax-obinutuzumab have not been reported with previously available CLL treatments, including FCR [fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab], which is currently considered the most efficacious regimen with limited-duration therapy,” wrote the investigators, led by Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute/Tennessee Oncology, Nashville.
Venetoclax-obinutuzumab combinations are meanwhile being tested in other studies – including the phase 3 CLL13 and CLL14 studies – which have enrolled previously untreated fit or unfit CLL patients, respectively.
“If the primary endpoints of these large-scale trials are met, venetoclax-obinutuzumab may become a new standard treatment option in [first-line] CLL, irrespective of clinical fitness,” Dr. Flinn and his colleagues wrote in their report.
The present phase 1b, dose-escalation study enrolled 32 patients who were previously untreated (median age, 63 years) and 46 patients who were relapsed or refractory to previous treatments (median age, 61 years).
Doses of venetoclax were escalated from 100 mg to 400 mg to determine its maximum tolerated dose when combined with obinutuzumab, the investigators wrote. Some patients received venetoclax first, while others received obinutuzumab first, for a total of 1 year of treatment.
The study confirmed favorable risk-benefit treatment used a dose of 400 mg venetoclax plus the standard dose of obinutuzumab, according to the researchers.
The overall best response rate was 95% for relapsed/refractory patients, including a 37% rate of complete response or complete response with incomplete marrow recovery. In previously untreated patients, the overall best response rate was 100%, including a 78% rate of complete responses by those criteria.
Undetectable minimal residual disease was observed in 64% of relapsed/refractory patients and 91% of previously untreated patients at 3 months after the last obinutuzumab dose, the investigators reported.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities in the study, no clinical tumor lysis syndrome, and no differences between the two schedules (venetoclax first or obinutuzumab first) in terms of adverse events, the investigators wrote.
Neutropenia was the most common serious (grade 3-4) adverse event, occurring in 58% of relapsed/refractory patients and 53% of patients treated in the first line. Grade 3-4 infections were seen in 29% and 13% of the relapsed/refractory and previously untreated patients, respectively.
There were no fatal infections among previously untreated patients, while three relapsed/refractory patients (7%) had fatal adverse events, including one case of acute respiratory failure in a patient with suspected Richter’s transformation, pneumonia in a patient with metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma, and another case of pneumonia occurring about 3 months after the last dose of venetoclax.
Genentech and AbbVie provided financial support for the study. Dr. Flinn reported receiving research funding for his institution from Genentech, AbbVie, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. Blood. 2019 Mar 12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-01-896290.
FROM BLOOD
Short telomeres predict poorer response to chemo in CLL
A telomere-length analysis tool appears to identify reliably which chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients will benefit from frontline chemotherapy, according to an analysis of 260 patients across two separate trials.
The analysis compared the use of high-throughput, single telomere–length analysis (HTSTELA) with other commonly used markers including beta-2 microglobulin, fluorescence-in-situ hybridization (FISH) cytogenetics, CD38 expression, ZAP70 expression, and IGHV mutation status. The researchers looked specifically at whether telomere length could predict response to frontline treatment with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab (FCR)–based regimens.
“[T]elomere length is a powerful predictor of both [progression-free survival] and [overall survival] in patients treated with FCR-based therapies. In contrast, CD38 expression and beta-2 microglobulin expression were not predictive, and IGHV mutation status was only predictive of PFS (progression-free survival),” Kevin Norris, PhD, of Cardiff (Wales) University and his colleagues wrote in Leukemia.
Previous studies have shown that telomere-length analysis offers independent prognostic information in all stages of CLL. In the present study, the researchers used HTSTELA to analyze patient samples taken from two concurrent, phase 2 clinical trials of frontline FCR-based treatment – ARCTIC and ADMIRE.
The researchers divided the cohort based on a threshold of telomere dysfunction – the point at which the chromosome end-capping function is lost and there is genomic instability. Shorter telomeres are inside the fusogenic range (TL-IFR) and longer telomeres are outside fusogenic range (TL-OFR).
Patients with TL-IFR had significantly shorter PFS on FCR-based treatment (P less than .0001). They also had reduced overall survival (OS; P = .0002). In the same cohort of patients, IGHV mutation status was predictive of PFS (P = .0016), but it was not predictive for OS (P = .38), while CD38 and beta-2 microglobulin were not predictive of PFS or OS.
The researchers also looked at the value of telomere length in predicting outcomes among IGHV-mutated and -unmutated patients.
Patients with IGHV-mutated disease and TL-IFR had worse PFS and OS than did patients with TL-OFR. TL-IFR patients in this cohort were more likely to progress (hazard ratio, 4.35; P less than .0001) and more likely to die from their disease (HR, 3.81; P = .006).
“Although the number of IGHV-mutated patients with TL-IFR was relatively small (n = 16), our data suggests that telomere length can identify a subset of “bad risk” IGHV-mutated patients who do not respond well to FCR,” the researchers wrote.
Among IGHV unmutated patients, those with short telomeres had worse PFS (HR, 1.48; P = .08) and OS (HR, 2.18; P = .025) than did those with longer telomeres.
In multivariate modeling of all the potential markers, telomere length was the statistically significant dominant covariable for both PFS and OS.
The study was funded by a Bloodwise grant and the Wales Cancer Research Center. Dr. Norris and three coauthors reported that they are coinventors of patents relevant to the study and hold shares in a company set to provide telomere length testing.
SOURCE: Norris K et al. Leukemia. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0389-9.
A telomere-length analysis tool appears to identify reliably which chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients will benefit from frontline chemotherapy, according to an analysis of 260 patients across two separate trials.
The analysis compared the use of high-throughput, single telomere–length analysis (HTSTELA) with other commonly used markers including beta-2 microglobulin, fluorescence-in-situ hybridization (FISH) cytogenetics, CD38 expression, ZAP70 expression, and IGHV mutation status. The researchers looked specifically at whether telomere length could predict response to frontline treatment with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab (FCR)–based regimens.
“[T]elomere length is a powerful predictor of both [progression-free survival] and [overall survival] in patients treated with FCR-based therapies. In contrast, CD38 expression and beta-2 microglobulin expression were not predictive, and IGHV mutation status was only predictive of PFS (progression-free survival),” Kevin Norris, PhD, of Cardiff (Wales) University and his colleagues wrote in Leukemia.
Previous studies have shown that telomere-length analysis offers independent prognostic information in all stages of CLL. In the present study, the researchers used HTSTELA to analyze patient samples taken from two concurrent, phase 2 clinical trials of frontline FCR-based treatment – ARCTIC and ADMIRE.
The researchers divided the cohort based on a threshold of telomere dysfunction – the point at which the chromosome end-capping function is lost and there is genomic instability. Shorter telomeres are inside the fusogenic range (TL-IFR) and longer telomeres are outside fusogenic range (TL-OFR).
Patients with TL-IFR had significantly shorter PFS on FCR-based treatment (P less than .0001). They also had reduced overall survival (OS; P = .0002). In the same cohort of patients, IGHV mutation status was predictive of PFS (P = .0016), but it was not predictive for OS (P = .38), while CD38 and beta-2 microglobulin were not predictive of PFS or OS.
The researchers also looked at the value of telomere length in predicting outcomes among IGHV-mutated and -unmutated patients.
Patients with IGHV-mutated disease and TL-IFR had worse PFS and OS than did patients with TL-OFR. TL-IFR patients in this cohort were more likely to progress (hazard ratio, 4.35; P less than .0001) and more likely to die from their disease (HR, 3.81; P = .006).
“Although the number of IGHV-mutated patients with TL-IFR was relatively small (n = 16), our data suggests that telomere length can identify a subset of “bad risk” IGHV-mutated patients who do not respond well to FCR,” the researchers wrote.
Among IGHV unmutated patients, those with short telomeres had worse PFS (HR, 1.48; P = .08) and OS (HR, 2.18; P = .025) than did those with longer telomeres.
In multivariate modeling of all the potential markers, telomere length was the statistically significant dominant covariable for both PFS and OS.
The study was funded by a Bloodwise grant and the Wales Cancer Research Center. Dr. Norris and three coauthors reported that they are coinventors of patents relevant to the study and hold shares in a company set to provide telomere length testing.
SOURCE: Norris K et al. Leukemia. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0389-9.
A telomere-length analysis tool appears to identify reliably which chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients will benefit from frontline chemotherapy, according to an analysis of 260 patients across two separate trials.
The analysis compared the use of high-throughput, single telomere–length analysis (HTSTELA) with other commonly used markers including beta-2 microglobulin, fluorescence-in-situ hybridization (FISH) cytogenetics, CD38 expression, ZAP70 expression, and IGHV mutation status. The researchers looked specifically at whether telomere length could predict response to frontline treatment with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab (FCR)–based regimens.
“[T]elomere length is a powerful predictor of both [progression-free survival] and [overall survival] in patients treated with FCR-based therapies. In contrast, CD38 expression and beta-2 microglobulin expression were not predictive, and IGHV mutation status was only predictive of PFS (progression-free survival),” Kevin Norris, PhD, of Cardiff (Wales) University and his colleagues wrote in Leukemia.
Previous studies have shown that telomere-length analysis offers independent prognostic information in all stages of CLL. In the present study, the researchers used HTSTELA to analyze patient samples taken from two concurrent, phase 2 clinical trials of frontline FCR-based treatment – ARCTIC and ADMIRE.
The researchers divided the cohort based on a threshold of telomere dysfunction – the point at which the chromosome end-capping function is lost and there is genomic instability. Shorter telomeres are inside the fusogenic range (TL-IFR) and longer telomeres are outside fusogenic range (TL-OFR).
Patients with TL-IFR had significantly shorter PFS on FCR-based treatment (P less than .0001). They also had reduced overall survival (OS; P = .0002). In the same cohort of patients, IGHV mutation status was predictive of PFS (P = .0016), but it was not predictive for OS (P = .38), while CD38 and beta-2 microglobulin were not predictive of PFS or OS.
The researchers also looked at the value of telomere length in predicting outcomes among IGHV-mutated and -unmutated patients.
Patients with IGHV-mutated disease and TL-IFR had worse PFS and OS than did patients with TL-OFR. TL-IFR patients in this cohort were more likely to progress (hazard ratio, 4.35; P less than .0001) and more likely to die from their disease (HR, 3.81; P = .006).
“Although the number of IGHV-mutated patients with TL-IFR was relatively small (n = 16), our data suggests that telomere length can identify a subset of “bad risk” IGHV-mutated patients who do not respond well to FCR,” the researchers wrote.
Among IGHV unmutated patients, those with short telomeres had worse PFS (HR, 1.48; P = .08) and OS (HR, 2.18; P = .025) than did those with longer telomeres.
In multivariate modeling of all the potential markers, telomere length was the statistically significant dominant covariable for both PFS and OS.
The study was funded by a Bloodwise grant and the Wales Cancer Research Center. Dr. Norris and three coauthors reported that they are coinventors of patents relevant to the study and hold shares in a company set to provide telomere length testing.
SOURCE: Norris K et al. Leukemia. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0389-9.
FROM LEUKEMIA
Bendamustine-rituximab shines in frontline treatment of MCL, iNHL
Frontline treatment with patients in the BRIGHT study.
The bendamustine-rituximab (BR) regimen had superior 5-year progression-free survival rates, event-free survival, and duration of response, compared with either rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) or rituximab with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CVP). The follow-up study did not find a significant difference in overall survival, however.
While the cumulative evidence from BRIGHT and other studies supports BR as a first-line treatment option for patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), the lack of an overall survival benefit indicates that the sequence of BR and R-CHOP or R-CVP “may not be critical,” Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute in Nashville, and his colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“[The] choice of regimen for the initial treatment of iNHL may be driven more by patient preferences regarding the differences in toxicity profile,” the researchers wrote.
Initial results from the BRIGHT study found that BR was noninferior to R-CHOP/R-CVP in terms of complete response rate (P = .0225 for noninferiority). The present study includes outcomes data for at least 5 years after completion of the study treatment.
For the entire study, the median follow-up was 65.0 months for patients in the BR group and 64.1 months for patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. Overall, the intention-to-treat population included 224 patients receiving BR and 223 patients receiving R-CHOP and R-CVP.
The median time to progression was not reached in either treatment group. The 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 65.5% in the BR group and 55.8% in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. The difference between these rates was significant, with a hazard ratio of 0.61 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.85; P = .0025).
Similarly, event-free survival was better in the BR group versus the R-CHOP/R-CVP group (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.46-0.84; P = .0020). Duration of response also favored the BR treatment regimen (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.47-0.92; P = .0134).
The long-term follow-up showed no significant difference in overall survival, with an HR of 1.15 for BR versus R-CHOP/R-CVP (95% CI, 0.72-1.84; P = .5461). Overall, there were 40 deaths in the BR treatment group and 32 deaths in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group.
Whether patients received maintenance rituximab did not affect the overall survival between groups. Similarly, there was no difference in overall survival by lymphoma type.
“Benefit from BR treatment did not translate to prolonged [overall survival], possibly because of the subsequent lines of therapy, including the use of BR in patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group,” the researchers wrote.
In terms of safety, the follow-up data showed no significant difference in early non–disease-related mortality between the treatment groups. However, the BRIGHT study showed higher rates of secondary malignancies in the BR group, compared with R-CHOP/R-CVP. That finding was not seen in the Study Group of Indolent Lymphomas Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (StiL NHL) 1 trial, and the authors could not provide an explanation for the increase in their research.
This study was supported by Teva Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Flinn reported receiving institutional research funding from Teva and receiving institutional research funding from or serving as a consultant to several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00605.
Frontline treatment with patients in the BRIGHT study.
The bendamustine-rituximab (BR) regimen had superior 5-year progression-free survival rates, event-free survival, and duration of response, compared with either rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) or rituximab with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CVP). The follow-up study did not find a significant difference in overall survival, however.
While the cumulative evidence from BRIGHT and other studies supports BR as a first-line treatment option for patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), the lack of an overall survival benefit indicates that the sequence of BR and R-CHOP or R-CVP “may not be critical,” Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute in Nashville, and his colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“[The] choice of regimen for the initial treatment of iNHL may be driven more by patient preferences regarding the differences in toxicity profile,” the researchers wrote.
Initial results from the BRIGHT study found that BR was noninferior to R-CHOP/R-CVP in terms of complete response rate (P = .0225 for noninferiority). The present study includes outcomes data for at least 5 years after completion of the study treatment.
For the entire study, the median follow-up was 65.0 months for patients in the BR group and 64.1 months for patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. Overall, the intention-to-treat population included 224 patients receiving BR and 223 patients receiving R-CHOP and R-CVP.
The median time to progression was not reached in either treatment group. The 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 65.5% in the BR group and 55.8% in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. The difference between these rates was significant, with a hazard ratio of 0.61 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.85; P = .0025).
Similarly, event-free survival was better in the BR group versus the R-CHOP/R-CVP group (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.46-0.84; P = .0020). Duration of response also favored the BR treatment regimen (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.47-0.92; P = .0134).
The long-term follow-up showed no significant difference in overall survival, with an HR of 1.15 for BR versus R-CHOP/R-CVP (95% CI, 0.72-1.84; P = .5461). Overall, there were 40 deaths in the BR treatment group and 32 deaths in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group.
Whether patients received maintenance rituximab did not affect the overall survival between groups. Similarly, there was no difference in overall survival by lymphoma type.
“Benefit from BR treatment did not translate to prolonged [overall survival], possibly because of the subsequent lines of therapy, including the use of BR in patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group,” the researchers wrote.
In terms of safety, the follow-up data showed no significant difference in early non–disease-related mortality between the treatment groups. However, the BRIGHT study showed higher rates of secondary malignancies in the BR group, compared with R-CHOP/R-CVP. That finding was not seen in the Study Group of Indolent Lymphomas Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (StiL NHL) 1 trial, and the authors could not provide an explanation for the increase in their research.
This study was supported by Teva Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Flinn reported receiving institutional research funding from Teva and receiving institutional research funding from or serving as a consultant to several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00605.
Frontline treatment with patients in the BRIGHT study.
The bendamustine-rituximab (BR) regimen had superior 5-year progression-free survival rates, event-free survival, and duration of response, compared with either rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) or rituximab with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CVP). The follow-up study did not find a significant difference in overall survival, however.
While the cumulative evidence from BRIGHT and other studies supports BR as a first-line treatment option for patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), the lack of an overall survival benefit indicates that the sequence of BR and R-CHOP or R-CVP “may not be critical,” Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute in Nashville, and his colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“[The] choice of regimen for the initial treatment of iNHL may be driven more by patient preferences regarding the differences in toxicity profile,” the researchers wrote.
Initial results from the BRIGHT study found that BR was noninferior to R-CHOP/R-CVP in terms of complete response rate (P = .0225 for noninferiority). The present study includes outcomes data for at least 5 years after completion of the study treatment.
For the entire study, the median follow-up was 65.0 months for patients in the BR group and 64.1 months for patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. Overall, the intention-to-treat population included 224 patients receiving BR and 223 patients receiving R-CHOP and R-CVP.
The median time to progression was not reached in either treatment group. The 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 65.5% in the BR group and 55.8% in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. The difference between these rates was significant, with a hazard ratio of 0.61 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.85; P = .0025).
Similarly, event-free survival was better in the BR group versus the R-CHOP/R-CVP group (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.46-0.84; P = .0020). Duration of response also favored the BR treatment regimen (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.47-0.92; P = .0134).
The long-term follow-up showed no significant difference in overall survival, with an HR of 1.15 for BR versus R-CHOP/R-CVP (95% CI, 0.72-1.84; P = .5461). Overall, there were 40 deaths in the BR treatment group and 32 deaths in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group.
Whether patients received maintenance rituximab did not affect the overall survival between groups. Similarly, there was no difference in overall survival by lymphoma type.
“Benefit from BR treatment did not translate to prolonged [overall survival], possibly because of the subsequent lines of therapy, including the use of BR in patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group,” the researchers wrote.
In terms of safety, the follow-up data showed no significant difference in early non–disease-related mortality between the treatment groups. However, the BRIGHT study showed higher rates of secondary malignancies in the BR group, compared with R-CHOP/R-CVP. That finding was not seen in the Study Group of Indolent Lymphomas Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (StiL NHL) 1 trial, and the authors could not provide an explanation for the increase in their research.
This study was supported by Teva Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Flinn reported receiving institutional research funding from Teva and receiving institutional research funding from or serving as a consultant to several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00605.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Analysis suggests ‘Burkitt-like lymphoma’ is a misnomer
They found that BLL-11q has a genomic and mutational profile more closely related to that of high grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL) or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) than typical Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
The researchers also found that BLL-11q has clinical, morphologic, and phenotypic features that are “more consistent” with HGBCL or DLBCL than with typical BL.
“These observations support a reconsideration of the ‘Burkitt-like’ term for these tumors,” Blanca Gonzalez-Farre, MD, of Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, and her colleagues wrote in Haematologica.
To reach this conclusion, the researchers performed copy number analysis and sequencing of B-cell lymphoma-related genes in 11 cases of BLL-11q.
The copy number analysis revealed that seven BLL-11q cases had the typical 11q gain/loss pattern, two had an 11q terminal deletion, one had two gains and two losses, and one had an 11q23.3-q25 copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity in addition to gain.
The BLL-11q cases also had frequent gains of 5q21.3-q32 and losses of 6q12.1-q21. However, they lacked the 1q gains observed in MYC-positive BL and alterations typically observed in germinal center B-cell like (GCB) DLBCL, such as gains in 2p16.1 and 7p.
Targeted sequencing of the BLL-11q cases revealed mutations typically observed in germinal center-derived lymphomas, including mutations in BTG2, DDX3X, ETS1, EP300, GNA13, CREBBP, KMT2C, EZH2, ARID1A, KMT2D, HIST1H1D, HIST1H2BC, and TMEM30A.
However, the BLL-11q cases lacked mutations in ID3, TCF3, and CCND3, which are typically observed in BL.
“In addition to the genetic differences, our BLL-11q differed clinically, morphologically, and phenotypically from conventional BL and instead showed features more consistent with HGBCL or DLBCL,” the researchers wrote.
Specifically, the BLL-11q patients were all younger than 40 years, with a median age of 15. Most presented with localized lymphadenopathy. And all had favorable treatment outcomes, remaining alive and free of disease at a median follow-up of 30 months.
All cases had a germinal center phenotype. They did not have the typical cytological features of BL, but they did have a high proliferative index, and some cases had a starry sky pattern.
The researchers said the BLL-11q cases were better classified as HGBCL not otherwise specified (n = 8), DLBCL (n = 2), and atypical BL (n = 1).
Considering these findings together, the team concluded that a more appropriate name for BLL-11q might be “aggressive B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberration.”
This research was supported by Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer and other organizations, as well as the government of Catalonia.
SOURCE: Gonzalez-Farre B et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.207928.
They found that BLL-11q has a genomic and mutational profile more closely related to that of high grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL) or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) than typical Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
The researchers also found that BLL-11q has clinical, morphologic, and phenotypic features that are “more consistent” with HGBCL or DLBCL than with typical BL.
“These observations support a reconsideration of the ‘Burkitt-like’ term for these tumors,” Blanca Gonzalez-Farre, MD, of Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, and her colleagues wrote in Haematologica.
To reach this conclusion, the researchers performed copy number analysis and sequencing of B-cell lymphoma-related genes in 11 cases of BLL-11q.
The copy number analysis revealed that seven BLL-11q cases had the typical 11q gain/loss pattern, two had an 11q terminal deletion, one had two gains and two losses, and one had an 11q23.3-q25 copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity in addition to gain.
The BLL-11q cases also had frequent gains of 5q21.3-q32 and losses of 6q12.1-q21. However, they lacked the 1q gains observed in MYC-positive BL and alterations typically observed in germinal center B-cell like (GCB) DLBCL, such as gains in 2p16.1 and 7p.
Targeted sequencing of the BLL-11q cases revealed mutations typically observed in germinal center-derived lymphomas, including mutations in BTG2, DDX3X, ETS1, EP300, GNA13, CREBBP, KMT2C, EZH2, ARID1A, KMT2D, HIST1H1D, HIST1H2BC, and TMEM30A.
However, the BLL-11q cases lacked mutations in ID3, TCF3, and CCND3, which are typically observed in BL.
“In addition to the genetic differences, our BLL-11q differed clinically, morphologically, and phenotypically from conventional BL and instead showed features more consistent with HGBCL or DLBCL,” the researchers wrote.
Specifically, the BLL-11q patients were all younger than 40 years, with a median age of 15. Most presented with localized lymphadenopathy. And all had favorable treatment outcomes, remaining alive and free of disease at a median follow-up of 30 months.
All cases had a germinal center phenotype. They did not have the typical cytological features of BL, but they did have a high proliferative index, and some cases had a starry sky pattern.
The researchers said the BLL-11q cases were better classified as HGBCL not otherwise specified (n = 8), DLBCL (n = 2), and atypical BL (n = 1).
Considering these findings together, the team concluded that a more appropriate name for BLL-11q might be “aggressive B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberration.”
This research was supported by Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer and other organizations, as well as the government of Catalonia.
SOURCE: Gonzalez-Farre B et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.207928.
They found that BLL-11q has a genomic and mutational profile more closely related to that of high grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL) or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) than typical Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
The researchers also found that BLL-11q has clinical, morphologic, and phenotypic features that are “more consistent” with HGBCL or DLBCL than with typical BL.
“These observations support a reconsideration of the ‘Burkitt-like’ term for these tumors,” Blanca Gonzalez-Farre, MD, of Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, and her colleagues wrote in Haematologica.
To reach this conclusion, the researchers performed copy number analysis and sequencing of B-cell lymphoma-related genes in 11 cases of BLL-11q.
The copy number analysis revealed that seven BLL-11q cases had the typical 11q gain/loss pattern, two had an 11q terminal deletion, one had two gains and two losses, and one had an 11q23.3-q25 copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity in addition to gain.
The BLL-11q cases also had frequent gains of 5q21.3-q32 and losses of 6q12.1-q21. However, they lacked the 1q gains observed in MYC-positive BL and alterations typically observed in germinal center B-cell like (GCB) DLBCL, such as gains in 2p16.1 and 7p.
Targeted sequencing of the BLL-11q cases revealed mutations typically observed in germinal center-derived lymphomas, including mutations in BTG2, DDX3X, ETS1, EP300, GNA13, CREBBP, KMT2C, EZH2, ARID1A, KMT2D, HIST1H1D, HIST1H2BC, and TMEM30A.
However, the BLL-11q cases lacked mutations in ID3, TCF3, and CCND3, which are typically observed in BL.
“In addition to the genetic differences, our BLL-11q differed clinically, morphologically, and phenotypically from conventional BL and instead showed features more consistent with HGBCL or DLBCL,” the researchers wrote.
Specifically, the BLL-11q patients were all younger than 40 years, with a median age of 15. Most presented with localized lymphadenopathy. And all had favorable treatment outcomes, remaining alive and free of disease at a median follow-up of 30 months.
All cases had a germinal center phenotype. They did not have the typical cytological features of BL, but they did have a high proliferative index, and some cases had a starry sky pattern.
The researchers said the BLL-11q cases were better classified as HGBCL not otherwise specified (n = 8), DLBCL (n = 2), and atypical BL (n = 1).
Considering these findings together, the team concluded that a more appropriate name for BLL-11q might be “aggressive B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberration.”
This research was supported by Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer and other organizations, as well as the government of Catalonia.
SOURCE: Gonzalez-Farre B et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.207928.
REPORTING FROM HAEMATOLOGICA
Gene expression signature reveals high-grade GCB DLBCL
New research suggests a gene expression signature can distinguish high-grade diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) from other germinal center B-cell–like (GCB) DLBCLs.
Researchers identified GCB DLBCL patients with this 104-gene signature who had a “distinct mutational landscape” and inferior treatment outcomes. David W. Scott, MBChB, PhD, of the British Columbia Cancer Research Centre in Vancouver, and his colleagues described these patients in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The findings were published alongside a related editorial and a similar study from another group.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues began their study by analyzing data from 157 patients with de novo GCB DLBCL. Twenty-five of these patients had double- or triple-hit high-grade B-cell lymphoma with BCL2 translocations (HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2).
The researchers identified 104 genes that were the “most significantly differentially expressed between HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 and other GCB DLBCLs” to create their double-hit gene signature (DHITsig).
The signature divided the patients into two groups — 42 patients (27%) whose tumors were positive for the DHITsig and 115 (73%) whose tumors were negative. Notably, 22 of the 25 HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 tumors were DHITsig-positive and 3 were negative.
The DHITsig was not associated with clinical variables such as tumor volume, but it was associated with prognosis. Treatment outcomes were inferior in patients who were DHITsig-positive.
The 5-year time to progression rate was 81% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 57% in those who were positive (P less than .001). The 5-year overall survival rate was 81% and 60%, respectively (P = .001).
The researchers observed similar results in a validation cohort of 262 patients with GCB-DLBCL who received rituximab-based therapy. The 5-year overall survival rate was 76% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 49% in those who were positive (P less than .001).
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also evaluated the DHITsig in a second validation cohort of 162 patients with GCB DLBCL.
In analyzing data from all three cohorts, the researchers found that mutations in MYC, BCL2, CREBBP, EZH2Y646, DDX3X, TP53, and KMT2D were more frequent in DHITsig-positive patients and mutations in TNFAIP3, KLHL6, NFKBIE, TET2, CD58, and STAT3 were more common in DHITsig-negative patients.
Additional analyses suggested the cell of origin for DHITsig-positive tumors comes from the intermediate zone or dark zone of the germinal center.
Finally, the researchers found they could use a “clinically relevant assay” to detect the DHITsig. They added a 30-gene module to the Lymph3Cx assay to create a NanoString-based assay called DLBCL90.
The team tested DLBCL90 in 171 GCB DLBCL patients. In this group, 26% of patients were DHITsig-positive, 64% were negative, and 10% were indeterminate. The prognostic significance of the signature was maintained with the assay results, according to the researchers.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also wanted to validate the association between the DHITsig and HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2, so they tested the DLBCL90 assay in two additional groups of patients.
First, the assay was used in 88 patients who had transformed follicular lymphoma with DLBCL morphology. Eleven of the 25 DHITsig-positive tumors and 4 of the 13 DHITsig-indeterminate tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2. However, none of the 50 DHITsig-negative tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2.
The researchers then used the DLBCL90 assay on 26 HGBL tumors. Twenty-three of these were DHITsig-positive and 3 were indeterminate.
This research was supported by the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute and other organizations. The researchers reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Roche, Janssen, Celgene, and various other companies.
SOURCE: Scott DW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 20;37(3):190-201.
New research suggests a gene expression signature can distinguish high-grade diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) from other germinal center B-cell–like (GCB) DLBCLs.
Researchers identified GCB DLBCL patients with this 104-gene signature who had a “distinct mutational landscape” and inferior treatment outcomes. David W. Scott, MBChB, PhD, of the British Columbia Cancer Research Centre in Vancouver, and his colleagues described these patients in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The findings were published alongside a related editorial and a similar study from another group.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues began their study by analyzing data from 157 patients with de novo GCB DLBCL. Twenty-five of these patients had double- or triple-hit high-grade B-cell lymphoma with BCL2 translocations (HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2).
The researchers identified 104 genes that were the “most significantly differentially expressed between HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 and other GCB DLBCLs” to create their double-hit gene signature (DHITsig).
The signature divided the patients into two groups — 42 patients (27%) whose tumors were positive for the DHITsig and 115 (73%) whose tumors were negative. Notably, 22 of the 25 HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 tumors were DHITsig-positive and 3 were negative.
The DHITsig was not associated with clinical variables such as tumor volume, but it was associated with prognosis. Treatment outcomes were inferior in patients who were DHITsig-positive.
The 5-year time to progression rate was 81% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 57% in those who were positive (P less than .001). The 5-year overall survival rate was 81% and 60%, respectively (P = .001).
The researchers observed similar results in a validation cohort of 262 patients with GCB-DLBCL who received rituximab-based therapy. The 5-year overall survival rate was 76% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 49% in those who were positive (P less than .001).
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also evaluated the DHITsig in a second validation cohort of 162 patients with GCB DLBCL.
In analyzing data from all three cohorts, the researchers found that mutations in MYC, BCL2, CREBBP, EZH2Y646, DDX3X, TP53, and KMT2D were more frequent in DHITsig-positive patients and mutations in TNFAIP3, KLHL6, NFKBIE, TET2, CD58, and STAT3 were more common in DHITsig-negative patients.
Additional analyses suggested the cell of origin for DHITsig-positive tumors comes from the intermediate zone or dark zone of the germinal center.
Finally, the researchers found they could use a “clinically relevant assay” to detect the DHITsig. They added a 30-gene module to the Lymph3Cx assay to create a NanoString-based assay called DLBCL90.
The team tested DLBCL90 in 171 GCB DLBCL patients. In this group, 26% of patients were DHITsig-positive, 64% were negative, and 10% were indeterminate. The prognostic significance of the signature was maintained with the assay results, according to the researchers.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also wanted to validate the association between the DHITsig and HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2, so they tested the DLBCL90 assay in two additional groups of patients.
First, the assay was used in 88 patients who had transformed follicular lymphoma with DLBCL morphology. Eleven of the 25 DHITsig-positive tumors and 4 of the 13 DHITsig-indeterminate tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2. However, none of the 50 DHITsig-negative tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2.
The researchers then used the DLBCL90 assay on 26 HGBL tumors. Twenty-three of these were DHITsig-positive and 3 were indeterminate.
This research was supported by the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute and other organizations. The researchers reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Roche, Janssen, Celgene, and various other companies.
SOURCE: Scott DW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 20;37(3):190-201.
New research suggests a gene expression signature can distinguish high-grade diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) from other germinal center B-cell–like (GCB) DLBCLs.
Researchers identified GCB DLBCL patients with this 104-gene signature who had a “distinct mutational landscape” and inferior treatment outcomes. David W. Scott, MBChB, PhD, of the British Columbia Cancer Research Centre in Vancouver, and his colleagues described these patients in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The findings were published alongside a related editorial and a similar study from another group.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues began their study by analyzing data from 157 patients with de novo GCB DLBCL. Twenty-five of these patients had double- or triple-hit high-grade B-cell lymphoma with BCL2 translocations (HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2).
The researchers identified 104 genes that were the “most significantly differentially expressed between HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 and other GCB DLBCLs” to create their double-hit gene signature (DHITsig).
The signature divided the patients into two groups — 42 patients (27%) whose tumors were positive for the DHITsig and 115 (73%) whose tumors were negative. Notably, 22 of the 25 HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 tumors were DHITsig-positive and 3 were negative.
The DHITsig was not associated with clinical variables such as tumor volume, but it was associated with prognosis. Treatment outcomes were inferior in patients who were DHITsig-positive.
The 5-year time to progression rate was 81% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 57% in those who were positive (P less than .001). The 5-year overall survival rate was 81% and 60%, respectively (P = .001).
The researchers observed similar results in a validation cohort of 262 patients with GCB-DLBCL who received rituximab-based therapy. The 5-year overall survival rate was 76% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 49% in those who were positive (P less than .001).
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also evaluated the DHITsig in a second validation cohort of 162 patients with GCB DLBCL.
In analyzing data from all three cohorts, the researchers found that mutations in MYC, BCL2, CREBBP, EZH2Y646, DDX3X, TP53, and KMT2D were more frequent in DHITsig-positive patients and mutations in TNFAIP3, KLHL6, NFKBIE, TET2, CD58, and STAT3 were more common in DHITsig-negative patients.
Additional analyses suggested the cell of origin for DHITsig-positive tumors comes from the intermediate zone or dark zone of the germinal center.
Finally, the researchers found they could use a “clinically relevant assay” to detect the DHITsig. They added a 30-gene module to the Lymph3Cx assay to create a NanoString-based assay called DLBCL90.
The team tested DLBCL90 in 171 GCB DLBCL patients. In this group, 26% of patients were DHITsig-positive, 64% were negative, and 10% were indeterminate. The prognostic significance of the signature was maintained with the assay results, according to the researchers.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also wanted to validate the association between the DHITsig and HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2, so they tested the DLBCL90 assay in two additional groups of patients.
First, the assay was used in 88 patients who had transformed follicular lymphoma with DLBCL morphology. Eleven of the 25 DHITsig-positive tumors and 4 of the 13 DHITsig-indeterminate tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2. However, none of the 50 DHITsig-negative tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2.
The researchers then used the DLBCL90 assay on 26 HGBL tumors. Twenty-three of these were DHITsig-positive and 3 were indeterminate.
This research was supported by the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute and other organizations. The researchers reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Roche, Janssen, Celgene, and various other companies.
SOURCE: Scott DW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 20;37(3):190-201.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Priority review granted to lenalidomide for FL, MZL
The Food and Drug Administration has granted priority review to a supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for lenalidomide (Revlimid).
Celgene is seeking approval for lenalidomide in combination with rituximab to treat patients with previously treated follicular lymphoma (FL) or marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
The FDA plans to make a decision on the sNDA by June 27, 2019.
The FDA aims to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it rather than the standard 10 months. The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that are expected to provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The sNDA for lenalidomide is supported by the phase 3 AUGMENT study (NCT01938001) in which researchers compared rituximab plus lenalidomide to rituximab plus placebo in patients with relapsed/refractory FL or MZL.
Results from AUGMENT were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Blood 2018 Nov 29;132:445).
According to the ASH abstract, the trial included 358 patients who were randomized to receive rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 178) or rituximab plus placebo (n = 180).
At a median follow-up of 28.3 months, the overall response rate was 78% in the lenalidomide arm and 53% in the placebo arm (P less than .0001). The complete response rate was 34% and 18%, respectively (P = .001).
The median progression-free survival was 39.4 months in the lenalidomide arm and 14.1 months in the placebo arm. Overall survival data were not mature, but there were 16 deaths reported in the lenalidomide arm and 26 deaths in the placebo arm.
Treatment-emergent adverse events that were more common in the lenalidomide arm than the placebo arm included infections, cutaneous reactions, constipation, thrombocytopenia, and tumor flare reaction.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted priority review to a supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for lenalidomide (Revlimid).
Celgene is seeking approval for lenalidomide in combination with rituximab to treat patients with previously treated follicular lymphoma (FL) or marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
The FDA plans to make a decision on the sNDA by June 27, 2019.
The FDA aims to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it rather than the standard 10 months. The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that are expected to provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The sNDA for lenalidomide is supported by the phase 3 AUGMENT study (NCT01938001) in which researchers compared rituximab plus lenalidomide to rituximab plus placebo in patients with relapsed/refractory FL or MZL.
Results from AUGMENT were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Blood 2018 Nov 29;132:445).
According to the ASH abstract, the trial included 358 patients who were randomized to receive rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 178) or rituximab plus placebo (n = 180).
At a median follow-up of 28.3 months, the overall response rate was 78% in the lenalidomide arm and 53% in the placebo arm (P less than .0001). The complete response rate was 34% and 18%, respectively (P = .001).
The median progression-free survival was 39.4 months in the lenalidomide arm and 14.1 months in the placebo arm. Overall survival data were not mature, but there were 16 deaths reported in the lenalidomide arm and 26 deaths in the placebo arm.
Treatment-emergent adverse events that were more common in the lenalidomide arm than the placebo arm included infections, cutaneous reactions, constipation, thrombocytopenia, and tumor flare reaction.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted priority review to a supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for lenalidomide (Revlimid).
Celgene is seeking approval for lenalidomide in combination with rituximab to treat patients with previously treated follicular lymphoma (FL) or marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
The FDA plans to make a decision on the sNDA by June 27, 2019.
The FDA aims to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it rather than the standard 10 months. The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that are expected to provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The sNDA for lenalidomide is supported by the phase 3 AUGMENT study (NCT01938001) in which researchers compared rituximab plus lenalidomide to rituximab plus placebo in patients with relapsed/refractory FL or MZL.
Results from AUGMENT were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Blood 2018 Nov 29;132:445).
According to the ASH abstract, the trial included 358 patients who were randomized to receive rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 178) or rituximab plus placebo (n = 180).
At a median follow-up of 28.3 months, the overall response rate was 78% in the lenalidomide arm and 53% in the placebo arm (P less than .0001). The complete response rate was 34% and 18%, respectively (P = .001).
The median progression-free survival was 39.4 months in the lenalidomide arm and 14.1 months in the placebo arm. Overall survival data were not mature, but there were 16 deaths reported in the lenalidomide arm and 26 deaths in the placebo arm.
Treatment-emergent adverse events that were more common in the lenalidomide arm than the placebo arm included infections, cutaneous reactions, constipation, thrombocytopenia, and tumor flare reaction.
Barriers to CAR T use in the spotlight at first European meeting
outcomes data suggest.
For that reason, and because bone marrow units are profit centers and CAR T-cell therapy reimbursement remains problematic, CAR T in the United States is “effectively being used as a bridge to transplant” – at a cost of more than $1 million per dose, economist Duane Schulthess told attendees at a recent, first-of-its-kind joint European CAR T-cell meeting in Paris, which was cosponsored by the European Hematology Association (EHA) and the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT).
“This is the way clinical practice is evolving right now; the price is not allowing enough experimentation for CAR T to flow up and be used in the less-diseased population,” said Mr. Schulthess, managing director of Vital Transformation, a consulting company based in Wezembeek-Oppem, Belgium.
In Europe, there is a slightly different problem in that health technology assessment bodies (HTAs) “have to figure out what they want to do” given the 2018 approvals of the first CAR T therapies there, he said, explaining that the data he presented was from a study commissioned by the Dutch government to help determine “what [CAR T] looks like from an effectiveness standpoint while they’re trying to figure out how much it’s worth and what they should pay.”
“Increasingly these are the big issues,” Mr. Schulthess said.
In August, the European Commission approved tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) on the recommendation of the European Medicines Agency. Kymriah was approved for pediatric and young adult patients up to age 25 years with refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in relapse after transplant or in second or later relapse, as well as for adults patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after failing at least two lines of systemic therapy, and Yescarta was approved for the latter and for the treatment of primary refractory mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma after at least two lines of systemic therapy.
The approvals have researchers and clinicians there clamoring for information about the therapy, which is revolutionizing the field of hematologic malignancies, according to Christian Chabannon, MD, PhD, chair of the EBMT Cellular Therapy & Immunobiology Working Party and vice-chair of the EBMT Scientific Council.
“An increasing number of European institutions are starting to administer this new category of medicinal products and increasingly contribute to ongoing clinical protocols and preclinical studies,” Dr. Chabannon said in an interview, explaining the urgency in planning the 1st European CAR T Cell Meeting just 6 months after the CAR T approvals in Europe.
EHA and EBMT brought together patient advocates, young investigators, and experts from across the globe to present the latest relevant information and data on topics ranging from current trials and experience, CAR T implementation and management, the preclinical and clinical pipelines, various CAR T applications, industry perspectives, and relevant economic issues, he said.
The latter is where Mr. Schulthess came in.
His research involved patient-level treatment pathway data from a database of more than 3 million patients treated with either allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HCT) or CAR T therapy across 5 years of experience. The data showed up to 85% response rates for each in the first-line setting. He and his colleagues then looked at therapy choices for those who failed to respond to second-line therapies and at how decisions were made regarding transplant and CAR T therapy – and specifically whether CAR T can be a substitute for transplant.
Ultimately, they looked at 29 allo-HCT recipients and 14 CAR T therapy recipients for a head-to-head comparison of the two treatments and performed an in-depth cost-efficacy analysis using a novel “visual pathology” methodology to account for limitations in the data.
The 3-year relapse-free survival probability was nearly 68% in the transplant recipients and 46% with CAR T.
“Now why is that? [Because] ... these populations are not the same; the CAR T population has a much higher disease burden,” Mr. Schulthess said. “So what we’re seeing [among] actual clinical doctors doing this for real – they are defaulting to bone marrow transplants, except in those cases where they do not have enough time or the patient does not respond. Then and only then are they giving CAR T.”
And that comes back to the fact that bone marrow units make money, he said.
CAR T is costly, and reimbursement can be problematic; these are disincentives for doctors to use CAR T therapy, at least in the United States, and while this is currently “being worked out,” the choice more often is “giving bone marrow transplant first and seeing what happens,” Mr. Schulthess said.
In Europe, that creates “a tough choice” for the HTAs, he said, noting that, in the absence of evidence of CAR T being curative in the subpopulation of patients with high disease burden who fail transplant and given the high cost, there is a push to determine at what point it begins to make sense economically.
“We think that you gain efficiency at ... roughly $277,000 [per dose] because [at that cost] you can do more CAR Ts than you can do bone marrow transplants. [CAR T] is less invasive, it’s lighter touch, it’s more efficient,” he said. “So if we were to see an efficiency cost of between $222,000 and $277,000, we think that works.”
Another recent study came to similar conclusions based on quality assessments, he said (J Clin Oncol. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.79.0642).
“We think that’s where this is going to end up, so we think that, if someone starts producing this for a couple hundred thousand bucks, then – certainly in Europe – it will make sense for this to start drifting up and being used as a substitute [to transplant],” he added.
Mr. Schulthess was one of scores of experts and investigators who presented at the EHA/EBMT joint meeting, which included numerous U.S. pioneers in the field and young European investigators, among others, Dr. Chabannon said.
Attesting to the enthusiasm in Europe regarding CAR T, Dr. Chabannon said that there were “more requests for registration than the venue could safely accommodate, a long waiting list, and a high number of individuals on the waiting list who registered for the live streaming” of the event.
“The field of CAR T cells is growing at a fast pace since the first clinical successes reported in the early 2010s, and one can wonder whether the expectations are not in excess of what reality will deliver,” he said. “Nevertheless, CAR T cells represent an essential innovation, not an incremental progress in biomedical sciences. They combine new mechanisms of action, clinical activity in advanced malignancies (and possibly beyond the field of cancer), transfer of manufacturing of human cell-based therapeutics to the industry, and potentially the first commercial success for a gene therapy.”
Surveys conducted by various professional associations, including EBMT, have clearly identified the potential for clinical successes that CAR T cells represent and the tremendous challenges raised by these innovations, he said, noting that “these include fulfilling specific educational needs.”
Therefore, EBMT and EHA have already announced that a second edition of the meeting is planned for Jan. 30 – Feb. 1, 2020, he noted.
Mr. Schulthess reported that his research was funded by the Dutch government.
outcomes data suggest.
For that reason, and because bone marrow units are profit centers and CAR T-cell therapy reimbursement remains problematic, CAR T in the United States is “effectively being used as a bridge to transplant” – at a cost of more than $1 million per dose, economist Duane Schulthess told attendees at a recent, first-of-its-kind joint European CAR T-cell meeting in Paris, which was cosponsored by the European Hematology Association (EHA) and the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT).
“This is the way clinical practice is evolving right now; the price is not allowing enough experimentation for CAR T to flow up and be used in the less-diseased population,” said Mr. Schulthess, managing director of Vital Transformation, a consulting company based in Wezembeek-Oppem, Belgium.
In Europe, there is a slightly different problem in that health technology assessment bodies (HTAs) “have to figure out what they want to do” given the 2018 approvals of the first CAR T therapies there, he said, explaining that the data he presented was from a study commissioned by the Dutch government to help determine “what [CAR T] looks like from an effectiveness standpoint while they’re trying to figure out how much it’s worth and what they should pay.”
“Increasingly these are the big issues,” Mr. Schulthess said.
In August, the European Commission approved tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) on the recommendation of the European Medicines Agency. Kymriah was approved for pediatric and young adult patients up to age 25 years with refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in relapse after transplant or in second or later relapse, as well as for adults patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after failing at least two lines of systemic therapy, and Yescarta was approved for the latter and for the treatment of primary refractory mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma after at least two lines of systemic therapy.
The approvals have researchers and clinicians there clamoring for information about the therapy, which is revolutionizing the field of hematologic malignancies, according to Christian Chabannon, MD, PhD, chair of the EBMT Cellular Therapy & Immunobiology Working Party and vice-chair of the EBMT Scientific Council.
“An increasing number of European institutions are starting to administer this new category of medicinal products and increasingly contribute to ongoing clinical protocols and preclinical studies,” Dr. Chabannon said in an interview, explaining the urgency in planning the 1st European CAR T Cell Meeting just 6 months after the CAR T approvals in Europe.
EHA and EBMT brought together patient advocates, young investigators, and experts from across the globe to present the latest relevant information and data on topics ranging from current trials and experience, CAR T implementation and management, the preclinical and clinical pipelines, various CAR T applications, industry perspectives, and relevant economic issues, he said.
The latter is where Mr. Schulthess came in.
His research involved patient-level treatment pathway data from a database of more than 3 million patients treated with either allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HCT) or CAR T therapy across 5 years of experience. The data showed up to 85% response rates for each in the first-line setting. He and his colleagues then looked at therapy choices for those who failed to respond to second-line therapies and at how decisions were made regarding transplant and CAR T therapy – and specifically whether CAR T can be a substitute for transplant.
Ultimately, they looked at 29 allo-HCT recipients and 14 CAR T therapy recipients for a head-to-head comparison of the two treatments and performed an in-depth cost-efficacy analysis using a novel “visual pathology” methodology to account for limitations in the data.
The 3-year relapse-free survival probability was nearly 68% in the transplant recipients and 46% with CAR T.
“Now why is that? [Because] ... these populations are not the same; the CAR T population has a much higher disease burden,” Mr. Schulthess said. “So what we’re seeing [among] actual clinical doctors doing this for real – they are defaulting to bone marrow transplants, except in those cases where they do not have enough time or the patient does not respond. Then and only then are they giving CAR T.”
And that comes back to the fact that bone marrow units make money, he said.
CAR T is costly, and reimbursement can be problematic; these are disincentives for doctors to use CAR T therapy, at least in the United States, and while this is currently “being worked out,” the choice more often is “giving bone marrow transplant first and seeing what happens,” Mr. Schulthess said.
In Europe, that creates “a tough choice” for the HTAs, he said, noting that, in the absence of evidence of CAR T being curative in the subpopulation of patients with high disease burden who fail transplant and given the high cost, there is a push to determine at what point it begins to make sense economically.
“We think that you gain efficiency at ... roughly $277,000 [per dose] because [at that cost] you can do more CAR Ts than you can do bone marrow transplants. [CAR T] is less invasive, it’s lighter touch, it’s more efficient,” he said. “So if we were to see an efficiency cost of between $222,000 and $277,000, we think that works.”
Another recent study came to similar conclusions based on quality assessments, he said (J Clin Oncol. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.79.0642).
“We think that’s where this is going to end up, so we think that, if someone starts producing this for a couple hundred thousand bucks, then – certainly in Europe – it will make sense for this to start drifting up and being used as a substitute [to transplant],” he added.
Mr. Schulthess was one of scores of experts and investigators who presented at the EHA/EBMT joint meeting, which included numerous U.S. pioneers in the field and young European investigators, among others, Dr. Chabannon said.
Attesting to the enthusiasm in Europe regarding CAR T, Dr. Chabannon said that there were “more requests for registration than the venue could safely accommodate, a long waiting list, and a high number of individuals on the waiting list who registered for the live streaming” of the event.
“The field of CAR T cells is growing at a fast pace since the first clinical successes reported in the early 2010s, and one can wonder whether the expectations are not in excess of what reality will deliver,” he said. “Nevertheless, CAR T cells represent an essential innovation, not an incremental progress in biomedical sciences. They combine new mechanisms of action, clinical activity in advanced malignancies (and possibly beyond the field of cancer), transfer of manufacturing of human cell-based therapeutics to the industry, and potentially the first commercial success for a gene therapy.”
Surveys conducted by various professional associations, including EBMT, have clearly identified the potential for clinical successes that CAR T cells represent and the tremendous challenges raised by these innovations, he said, noting that “these include fulfilling specific educational needs.”
Therefore, EBMT and EHA have already announced that a second edition of the meeting is planned for Jan. 30 – Feb. 1, 2020, he noted.
Mr. Schulthess reported that his research was funded by the Dutch government.
outcomes data suggest.
For that reason, and because bone marrow units are profit centers and CAR T-cell therapy reimbursement remains problematic, CAR T in the United States is “effectively being used as a bridge to transplant” – at a cost of more than $1 million per dose, economist Duane Schulthess told attendees at a recent, first-of-its-kind joint European CAR T-cell meeting in Paris, which was cosponsored by the European Hematology Association (EHA) and the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT).
“This is the way clinical practice is evolving right now; the price is not allowing enough experimentation for CAR T to flow up and be used in the less-diseased population,” said Mr. Schulthess, managing director of Vital Transformation, a consulting company based in Wezembeek-Oppem, Belgium.
In Europe, there is a slightly different problem in that health technology assessment bodies (HTAs) “have to figure out what they want to do” given the 2018 approvals of the first CAR T therapies there, he said, explaining that the data he presented was from a study commissioned by the Dutch government to help determine “what [CAR T] looks like from an effectiveness standpoint while they’re trying to figure out how much it’s worth and what they should pay.”
“Increasingly these are the big issues,” Mr. Schulthess said.
In August, the European Commission approved tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) on the recommendation of the European Medicines Agency. Kymriah was approved for pediatric and young adult patients up to age 25 years with refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in relapse after transplant or in second or later relapse, as well as for adults patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after failing at least two lines of systemic therapy, and Yescarta was approved for the latter and for the treatment of primary refractory mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma after at least two lines of systemic therapy.
The approvals have researchers and clinicians there clamoring for information about the therapy, which is revolutionizing the field of hematologic malignancies, according to Christian Chabannon, MD, PhD, chair of the EBMT Cellular Therapy & Immunobiology Working Party and vice-chair of the EBMT Scientific Council.
“An increasing number of European institutions are starting to administer this new category of medicinal products and increasingly contribute to ongoing clinical protocols and preclinical studies,” Dr. Chabannon said in an interview, explaining the urgency in planning the 1st European CAR T Cell Meeting just 6 months after the CAR T approvals in Europe.
EHA and EBMT brought together patient advocates, young investigators, and experts from across the globe to present the latest relevant information and data on topics ranging from current trials and experience, CAR T implementation and management, the preclinical and clinical pipelines, various CAR T applications, industry perspectives, and relevant economic issues, he said.
The latter is where Mr. Schulthess came in.
His research involved patient-level treatment pathway data from a database of more than 3 million patients treated with either allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HCT) or CAR T therapy across 5 years of experience. The data showed up to 85% response rates for each in the first-line setting. He and his colleagues then looked at therapy choices for those who failed to respond to second-line therapies and at how decisions were made regarding transplant and CAR T therapy – and specifically whether CAR T can be a substitute for transplant.
Ultimately, they looked at 29 allo-HCT recipients and 14 CAR T therapy recipients for a head-to-head comparison of the two treatments and performed an in-depth cost-efficacy analysis using a novel “visual pathology” methodology to account for limitations in the data.
The 3-year relapse-free survival probability was nearly 68% in the transplant recipients and 46% with CAR T.
“Now why is that? [Because] ... these populations are not the same; the CAR T population has a much higher disease burden,” Mr. Schulthess said. “So what we’re seeing [among] actual clinical doctors doing this for real – they are defaulting to bone marrow transplants, except in those cases where they do not have enough time or the patient does not respond. Then and only then are they giving CAR T.”
And that comes back to the fact that bone marrow units make money, he said.
CAR T is costly, and reimbursement can be problematic; these are disincentives for doctors to use CAR T therapy, at least in the United States, and while this is currently “being worked out,” the choice more often is “giving bone marrow transplant first and seeing what happens,” Mr. Schulthess said.
In Europe, that creates “a tough choice” for the HTAs, he said, noting that, in the absence of evidence of CAR T being curative in the subpopulation of patients with high disease burden who fail transplant and given the high cost, there is a push to determine at what point it begins to make sense economically.
“We think that you gain efficiency at ... roughly $277,000 [per dose] because [at that cost] you can do more CAR Ts than you can do bone marrow transplants. [CAR T] is less invasive, it’s lighter touch, it’s more efficient,” he said. “So if we were to see an efficiency cost of between $222,000 and $277,000, we think that works.”
Another recent study came to similar conclusions based on quality assessments, he said (J Clin Oncol. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.79.0642).
“We think that’s where this is going to end up, so we think that, if someone starts producing this for a couple hundred thousand bucks, then – certainly in Europe – it will make sense for this to start drifting up and being used as a substitute [to transplant],” he added.
Mr. Schulthess was one of scores of experts and investigators who presented at the EHA/EBMT joint meeting, which included numerous U.S. pioneers in the field and young European investigators, among others, Dr. Chabannon said.
Attesting to the enthusiasm in Europe regarding CAR T, Dr. Chabannon said that there were “more requests for registration than the venue could safely accommodate, a long waiting list, and a high number of individuals on the waiting list who registered for the live streaming” of the event.
“The field of CAR T cells is growing at a fast pace since the first clinical successes reported in the early 2010s, and one can wonder whether the expectations are not in excess of what reality will deliver,” he said. “Nevertheless, CAR T cells represent an essential innovation, not an incremental progress in biomedical sciences. They combine new mechanisms of action, clinical activity in advanced malignancies (and possibly beyond the field of cancer), transfer of manufacturing of human cell-based therapeutics to the industry, and potentially the first commercial success for a gene therapy.”
Surveys conducted by various professional associations, including EBMT, have clearly identified the potential for clinical successes that CAR T cells represent and the tremendous challenges raised by these innovations, he said, noting that “these include fulfilling specific educational needs.”
Therefore, EBMT and EHA have already announced that a second edition of the meeting is planned for Jan. 30 – Feb. 1, 2020, he noted.
Mr. Schulthess reported that his research was funded by the Dutch government.