User login
Checkpoint inhibitor plus rituximab is active in non-Hodgkin lymphoma
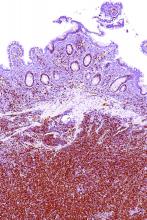
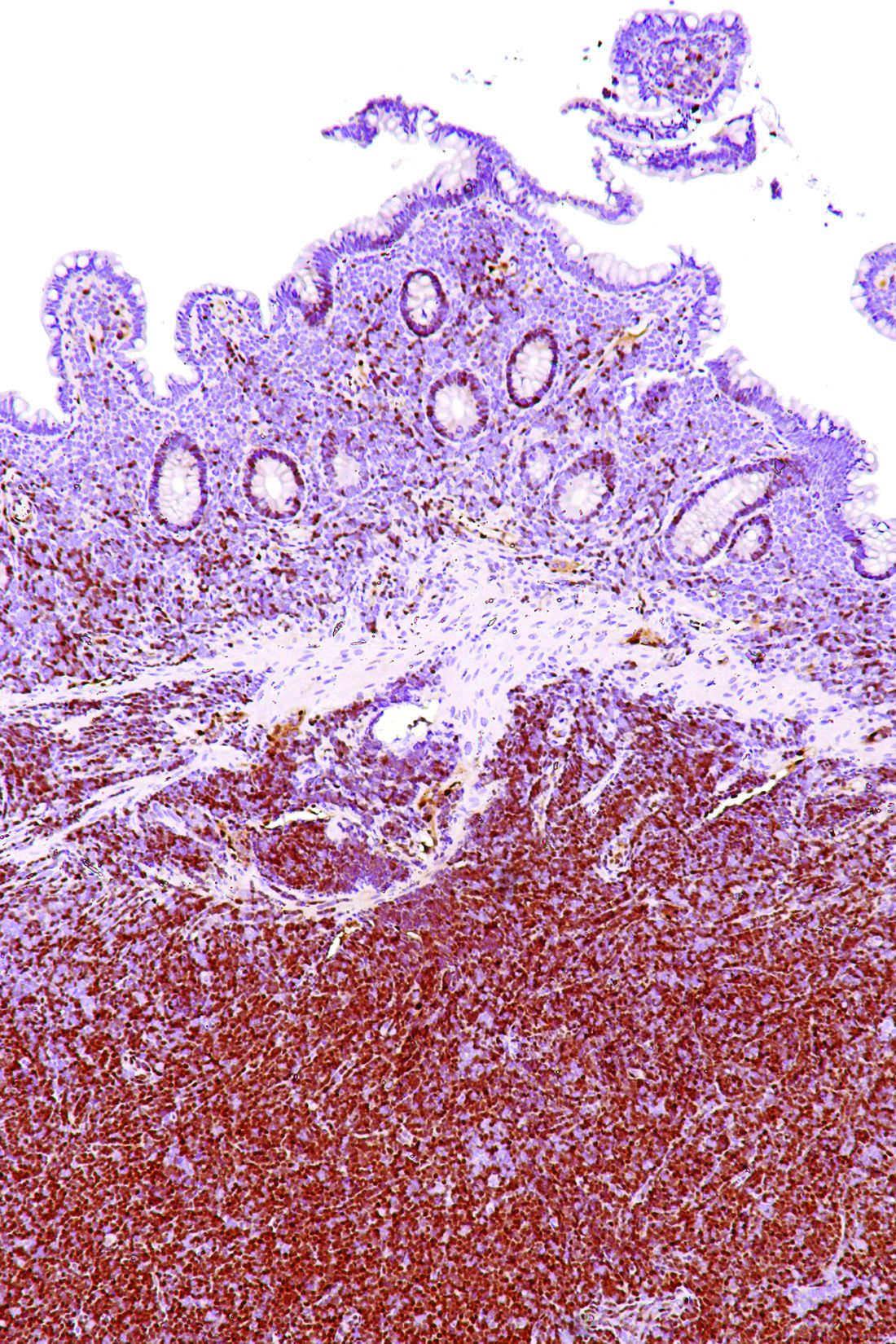
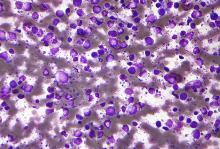
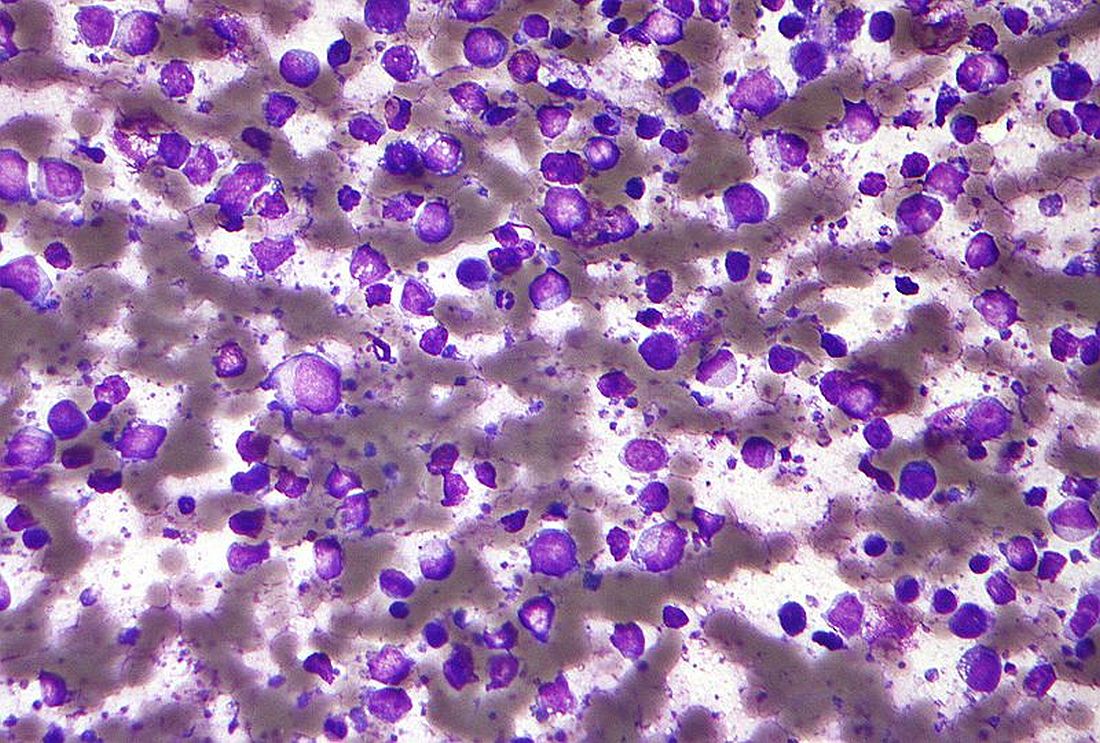
A macrophage-activating immune checkpoint inhibitor, combined with rituximab therapy, was safe and produced durable complete responses in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, according to results of a phase 1b study.
Mainly low-grade toxic effects were seen on treatment with Hu5F9-G4 (5F9) and rituximab, which induced responses in more than half of patients, of which more than one-third were complete responses, the study investigators reported.
Most of the responses were ongoing at the time of data cutoff, suggesting durable responses with the combination of rituximab and 5F9 – a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks CD47, an antiphagocytic or “do not eat me” signal overexpressed by most cancers, Ranjana Advani, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and her coauthors wrote.
“The macrophage-mediated activity of 5F9 plus rituximab may serve as an effective new immunotherapy for stimulating the innate immune system,” Dr. Advani and her colleagues reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study included 22 patients, including 15 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 7 with follicular lymphoma, who had received a median of four prior therapies. Almost all of the non-Hodgkin lymphomas (21, or 95%) were refractory to rituximab.
All patients received intravenous 5F9 starting with a priming dose of 1 mg/kg followed by weekly maintenance doses of 10-30 mg/kg in three dose-escalation cohorts, given until disease progression or lack of clinical benefit. Intravenous rituximab at 375 mg/m2 weekly was started on the second week of the first cycle, and then monthly for cycles 2 through 6.
“Substantial antitumor activity” was seen with this chemotherapy-free regimen in a group of heavily pretreated, largely rituximab-refractory patients, Dr. Advani and her coauthors wrote in their report.
The objective response rate was 50%, including a 36% complete response rate in the intent-to-treat analysis. For DLBCL, the rates of objective and complete responses were 40% and 33%, while for follicular lymphoma, they were 71% and 43%.
The median duration of response was not reached in either disease cohort with a median follow-up of 6.2 months for DLBCL and 8.1 months for follicular lymphoma. Of the 11 patients who responded, 10 (91%) were still in response at the time of data cutoff. “Longer follow-up is needed,” the investigators wrote.
Most adverse events were seen within the first few weeks of treatment and mainly included anemia and infusion-related reactions. The anemia was an expected, on-target effect of 5F9 because of selective clearance of older red cells, which was predictable, transient, and mitigated by the maintenance dosing strategy employed in this phase 1b trial.
“As red cells age, they lose CD47 expression and gain expression of prophagocytic signals, leading to homeostatic clearance,” they wrote.
The activity of 5F9 and rituximab is “synergistic” based on the results of previous, preclinical investigations in models of lymphoma, Dr. Advani and her coauthors added.
A phase 2 trial of 5F9 plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma is ongoing, according to their report.
The study was supported by Forty Seven and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Dr. Advani reported disclosures related to Forty Seven, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Roche/Genentech, among others.
SOURCE: Advani R et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1711-21.
A macrophage-activating immune checkpoint inhibitor, combined with rituximab therapy, was safe and produced durable complete responses in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, according to results of a phase 1b study.
Mainly low-grade toxic effects were seen on treatment with Hu5F9-G4 (5F9) and rituximab, which induced responses in more than half of patients, of which more than one-third were complete responses, the study investigators reported.
Most of the responses were ongoing at the time of data cutoff, suggesting durable responses with the combination of rituximab and 5F9 – a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks CD47, an antiphagocytic or “do not eat me” signal overexpressed by most cancers, Ranjana Advani, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and her coauthors wrote.
“The macrophage-mediated activity of 5F9 plus rituximab may serve as an effective new immunotherapy for stimulating the innate immune system,” Dr. Advani and her colleagues reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study included 22 patients, including 15 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 7 with follicular lymphoma, who had received a median of four prior therapies. Almost all of the non-Hodgkin lymphomas (21, or 95%) were refractory to rituximab.
All patients received intravenous 5F9 starting with a priming dose of 1 mg/kg followed by weekly maintenance doses of 10-30 mg/kg in three dose-escalation cohorts, given until disease progression or lack of clinical benefit. Intravenous rituximab at 375 mg/m2 weekly was started on the second week of the first cycle, and then monthly for cycles 2 through 6.
“Substantial antitumor activity” was seen with this chemotherapy-free regimen in a group of heavily pretreated, largely rituximab-refractory patients, Dr. Advani and her coauthors wrote in their report.
The objective response rate was 50%, including a 36% complete response rate in the intent-to-treat analysis. For DLBCL, the rates of objective and complete responses were 40% and 33%, while for follicular lymphoma, they were 71% and 43%.
The median duration of response was not reached in either disease cohort with a median follow-up of 6.2 months for DLBCL and 8.1 months for follicular lymphoma. Of the 11 patients who responded, 10 (91%) were still in response at the time of data cutoff. “Longer follow-up is needed,” the investigators wrote.
Most adverse events were seen within the first few weeks of treatment and mainly included anemia and infusion-related reactions. The anemia was an expected, on-target effect of 5F9 because of selective clearance of older red cells, which was predictable, transient, and mitigated by the maintenance dosing strategy employed in this phase 1b trial.
“As red cells age, they lose CD47 expression and gain expression of prophagocytic signals, leading to homeostatic clearance,” they wrote.
The activity of 5F9 and rituximab is “synergistic” based on the results of previous, preclinical investigations in models of lymphoma, Dr. Advani and her coauthors added.
A phase 2 trial of 5F9 plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma is ongoing, according to their report.
The study was supported by Forty Seven and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Dr. Advani reported disclosures related to Forty Seven, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Roche/Genentech, among others.
SOURCE: Advani R et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1711-21.
A macrophage-activating immune checkpoint inhibitor, combined with rituximab therapy, was safe and produced durable complete responses in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, according to results of a phase 1b study.
Mainly low-grade toxic effects were seen on treatment with Hu5F9-G4 (5F9) and rituximab, which induced responses in more than half of patients, of which more than one-third were complete responses, the study investigators reported.
Most of the responses were ongoing at the time of data cutoff, suggesting durable responses with the combination of rituximab and 5F9 – a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks CD47, an antiphagocytic or “do not eat me” signal overexpressed by most cancers, Ranjana Advani, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and her coauthors wrote.
“The macrophage-mediated activity of 5F9 plus rituximab may serve as an effective new immunotherapy for stimulating the innate immune system,” Dr. Advani and her colleagues reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study included 22 patients, including 15 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 7 with follicular lymphoma, who had received a median of four prior therapies. Almost all of the non-Hodgkin lymphomas (21, or 95%) were refractory to rituximab.
All patients received intravenous 5F9 starting with a priming dose of 1 mg/kg followed by weekly maintenance doses of 10-30 mg/kg in three dose-escalation cohorts, given until disease progression or lack of clinical benefit. Intravenous rituximab at 375 mg/m2 weekly was started on the second week of the first cycle, and then monthly for cycles 2 through 6.
“Substantial antitumor activity” was seen with this chemotherapy-free regimen in a group of heavily pretreated, largely rituximab-refractory patients, Dr. Advani and her coauthors wrote in their report.
The objective response rate was 50%, including a 36% complete response rate in the intent-to-treat analysis. For DLBCL, the rates of objective and complete responses were 40% and 33%, while for follicular lymphoma, they were 71% and 43%.
The median duration of response was not reached in either disease cohort with a median follow-up of 6.2 months for DLBCL and 8.1 months for follicular lymphoma. Of the 11 patients who responded, 10 (91%) were still in response at the time of data cutoff. “Longer follow-up is needed,” the investigators wrote.
Most adverse events were seen within the first few weeks of treatment and mainly included anemia and infusion-related reactions. The anemia was an expected, on-target effect of 5F9 because of selective clearance of older red cells, which was predictable, transient, and mitigated by the maintenance dosing strategy employed in this phase 1b trial.
“As red cells age, they lose CD47 expression and gain expression of prophagocytic signals, leading to homeostatic clearance,” they wrote.
The activity of 5F9 and rituximab is “synergistic” based on the results of previous, preclinical investigations in models of lymphoma, Dr. Advani and her coauthors added.
A phase 2 trial of 5F9 plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma is ongoing, according to their report.
The study was supported by Forty Seven and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Dr. Advani reported disclosures related to Forty Seven, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Roche/Genentech, among others.
SOURCE: Advani R et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1711-21.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Rates of overall and complete responses were 50% and 36%, respectively, with most responses ongoing at the time of data cutoff.
Study details: A phase 1b study of 22 patients, including 15 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and 7 with follicular lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study was supported by Forty Seven and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Study authors reported disclosures related to Forty Seven, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Roche/Genentech, among others.
Source: Advani R et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1711-21.
Collaboration is key to bridging the AYA cancer care divide
Survival gains among adolescents and young adults (AYAs) with cancer continue to lag behind outcomes for children and older adult patients. It’s a trend that spans decades, but clinicians and researchers are finally getting serious about trying to understand the underlying causes and are re-examining prevailing practices in an effort to address the discrepancies.
“This is a very heterogeneous group of disorders,” Rabi Hanna, MD, a pediatric hematologist and oncologist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s Hospital, Ohio, said in an interview. He’s specifically referring to the cancers that affect AYAs, who are broadly defined as patients aged 15 through 39 years. “A few cancers, such as [acute lymphoblastic leukemia], are more common in children, and others, such as breast cancer, are more common in adults. The biology may be different in the adolescent and young adult patients, which may lead to different outcomes.”
In addition, the psychosocial needs in this age group differ vastly from those in other groups. “Many of these patients are in college or have just started their families, so we have to pay more attention to [issues related to] financial toxicity and fertility, for example,” said Dr Hanna, who is the director of pediatric bone marrow transplantation at the clinic. (The term “financial toxicity” describes the cumulative negative impact of the high cost of care, lost work time, and delays in reaching educational and career goals on patients with cancer and their families.)
Another factor that likely contributes to the outcome disparities between AYAs and other populations with cancer is the relative lack of clinical trial involvement among AYAs.
A recent series of articles published in the journal Blood addressed these and other issues, among them, whether AYAs with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)1 or aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2 should be treated as children or adults; treatment strategies for those with acute myeloid leukemias (AMLs); 3 management of Hodgkin lymphoma;4 and psychosocial challenges and health-related quality of life (QoL) in AYAs with hematologic malignancies.5
In the introduction to the series, Jorge Cortes, MD, an assistant editor on the journal, wrote that hematologic malignancies in AYAs “represent a unique challenge because of their special biological features and distinctive therapeutic requirements, as well as the unique medical, social, and psychological characteristics of this patient population.”6
He noted, however, that “not much has been done to explore unique molecular and biological features of AYA hematologic malignancies. The discussion on the management of AYAs often centers on whether these patients should be treated in a pediatric setting or an adult setting, or with regimens designed for children or for adults,” noted Dr Cortes, professor and chair of the chronic myeloid leukemia section in the department of leukemia at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Therapeutic options: pediatric or adult protocols?
In their article on ALL in AYAs, Nicolas Boissel, MD, and André Baruchel, MD, note that the use of “fully pediatric protocols” in patients aged 15 through 20 years is supported by findings from numerous studies. In young adults, evidence increasingly supports “pediatric-inspired or even fully pediatric approaches” because they have been shown to significantly improve outcomes, with long-term survival rates nearing 70%.1 Patients in these age groups require specific programs that factor in access to care and to trials, an increased risk of acute toxicities, and treatment adherence, which can be particularly problematic in AYAs, they concluded.
However, Kristen O’Dwyer, MD, and colleagues, argue in an article on AML treatment in AYAs that neither the pediatric nor adult approaches are ideally suited for AYAs because of the “distinguishing characteristics of AYAs with AML.” Rather, they conclude that AYA-specific approaches merit consideration.3
Similarly, Kieron Dunleavy, MD, and Thomas G Gross, MD, note in an article on managing aggressive B-cell NHLs in AYAs that there is a “remarkable divide” in the treatment of patients younger than 18 years with lymphoma compared with their young adult counterparts, and that it underscores the need for collaboration in developing consensus regarding treatment of AYAs.2
Clinical setting: pediatric or adult?
Consideration is also being given to the clinical setting in which AYA patients receive their treatment. Lori Muffly, MD, MS, and colleagues have reported that survival was superior for AYA patients with ALL who were treated in pediatric cancer settings,7 and other researchers have reported similar findings.
However, those improved outcomes in the pediatric setting might be offset by a higher use of resources and therefore higher costs, based on recent findings in a Canadian study by Paul C Nathan, MD, and colleagues.8 Among 1,356 patients aged 15-17 years who were diagnosed with cancer between 1996 and 2010, the authors found that the cost of care was higher when treatment took place in a pediatric setting compared with in an adult institution, and that it was driven in part by higher hospitalization rates and longer hospital stays. These findings were true across different diagnoses, including leukemias, lymphomas, sarcomas, and germ cell tumors, but only during the initial treatment phase.
In an accompanying editorial, Helen M Parsons, PhD, and her co-authors wrote that adolescents who receive treatment in the pediatric setting “tended to seek more [emergency department (ED)] care immediately before diagnosis and during the initial treatment phase; these adolescents also used more home care services during initial treatment and survivorship.9 They pointed out that the findings of higher inpatient days in the pediatric setting was not surprising given that induction therapies for pediatric ALL tend to be more complex and intensive than therapies commonly used in adults with ALL, and that pediatric cancer hospitals tend to have a wider array of services, including psychosocial and family support services.
“What is less clear is why individuals seen in pediatric settings have higher rates of ED care directly before diagnosis and during the initial treatment phase,” they wrote, adding that further investigation was needed on this topic to better understand those trends. “The finding that adolescents treated in pediatric institutions had higher resource use across diagnostic groups demonstrates that resource utilization may be driven just as much by care setting as diagnosis.” 9
The authors of the editorial emphasized that because of the differences in health care delivery and payment structures between the United States and Canada, where the Nathan study was done, it was important that similar studies are done in the United States to confirm these findings.
Disease and developmental biology
As Dr Hanna noted, biological differences and changes over time suggest that different age groups need varying approaches to treatment and that they may have different outcomes with the same treatments.
For example, the biology of AML is known to change with age, Dr O'Dwyer and her colleagues noted,3 citing a recent European study of 5,564 patients with de novo AML that showed that the frequency of favorable cytogenetics was low in infants (13.7%), increased in children (25%) and young adults (44%), and decreased again in middle age and older patients.10
“Most unfavorable cytogenetic abnormalities are rare across all age groups, though complex cytogenetics are relatively more frequent in infants, decrease in frequency in AYAs, and then increase in frequency beyond AYA,” Dr O'Dwyer and her colleagues wrote.3 It was also becoming more apparent that age influences the presence of AML-related molecular abnormalities, and recognition of age-related differences in disease biology “will provide the best opportunity to improve the clinical outcomes that have been static for decades.”
Dr Boissel and Dr Baruchel also noted in their report that light was finally being shed on the “black hole” of understanding ALL biology in AYAs, and research has shown that there is a continuum between childhood and adult ALL.1 They concluded that “risk stratification based on recent biology findings and sequential [minimum residual disease] evaluations should now be implemented, as well as new therapeutic options including immunotherapy and targeted therapies, at best within the setting of integrated pediatric and AYA protocols.”
Psychosocial factors
“Cancer is a non-normative event for AYAs. It is extremely disruptive to them physically, psychologically, and vocationally ... and this poses significant challenges,” John Salsman, PhD, director of clinical research in AYA oncology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, NC, said in an interview.
These patients have 5-year survival rates that haven’t improved in tandem with those in pediatric and adult populations over the last 3 decades, and in addition to the financial toxicity and strain, they also have higher rates of depression and anxiety, including fear of recurrence, he added. “Quality of life is incredibly important, and these things need to be addressed because of the developmental changes AYAs are navigating; there are issues of positive body image, family and career decisions ... these are challenging for anyone, and when you throw a cancer diagnosis into the mix they become disproportionately so.”
In a 2014 study, Dr Salsman and his colleagues found that AYAs with cancer had poorer physical and emotional quality of life when compared with matched controls, but better social quality of life.11 The latter finding was surprising and highlights the importance of the social dimension in the lives of AYAs. “Patient after patient will say ‘I found out who my real friends are,’ ” he said. “There’s this refinement and deepening of the social network among some posttreatment survivors.”
Dr Salsman and his colleagues are using those findings to develop interventions that can maximize self-care in posttreatment survivorship – a time when AYAs may feel they have a new lease on life and may be more motivated to adhere to recommendations and take care of themselves. For example, a randomized controlled pilot study that incorporates social media apps and other technologies to build on the positive social components of their lives in promoting physical activity interventions is underway.
Another intervention targets emotional well-being through the use of web-based tools to increase positive affect. A proof-of-concept study showed that the approach was feasible and well received, and a larger-scale randomized controlled trial is being planned, he said.
Dr Salsman also praised the PRISM (Promoting Resilience in Stress Management) tool developed by researchers at Seattle Children’s Hospital. It was created to help AYAs with cancer and other illnesses learn coping skills to manage stress after their diagnosis and to boost quality of life beyond treatment. A digital app has also been developed to be used in conjunction with the program.
Trial enrollment
In his editorial introducing the Blood series on AYAs and cancer, Dr Cortes noted a paucity of clinical trials specifically designed for this population. “At the time of this writing, I could identify four therapeutic trials registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov that appeared to be somewhat specifically designed for AYAs (some included children also),” he wrote, describing AYA enrollment in clinical trials in cancer as “suboptimal at best.”6
Dr Salsman said these dismal enrolment numbers could in part be related to treatment setting. Data suggest that most AYAs with cancer are treated in community-based practices rather than comprehensive cancer centers where the bulk of research is being done, he explained.
Dr Hanna agreed that more research involving AYAs was needed as is a better understanding of why enrollment is so much lower in this population. He pointed out that in 2017 the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Friends of Cancer Research released a statement recommending that pediatric patients be considered for enrollment in later-phase trials for cancer types that span both adults and children.12 The organizations said that individuals aged 12 years and older should routinely be included in such trials because their drug metabolism is similar to adults, and inclusion of younger patients may also be appropriate if they are part of the population affected by the disease, depending on specific disease biology, action of the drug, and available safety information.
Officials at the Food and Drug Administration are considering that possibility, Dr Hanna said.
Dr Salsman added there has been an increase in recent years in the attention paid to disparities in survival improvements and trial involvement among AYAs with cancer, compared with other age groups. For example, about 5 years ago, the National Clinical Trials Network formed a working group that developed a number of specific objectives for incorporating more AYAs into cancer trials and finding better ways to study this population;13 the Institute of Medicine held a forum on the care of AYAs with cancer;14 and the National Cancer Institute held a state-of-the-science meeting that focused on identifying strategic priorities for AYA oncology,15 he noted.
Dr Hanna added that “scientific groups such as Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) and Children’s Oncology Group (COG) also have AYA committees now. One of the success stories of working together between SWOG and COG was the intergroup study C10403 for patients with ALL. And now there are efforts for an intergroup AYA-AML task force to include representatives from each of the cooperative groups that historically co-ordinated myeloid disease clinical trials – COG, SWOG, Alliance, and ECOG-ACRIN,” he said.
In fact, all of the National Clinical Trials Network groups have some initiative in place to address AYA concerns, said Dr Salsman, who chairs the ECOG-ACRIN AYA oncology subcommittee.
Despite these efforts, and many others, long-term survival improvements among AYAs with cancer still fall short, compared with those of other age groups.16
Next steps
Among the recommendations from authors in the AYA series in Blood is a call for assessing AYA-specific therapy in future clinical trials, as well as improved collaboration between adult and pediatric teams and the involvement of multidisciplinary teams in care for this population.
Many centers are already working on models for collaborative care, Dr Salsman said, citing the Fort Worth AYA Oncology Coalition led by medical director Karen Albritton, MD, as an example of a program that has been successful in helping clinical and supportive caregivers and their AYA patients “have a shared vision” as they work to maximize improvements in outcomes.
Patients are also taking the lead in demanding better care and attention to their psychosocial needs, Dr Hanna said. In the case of the community-powered advocacy organization Critical Mass, members have succeeded in getting lawmakers to introduce a bill in the US House of Representatives that would allow college students to defer loan payments while undergoing cancer treatment.
1. Boissel N, Baruchel A. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adolescent and young adults: treat as adults or as children? Blood. 2018;132:351-361.
2. Dunleavy K, Gross TG. Management of aggressive B-cell NHLs in the AYA population: an adult vs pediatric perspective. Blood. 2018;132:369-375.
3. O’Dwyer K, Freyer DR, Horan JT. Treatment strategies for adolescent and young adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2018;132:362-368.
4. Flerlage JE, Metzger ML, Bhakta N. The management of Hodgkin lymphoma in adolescents and young adults: burden of disease or burden of choice? Blood. 2018;132:376-384.
5. Husson O, Huijgens PC, van der Graaf WTA. Psychosocial challenges and health-related quality of life of adolescents and young adults with hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2018;132:385-392.
6. Cortes J. Introduction to a review series on adolescent and young adult malignant hematology. Blood. 2018;132:345-346.
7. Muffly L, Alvarez E, Lichtensztajn D, Abrahão R, Gomez SL, Keegan T. Patterns of care and outcomes in adolescent and young adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a population-based study. Blood Adv. 2018;2(8):895-903.
8. Nathan PC, Bremner KE, Liu N, et al. Resource utilization and costs in adolescents treated for cancer in pediatric vs adult institutions. J Natl Cancer Inst. July 19, 2018. [Epub ahead of print.]
9. Parsons HM, Muffly L, Alvarez EM, Keegan THM. Does treatment setting matter? Evaluating resource utilization for adolescents treated in pediatric vs adult cancer institutions. https://academic.oup.com/jnci/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jnci/djy123/5056313?searchresult=1. Published July 19, 2018. Last accessed October 12, 2018.
10. Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Reinhardt D, et al. Changes in cytogenetics and molecular genetics in acute myeloid leukemia from childhood to adult age groups. Cancer. 2016;122(24):3821-3830.
11. Salsman JM, Garcia SF, Yanez B, et al. Physical, emotional, and social health differences between posttreatment young adults with cancer and matched healthy controls. Cancer. 2014;120(15):2247-2254.
12. Kim ES, Bruinooge SS, Roberts S, et al. Broadening eligibility criteria to make clinical trials more representative: American Society of Clinical Oncology and Friends of Cancer Research joint research statement. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(33):3737-3744.
13. Freyer DR, Seibel NL. The clinical trials gap for adolescents and young adults with cancer: recent progress and conceptual framework for continued research. Curr Pediatr Rep. Published online February 18, 2015. DOI 10.1007/s40124-015-0075-y.
14. Nass SJ, Beaupin LK, Demark-Wahnefried W, et al. Identifying and addressing the needs of adolescents and young adults with cancer: summary of an Institute of Medicine workshop. Oncologist. 2015;20(2):186-195.
15. Wilder Smith A, Seibel NL, Lewis DR, et al. Next steps for adolescent and young adult oncology workshop: An update on progress and recommendations for the future. Cancer. 2016;122(7):988-999.
16. Keegan THM, Ries LAG, Barr RD, et al. Comparison of cancer survival trends in the United States of adolescents and young adults with those in children and older adults. Cancer. 2016;122(7):1009-1016.
Survival gains among adolescents and young adults (AYAs) with cancer continue to lag behind outcomes for children and older adult patients. It’s a trend that spans decades, but clinicians and researchers are finally getting serious about trying to understand the underlying causes and are re-examining prevailing practices in an effort to address the discrepancies.
“This is a very heterogeneous group of disorders,” Rabi Hanna, MD, a pediatric hematologist and oncologist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s Hospital, Ohio, said in an interview. He’s specifically referring to the cancers that affect AYAs, who are broadly defined as patients aged 15 through 39 years. “A few cancers, such as [acute lymphoblastic leukemia], are more common in children, and others, such as breast cancer, are more common in adults. The biology may be different in the adolescent and young adult patients, which may lead to different outcomes.”
In addition, the psychosocial needs in this age group differ vastly from those in other groups. “Many of these patients are in college or have just started their families, so we have to pay more attention to [issues related to] financial toxicity and fertility, for example,” said Dr Hanna, who is the director of pediatric bone marrow transplantation at the clinic. (The term “financial toxicity” describes the cumulative negative impact of the high cost of care, lost work time, and delays in reaching educational and career goals on patients with cancer and their families.)
Another factor that likely contributes to the outcome disparities between AYAs and other populations with cancer is the relative lack of clinical trial involvement among AYAs.
A recent series of articles published in the journal Blood addressed these and other issues, among them, whether AYAs with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)1 or aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2 should be treated as children or adults; treatment strategies for those with acute myeloid leukemias (AMLs); 3 management of Hodgkin lymphoma;4 and psychosocial challenges and health-related quality of life (QoL) in AYAs with hematologic malignancies.5
In the introduction to the series, Jorge Cortes, MD, an assistant editor on the journal, wrote that hematologic malignancies in AYAs “represent a unique challenge because of their special biological features and distinctive therapeutic requirements, as well as the unique medical, social, and psychological characteristics of this patient population.”6
He noted, however, that “not much has been done to explore unique molecular and biological features of AYA hematologic malignancies. The discussion on the management of AYAs often centers on whether these patients should be treated in a pediatric setting or an adult setting, or with regimens designed for children or for adults,” noted Dr Cortes, professor and chair of the chronic myeloid leukemia section in the department of leukemia at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Therapeutic options: pediatric or adult protocols?
In their article on ALL in AYAs, Nicolas Boissel, MD, and André Baruchel, MD, note that the use of “fully pediatric protocols” in patients aged 15 through 20 years is supported by findings from numerous studies. In young adults, evidence increasingly supports “pediatric-inspired or even fully pediatric approaches” because they have been shown to significantly improve outcomes, with long-term survival rates nearing 70%.1 Patients in these age groups require specific programs that factor in access to care and to trials, an increased risk of acute toxicities, and treatment adherence, which can be particularly problematic in AYAs, they concluded.
However, Kristen O’Dwyer, MD, and colleagues, argue in an article on AML treatment in AYAs that neither the pediatric nor adult approaches are ideally suited for AYAs because of the “distinguishing characteristics of AYAs with AML.” Rather, they conclude that AYA-specific approaches merit consideration.3
Similarly, Kieron Dunleavy, MD, and Thomas G Gross, MD, note in an article on managing aggressive B-cell NHLs in AYAs that there is a “remarkable divide” in the treatment of patients younger than 18 years with lymphoma compared with their young adult counterparts, and that it underscores the need for collaboration in developing consensus regarding treatment of AYAs.2
Clinical setting: pediatric or adult?
Consideration is also being given to the clinical setting in which AYA patients receive their treatment. Lori Muffly, MD, MS, and colleagues have reported that survival was superior for AYA patients with ALL who were treated in pediatric cancer settings,7 and other researchers have reported similar findings.
However, those improved outcomes in the pediatric setting might be offset by a higher use of resources and therefore higher costs, based on recent findings in a Canadian study by Paul C Nathan, MD, and colleagues.8 Among 1,356 patients aged 15-17 years who were diagnosed with cancer between 1996 and 2010, the authors found that the cost of care was higher when treatment took place in a pediatric setting compared with in an adult institution, and that it was driven in part by higher hospitalization rates and longer hospital stays. These findings were true across different diagnoses, including leukemias, lymphomas, sarcomas, and germ cell tumors, but only during the initial treatment phase.
In an accompanying editorial, Helen M Parsons, PhD, and her co-authors wrote that adolescents who receive treatment in the pediatric setting “tended to seek more [emergency department (ED)] care immediately before diagnosis and during the initial treatment phase; these adolescents also used more home care services during initial treatment and survivorship.9 They pointed out that the findings of higher inpatient days in the pediatric setting was not surprising given that induction therapies for pediatric ALL tend to be more complex and intensive than therapies commonly used in adults with ALL, and that pediatric cancer hospitals tend to have a wider array of services, including psychosocial and family support services.
“What is less clear is why individuals seen in pediatric settings have higher rates of ED care directly before diagnosis and during the initial treatment phase,” they wrote, adding that further investigation was needed on this topic to better understand those trends. “The finding that adolescents treated in pediatric institutions had higher resource use across diagnostic groups demonstrates that resource utilization may be driven just as much by care setting as diagnosis.” 9
The authors of the editorial emphasized that because of the differences in health care delivery and payment structures between the United States and Canada, where the Nathan study was done, it was important that similar studies are done in the United States to confirm these findings.
Disease and developmental biology
As Dr Hanna noted, biological differences and changes over time suggest that different age groups need varying approaches to treatment and that they may have different outcomes with the same treatments.
For example, the biology of AML is known to change with age, Dr O'Dwyer and her colleagues noted,3 citing a recent European study of 5,564 patients with de novo AML that showed that the frequency of favorable cytogenetics was low in infants (13.7%), increased in children (25%) and young adults (44%), and decreased again in middle age and older patients.10
“Most unfavorable cytogenetic abnormalities are rare across all age groups, though complex cytogenetics are relatively more frequent in infants, decrease in frequency in AYAs, and then increase in frequency beyond AYA,” Dr O'Dwyer and her colleagues wrote.3 It was also becoming more apparent that age influences the presence of AML-related molecular abnormalities, and recognition of age-related differences in disease biology “will provide the best opportunity to improve the clinical outcomes that have been static for decades.”
Dr Boissel and Dr Baruchel also noted in their report that light was finally being shed on the “black hole” of understanding ALL biology in AYAs, and research has shown that there is a continuum between childhood and adult ALL.1 They concluded that “risk stratification based on recent biology findings and sequential [minimum residual disease] evaluations should now be implemented, as well as new therapeutic options including immunotherapy and targeted therapies, at best within the setting of integrated pediatric and AYA protocols.”
Psychosocial factors
“Cancer is a non-normative event for AYAs. It is extremely disruptive to them physically, psychologically, and vocationally ... and this poses significant challenges,” John Salsman, PhD, director of clinical research in AYA oncology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, NC, said in an interview.
These patients have 5-year survival rates that haven’t improved in tandem with those in pediatric and adult populations over the last 3 decades, and in addition to the financial toxicity and strain, they also have higher rates of depression and anxiety, including fear of recurrence, he added. “Quality of life is incredibly important, and these things need to be addressed because of the developmental changes AYAs are navigating; there are issues of positive body image, family and career decisions ... these are challenging for anyone, and when you throw a cancer diagnosis into the mix they become disproportionately so.”
In a 2014 study, Dr Salsman and his colleagues found that AYAs with cancer had poorer physical and emotional quality of life when compared with matched controls, but better social quality of life.11 The latter finding was surprising and highlights the importance of the social dimension in the lives of AYAs. “Patient after patient will say ‘I found out who my real friends are,’ ” he said. “There’s this refinement and deepening of the social network among some posttreatment survivors.”
Dr Salsman and his colleagues are using those findings to develop interventions that can maximize self-care in posttreatment survivorship – a time when AYAs may feel they have a new lease on life and may be more motivated to adhere to recommendations and take care of themselves. For example, a randomized controlled pilot study that incorporates social media apps and other technologies to build on the positive social components of their lives in promoting physical activity interventions is underway.
Another intervention targets emotional well-being through the use of web-based tools to increase positive affect. A proof-of-concept study showed that the approach was feasible and well received, and a larger-scale randomized controlled trial is being planned, he said.
Dr Salsman also praised the PRISM (Promoting Resilience in Stress Management) tool developed by researchers at Seattle Children’s Hospital. It was created to help AYAs with cancer and other illnesses learn coping skills to manage stress after their diagnosis and to boost quality of life beyond treatment. A digital app has also been developed to be used in conjunction with the program.
Trial enrollment
In his editorial introducing the Blood series on AYAs and cancer, Dr Cortes noted a paucity of clinical trials specifically designed for this population. “At the time of this writing, I could identify four therapeutic trials registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov that appeared to be somewhat specifically designed for AYAs (some included children also),” he wrote, describing AYA enrollment in clinical trials in cancer as “suboptimal at best.”6
Dr Salsman said these dismal enrolment numbers could in part be related to treatment setting. Data suggest that most AYAs with cancer are treated in community-based practices rather than comprehensive cancer centers where the bulk of research is being done, he explained.
Dr Hanna agreed that more research involving AYAs was needed as is a better understanding of why enrollment is so much lower in this population. He pointed out that in 2017 the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Friends of Cancer Research released a statement recommending that pediatric patients be considered for enrollment in later-phase trials for cancer types that span both adults and children.12 The organizations said that individuals aged 12 years and older should routinely be included in such trials because their drug metabolism is similar to adults, and inclusion of younger patients may also be appropriate if they are part of the population affected by the disease, depending on specific disease biology, action of the drug, and available safety information.
Officials at the Food and Drug Administration are considering that possibility, Dr Hanna said.
Dr Salsman added there has been an increase in recent years in the attention paid to disparities in survival improvements and trial involvement among AYAs with cancer, compared with other age groups. For example, about 5 years ago, the National Clinical Trials Network formed a working group that developed a number of specific objectives for incorporating more AYAs into cancer trials and finding better ways to study this population;13 the Institute of Medicine held a forum on the care of AYAs with cancer;14 and the National Cancer Institute held a state-of-the-science meeting that focused on identifying strategic priorities for AYA oncology,15 he noted.
Dr Hanna added that “scientific groups such as Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) and Children’s Oncology Group (COG) also have AYA committees now. One of the success stories of working together between SWOG and COG was the intergroup study C10403 for patients with ALL. And now there are efforts for an intergroup AYA-AML task force to include representatives from each of the cooperative groups that historically co-ordinated myeloid disease clinical trials – COG, SWOG, Alliance, and ECOG-ACRIN,” he said.
In fact, all of the National Clinical Trials Network groups have some initiative in place to address AYA concerns, said Dr Salsman, who chairs the ECOG-ACRIN AYA oncology subcommittee.
Despite these efforts, and many others, long-term survival improvements among AYAs with cancer still fall short, compared with those of other age groups.16
Next steps
Among the recommendations from authors in the AYA series in Blood is a call for assessing AYA-specific therapy in future clinical trials, as well as improved collaboration between adult and pediatric teams and the involvement of multidisciplinary teams in care for this population.
Many centers are already working on models for collaborative care, Dr Salsman said, citing the Fort Worth AYA Oncology Coalition led by medical director Karen Albritton, MD, as an example of a program that has been successful in helping clinical and supportive caregivers and their AYA patients “have a shared vision” as they work to maximize improvements in outcomes.
Patients are also taking the lead in demanding better care and attention to their psychosocial needs, Dr Hanna said. In the case of the community-powered advocacy organization Critical Mass, members have succeeded in getting lawmakers to introduce a bill in the US House of Representatives that would allow college students to defer loan payments while undergoing cancer treatment.
Survival gains among adolescents and young adults (AYAs) with cancer continue to lag behind outcomes for children and older adult patients. It’s a trend that spans decades, but clinicians and researchers are finally getting serious about trying to understand the underlying causes and are re-examining prevailing practices in an effort to address the discrepancies.
“This is a very heterogeneous group of disorders,” Rabi Hanna, MD, a pediatric hematologist and oncologist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s Hospital, Ohio, said in an interview. He’s specifically referring to the cancers that affect AYAs, who are broadly defined as patients aged 15 through 39 years. “A few cancers, such as [acute lymphoblastic leukemia], are more common in children, and others, such as breast cancer, are more common in adults. The biology may be different in the adolescent and young adult patients, which may lead to different outcomes.”
In addition, the psychosocial needs in this age group differ vastly from those in other groups. “Many of these patients are in college or have just started their families, so we have to pay more attention to [issues related to] financial toxicity and fertility, for example,” said Dr Hanna, who is the director of pediatric bone marrow transplantation at the clinic. (The term “financial toxicity” describes the cumulative negative impact of the high cost of care, lost work time, and delays in reaching educational and career goals on patients with cancer and their families.)
Another factor that likely contributes to the outcome disparities between AYAs and other populations with cancer is the relative lack of clinical trial involvement among AYAs.
A recent series of articles published in the journal Blood addressed these and other issues, among them, whether AYAs with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)1 or aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2 should be treated as children or adults; treatment strategies for those with acute myeloid leukemias (AMLs); 3 management of Hodgkin lymphoma;4 and psychosocial challenges and health-related quality of life (QoL) in AYAs with hematologic malignancies.5
In the introduction to the series, Jorge Cortes, MD, an assistant editor on the journal, wrote that hematologic malignancies in AYAs “represent a unique challenge because of their special biological features and distinctive therapeutic requirements, as well as the unique medical, social, and psychological characteristics of this patient population.”6
He noted, however, that “not much has been done to explore unique molecular and biological features of AYA hematologic malignancies. The discussion on the management of AYAs often centers on whether these patients should be treated in a pediatric setting or an adult setting, or with regimens designed for children or for adults,” noted Dr Cortes, professor and chair of the chronic myeloid leukemia section in the department of leukemia at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Therapeutic options: pediatric or adult protocols?
In their article on ALL in AYAs, Nicolas Boissel, MD, and André Baruchel, MD, note that the use of “fully pediatric protocols” in patients aged 15 through 20 years is supported by findings from numerous studies. In young adults, evidence increasingly supports “pediatric-inspired or even fully pediatric approaches” because they have been shown to significantly improve outcomes, with long-term survival rates nearing 70%.1 Patients in these age groups require specific programs that factor in access to care and to trials, an increased risk of acute toxicities, and treatment adherence, which can be particularly problematic in AYAs, they concluded.
However, Kristen O’Dwyer, MD, and colleagues, argue in an article on AML treatment in AYAs that neither the pediatric nor adult approaches are ideally suited for AYAs because of the “distinguishing characteristics of AYAs with AML.” Rather, they conclude that AYA-specific approaches merit consideration.3
Similarly, Kieron Dunleavy, MD, and Thomas G Gross, MD, note in an article on managing aggressive B-cell NHLs in AYAs that there is a “remarkable divide” in the treatment of patients younger than 18 years with lymphoma compared with their young adult counterparts, and that it underscores the need for collaboration in developing consensus regarding treatment of AYAs.2
Clinical setting: pediatric or adult?
Consideration is also being given to the clinical setting in which AYA patients receive their treatment. Lori Muffly, MD, MS, and colleagues have reported that survival was superior for AYA patients with ALL who were treated in pediatric cancer settings,7 and other researchers have reported similar findings.
However, those improved outcomes in the pediatric setting might be offset by a higher use of resources and therefore higher costs, based on recent findings in a Canadian study by Paul C Nathan, MD, and colleagues.8 Among 1,356 patients aged 15-17 years who were diagnosed with cancer between 1996 and 2010, the authors found that the cost of care was higher when treatment took place in a pediatric setting compared with in an adult institution, and that it was driven in part by higher hospitalization rates and longer hospital stays. These findings were true across different diagnoses, including leukemias, lymphomas, sarcomas, and germ cell tumors, but only during the initial treatment phase.
In an accompanying editorial, Helen M Parsons, PhD, and her co-authors wrote that adolescents who receive treatment in the pediatric setting “tended to seek more [emergency department (ED)] care immediately before diagnosis and during the initial treatment phase; these adolescents also used more home care services during initial treatment and survivorship.9 They pointed out that the findings of higher inpatient days in the pediatric setting was not surprising given that induction therapies for pediatric ALL tend to be more complex and intensive than therapies commonly used in adults with ALL, and that pediatric cancer hospitals tend to have a wider array of services, including psychosocial and family support services.
“What is less clear is why individuals seen in pediatric settings have higher rates of ED care directly before diagnosis and during the initial treatment phase,” they wrote, adding that further investigation was needed on this topic to better understand those trends. “The finding that adolescents treated in pediatric institutions had higher resource use across diagnostic groups demonstrates that resource utilization may be driven just as much by care setting as diagnosis.” 9
The authors of the editorial emphasized that because of the differences in health care delivery and payment structures between the United States and Canada, where the Nathan study was done, it was important that similar studies are done in the United States to confirm these findings.
Disease and developmental biology
As Dr Hanna noted, biological differences and changes over time suggest that different age groups need varying approaches to treatment and that they may have different outcomes with the same treatments.
For example, the biology of AML is known to change with age, Dr O'Dwyer and her colleagues noted,3 citing a recent European study of 5,564 patients with de novo AML that showed that the frequency of favorable cytogenetics was low in infants (13.7%), increased in children (25%) and young adults (44%), and decreased again in middle age and older patients.10
“Most unfavorable cytogenetic abnormalities are rare across all age groups, though complex cytogenetics are relatively more frequent in infants, decrease in frequency in AYAs, and then increase in frequency beyond AYA,” Dr O'Dwyer and her colleagues wrote.3 It was also becoming more apparent that age influences the presence of AML-related molecular abnormalities, and recognition of age-related differences in disease biology “will provide the best opportunity to improve the clinical outcomes that have been static for decades.”
Dr Boissel and Dr Baruchel also noted in their report that light was finally being shed on the “black hole” of understanding ALL biology in AYAs, and research has shown that there is a continuum between childhood and adult ALL.1 They concluded that “risk stratification based on recent biology findings and sequential [minimum residual disease] evaluations should now be implemented, as well as new therapeutic options including immunotherapy and targeted therapies, at best within the setting of integrated pediatric and AYA protocols.”
Psychosocial factors
“Cancer is a non-normative event for AYAs. It is extremely disruptive to them physically, psychologically, and vocationally ... and this poses significant challenges,” John Salsman, PhD, director of clinical research in AYA oncology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, NC, said in an interview.
These patients have 5-year survival rates that haven’t improved in tandem with those in pediatric and adult populations over the last 3 decades, and in addition to the financial toxicity and strain, they also have higher rates of depression and anxiety, including fear of recurrence, he added. “Quality of life is incredibly important, and these things need to be addressed because of the developmental changes AYAs are navigating; there are issues of positive body image, family and career decisions ... these are challenging for anyone, and when you throw a cancer diagnosis into the mix they become disproportionately so.”
In a 2014 study, Dr Salsman and his colleagues found that AYAs with cancer had poorer physical and emotional quality of life when compared with matched controls, but better social quality of life.11 The latter finding was surprising and highlights the importance of the social dimension in the lives of AYAs. “Patient after patient will say ‘I found out who my real friends are,’ ” he said. “There’s this refinement and deepening of the social network among some posttreatment survivors.”
Dr Salsman and his colleagues are using those findings to develop interventions that can maximize self-care in posttreatment survivorship – a time when AYAs may feel they have a new lease on life and may be more motivated to adhere to recommendations and take care of themselves. For example, a randomized controlled pilot study that incorporates social media apps and other technologies to build on the positive social components of their lives in promoting physical activity interventions is underway.
Another intervention targets emotional well-being through the use of web-based tools to increase positive affect. A proof-of-concept study showed that the approach was feasible and well received, and a larger-scale randomized controlled trial is being planned, he said.
Dr Salsman also praised the PRISM (Promoting Resilience in Stress Management) tool developed by researchers at Seattle Children’s Hospital. It was created to help AYAs with cancer and other illnesses learn coping skills to manage stress after their diagnosis and to boost quality of life beyond treatment. A digital app has also been developed to be used in conjunction with the program.
Trial enrollment
In his editorial introducing the Blood series on AYAs and cancer, Dr Cortes noted a paucity of clinical trials specifically designed for this population. “At the time of this writing, I could identify four therapeutic trials registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov that appeared to be somewhat specifically designed for AYAs (some included children also),” he wrote, describing AYA enrollment in clinical trials in cancer as “suboptimal at best.”6
Dr Salsman said these dismal enrolment numbers could in part be related to treatment setting. Data suggest that most AYAs with cancer are treated in community-based practices rather than comprehensive cancer centers where the bulk of research is being done, he explained.
Dr Hanna agreed that more research involving AYAs was needed as is a better understanding of why enrollment is so much lower in this population. He pointed out that in 2017 the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Friends of Cancer Research released a statement recommending that pediatric patients be considered for enrollment in later-phase trials for cancer types that span both adults and children.12 The organizations said that individuals aged 12 years and older should routinely be included in such trials because their drug metabolism is similar to adults, and inclusion of younger patients may also be appropriate if they are part of the population affected by the disease, depending on specific disease biology, action of the drug, and available safety information.
Officials at the Food and Drug Administration are considering that possibility, Dr Hanna said.
Dr Salsman added there has been an increase in recent years in the attention paid to disparities in survival improvements and trial involvement among AYAs with cancer, compared with other age groups. For example, about 5 years ago, the National Clinical Trials Network formed a working group that developed a number of specific objectives for incorporating more AYAs into cancer trials and finding better ways to study this population;13 the Institute of Medicine held a forum on the care of AYAs with cancer;14 and the National Cancer Institute held a state-of-the-science meeting that focused on identifying strategic priorities for AYA oncology,15 he noted.
Dr Hanna added that “scientific groups such as Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) and Children’s Oncology Group (COG) also have AYA committees now. One of the success stories of working together between SWOG and COG was the intergroup study C10403 for patients with ALL. And now there are efforts for an intergroup AYA-AML task force to include representatives from each of the cooperative groups that historically co-ordinated myeloid disease clinical trials – COG, SWOG, Alliance, and ECOG-ACRIN,” he said.
In fact, all of the National Clinical Trials Network groups have some initiative in place to address AYA concerns, said Dr Salsman, who chairs the ECOG-ACRIN AYA oncology subcommittee.
Despite these efforts, and many others, long-term survival improvements among AYAs with cancer still fall short, compared with those of other age groups.16
Next steps
Among the recommendations from authors in the AYA series in Blood is a call for assessing AYA-specific therapy in future clinical trials, as well as improved collaboration between adult and pediatric teams and the involvement of multidisciplinary teams in care for this population.
Many centers are already working on models for collaborative care, Dr Salsman said, citing the Fort Worth AYA Oncology Coalition led by medical director Karen Albritton, MD, as an example of a program that has been successful in helping clinical and supportive caregivers and their AYA patients “have a shared vision” as they work to maximize improvements in outcomes.
Patients are also taking the lead in demanding better care and attention to their psychosocial needs, Dr Hanna said. In the case of the community-powered advocacy organization Critical Mass, members have succeeded in getting lawmakers to introduce a bill in the US House of Representatives that would allow college students to defer loan payments while undergoing cancer treatment.
1. Boissel N, Baruchel A. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adolescent and young adults: treat as adults or as children? Blood. 2018;132:351-361.
2. Dunleavy K, Gross TG. Management of aggressive B-cell NHLs in the AYA population: an adult vs pediatric perspective. Blood. 2018;132:369-375.
3. O’Dwyer K, Freyer DR, Horan JT. Treatment strategies for adolescent and young adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2018;132:362-368.
4. Flerlage JE, Metzger ML, Bhakta N. The management of Hodgkin lymphoma in adolescents and young adults: burden of disease or burden of choice? Blood. 2018;132:376-384.
5. Husson O, Huijgens PC, van der Graaf WTA. Psychosocial challenges and health-related quality of life of adolescents and young adults with hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2018;132:385-392.
6. Cortes J. Introduction to a review series on adolescent and young adult malignant hematology. Blood. 2018;132:345-346.
7. Muffly L, Alvarez E, Lichtensztajn D, Abrahão R, Gomez SL, Keegan T. Patterns of care and outcomes in adolescent and young adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a population-based study. Blood Adv. 2018;2(8):895-903.
8. Nathan PC, Bremner KE, Liu N, et al. Resource utilization and costs in adolescents treated for cancer in pediatric vs adult institutions. J Natl Cancer Inst. July 19, 2018. [Epub ahead of print.]
9. Parsons HM, Muffly L, Alvarez EM, Keegan THM. Does treatment setting matter? Evaluating resource utilization for adolescents treated in pediatric vs adult cancer institutions. https://academic.oup.com/jnci/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jnci/djy123/5056313?searchresult=1. Published July 19, 2018. Last accessed October 12, 2018.
10. Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Reinhardt D, et al. Changes in cytogenetics and molecular genetics in acute myeloid leukemia from childhood to adult age groups. Cancer. 2016;122(24):3821-3830.
11. Salsman JM, Garcia SF, Yanez B, et al. Physical, emotional, and social health differences between posttreatment young adults with cancer and matched healthy controls. Cancer. 2014;120(15):2247-2254.
12. Kim ES, Bruinooge SS, Roberts S, et al. Broadening eligibility criteria to make clinical trials more representative: American Society of Clinical Oncology and Friends of Cancer Research joint research statement. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(33):3737-3744.
13. Freyer DR, Seibel NL. The clinical trials gap for adolescents and young adults with cancer: recent progress and conceptual framework for continued research. Curr Pediatr Rep. Published online February 18, 2015. DOI 10.1007/s40124-015-0075-y.
14. Nass SJ, Beaupin LK, Demark-Wahnefried W, et al. Identifying and addressing the needs of adolescents and young adults with cancer: summary of an Institute of Medicine workshop. Oncologist. 2015;20(2):186-195.
15. Wilder Smith A, Seibel NL, Lewis DR, et al. Next steps for adolescent and young adult oncology workshop: An update on progress and recommendations for the future. Cancer. 2016;122(7):988-999.
16. Keegan THM, Ries LAG, Barr RD, et al. Comparison of cancer survival trends in the United States of adolescents and young adults with those in children and older adults. Cancer. 2016;122(7):1009-1016.
1. Boissel N, Baruchel A. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adolescent and young adults: treat as adults or as children? Blood. 2018;132:351-361.
2. Dunleavy K, Gross TG. Management of aggressive B-cell NHLs in the AYA population: an adult vs pediatric perspective. Blood. 2018;132:369-375.
3. O’Dwyer K, Freyer DR, Horan JT. Treatment strategies for adolescent and young adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2018;132:362-368.
4. Flerlage JE, Metzger ML, Bhakta N. The management of Hodgkin lymphoma in adolescents and young adults: burden of disease or burden of choice? Blood. 2018;132:376-384.
5. Husson O, Huijgens PC, van der Graaf WTA. Psychosocial challenges and health-related quality of life of adolescents and young adults with hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2018;132:385-392.
6. Cortes J. Introduction to a review series on adolescent and young adult malignant hematology. Blood. 2018;132:345-346.
7. Muffly L, Alvarez E, Lichtensztajn D, Abrahão R, Gomez SL, Keegan T. Patterns of care and outcomes in adolescent and young adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a population-based study. Blood Adv. 2018;2(8):895-903.
8. Nathan PC, Bremner KE, Liu N, et al. Resource utilization and costs in adolescents treated for cancer in pediatric vs adult institutions. J Natl Cancer Inst. July 19, 2018. [Epub ahead of print.]
9. Parsons HM, Muffly L, Alvarez EM, Keegan THM. Does treatment setting matter? Evaluating resource utilization for adolescents treated in pediatric vs adult cancer institutions. https://academic.oup.com/jnci/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jnci/djy123/5056313?searchresult=1. Published July 19, 2018. Last accessed October 12, 2018.
10. Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Reinhardt D, et al. Changes in cytogenetics and molecular genetics in acute myeloid leukemia from childhood to adult age groups. Cancer. 2016;122(24):3821-3830.
11. Salsman JM, Garcia SF, Yanez B, et al. Physical, emotional, and social health differences between posttreatment young adults with cancer and matched healthy controls. Cancer. 2014;120(15):2247-2254.
12. Kim ES, Bruinooge SS, Roberts S, et al. Broadening eligibility criteria to make clinical trials more representative: American Society of Clinical Oncology and Friends of Cancer Research joint research statement. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(33):3737-3744.
13. Freyer DR, Seibel NL. The clinical trials gap for adolescents and young adults with cancer: recent progress and conceptual framework for continued research. Curr Pediatr Rep. Published online February 18, 2015. DOI 10.1007/s40124-015-0075-y.
14. Nass SJ, Beaupin LK, Demark-Wahnefried W, et al. Identifying and addressing the needs of adolescents and young adults with cancer: summary of an Institute of Medicine workshop. Oncologist. 2015;20(2):186-195.
15. Wilder Smith A, Seibel NL, Lewis DR, et al. Next steps for adolescent and young adult oncology workshop: An update on progress and recommendations for the future. Cancer. 2016;122(7):988-999.
16. Keegan THM, Ries LAG, Barr RD, et al. Comparison of cancer survival trends in the United States of adolescents and young adults with those in children and older adults. Cancer. 2016;122(7):1009-1016.
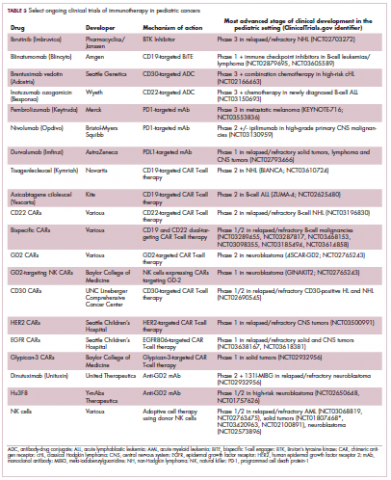
Game changers in pediatric cancer
Although there have been significant improvements in patient outcomes for some forms of pediatric cancer, progress has been painfully slow for others. An increasing understanding of pediatric cancers is highlighting the unique molecular drivers and challenging the assumption that drugs developed in adults can be applied to children and young adults. Here, we discuss game-changing therapeutic advances and a shifting view of childhood cancers.
Unique genomic background
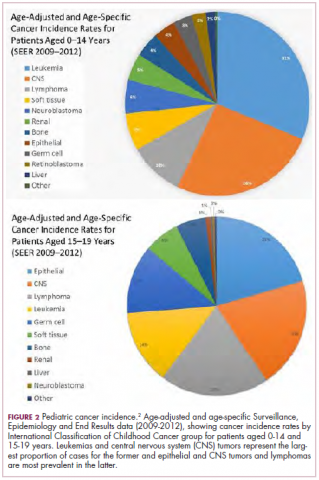
Although pediatric cancers are rare, representing just 1% of all new cancers diagnosed annually in the United States, they are the second leading cause of death in children aged 1 to 14 years. There are many different histological tumor types under the umbrella of childhood cancers, of which the most common are leukemias, central nervous system tumors, and lymphomas (Figure 1).1,2
Significant progress has been made in the treatment of certain pediatric cancers in recent decades, exemplified by pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), which has been transformed from a virtually incurable cancer to one in which 5-year survival rates now reach up to 90%. In other forms of pediatric cancer, however, survival rates have stagnated and little progress has been made in the development of effective new therapies.3
Because of their rarity, pediatric cancers are difficult to study and adequate enrollment of children in clinical trials can be challenging. Pharmaceutical companies are often hesitant to test drugs in the pediatric population in patients who often cannot advocate for themselves. As a result, the activity of drugs developed in adult patients has often been inferred in pediatric patients with the same tumor type or molecular aberrations. However, as researchers have gathered more information about pediatric cancers, there has been increasing recognition of their unique attributes and the need for dedicated clinical trials in this patient population.
Pediatric cancers tend to be found in the developing mesodermic tissue, whereas adult cancers are more prevalent in the epithelial tissues. Genome sequencing studies have revealed a much lower mutational burden in pediatric cancers and the mechanisms of oncogenesis are also quite different; adult tumors can develop from a series of acquired gene mutations, but pediatric tumors tend to develop from a single catastrophic event.4,5
Even the same type of cancer in a pediatric and adult patient can be quite different, with very different underlying molecular mechanisms. In a recent genomic analysis of different types of pediatric cancer by researchers at St Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital, less than half of the identified mutated genes were found to be similar to those found in adult patients.6
A ‘magic bullet’?
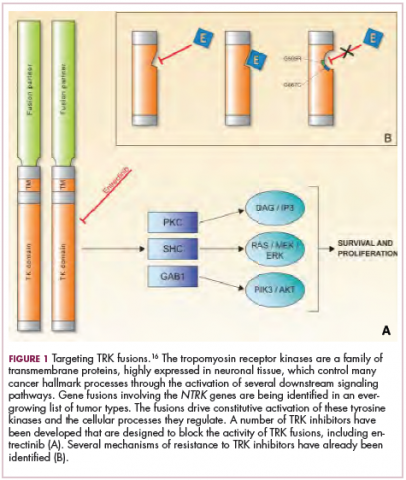
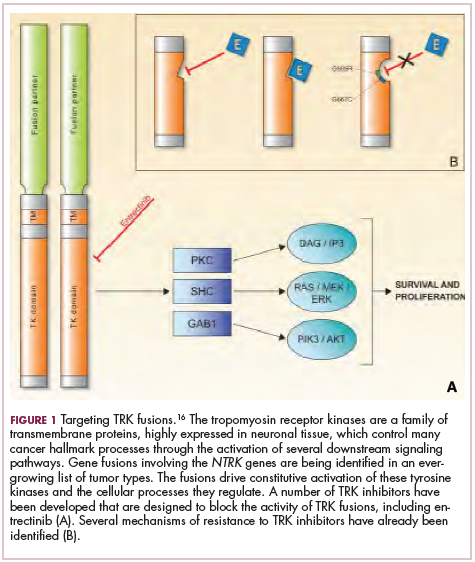
Chromosomal rearrangements are common in pediatric cancers. This type of molecular abnormality can result in a fusion of 2 different genes when the chromosome breaks apart and the pieces join back together in a muddled order. If the genetic code fuses in a manner that is “readable” by the cell, then it can drive aberrant activation of one or both genes.7 Gene fusions often involve kinase enzymes that are essential players in cell signaling pathways regulating hallmark cancer processes, such as unchecked cell proliferation. The fusion drives the constitutive activation of the kinase and, thus, these downstream signaling pathways.
One of the first chromosomal rearrangements linked to cancer, BCR-ABL1 – more commonly known as the Philadelphia chromosome – results in aberrant activation of the ABL1 kinase. It is present in nearly all cases of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and 3% to 5% of patients with ALL, and thus became the central focus of targeted drug development. Imatinib was initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2001 for the treatment of adult patients with CML and had such a significant impact on the treatment landscape that it made the cover of Time magazine as a “magic bullet” in the war on cancer.8
Approval was expanded into pediatric patients in 2006 and for pediatric patients with ALL in 2013. However, as with the use of most kinase inhibitors, tumors can evolve under the selective pressure of treatment, developing additional molecular abnormalities that drive resistance.9
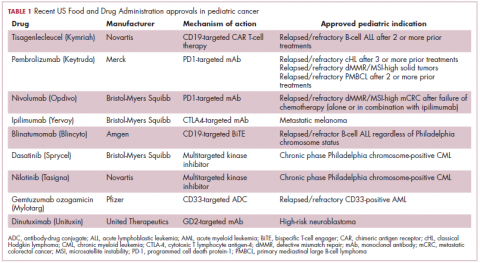
Next-generation multikinase inhibitors that more potently inhibit the BCR-ABL1 fusion protein have been developed to provide additional treatment options for patients who become resistant to imatinib. Dasatinib and nilotinib are among several drugs that have recently been approved for pediatric cancer therapy (Table 1). Both therapies were approved to treat children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive CML in the chronic phase in either the front- or second-line setting after failure of imatinib.
The approval of dasatinib was based on data from 97 patients across 2 trials, 51 of whom were newly diagnosed and 46 previously treated with imatinib. Most of the patients were treated with dasatinib 60 mg/m2 once daily. After 2 years of follow-up, more than 95% of newly diagnosed patients and 82.6% of relapsed/refractory patients had complete cytogenetic response.10
Nilotinib was approved on the basis of findings from 2 clinical trials including 69 patients – 1 trial involving patients who were refractory to or relapsed after dasatinib and imatinib treatment, and 1 that included both relapsed/refractory and newly diagnosed patients. Patients received nilotinib 230 mg/m2 twice daily, rounded to the nearest 50-mg dose, in 28-day cycles. By cycle 12, the cumulative major molecular response rate (MMR) was 47.7% in patients with relapsed/refractory disease, and 64% in newly diagnosed patients.11 Clinical trials of both drugs in the pediatric setting are ongoing.
Other prominent gene fusions
Gene fusions involving the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) occur in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer and ALK inhibitors have provided an effective new treatment option for patients whose tumors display this abnormality.
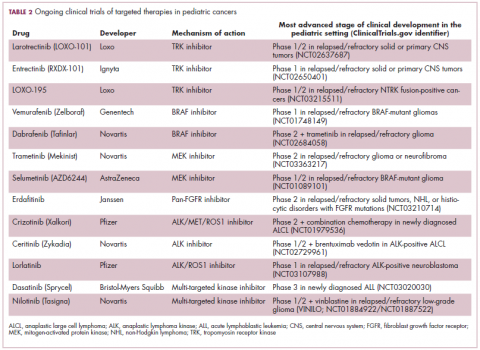
ALK fusions are also a prominent feature of several kinds of pediatric cancers and ALK inhibitors offer promise in this setting.7,12 An NPM-ALK fusion is found in 90% of pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) cases,13 whereas a variety of ALK fusions are found in up to half of patients with inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT), a rare form of soft tissue sarcoma.14 ALK inhibitors are being tested in a variety of clinical trials in pediatric patients (Table 2).
The results of a small phase 1 study of crizotinib in pediatric patients with ALK-positive ALCL (n = 26) or IMT (n = 14) were recently published. ALCL patients received crizotinib at a dose of 165 mg/m2, while IMT patients were given 100, 165, or 280 mg/m2. For the latter, the results were presented as a pooled cohort since safety and efficacy data were similar across dose levels. The overall response rate (ORR) was 83% for patients with ALCL and 86% for those with IMT. Grade 3/4 adverse events occurred in 83% and 71% of patients, respectively, and most commonly involved reduced neutrophil count.15
Most recently and perhaps most promisingly, fusions involving the neurotrophic tropomyosin receptor kinase (NTRK) gene have generated significant buzz. There are 3 NTRK genes, NTRK1, 2, and 3, which encode the TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC proteins, respectively.
To date, 22 different partner genes have been identified that can fuse with the NTRK genes and, as with other kinase fusions, drive constitutive activation of the receptor proteins and downstream oncogenic signaling pathways, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway (Figure 2).
NTRK fusions are being identified in an ever-growing number of cancer types, but are typically found in a small percentage of patients. However, in certain rare pediatric tumors, including congenital infantile fibrosarcoma and papillary thyroid cancer, they are found at much higher frequencies.
TRK inhibitors have been developed to target the fusion proteins and, given the spread of NTRK fusions across different types of cancers, they offer the most substantial promise as the next tumor agnostic cancer therapy – to treat patients based on the shared presence of a molecular aberration, irrespective of the type of cancer.16
The ongoing SCOUT trial is evaluating larotrectinib (LOXO-101) in pediatric patients. Among 24 patients (17 with NTRK fusions and 7 without) with infantile fibrosarcoma (47%), soft tissue sarcoma (41%) or papillary thyroid cancer (12%), the ORR was 93%, including complete response (CR) in 13% of patients.17
Preliminary results from an ongoing phase 1/2 study of entrectinib in pediatric patients with extracranial solid tumors were also recently presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Clinical Oncology (ASCO). Among 15 evaluable patients enrolled to date, 3 have NTRK fusions and all experienced an objective response, with 1 (a patient with IMT) ongoing at 10 months.18
CAR T cells transformative in ALL
A variety of different types of immunotherapy have been tested in patients with pediatric cancers. In general, immunotherapy has proved less effective than in adult cancers, possibly because of the lower tumor mutation burden in pediatric cancers, which means there are likely fewer cancer antigens to provoke an anti-tumor immune response.
There are notable exceptions among the disappointments, however, and most exciting is the development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. CAR T cells fall into a category of immunotherapy known as adoptive cell therapy (ACT), in which immune cells are harvested from a patient and grown outside the body to increase their numbers before being reinfused into the patient.
In the case of CAR T-cell therapy, the cells are genetically engineered to express a CAR that endows them with tumor-targeting capabilities. To date, the development of CAR T cells has focused on the use of the CD19 antigen as a target, which is highly expressed on a variety of B-cell malignancies, including several of the most common forms of pediatric cancer. ASCO shined the spotlight on CAR T-cell therapy this year, naming it the Advance of the Year for 2018, saying that the treatment is “poised to transform childhood ALL.”19
Two CD19-targeted CAR T-cell therapies – tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel – were brought to market in 2017. Only tisagenlecleucel is approved in the pediatric ALL population, however, having been awarded approval for the treatment of patients aged up to 25 years whose disease is refractory to or relapsed after receiving at least 2 prior therapies. In the pivotal trial, complete responses were observed in more than 60% of patients.20 Clinical trials of both CAR T-cell therapies in pediatric ALL and non-Hodgkin lymphoma are ongoing (Table 3).
CD19 has also proven to be a promising target for other forms of immunotherapy, including a new type of antibody known as a bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE). In 2014, blinatumomab became the first BiTE to receive regulatory approval, for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory ALL. Blinatumomab also targets the CD3 protein on T cells and helps to bring cancer cells and cytotoxic immune cells into close enough proximity that an immunological synapse can be formed between the two, facilitating tumor cell killing.21
In 2016, the approved indication was expanded into the pediatric population based on the results of a phase 1/2 study in which the safety and efficacy of blinatumomab were evaluated in 93 pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory ALL. Among the 70 patients who received the recommended dose of 5µg/m2 a day for the first 7 days, followed by 15µg/m2 a day thereafter, 51% achieved complete remission within the first 2 cycles, 52% of whom achieved minimal residual disease (MRD).22 Most recently, the FDA expanded the indication for blinatumomab to include patients (both adults and children) who are in remission, but MRD positive.23Despite the dramatic responses, many patients relapse after treatment with CD19-targeted CAR T cells, and researchers have uncovered numerous mechanisms of resistance. Among them is the loss of the CD19 antigen on the surface of target cells, such that a CD19-positive tumor becomes CD19-negative after treatment, driving relapse.24-26Several strategies for overcoming CD19-negative relapse are already being investigated, including the development of CD22-targeted CAR T cells and bispecific CAR T cells that target both CD19 and CD22. The results of a first-in-human trial of anti-CD22 CAR T-cell therapy were recently published. Among 21 pediatric and adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell ALL who were treated with either 3 x 105 cells/kg, 1 x 106 cells/kg, or 3 x 106 cells/kg, complete responses were observed in 57%.27
Results from 15 pediatric patients enrolled in a trial evaluating CD22-targeted CAR T cells as salvage therapy for those who relapse after CD19-targeted CAR T cell therapy were presented at the recent Congress of the European Hematology Association in Stockholm, Sweden. Patients who had undergone a stem cell transplant received the CAR T cells at a dose of 0.9 x 105 cell/kg and those who had not undergone a transplant received a dose of 8.2 x 105 cells/kg. At 30 days after CAR T cell infusion, the CR rate was 80% and the treatment was well tolerated.28
More immunotherapy approvals
The immune checkpoint inhibitors, which work by blocking inhibitory receptors on the surface of T cells, have also had recent approvals in pediatric patient populations. Pembrolizumab and nivolumab, inhibitors of the programmed cell death receptor 1 (PD-1) protein, have both been approved for use in adult and pediatric patients (older than 12 years) with relapsed/refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (and other solid tumors in the case of pembrolizumab) that display defects in the mismatch repair pathway that fixes damaged DNA or in patients that have high levels of microsatellite instability. Both deficient mismatch repair and microsatellite instability–high can indicate a high mutation burden in a tumor, which may predict increased sensitivity to immunotherapy.29
The approval in pediatric patients in both of those instances, however, was not based on data in pediatric patient populations but extrapolated from adult patients. Pembrolizumab is also approved for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) after 3 or more previous treatments, but once again efficacy in the pediatric population was inferred from clinical trials performed in adults. Most recently, pembrolizumab was approved for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with relapsed or refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma.30Ipilimumab, which targets a different T cell receptor – cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) – has been approved for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with metastatic melanoma. This expanded indication, following on from its approval in adult patients in 2011, was based on data from 2 trials in which objective responses were observed in 2 out of 17 patients, including 1 partial response that lasted 16 months.31Finally, antibody-drug conjugates (ADC), in which tumor antigen-targeting monoclonal antibodies are conjugated to cytotoxic payloads to combine the specificity of an antibody with the cell-killing potency of chemotherapy, have also generated some recent successes in pediatric cancers.
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin is an ADC that targets the CD33 protein, which is highly expressed on 85%-90% of cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In 2000, it was the first ADC to be brought to market in the United States, but it was subsequently voluntarily withdrawn by the manufacturer in 2010 after confirmatory trials failed to show a survival benefit.
Recently, a meta-analysis of gemtuzumab ozogamicin trials suggested that the drug likely does improve long-term overall survival (OS) and reduce the risk of relapse and researchers developed an intermittent dosing schedule to help mitigate toxicity.32 This new dosing regimen received FDA approval in 2017 for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 2 years and older on the basis of 2 clinical trials.
In the MyloFrance-1 trial, 57 patients were administered 3 mg/m2 gemtuzumab ozogamicin on days 1, 4, and 7 followed by cytarabine consolidation therapy and demonstrated a 26% CR rate and median recurrence-free survival of 11.6 months. In the phase 3 AML-19 trial, 237 patients received gemtuzumab ozogamicin at a dose of 6 mg/m2 on day 1 and 3 mg/m2 on day 8 or best supportive care. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin improved OS from 3.6 to 4.9 months.33,34
Inotuzumab ozogamicin is a CD22-targeting ADC that has been FDA approved for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell precursor ALL since last year. The therapy has been available to pediatric patients through a compassionate access program, but it has not been extensively evaluated in this population. The results of a retrospective analysis of pediatric patients who received at least 1 dose of inotuzumab ozogamicin were presented at ASCO in 2017. Among 29 patients with heavily pretreated disease the CR rate was 62%, 72% of whom achieved MRD negativity.35
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for childhood cancers. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-in-children/key-statistics.html. Last revised September 10, 2018. Accessed September 16, 2018.
2. NHI/National Cancer Institute website. Unusual cancers of childhood treatment (PDQ) - Health Professional Version. https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/hp/unusual-cancers-childhood-pdq. Last updated August 28, 2018. Accessed September 8, 2018.
3. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7-30.
4. Marshall GM, Carter DR, Cheung BB, et al. The prenatal origins of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(4):277-289.
5. Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA, Jr, Kinzler KW. Cancer genome landscapes. Science. 2013;339(6127):1546-1558.
6. Ma X, Liu Y, Liu Y, et al. Pan-cancer genome and transcriptome analyses of 1,699 paediatric leukaemias and solid tumours. Nature. 2018;555:371.
7. Dupain C, Harttrampf AC, Urbinati G, Geoerger B, Massaad-Massade L. Relevance of fusion genes in pediatric cancers: toward precision medicine. Molec Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;6:315-326.
8. Lemonick MD, Park A. New hope for cancer. http://content.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,2047900-2,00.html. Published May 28, 2001. Last accessed September 13, 2018.
9. Iqbal N, Iqbal N. Imatinib: a breakthrough of targeted therapy in cancer. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/cherp/2014/357027/. Published May 19, 2014. Accessed September 16, 2018.
10. Gore L, Kearns PR, Martino MLd, et al. Dasatinib in pediatric patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: results from a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(13):1330-1338.
11. Novartis press release. Novartis drug Tasigna approved by FDA to treat children with rare form of leukemia. 2018; https://www.novartis.com/news/media-releases/novartis-drug-tasignar-approved-fda-treat-children-rare-form-leukemia. Released March 22, 2018. Accessed September 16, 2018.
12. Takita J. The role of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in pediatric cancers. Cancer Sci. 2017;108(10):1913-1920.
13. Turner SD, Lamant L, Kenner L, Brugieres L. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma in paediatric and young adult patients. Br J Haematol. 2016;173(4):560-572.
14. Antonescu CR, Suurmeijer AJH, Zhang L, et al. Molecular characterization of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors with frequent ALK and ROS1 fusions and rare novel RET gene rearrangement. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39(7):957-967.
15. Mosse YP, Voss SD, Lim MS, et al. Targeting ALK with crizotinib in pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma and inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: a children's oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(28):3215-3221.
16. Amatu A, Sartore-Bianchi A, Siena S. NTRK gene fusions as novel targets of cancer therapy across multiple tumour types. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5070277/. Published online March 18, 2016. Accessed September 16, 2018.
17. [Behind paywall.] Laetsch TW, DuBois SG, Mascarenhas L, et al. Larotrectinib for paediatric solid tumours harbouring NTRK gene fusions: phase 1 results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(5):705-714.
18. Desai AV, Brodeur GM, Foster J, et al. Phase 1 study of entrectinib (RXDX-101), a TRK, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor, in children, adolescents, and young adults with recurrent or refractory solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(suppl;):abstr 10536.
19. Heymach J, Krilov L, Alberg A, et al. Clinical cancer advances 2018: annual report on progress against cancer from the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(10):1020-1044.
20. Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. NEJM. 2018;378(5):439-448.
21. Wu J, Fu J, Zhang M, Liu D. Blinatumomab: a bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) antibody against CD19/CD3 for refractory acute lymphoid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:104.
22. Stackelberg Av, Locatelli F, Zugmaier G, et al. Phase I/phase II study of blinatumomab in pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(36):4381-4389.
23. Gokbuget N, Dombret H, Bonifacio M, et al. Blinatumomab for minimal residual disease in adults with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2018;131(14):1522-1531.
24. Fischer J, Paret C, El Malki K, et al. CD19 isoforms enabling resistance to CART-19 immunotherapy are expressed in B-ALL patients at initial diagnosis. J Immunother. 2017;40(5):187-195.
25. Fousek K, Watanabe J, George A, et al. Targeting CD19-negative relapsed B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia using trivalent CAR T cells. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(5_suppl):121-121.
26. Mejstríková E, Hrusak O, Borowitz MJ, et al. CD19-negative relapse of pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia following blinatumomab treatment. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7(12):659.
27. Fry TJ, Shah NN, Orentas RJ, et al. CD22-targeted CAR T cells induce remission in B-ALL that is naive or resistant to CD19-targeted CAR immunotherapy. Nat Med. 2018;24(1):20-28.
28. Pan J, Deng B, Liu S, et al. Efficacy and safety of CD22-directed CAR T-cell therapy in 15 pediatric refractory or relapsed b acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Paper presented at 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association 2018; Stockholm, Sweden.
29. Boyiadzis MM, Kirkwood JM, Marshall JL, Pritchard CC, Azad NS, Gulley JL. Significance and implications of FDA approval of pembrolizumab for biomarker-defined disease. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6:35.
30. Drugs.com. Keytruda approval history. 2018; https://www.drugs.com/history/keytruda.html. Last update information not given. Accessed September 16, 2018.
31. Bristol Myers Squibb press release. US Food and Drug Administration expands approval of Yervoy (ipilimumab) to include pediatric patients 12 years and older with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. https://news.bms.com/press-release/corporatefinancial-news/us-food-and-drug-administration-expands-approval-yervoy-ipilim. Released July 24, 2017. Accessed September 16, 2018.
32. Hills RK, Castaigne S, Appelbaum FR, et al. Addition of gemtuzumab ozogamicin to induction chemotherapy in adult patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(9):986-996.
33. Amadori S, Suciu S, Selleslag D, et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin versus best supportive care in older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia unsuitable for intensive chemotherapy: results of the randomized phase III EORTC-GIMEMA AML-19 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(9):972-979.
34. Taksin AL, Legrand O, Raffoux E, et al. High efficacy and safety profile of fractionated doses of Mylotarg as induction therapy in patients with relapsed acute myeloblastic leukemia: a prospective study of the alfa group. Leukemia. 2007;21(1):66-71.
35. Bhojwani D, Sposto R, Shah N, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin in pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (R/R ALL). J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(15_suppl):10512-10512.
Although there have been significant improvements in patient outcomes for some forms of pediatric cancer, progress has been painfully slow for others. An increasing understanding of pediatric cancers is highlighting the unique molecular drivers and challenging the assumption that drugs developed in adults can be applied to children and young adults. Here, we discuss game-changing therapeutic advances and a shifting view of childhood cancers.
Unique genomic background
Although pediatric cancers are rare, representing just 1% of all new cancers diagnosed annually in the United States, they are the second leading cause of death in children aged 1 to 14 years. There are many different histological tumor types under the umbrella of childhood cancers, of which the most common are leukemias, central nervous system tumors, and lymphomas (Figure 1).1,2
Significant progress has been made in the treatment of certain pediatric cancers in recent decades, exemplified by pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), which has been transformed from a virtually incurable cancer to one in which 5-year survival rates now reach up to 90%. In other forms of pediatric cancer, however, survival rates have stagnated and little progress has been made in the development of effective new therapies.3
Because of their rarity, pediatric cancers are difficult to study and adequate enrollment of children in clinical trials can be challenging. Pharmaceutical companies are often hesitant to test drugs in the pediatric population in patients who often cannot advocate for themselves. As a result, the activity of drugs developed in adult patients has often been inferred in pediatric patients with the same tumor type or molecular aberrations. However, as researchers have gathered more information about pediatric cancers, there has been increasing recognition of their unique attributes and the need for dedicated clinical trials in this patient population.
Pediatric cancers tend to be found in the developing mesodermic tissue, whereas adult cancers are more prevalent in the epithelial tissues. Genome sequencing studies have revealed a much lower mutational burden in pediatric cancers and the mechanisms of oncogenesis are also quite different; adult tumors can develop from a series of acquired gene mutations, but pediatric tumors tend to develop from a single catastrophic event.4,5
Even the same type of cancer in a pediatric and adult patient can be quite different, with very different underlying molecular mechanisms. In a recent genomic analysis of different types of pediatric cancer by researchers at St Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital, less than half of the identified mutated genes were found to be similar to those found in adult patients.6
A ‘magic bullet’?
Chromosomal rearrangements are common in pediatric cancers. This type of molecular abnormality can result in a fusion of 2 different genes when the chromosome breaks apart and the pieces join back together in a muddled order. If the genetic code fuses in a manner that is “readable” by the cell, then it can drive aberrant activation of one or both genes.7 Gene fusions often involve kinase enzymes that are essential players in cell signaling pathways regulating hallmark cancer processes, such as unchecked cell proliferation. The fusion drives the constitutive activation of the kinase and, thus, these downstream signaling pathways.
One of the first chromosomal rearrangements linked to cancer, BCR-ABL1 – more commonly known as the Philadelphia chromosome – results in aberrant activation of the ABL1 kinase. It is present in nearly all cases of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and 3% to 5% of patients with ALL, and thus became the central focus of targeted drug development. Imatinib was initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2001 for the treatment of adult patients with CML and had such a significant impact on the treatment landscape that it made the cover of Time magazine as a “magic bullet” in the war on cancer.8
Approval was expanded into pediatric patients in 2006 and for pediatric patients with ALL in 2013. However, as with the use of most kinase inhibitors, tumors can evolve under the selective pressure of treatment, developing additional molecular abnormalities that drive resistance.9
Next-generation multikinase inhibitors that more potently inhibit the BCR-ABL1 fusion protein have been developed to provide additional treatment options for patients who become resistant to imatinib. Dasatinib and nilotinib are among several drugs that have recently been approved for pediatric cancer therapy (Table 1). Both therapies were approved to treat children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive CML in the chronic phase in either the front- or second-line setting after failure of imatinib.
The approval of dasatinib was based on data from 97 patients across 2 trials, 51 of whom were newly diagnosed and 46 previously treated with imatinib. Most of the patients were treated with dasatinib 60 mg/m2 once daily. After 2 years of follow-up, more than 95% of newly diagnosed patients and 82.6% of relapsed/refractory patients had complete cytogenetic response.10
Nilotinib was approved on the basis of findings from 2 clinical trials including 69 patients – 1 trial involving patients who were refractory to or relapsed after dasatinib and imatinib treatment, and 1 that included both relapsed/refractory and newly diagnosed patients. Patients received nilotinib 230 mg/m2 twice daily, rounded to the nearest 50-mg dose, in 28-day cycles. By cycle 12, the cumulative major molecular response rate (MMR) was 47.7% in patients with relapsed/refractory disease, and 64% in newly diagnosed patients.11 Clinical trials of both drugs in the pediatric setting are ongoing.
Other prominent gene fusions
Gene fusions involving the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) occur in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer and ALK inhibitors have provided an effective new treatment option for patients whose tumors display this abnormality.
ALK fusions are also a prominent feature of several kinds of pediatric cancers and ALK inhibitors offer promise in this setting.7,12 An NPM-ALK fusion is found in 90% of pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) cases,13 whereas a variety of ALK fusions are found in up to half of patients with inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT), a rare form of soft tissue sarcoma.14 ALK inhibitors are being tested in a variety of clinical trials in pediatric patients (Table 2).
The results of a small phase 1 study of crizotinib in pediatric patients with ALK-positive ALCL (n = 26) or IMT (n = 14) were recently published. ALCL patients received crizotinib at a dose of 165 mg/m2, while IMT patients were given 100, 165, or 280 mg/m2. For the latter, the results were presented as a pooled cohort since safety and efficacy data were similar across dose levels. The overall response rate (ORR) was 83% for patients with ALCL and 86% for those with IMT. Grade 3/4 adverse events occurred in 83% and 71% of patients, respectively, and most commonly involved reduced neutrophil count.15
Most recently and perhaps most promisingly, fusions involving the neurotrophic tropomyosin receptor kinase (NTRK) gene have generated significant buzz. There are 3 NTRK genes, NTRK1, 2, and 3, which encode the TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC proteins, respectively.
To date, 22 different partner genes have been identified that can fuse with the NTRK genes and, as with other kinase fusions, drive constitutive activation of the receptor proteins and downstream oncogenic signaling pathways, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway (Figure 2).
NTRK fusions are being identified in an ever-growing number of cancer types, but are typically found in a small percentage of patients. However, in certain rare pediatric tumors, including congenital infantile fibrosarcoma and papillary thyroid cancer, they are found at much higher frequencies.
TRK inhibitors have been developed to target the fusion proteins and, given the spread of NTRK fusions across different types of cancers, they offer the most substantial promise as the next tumor agnostic cancer therapy – to treat patients based on the shared presence of a molecular aberration, irrespective of the type of cancer.16
The ongoing SCOUT trial is evaluating larotrectinib (LOXO-101) in pediatric patients. Among 24 patients (17 with NTRK fusions and 7 without) with infantile fibrosarcoma (47%), soft tissue sarcoma (41%) or papillary thyroid cancer (12%), the ORR was 93%, including complete response (CR) in 13% of patients.17
Preliminary results from an ongoing phase 1/2 study of entrectinib in pediatric patients with extracranial solid tumors were also recently presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Clinical Oncology (ASCO). Among 15 evaluable patients enrolled to date, 3 have NTRK fusions and all experienced an objective response, with 1 (a patient with IMT) ongoing at 10 months.18
CAR T cells transformative in ALL
A variety of different types of immunotherapy have been tested in patients with pediatric cancers. In general, immunotherapy has proved less effective than in adult cancers, possibly because of the lower tumor mutation burden in pediatric cancers, which means there are likely fewer cancer antigens to provoke an anti-tumor immune response.
There are notable exceptions among the disappointments, however, and most exciting is the development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. CAR T cells fall into a category of immunotherapy known as adoptive cell therapy (ACT), in which immune cells are harvested from a patient and grown outside the body to increase their numbers before being reinfused into the patient.
In the case of CAR T-cell therapy, the cells are genetically engineered to express a CAR that endows them with tumor-targeting capabilities. To date, the development of CAR T cells has focused on the use of the CD19 antigen as a target, which is highly expressed on a variety of B-cell malignancies, including several of the most common forms of pediatric cancer. ASCO shined the spotlight on CAR T-cell therapy this year, naming it the Advance of the Year for 2018, saying that the treatment is “poised to transform childhood ALL.”19
Two CD19-targeted CAR T-cell therapies – tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel – were brought to market in 2017. Only tisagenlecleucel is approved in the pediatric ALL population, however, having been awarded approval for the treatment of patients aged up to 25 years whose disease is refractory to or relapsed after receiving at least 2 prior therapies. In the pivotal trial, complete responses were observed in more than 60% of patients.20 Clinical trials of both CAR T-cell therapies in pediatric ALL and non-Hodgkin lymphoma are ongoing (Table 3).
CD19 has also proven to be a promising target for other forms of immunotherapy, including a new type of antibody known as a bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE). In 2014, blinatumomab became the first BiTE to receive regulatory approval, for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory ALL. Blinatumomab also targets the CD3 protein on T cells and helps to bring cancer cells and cytotoxic immune cells into close enough proximity that an immunological synapse can be formed between the two, facilitating tumor cell killing.21
In 2016, the approved indication was expanded into the pediatric population based on the results of a phase 1/2 study in which the safety and efficacy of blinatumomab were evaluated in 93 pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory ALL. Among the 70 patients who received the recommended dose of 5µg/m2 a day for the first 7 days, followed by 15µg/m2 a day thereafter, 51% achieved complete remission within the first 2 cycles, 52% of whom achieved minimal residual disease (MRD).22 Most recently, the FDA expanded the indication for blinatumomab to include patients (both adults and children) who are in remission, but MRD positive.23Despite the dramatic responses, many patients relapse after treatment with CD19-targeted CAR T cells, and researchers have uncovered numerous mechanisms of resistance. Among them is the loss of the CD19 antigen on the surface of target cells, such that a CD19-positive tumor becomes CD19-negative after treatment, driving relapse.24-26Several strategies for overcoming CD19-negative relapse are already being investigated, including the development of CD22-targeted CAR T cells and bispecific CAR T cells that target both CD19 and CD22. The results of a first-in-human trial of anti-CD22 CAR T-cell therapy were recently published. Among 21 pediatric and adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell ALL who were treated with either 3 x 105 cells/kg, 1 x 106 cells/kg, or 3 x 106 cells/kg, complete responses were observed in 57%.27
Results from 15 pediatric patients enrolled in a trial evaluating CD22-targeted CAR T cells as salvage therapy for those who relapse after CD19-targeted CAR T cell therapy were presented at the recent Congress of the European Hematology Association in Stockholm, Sweden. Patients who had undergone a stem cell transplant received the CAR T cells at a dose of 0.9 x 105 cell/kg and those who had not undergone a transplant received a dose of 8.2 x 105 cells/kg. At 30 days after CAR T cell infusion, the CR rate was 80% and the treatment was well tolerated.28
More immunotherapy approvals
The immune checkpoint inhibitors, which work by blocking inhibitory receptors on the surface of T cells, have also had recent approvals in pediatric patient populations. Pembrolizumab and nivolumab, inhibitors of the programmed cell death receptor 1 (PD-1) protein, have both been approved for use in adult and pediatric patients (older than 12 years) with relapsed/refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (and other solid tumors in the case of pembrolizumab) that display defects in the mismatch repair pathway that fixes damaged DNA or in patients that have high levels of microsatellite instability. Both deficient mismatch repair and microsatellite instability–high can indicate a high mutation burden in a tumor, which may predict increased sensitivity to immunotherapy.29
The approval in pediatric patients in both of those instances, however, was not based on data in pediatric patient populations but extrapolated from adult patients. Pembrolizumab is also approved for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) after 3 or more previous treatments, but once again efficacy in the pediatric population was inferred from clinical trials performed in adults. Most recently, pembrolizumab was approved for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with relapsed or refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma.30Ipilimumab, which targets a different T cell receptor – cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) – has been approved for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with metastatic melanoma. This expanded indication, following on from its approval in adult patients in 2011, was based on data from 2 trials in which objective responses were observed in 2 out of 17 patients, including 1 partial response that lasted 16 months.31Finally, antibody-drug conjugates (ADC), in which tumor antigen-targeting monoclonal antibodies are conjugated to cytotoxic payloads to combine the specificity of an antibody with the cell-killing potency of chemotherapy, have also generated some recent successes in pediatric cancers.
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin is an ADC that targets the CD33 protein, which is highly expressed on 85%-90% of cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In 2000, it was the first ADC to be brought to market in the United States, but it was subsequently voluntarily withdrawn by the manufacturer in 2010 after confirmatory trials failed to show a survival benefit.
Recently, a meta-analysis of gemtuzumab ozogamicin trials suggested that the drug likely does improve long-term overall survival (OS) and reduce the risk of relapse and researchers developed an intermittent dosing schedule to help mitigate toxicity.32 This new dosing regimen received FDA approval in 2017 for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 2 years and older on the basis of 2 clinical trials.
In the MyloFrance-1 trial, 57 patients were administered 3 mg/m2 gemtuzumab ozogamicin on days 1, 4, and 7 followed by cytarabine consolidation therapy and demonstrated a 26% CR rate and median recurrence-free survival of 11.6 months. In the phase 3 AML-19 trial, 237 patients received gemtuzumab ozogamicin at a dose of 6 mg/m2 on day 1 and 3 mg/m2 on day 8 or best supportive care. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin improved OS from 3.6 to 4.9 months.33,34
Inotuzumab ozogamicin is a CD22-targeting ADC that has been FDA approved for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell precursor ALL since last year. The therapy has been available to pediatric patients through a compassionate access program, but it has not been extensively evaluated in this population. The results of a retrospective analysis of pediatric patients who received at least 1 dose of inotuzumab ozogamicin were presented at ASCO in 2017. Among 29 patients with heavily pretreated disease the CR rate was 62%, 72% of whom achieved MRD negativity.35
Although there have been significant improvements in patient outcomes for some forms of pediatric cancer, progress has been painfully slow for others. An increasing understanding of pediatric cancers is highlighting the unique molecular drivers and challenging the assumption that drugs developed in adults can be applied to children and young adults. Here, we discuss game-changing therapeutic advances and a shifting view of childhood cancers.
Unique genomic background
Although pediatric cancers are rare, representing just 1% of all new cancers diagnosed annually in the United States, they are the second leading cause of death in children aged 1 to 14 years. There are many different histological tumor types under the umbrella of childhood cancers, of which the most common are leukemias, central nervous system tumors, and lymphomas (Figure 1).1,2
Significant progress has been made in the treatment of certain pediatric cancers in recent decades, exemplified by pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), which has been transformed from a virtually incurable cancer to one in which 5-year survival rates now reach up to 90%. In other forms of pediatric cancer, however, survival rates have stagnated and little progress has been made in the development of effective new therapies.3
Because of their rarity, pediatric cancers are difficult to study and adequate enrollment of children in clinical trials can be challenging. Pharmaceutical companies are often hesitant to test drugs in the pediatric population in patients who often cannot advocate for themselves. As a result, the activity of drugs developed in adult patients has often been inferred in pediatric patients with the same tumor type or molecular aberrations. However, as researchers have gathered more information about pediatric cancers, there has been increasing recognition of their unique attributes and the need for dedicated clinical trials in this patient population.
Pediatric cancers tend to be found in the developing mesodermic tissue, whereas adult cancers are more prevalent in the epithelial tissues. Genome sequencing studies have revealed a much lower mutational burden in pediatric cancers and the mechanisms of oncogenesis are also quite different; adult tumors can develop from a series of acquired gene mutations, but pediatric tumors tend to develop from a single catastrophic event.4,5
Even the same type of cancer in a pediatric and adult patient can be quite different, with very different underlying molecular mechanisms. In a recent genomic analysis of different types of pediatric cancer by researchers at St Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital, less than half of the identified mutated genes were found to be similar to those found in adult patients.6
A ‘magic bullet’?
Chromosomal rearrangements are common in pediatric cancers. This type of molecular abnormality can result in a fusion of 2 different genes when the chromosome breaks apart and the pieces join back together in a muddled order. If the genetic code fuses in a manner that is “readable” by the cell, then it can drive aberrant activation of one or both genes.7 Gene fusions often involve kinase enzymes that are essential players in cell signaling pathways regulating hallmark cancer processes, such as unchecked cell proliferation. The fusion drives the constitutive activation of the kinase and, thus, these downstream signaling pathways.
One of the first chromosomal rearrangements linked to cancer, BCR-ABL1 – more commonly known as the Philadelphia chromosome – results in aberrant activation of the ABL1 kinase. It is present in nearly all cases of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and 3% to 5% of patients with ALL, and thus became the central focus of targeted drug development. Imatinib was initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2001 for the treatment of adult patients with CML and had such a significant impact on the treatment landscape that it made the cover of Time magazine as a “magic bullet” in the war on cancer.8
Approval was expanded into pediatric patients in 2006 and for pediatric patients with ALL in 2013. However, as with the use of most kinase inhibitors, tumors can evolve under the selective pressure of treatment, developing additional molecular abnormalities that drive resistance.9
Next-generation multikinase inhibitors that more potently inhibit the BCR-ABL1 fusion protein have been developed to provide additional treatment options for patients who become resistant to imatinib. Dasatinib and nilotinib are among several drugs that have recently been approved for pediatric cancer therapy (Table 1). Both therapies were approved to treat children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive CML in the chronic phase in either the front- or second-line setting after failure of imatinib.
The approval of dasatinib was based on data from 97 patients across 2 trials, 51 of whom were newly diagnosed and 46 previously treated with imatinib. Most of the patients were treated with dasatinib 60 mg/m2 once daily. After 2 years of follow-up, more than 95% of newly diagnosed patients and 82.6% of relapsed/refractory patients had complete cytogenetic response.10
Nilotinib was approved on the basis of findings from 2 clinical trials including 69 patients – 1 trial involving patients who were refractory to or relapsed after dasatinib and imatinib treatment, and 1 that included both relapsed/refractory and newly diagnosed patients. Patients received nilotinib 230 mg/m2 twice daily, rounded to the nearest 50-mg dose, in 28-day cycles. By cycle 12, the cumulative major molecular response rate (MMR) was 47.7% in patients with relapsed/refractory disease, and 64% in newly diagnosed patients.11 Clinical trials of both drugs in the pediatric setting are ongoing.
Other prominent gene fusions
Gene fusions involving the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) occur in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer and ALK inhibitors have provided an effective new treatment option for patients whose tumors display this abnormality.
ALK fusions are also a prominent feature of several kinds of pediatric cancers and ALK inhibitors offer promise in this setting.7,12 An NPM-ALK fusion is found in 90% of pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) cases,13 whereas a variety of ALK fusions are found in up to half of patients with inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT), a rare form of soft tissue sarcoma.14 ALK inhibitors are being tested in a variety of clinical trials in pediatric patients (Table 2).
The results of a small phase 1 study of crizotinib in pediatric patients with ALK-positive ALCL (n = 26) or IMT (n = 14) were recently published. ALCL patients received crizotinib at a dose of 165 mg/m2, while IMT patients were given 100, 165, or 280 mg/m2. For the latter, the results were presented as a pooled cohort since safety and efficacy data were similar across dose levels. The overall response rate (ORR) was 83% for patients with ALCL and 86% for those with IMT. Grade 3/4 adverse events occurred in 83% and 71% of patients, respectively, and most commonly involved reduced neutrophil count.15
Most recently and perhaps most promisingly, fusions involving the neurotrophic tropomyosin receptor kinase (NTRK) gene have generated significant buzz. There are 3 NTRK genes, NTRK1, 2, and 3, which encode the TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC proteins, respectively.
To date, 22 different partner genes have been identified that can fuse with the NTRK genes and, as with other kinase fusions, drive constitutive activation of the receptor proteins and downstream oncogenic signaling pathways, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway (Figure 2).
NTRK fusions are being identified in an ever-growing number of cancer types, but are typically found in a small percentage of patients. However, in certain rare pediatric tumors, including congenital infantile fibrosarcoma and papillary thyroid cancer, they are found at much higher frequencies.
TRK inhibitors have been developed to target the fusion proteins and, given the spread of NTRK fusions across different types of cancers, they offer the most substantial promise as the next tumor agnostic cancer therapy – to treat patients based on the shared presence of a molecular aberration, irrespective of the type of cancer.16
The ongoing SCOUT trial is evaluating larotrectinib (LOXO-101) in pediatric patients. Among 24 patients (17 with NTRK fusions and 7 without) with infantile fibrosarcoma (47%), soft tissue sarcoma (41%) or papillary thyroid cancer (12%), the ORR was 93%, including complete response (CR) in 13% of patients.17
Preliminary results from an ongoing phase 1/2 study of entrectinib in pediatric patients with extracranial solid tumors were also recently presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Clinical Oncology (ASCO). Among 15 evaluable patients enrolled to date, 3 have NTRK fusions and all experienced an objective response, with 1 (a patient with IMT) ongoing at 10 months.18
CAR T cells transformative in ALL
A variety of different types of immunotherapy have been tested in patients with pediatric cancers. In general, immunotherapy has proved less effective than in adult cancers, possibly because of the lower tumor mutation burden in pediatric cancers, which means there are likely fewer cancer antigens to provoke an anti-tumor immune response.
There are notable exceptions among the disappointments, however, and most exciting is the development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. CAR T cells fall into a category of immunotherapy known as adoptive cell therapy (ACT), in which immune cells are harvested from a patient and grown outside the body to increase their numbers before being reinfused into the patient.
In the case of CAR T-cell therapy, the cells are genetically engineered to express a CAR that endows them with tumor-targeting capabilities. To date, the development of CAR T cells has focused on the use of the CD19 antigen as a target, which is highly expressed on a variety of B-cell malignancies, including several of the most common forms of pediatric cancer. ASCO shined the spotlight on CAR T-cell therapy this year, naming it the Advance of the Year for 2018, saying that the treatment is “poised to transform childhood ALL.”19
Two CD19-targeted CAR T-cell therapies – tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel – were brought to market in 2017. Only tisagenlecleucel is approved in the pediatric ALL population, however, having been awarded approval for the treatment of patients aged up to 25 years whose disease is refractory to or relapsed after receiving at least 2 prior therapies. In the pivotal trial, complete responses were observed in more than 60% of patients.20 Clinical trials of both CAR T-cell therapies in pediatric ALL and non-Hodgkin lymphoma are ongoing (Table 3).
CD19 has also proven to be a promising target for other forms of immunotherapy, including a new type of antibody known as a bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE). In 2014, blinatumomab became the first BiTE to receive regulatory approval, for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory ALL. Blinatumomab also targets the CD3 protein on T cells and helps to bring cancer cells and cytotoxic immune cells into close enough proximity that an immunological synapse can be formed between the two, facilitating tumor cell killing.21
In 2016, the approved indication was expanded into the pediatric population based on the results of a phase 1/2 study in which the safety and efficacy of blinatumomab were evaluated in 93 pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory ALL. Among the 70 patients who received the recommended dose of 5µg/m2 a day for the first 7 days, followed by 15µg/m2 a day thereafter, 51% achieved complete remission within the first 2 cycles, 52% of whom achieved minimal residual disease (MRD).22 Most recently, the FDA expanded the indication for blinatumomab to include patients (both adults and children) who are in remission, but MRD positive.23Despite the dramatic responses, many patients relapse after treatment with CD19-targeted CAR T cells, and researchers have uncovered numerous mechanisms of resistance. Among them is the loss of the CD19 antigen on the surface of target cells, such that a CD19-positive tumor becomes CD19-negative after treatment, driving relapse.24-26Several strategies for overcoming CD19-negative relapse are already being investigated, including the development of CD22-targeted CAR T cells and bispecific CAR T cells that target both CD19 and CD22. The results of a first-in-human trial of anti-CD22 CAR T-cell therapy were recently published. Among 21 pediatric and adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell ALL who were treated with either 3 x 105 cells/kg, 1 x 106 cells/kg, or 3 x 106 cells/kg, complete responses were observed in 57%.27
Results from 15 pediatric patients enrolled in a trial evaluating CD22-targeted CAR T cells as salvage therapy for those who relapse after CD19-targeted CAR T cell therapy were presented at the recent Congress of the European Hematology Association in Stockholm, Sweden. Patients who had undergone a stem cell transplant received the CAR T cells at a dose of 0.9 x 105 cell/kg and those who had not undergone a transplant received a dose of 8.2 x 105 cells/kg. At 30 days after CAR T cell infusion, the CR rate was 80% and the treatment was well tolerated.28
More immunotherapy approvals
The immune checkpoint inhibitors, which work by blocking inhibitory receptors on the surface of T cells, have also had recent approvals in pediatric patient populations. Pembrolizumab and nivolumab, inhibitors of the programmed cell death receptor 1 (PD-1) protein, have both been approved for use in adult and pediatric patients (older than 12 years) with relapsed/refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (and other solid tumors in the case of pembrolizumab) that display defects in the mismatch repair pathway that fixes damaged DNA or in patients that have high levels of microsatellite instability. Both deficient mismatch repair and microsatellite instability–high can indicate a high mutation burden in a tumor, which may predict increased sensitivity to immunotherapy.29
The approval in pediatric patients in both of those instances, however, was not based on data in pediatric patient populations but extrapolated from adult patients. Pembrolizumab is also approved for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) after 3 or more previous treatments, but once again efficacy in the pediatric population was inferred from clinical trials performed in adults. Most recently, pembrolizumab was approved for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with relapsed or refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma.30Ipilimumab, which targets a different T cell receptor – cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) – has been approved for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with metastatic melanoma. This expanded indication, following on from its approval in adult patients in 2011, was based on data from 2 trials in which objective responses were observed in 2 out of 17 patients, including 1 partial response that lasted 16 months.31Finally, antibody-drug conjugates (ADC), in which tumor antigen-targeting monoclonal antibodies are conjugated to cytotoxic payloads to combine the specificity of an antibody with the cell-killing potency of chemotherapy, have also generated some recent successes in pediatric cancers.
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin is an ADC that targets the CD33 protein, which is highly expressed on 85%-90% of cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In 2000, it was the first ADC to be brought to market in the United States, but it was subsequently voluntarily withdrawn by the manufacturer in 2010 after confirmatory trials failed to show a survival benefit.
Recently, a meta-analysis of gemtuzumab ozogamicin trials suggested that the drug likely does improve long-term overall survival (OS) and reduce the risk of relapse and researchers developed an intermittent dosing schedule to help mitigate toxicity.32 This new dosing regimen received FDA approval in 2017 for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 2 years and older on the basis of 2 clinical trials.
In the MyloFrance-1 trial, 57 patients were administered 3 mg/m2 gemtuzumab ozogamicin on days 1, 4, and 7 followed by cytarabine consolidation therapy and demonstrated a 26% CR rate and median recurrence-free survival of 11.6 months. In the phase 3 AML-19 trial, 237 patients received gemtuzumab ozogamicin at a dose of 6 mg/m2 on day 1 and 3 mg/m2 on day 8 or best supportive care. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin improved OS from 3.6 to 4.9 months.33,34
Inotuzumab ozogamicin is a CD22-targeting ADC that has been FDA approved for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell precursor ALL since last year. The therapy has been available to pediatric patients through a compassionate access program, but it has not been extensively evaluated in this population. The results of a retrospective analysis of pediatric patients who received at least 1 dose of inotuzumab ozogamicin were presented at ASCO in 2017. Among 29 patients with heavily pretreated disease the CR rate was 62%, 72% of whom achieved MRD negativity.35
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for childhood cancers. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-in-children/key-statistics.html. Last revised September 10, 2018. Accessed September 16, 2018.
2. NHI/National Cancer Institute website. Unusual cancers of childhood treatment (PDQ) - Health Professional Version. https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/hp/unusual-cancers-childhood-pdq. Last updated August 28, 2018. Accessed September 8, 2018.
3. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7-30.
4. Marshall GM, Carter DR, Cheung BB, et al. The prenatal origins of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(4):277-289.
5. Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA, Jr, Kinzler KW. Cancer genome landscapes. Science. 2013;339(6127):1546-1558.
6. Ma X, Liu Y, Liu Y, et al. Pan-cancer genome and transcriptome analyses of 1,699 paediatric leukaemias and solid tumours. Nature. 2018;555:371.
7. Dupain C, Harttrampf AC, Urbinati G, Geoerger B, Massaad-Massade L. Relevance of fusion genes in pediatric cancers: toward precision medicine. Molec Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;6:315-326.
8. Lemonick MD, Park A. New hope for cancer. http://content.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,2047900-2,00.html. Published May 28, 2001. Last accessed September 13, 2018.
9. Iqbal N, Iqbal N. Imatinib: a breakthrough of targeted therapy in cancer. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/cherp/2014/357027/. Published May 19, 2014. Accessed September 16, 2018.
10. Gore L, Kearns PR, Martino MLd, et al. Dasatinib in pediatric patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: results from a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(13):1330-1338.
11. Novartis press release. Novartis drug Tasigna approved by FDA to treat children with rare form of leukemia. 2018; https://www.novartis.com/news/media-releases/novartis-drug-tasignar-approved-fda-treat-children-rare-form-leukemia. Released March 22, 2018. Accessed September 16, 2018.
12. Takita J. The role of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in pediatric cancers. Cancer Sci. 2017;108(10):1913-1920.
13. Turner SD, Lamant L, Kenner L, Brugieres L. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma in paediatric and young adult patients. Br J Haematol. 2016;173(4):560-572.
14. Antonescu CR, Suurmeijer AJH, Zhang L, et al. Molecular characterization of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors with frequent ALK and ROS1 fusions and rare novel RET gene rearrangement. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39(7):957-967.
15. Mosse YP, Voss SD, Lim MS, et al. Targeting ALK with crizotinib in pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma and inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: a children's oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(28):3215-3221.
16. Amatu A, Sartore-Bianchi A, Siena S. NTRK gene fusions as novel targets of cancer therapy across multiple tumour types. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5070277/. Published online March 18, 2016. Accessed September 16, 2018.
17. [Behind paywall.] Laetsch TW, DuBois SG, Mascarenhas L, et al. Larotrectinib for paediatric solid tumours harbouring NTRK gene fusions: phase 1 results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(5):705-714.
18. Desai AV, Brodeur GM, Foster J, et al. Phase 1 study of entrectinib (RXDX-101), a TRK, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor, in children, adolescents, and young adults with recurrent or refractory solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(suppl;):abstr 10536.
19. Heymach J, Krilov L, Alberg A, et al. Clinical cancer advances 2018: annual report on progress against cancer from the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(10):1020-1044.
20. Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. NEJM. 2018;378(5):439-448.
21. Wu J, Fu J, Zhang M, Liu D. Blinatumomab: a bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) antibody against CD19/CD3 for refractory acute lymphoid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:104.
22. Stackelberg Av, Locatelli F, Zugmaier G, et al. Phase I/phase II study of blinatumomab in pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(36):4381-4389.
23. Gokbuget N, Dombret H, Bonifacio M, et al. Blinatumomab for minimal residual disease in adults with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2018;131(14):1522-1531.
24. Fischer J, Paret C, El Malki K, et al. CD19 isoforms enabling resistance to CART-19 immunotherapy are expressed in B-ALL patients at initial diagnosis. J Immunother. 2017;40(5):187-195.
25. Fousek K, Watanabe J, George A, et al. Targeting CD19-negative relapsed B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia using trivalent CAR T cells. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(5_suppl):121-121.
26. Mejstríková E, Hrusak O, Borowitz MJ, et al. CD19-negative relapse of pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia following blinatumomab treatment. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7(12):659.
27. Fry TJ, Shah NN, Orentas RJ, et al. CD22-targeted CAR T cells induce remission in B-ALL that is naive or resistant to CD19-targeted CAR immunotherapy. Nat Med. 2018;24(1):20-28.
28. Pan J, Deng B, Liu S, et al. Efficacy and safety of CD22-directed CAR T-cell therapy in 15 pediatric refractory or relapsed b acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Paper presented at 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association 2018; Stockholm, Sweden.
29. Boyiadzis MM, Kirkwood JM, Marshall JL, Pritchard CC, Azad NS, Gulley JL. Significance and implications of FDA approval of pembrolizumab for biomarker-defined disease. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6:35.
30. Drugs.com. Keytruda approval history. 2018; https://www.drugs.com/history/keytruda.html. Last update information not given. Accessed September 16, 2018.
31. Bristol Myers Squibb press release. US Food and Drug Administration expands approval of Yervoy (ipilimumab) to include pediatric patients 12 years and older with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. https://news.bms.com/press-release/corporatefinancial-news/us-food-and-drug-administration-expands-approval-yervoy-ipilim. Released July 24, 2017. Accessed September 16, 2018.
32. Hills RK, Castaigne S, Appelbaum FR, et al. Addition of gemtuzumab ozogamicin to induction chemotherapy in adult patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(9):986-996.
33. Amadori S, Suciu S, Selleslag D, et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin versus best supportive care in older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia unsuitable for intensive chemotherapy: results of the randomized phase III EORTC-GIMEMA AML-19 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(9):972-979.
34. Taksin AL, Legrand O, Raffoux E, et al. High efficacy and safety profile of fractionated doses of Mylotarg as induction therapy in patients with relapsed acute myeloblastic leukemia: a prospective study of the alfa group. Leukemia. 2007;21(1):66-71.
35. Bhojwani D, Sposto R, Shah N, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin in pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (R/R ALL). J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(15_suppl):10512-10512.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for childhood cancers. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-in-children/key-statistics.html. Last revised September 10, 2018. Accessed September 16, 2018.
2. NHI/National Cancer Institute website. Unusual cancers of childhood treatment (PDQ) - Health Professional Version. https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/hp/unusual-cancers-childhood-pdq. Last updated August 28, 2018. Accessed September 8, 2018.
3. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7-30.
4. Marshall GM, Carter DR, Cheung BB, et al. The prenatal origins of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(4):277-289.
5. Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA, Jr, Kinzler KW. Cancer genome landscapes. Science. 2013;339(6127):1546-1558.
6. Ma X, Liu Y, Liu Y, et al. Pan-cancer genome and transcriptome analyses of 1,699 paediatric leukaemias and solid tumours. Nature. 2018;555:371.
7. Dupain C, Harttrampf AC, Urbinati G, Geoerger B, Massaad-Massade L. Relevance of fusion genes in pediatric cancers: toward precision medicine. Molec Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;6:315-326.
8. Lemonick MD, Park A. New hope for cancer. http://content.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,2047900-2,00.html. Published May 28, 2001. Last accessed September 13, 2018.
9. Iqbal N, Iqbal N. Imatinib: a breakthrough of targeted therapy in cancer. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/cherp/2014/357027/. Published May 19, 2014. Accessed September 16, 2018.
10. Gore L, Kearns PR, Martino MLd, et al. Dasatinib in pediatric patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: results from a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(13):1330-1338.
11. Novartis press release. Novartis drug Tasigna approved by FDA to treat children with rare form of leukemia. 2018; https://www.novartis.com/news/media-releases/novartis-drug-tasignar-approved-fda-treat-children-rare-form-leukemia. Released March 22, 2018. Accessed September 16, 2018.
12. Takita J. The role of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in pediatric cancers. Cancer Sci. 2017;108(10):1913-1920.
13. Turner SD, Lamant L, Kenner L, Brugieres L. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma in paediatric and young adult patients. Br J Haematol. 2016;173(4):560-572.
14. Antonescu CR, Suurmeijer AJH, Zhang L, et al. Molecular characterization of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors with frequent ALK and ROS1 fusions and rare novel RET gene rearrangement. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39(7):957-967.
15. Mosse YP, Voss SD, Lim MS, et al. Targeting ALK with crizotinib in pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma and inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: a children's oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(28):3215-3221.
16. Amatu A, Sartore-Bianchi A, Siena S. NTRK gene fusions as novel targets of cancer therapy across multiple tumour types. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5070277/. Published online March 18, 2016. Accessed September 16, 2018.
17. [Behind paywall.] Laetsch TW, DuBois SG, Mascarenhas L, et al. Larotrectinib for paediatric solid tumours harbouring NTRK gene fusions: phase 1 results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(5):705-714.
18. Desai AV, Brodeur GM, Foster J, et al. Phase 1 study of entrectinib (RXDX-101), a TRK, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor, in children, adolescents, and young adults with recurrent or refractory solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(suppl;):abstr 10536.
19. Heymach J, Krilov L, Alberg A, et al. Clinical cancer advances 2018: annual report on progress against cancer from the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(10):1020-1044.
20. Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. NEJM. 2018;378(5):439-448.
21. Wu J, Fu J, Zhang M, Liu D. Blinatumomab: a bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) antibody against CD19/CD3 for refractory acute lymphoid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:104.
22. Stackelberg Av, Locatelli F, Zugmaier G, et al. Phase I/phase II study of blinatumomab in pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(36):4381-4389.
23. Gokbuget N, Dombret H, Bonifacio M, et al. Blinatumomab for minimal residual disease in adults with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2018;131(14):1522-1531.
24. Fischer J, Paret C, El Malki K, et al. CD19 isoforms enabling resistance to CART-19 immunotherapy are expressed in B-ALL patients at initial diagnosis. J Immunother. 2017;40(5):187-195.
25. Fousek K, Watanabe J, George A, et al. Targeting CD19-negative relapsed B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia using trivalent CAR T cells. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(5_suppl):121-121.
26. Mejstríková E, Hrusak O, Borowitz MJ, et al. CD19-negative relapse of pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia following blinatumomab treatment. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7(12):659.
27. Fry TJ, Shah NN, Orentas RJ, et al. CD22-targeted CAR T cells induce remission in B-ALL that is naive or resistant to CD19-targeted CAR immunotherapy. Nat Med. 2018;24(1):20-28.
28. Pan J, Deng B, Liu S, et al. Efficacy and safety of CD22-directed CAR T-cell therapy in 15 pediatric refractory or relapsed b acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Paper presented at 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association 2018; Stockholm, Sweden.
29. Boyiadzis MM, Kirkwood JM, Marshall JL, Pritchard CC, Azad NS, Gulley JL. Significance and implications of FDA approval of pembrolizumab for biomarker-defined disease. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6:35.
30. Drugs.com. Keytruda approval history. 2018; https://www.drugs.com/history/keytruda.html. Last update information not given. Accessed September 16, 2018.
31. Bristol Myers Squibb press release. US Food and Drug Administration expands approval of Yervoy (ipilimumab) to include pediatric patients 12 years and older with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. https://news.bms.com/press-release/corporatefinancial-news/us-food-and-drug-administration-expands-approval-yervoy-ipilim. Released July 24, 2017. Accessed September 16, 2018.
32. Hills RK, Castaigne S, Appelbaum FR, et al. Addition of gemtuzumab ozogamicin to induction chemotherapy in adult patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(9):986-996.
33. Amadori S, Suciu S, Selleslag D, et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin versus best supportive care in older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia unsuitable for intensive chemotherapy: results of the randomized phase III EORTC-GIMEMA AML-19 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(9):972-979.
34. Taksin AL, Legrand O, Raffoux E, et al. High efficacy and safety profile of fractionated doses of Mylotarg as induction therapy in patients with relapsed acute myeloblastic leukemia: a prospective study of the alfa group. Leukemia. 2007;21(1):66-71.
35. Bhojwani D, Sposto R, Shah N, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin in pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (R/R ALL). J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(15_suppl):10512-10512.
Line complications plague dose-adjusted EPOCH-R in non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R), which is used to treat several types of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas, is associated with high rates of line-associated complications, a new study suggests.
These findings, published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, confirm other recent findings that DA-EPOCH-R has a significantly greater rate of complications, compared with that of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) therapy.
The authors note that the use of DA-EPOCH-R is based on data from early phase trials, as well as retrospective data, that support its use as induction chemotherapy in high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2, and/or BCL6 translocations. But currently, there are no data published from randomized trials that support the use of upfront DA-EPOCH-R therapy.
DA-EPOCH-R is an infusion-based therapy that requires a central venous catheter.
In their study, Rachel J. David, MD, of Wilmot Cancer Institute, Rochester, N.Y., and her colleagues conducted a retrospective study that included all patients treated with DA-EPOCH-R at their institution between March 2011 and July 2016, and also included a concurrent cohort of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who were treated with R-CHOP. The goal was to identify the rates and predictors of line-associated complications linked with the use of DA-EPOCH-R therapy in this population.
The patient cohort comprised 43 patients who received DA-EPOCH-R and 44 patients who received RCHOP.
Patients in the DA-EPOCH-R cohort experienced a significantly higher rate of complications (P =.03), compared with the R-CHOP group.
In the DA-EPOCH-R cohort, 17 patients (39.5%) reported at least one LAC, which included venous thromboembolism, chemotherapy extravasation, and line-associated infection, during the study period. Grade 3 toxicity was observed in 41% of these patients.
In contrast, eight patients (18.2%) in the R-CHOP arm experienced at least one complication, with five of the eight patients experiencing grade 3-4 toxicity.
In a univariate analysis, body mass index of 35 kg/m2 and the use of a peripherally inserted central catheter line were both significantly associated with a higher risk of venous thromboembolism (P = .04 and P = .02, respectively).
“For patients undergoing treatment with DA-EPOCH-R in whom the use of [central venous catheters] cannot be avoided, the morbidity of [line-associated complications] should be factored in by the clinician when determining upfront treatment,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: David RJ et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug 29. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.08.014.
Dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R), which is used to treat several types of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas, is associated with high rates of line-associated complications, a new study suggests.
These findings, published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, confirm other recent findings that DA-EPOCH-R has a significantly greater rate of complications, compared with that of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) therapy.
The authors note that the use of DA-EPOCH-R is based on data from early phase trials, as well as retrospective data, that support its use as induction chemotherapy in high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2, and/or BCL6 translocations. But currently, there are no data published from randomized trials that support the use of upfront DA-EPOCH-R therapy.
DA-EPOCH-R is an infusion-based therapy that requires a central venous catheter.
In their study, Rachel J. David, MD, of Wilmot Cancer Institute, Rochester, N.Y., and her colleagues conducted a retrospective study that included all patients treated with DA-EPOCH-R at their institution between March 2011 and July 2016, and also included a concurrent cohort of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who were treated with R-CHOP. The goal was to identify the rates and predictors of line-associated complications linked with the use of DA-EPOCH-R therapy in this population.
The patient cohort comprised 43 patients who received DA-EPOCH-R and 44 patients who received RCHOP.
Patients in the DA-EPOCH-R cohort experienced a significantly higher rate of complications (P =.03), compared with the R-CHOP group.
In the DA-EPOCH-R cohort, 17 patients (39.5%) reported at least one LAC, which included venous thromboembolism, chemotherapy extravasation, and line-associated infection, during the study period. Grade 3 toxicity was observed in 41% of these patients.
In contrast, eight patients (18.2%) in the R-CHOP arm experienced at least one complication, with five of the eight patients experiencing grade 3-4 toxicity.
In a univariate analysis, body mass index of 35 kg/m2 and the use of a peripherally inserted central catheter line were both significantly associated with a higher risk of venous thromboembolism (P = .04 and P = .02, respectively).
“For patients undergoing treatment with DA-EPOCH-R in whom the use of [central venous catheters] cannot be avoided, the morbidity of [line-associated complications] should be factored in by the clinician when determining upfront treatment,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: David RJ et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug 29. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.08.014.
Dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R), which is used to treat several types of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas, is associated with high rates of line-associated complications, a new study suggests.
These findings, published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, confirm other recent findings that DA-EPOCH-R has a significantly greater rate of complications, compared with that of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) therapy.
The authors note that the use of DA-EPOCH-R is based on data from early phase trials, as well as retrospective data, that support its use as induction chemotherapy in high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2, and/or BCL6 translocations. But currently, there are no data published from randomized trials that support the use of upfront DA-EPOCH-R therapy.
DA-EPOCH-R is an infusion-based therapy that requires a central venous catheter.
In their study, Rachel J. David, MD, of Wilmot Cancer Institute, Rochester, N.Y., and her colleagues conducted a retrospective study that included all patients treated with DA-EPOCH-R at their institution between March 2011 and July 2016, and also included a concurrent cohort of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who were treated with R-CHOP. The goal was to identify the rates and predictors of line-associated complications linked with the use of DA-EPOCH-R therapy in this population.
The patient cohort comprised 43 patients who received DA-EPOCH-R and 44 patients who received RCHOP.
Patients in the DA-EPOCH-R cohort experienced a significantly higher rate of complications (P =.03), compared with the R-CHOP group.
In the DA-EPOCH-R cohort, 17 patients (39.5%) reported at least one LAC, which included venous thromboembolism, chemotherapy extravasation, and line-associated infection, during the study period. Grade 3 toxicity was observed in 41% of these patients.
In contrast, eight patients (18.2%) in the R-CHOP arm experienced at least one complication, with five of the eight patients experiencing grade 3-4 toxicity.
In a univariate analysis, body mass index of 35 kg/m2 and the use of a peripherally inserted central catheter line were both significantly associated with a higher risk of venous thromboembolism (P = .04 and P = .02, respectively).
“For patients undergoing treatment with DA-EPOCH-R in whom the use of [central venous catheters] cannot be avoided, the morbidity of [line-associated complications] should be factored in by the clinician when determining upfront treatment,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: David RJ et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug 29. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.08.014.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: In all, 17 dose-adjusted R-EPOCH patients (39.5%) experienced at least one line-associated complication, versus 8 patients (18.2%) in the R-CHOP group.
Study details: A retrospective single-institution study with 87 patients.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
Source: David RJ et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug 29. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.08.014.
First-line bortezomib prolongs survival in MCL
Bortezomib in combination with rituximab plus chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), compared with standard treatment, according to final results from the international, phase 3 LYM-3002 trial.
After a median follow-up period of 82.0 months, median overall survival was 90.7 months among participants who were given first-line bortezomib in addition to rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) versus 55.7 months in the control arm, where patients were given rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), for a hazard ratio of 0.66 (95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.85; P = .001).
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues also reported that patients in the bortezomib arm experienced two novel adverse effects, which were different from findings reported in the primary analysis. Each case was classified as grade 4; there was one case of gastric cancer and one case of lung adenocarcinoma.
The findings were reported in the Lancet Oncology.
Among 268 patients in the follow-up analysis set, the median age was 66 years and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI). For those considered high risk, no significant difference was noted when comparing the two groups on the basis of overall survival.
“When analyzed according to MIPI risk category, VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved overall survival, compared with R-CHOP in the low-risk and intermediate-risk categories, but not in the high-risk category,” the investigators wrote.
The authors acknowledged a key limitation of the study was that rituximab was not given as a maintenance therapy since it was not considered standard of care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommended that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The study was sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. The authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and others.
SOURCE: Robak T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30685-5.
The proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, represents a “substantial advance” for the treatment of newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma, according to Simon Rule, MD.
In an accompanying commentary, he stated that bortezomib-based VR-CAP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone) showed a clear survival benefit in the LYM-3002 trial, compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP). However, in order to use this combination in elderly patients, the administration method must be considered. Additionally, it makes sense to routinely use rituximab maintenance.
While the final analysis of the LYM-3002 trial is positive, there are caveats to consider before changing practice, particularly for elderly patients. First, the study had a somewhat younger population and fewer high-risk patients, compared with the only similar study of R-CHOP regimen in an elderly population. The bortezomib plus VR-CAP combination also had significant toxicity that could limit its widespread use in elderly patients.
Dr. Rule also noted that, internationally, bendamustine-based therapy is increasingly being chosen over R-CHOP for older patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
“Whether VR-CAP or the combination of bortezomib and bendamustine-based regimens will be the optimal approach has yet to be established. However, if R-CHOP is being considered, then the long-term survival results reported by Robak and colleagues strongly support the use of VR-CAP as an alternative,” Dr. Rule wrote.
Dr. Rule is with the University of Plymouth (England). These comments are adapted from his commentary (Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045[18]30743-5). Dr. Rule reported receiving grants and personal fees from Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
The proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, represents a “substantial advance” for the treatment of newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma, according to Simon Rule, MD.
In an accompanying commentary, he stated that bortezomib-based VR-CAP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone) showed a clear survival benefit in the LYM-3002 trial, compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP). However, in order to use this combination in elderly patients, the administration method must be considered. Additionally, it makes sense to routinely use rituximab maintenance.
While the final analysis of the LYM-3002 trial is positive, there are caveats to consider before changing practice, particularly for elderly patients. First, the study had a somewhat younger population and fewer high-risk patients, compared with the only similar study of R-CHOP regimen in an elderly population. The bortezomib plus VR-CAP combination also had significant toxicity that could limit its widespread use in elderly patients.
Dr. Rule also noted that, internationally, bendamustine-based therapy is increasingly being chosen over R-CHOP for older patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
“Whether VR-CAP or the combination of bortezomib and bendamustine-based regimens will be the optimal approach has yet to be established. However, if R-CHOP is being considered, then the long-term survival results reported by Robak and colleagues strongly support the use of VR-CAP as an alternative,” Dr. Rule wrote.
Dr. Rule is with the University of Plymouth (England). These comments are adapted from his commentary (Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045[18]30743-5). Dr. Rule reported receiving grants and personal fees from Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
The proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, represents a “substantial advance” for the treatment of newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma, according to Simon Rule, MD.
In an accompanying commentary, he stated that bortezomib-based VR-CAP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone) showed a clear survival benefit in the LYM-3002 trial, compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP). However, in order to use this combination in elderly patients, the administration method must be considered. Additionally, it makes sense to routinely use rituximab maintenance.
While the final analysis of the LYM-3002 trial is positive, there are caveats to consider before changing practice, particularly for elderly patients. First, the study had a somewhat younger population and fewer high-risk patients, compared with the only similar study of R-CHOP regimen in an elderly population. The bortezomib plus VR-CAP combination also had significant toxicity that could limit its widespread use in elderly patients.
Dr. Rule also noted that, internationally, bendamustine-based therapy is increasingly being chosen over R-CHOP for older patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
“Whether VR-CAP or the combination of bortezomib and bendamustine-based regimens will be the optimal approach has yet to be established. However, if R-CHOP is being considered, then the long-term survival results reported by Robak and colleagues strongly support the use of VR-CAP as an alternative,” Dr. Rule wrote.
Dr. Rule is with the University of Plymouth (England). These comments are adapted from his commentary (Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045[18]30743-5). Dr. Rule reported receiving grants and personal fees from Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Bortezomib in combination with rituximab plus chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), compared with standard treatment, according to final results from the international, phase 3 LYM-3002 trial.
After a median follow-up period of 82.0 months, median overall survival was 90.7 months among participants who were given first-line bortezomib in addition to rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) versus 55.7 months in the control arm, where patients were given rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), for a hazard ratio of 0.66 (95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.85; P = .001).
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues also reported that patients in the bortezomib arm experienced two novel adverse effects, which were different from findings reported in the primary analysis. Each case was classified as grade 4; there was one case of gastric cancer and one case of lung adenocarcinoma.
The findings were reported in the Lancet Oncology.
Among 268 patients in the follow-up analysis set, the median age was 66 years and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI). For those considered high risk, no significant difference was noted when comparing the two groups on the basis of overall survival.
“When analyzed according to MIPI risk category, VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved overall survival, compared with R-CHOP in the low-risk and intermediate-risk categories, but not in the high-risk category,” the investigators wrote.
The authors acknowledged a key limitation of the study was that rituximab was not given as a maintenance therapy since it was not considered standard of care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommended that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The study was sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. The authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and others.
SOURCE: Robak T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30685-5.
Bortezomib in combination with rituximab plus chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), compared with standard treatment, according to final results from the international, phase 3 LYM-3002 trial.
After a median follow-up period of 82.0 months, median overall survival was 90.7 months among participants who were given first-line bortezomib in addition to rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) versus 55.7 months in the control arm, where patients were given rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), for a hazard ratio of 0.66 (95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.85; P = .001).
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues also reported that patients in the bortezomib arm experienced two novel adverse effects, which were different from findings reported in the primary analysis. Each case was classified as grade 4; there was one case of gastric cancer and one case of lung adenocarcinoma.
The findings were reported in the Lancet Oncology.
Among 268 patients in the follow-up analysis set, the median age was 66 years and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI). For those considered high risk, no significant difference was noted when comparing the two groups on the basis of overall survival.
“When analyzed according to MIPI risk category, VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved overall survival, compared with R-CHOP in the low-risk and intermediate-risk categories, but not in the high-risk category,” the investigators wrote.
The authors acknowledged a key limitation of the study was that rituximab was not given as a maintenance therapy since it was not considered standard of care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommended that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The study was sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. The authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and others.
SOURCE: Robak T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30685-5.
FROM THE LANCET ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Median overall survival was 90.7 months in the intervention arm (bortezomib in addition to rituximab plus chemotherapy) versus 55.7 months in the control arm (hazard ratio, 0.66; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.85; P = .001).
Study details: LYM-3002 was a phase 3, randomized, open-label study of 487 transplant-ineligible patients with untreated mantle cell lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. The authors reported financial ties with Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and others.
Source: Robak T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30685-5.
Combo can prolong overall survival in MCL
Final results of a phase 3 trial suggest bortezomib plus rituximab and chemotherapy can significantly improve overall survival (OS) in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
In the LYM-3002 trial, researchers compared bortezomib plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) to rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP).
The median OS was significantly longer in patients who received VR-CAP than in those who received R-CHOP—90.7 months and 55.7 months, respectively.
This survival benefit was observed in patients with low- and intermediate-risk disease but not high-risk disease.
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues reported these results in The Lancet Oncology alongside a related commentary.
The LYM-3002 trial began more than a decade ago, and initial results were published in 2015. At that time, the VR-CAP group showed a significant increase in progression-free survival compared with the R-CHOP group.
The final analysis of LYM-3002 included 268 of the original 487 MCL patients. Twenty-three percent of patients in the VR-CAP group (n=32) discontinued due to death, as did 40% of patients in the R-CHOP group (n=51). The main cause of death was progression—29% and 14%, respectively.
Among the 268 patients in the final analysis, 140 belonged to the VR-CAP group and 128 to the R-CHOP group. The patients’ median age was 66 (range, 26-83), 71% (n=190) were male, 74% (n=199) had stage IV disease, and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
About half of patients received therapies after the trial interventions (n=255, 52%)—43% (n=104) in the VR-CAP group and 62% (n=151) in the R-CHOP group. Most patients received subsequent antineoplastic therapy—77% (n=80) and 81% (n=123), respectively—and more than half received rituximab as second-line therapy—53% (n=55) and 59% (n=89), respectively.
Results
At a median follow-up of 82.0 months, the median OS was significantly longer in the VR-CAP group than in the R-CHOP group—90.7 months (95% CI, 71.4 to not estimable) and 55.7 months (95% CI, 47.2 to 68.9), respectively (hazard ratio [HR]=0.66 [95% CI, 0.51–0.85]; P=0.001).
The 4-year OS was 67.3% in the VR-CAP group and 54.3% in the R-CHOP group. The 6-year OS was 56.6% and 42.0%, respectively.
The researchers noted that VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved OS among patients in the low-risk and intermediate-risk MIPI categories but not in the high-risk category.
In the low-risk cohort, the median OS was 81.7 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.54 [95% CI, 0.30–0.95]; P≤0.05).
In the intermediate-risk cohort, the median OS was 62.2 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.55 [95% CI, 0.36–0.85]; P≤0.01).
In the high-risk cohort, the median OS was 37.1 months in the R-CHOP group and 30.4 months in the VR-CAP group (HR=1.02 [95% CI, 0.69–1.50]).
The researchers reported three new adverse events in the final analysis—grade 4 lung adenocarcinoma and grade 4 gastric cancer in the VR-CAP group as well as grade 2 pneumonia in the R-CHOP group.
The team acknowledged that a key limitation of this study was that rituximab was not given as maintenance since it was not considered standard care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommend that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The LYM-3002 study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. The study authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and other companies.
Final results of a phase 3 trial suggest bortezomib plus rituximab and chemotherapy can significantly improve overall survival (OS) in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
In the LYM-3002 trial, researchers compared bortezomib plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) to rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP).
The median OS was significantly longer in patients who received VR-CAP than in those who received R-CHOP—90.7 months and 55.7 months, respectively.
This survival benefit was observed in patients with low- and intermediate-risk disease but not high-risk disease.
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues reported these results in The Lancet Oncology alongside a related commentary.
The LYM-3002 trial began more than a decade ago, and initial results were published in 2015. At that time, the VR-CAP group showed a significant increase in progression-free survival compared with the R-CHOP group.
The final analysis of LYM-3002 included 268 of the original 487 MCL patients. Twenty-three percent of patients in the VR-CAP group (n=32) discontinued due to death, as did 40% of patients in the R-CHOP group (n=51). The main cause of death was progression—29% and 14%, respectively.
Among the 268 patients in the final analysis, 140 belonged to the VR-CAP group and 128 to the R-CHOP group. The patients’ median age was 66 (range, 26-83), 71% (n=190) were male, 74% (n=199) had stage IV disease, and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
About half of patients received therapies after the trial interventions (n=255, 52%)—43% (n=104) in the VR-CAP group and 62% (n=151) in the R-CHOP group. Most patients received subsequent antineoplastic therapy—77% (n=80) and 81% (n=123), respectively—and more than half received rituximab as second-line therapy—53% (n=55) and 59% (n=89), respectively.
Results
At a median follow-up of 82.0 months, the median OS was significantly longer in the VR-CAP group than in the R-CHOP group—90.7 months (95% CI, 71.4 to not estimable) and 55.7 months (95% CI, 47.2 to 68.9), respectively (hazard ratio [HR]=0.66 [95% CI, 0.51–0.85]; P=0.001).
The 4-year OS was 67.3% in the VR-CAP group and 54.3% in the R-CHOP group. The 6-year OS was 56.6% and 42.0%, respectively.
The researchers noted that VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved OS among patients in the low-risk and intermediate-risk MIPI categories but not in the high-risk category.
In the low-risk cohort, the median OS was 81.7 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.54 [95% CI, 0.30–0.95]; P≤0.05).
In the intermediate-risk cohort, the median OS was 62.2 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.55 [95% CI, 0.36–0.85]; P≤0.01).
In the high-risk cohort, the median OS was 37.1 months in the R-CHOP group and 30.4 months in the VR-CAP group (HR=1.02 [95% CI, 0.69–1.50]).
The researchers reported three new adverse events in the final analysis—grade 4 lung adenocarcinoma and grade 4 gastric cancer in the VR-CAP group as well as grade 2 pneumonia in the R-CHOP group.
The team acknowledged that a key limitation of this study was that rituximab was not given as maintenance since it was not considered standard care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommend that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The LYM-3002 study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. The study authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and other companies.
Final results of a phase 3 trial suggest bortezomib plus rituximab and chemotherapy can significantly improve overall survival (OS) in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
In the LYM-3002 trial, researchers compared bortezomib plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) to rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP).
The median OS was significantly longer in patients who received VR-CAP than in those who received R-CHOP—90.7 months and 55.7 months, respectively.
This survival benefit was observed in patients with low- and intermediate-risk disease but not high-risk disease.
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues reported these results in The Lancet Oncology alongside a related commentary.
The LYM-3002 trial began more than a decade ago, and initial results were published in 2015. At that time, the VR-CAP group showed a significant increase in progression-free survival compared with the R-CHOP group.
The final analysis of LYM-3002 included 268 of the original 487 MCL patients. Twenty-three percent of patients in the VR-CAP group (n=32) discontinued due to death, as did 40% of patients in the R-CHOP group (n=51). The main cause of death was progression—29% and 14%, respectively.
Among the 268 patients in the final analysis, 140 belonged to the VR-CAP group and 128 to the R-CHOP group. The patients’ median age was 66 (range, 26-83), 71% (n=190) were male, 74% (n=199) had stage IV disease, and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
About half of patients received therapies after the trial interventions (n=255, 52%)—43% (n=104) in the VR-CAP group and 62% (n=151) in the R-CHOP group. Most patients received subsequent antineoplastic therapy—77% (n=80) and 81% (n=123), respectively—and more than half received rituximab as second-line therapy—53% (n=55) and 59% (n=89), respectively.
Results
At a median follow-up of 82.0 months, the median OS was significantly longer in the VR-CAP group than in the R-CHOP group—90.7 months (95% CI, 71.4 to not estimable) and 55.7 months (95% CI, 47.2 to 68.9), respectively (hazard ratio [HR]=0.66 [95% CI, 0.51–0.85]; P=0.001).
The 4-year OS was 67.3% in the VR-CAP group and 54.3% in the R-CHOP group. The 6-year OS was 56.6% and 42.0%, respectively.
The researchers noted that VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved OS among patients in the low-risk and intermediate-risk MIPI categories but not in the high-risk category.
In the low-risk cohort, the median OS was 81.7 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.54 [95% CI, 0.30–0.95]; P≤0.05).
In the intermediate-risk cohort, the median OS was 62.2 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.55 [95% CI, 0.36–0.85]; P≤0.01).
In the high-risk cohort, the median OS was 37.1 months in the R-CHOP group and 30.4 months in the VR-CAP group (HR=1.02 [95% CI, 0.69–1.50]).
The researchers reported three new adverse events in the final analysis—grade 4 lung adenocarcinoma and grade 4 gastric cancer in the VR-CAP group as well as grade 2 pneumonia in the R-CHOP group.
The team acknowledged that a key limitation of this study was that rituximab was not given as maintenance since it was not considered standard care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommend that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The LYM-3002 study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. The study authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and other companies.
Older age predicts mortality after alloHCT in NHL, but not relapse
Elderly patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) are more likely to die, but not relapse, within 1 year of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT), compared with younger or middle-age patients, according to investigators.
Comorbidities also increased risks of nonrelapse mortality (NRM) at 1 year, but to a lesser extent than that of elderly status, reported lead author Charalampia Kyriakou, MD, PhD, of the department of haematology at University College London Hospital and London North West University Healthcare NHS Trust, and her colleagues.
“Although alloHCT is feasible and effective in very old patients, the increased NRM risk must be taken into account when assessing the indication for alloHCT for NHL in this age group,” the investigators wrote in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
This decision is becoming more common, they noted. “With the advent of reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) strategies and other improvements in transplantation technology, alloHCT is being increasingly considered in elderly patients with [relapsed and refractory] NHL.”
The retrospective study analyzed 3,919 patients with NHL who underwent alloHCT between 2003 and 2013. Patients were sorted into three age groups: young (18-50 years), middle age (51-65 years), or elderly (66-77 years).
Disease types also were reported: 1,461 patients had follicular lymphoma (FL; 37%), 1,192 had diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL; 30%), 823 had mantle cell lymphoma (MCL; 21%), and 443 had peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL; 11%).
At the time of alloHCT, about 85% of patients were chemosensitive, with the remainder being chemorefractory. The age groups had similar patient characteristics, with exceptions noted for unrelated donors, MCL, and RIC, which became increasingly overrepresented with age.
The results showed that NRM at 1 year was 13% for young patients, 20% for middle-age patients, and 33% for elderly patients (P less than .001). Overall survival at 3 years followed an inverse trend, decreasing with age from 60% in young patients to 54% in middle-age patients, before dropping more dramatically to 38% in the elderly (P less than .001).
In contrast to these significant associations between age and survival, relapse risk at 3 years remained relatively consistent, with young patients at 30%, middle-age patients at 31%, and elderly patients at 28% (P = .355).
The investigators noted that the risk of NRM increased most dramatically between middle age and old age, with less significant differences between the middle-age and young groups. They suggested that “age per se should have a limited impact on the indication for alloHCT for NHL in patients up to age 65 years.”
The increased risk with elderly status could not be fully explained by comorbidities, although these were more common in elderly patients. After analyzing information from a subset of patients, the investigators concluded that “the presence of comorbidities is a significant risk factor for NRM and survival, but this does not fully explain the outcome disadvantages in our [elderly] group.” Therefore, age remains an independent risk factor.
“The information provided in this cohort of patients with NHL, the largest reported to date, is useful and relevant, especially in the era of evolving therapies,” the investigators wrote. They added that the information is “even more relevant now with the availability of treatment with ... chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells ... after relapse post-alloHCT.”
The investigators reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Kyriakou C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.08.025.
Elderly patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) are more likely to die, but not relapse, within 1 year of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT), compared with younger or middle-age patients, according to investigators.
Comorbidities also increased risks of nonrelapse mortality (NRM) at 1 year, but to a lesser extent than that of elderly status, reported lead author Charalampia Kyriakou, MD, PhD, of the department of haematology at University College London Hospital and London North West University Healthcare NHS Trust, and her colleagues.
“Although alloHCT is feasible and effective in very old patients, the increased NRM risk must be taken into account when assessing the indication for alloHCT for NHL in this age group,” the investigators wrote in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
This decision is becoming more common, they noted. “With the advent of reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) strategies and other improvements in transplantation technology, alloHCT is being increasingly considered in elderly patients with [relapsed and refractory] NHL.”
The retrospective study analyzed 3,919 patients with NHL who underwent alloHCT between 2003 and 2013. Patients were sorted into three age groups: young (18-50 years), middle age (51-65 years), or elderly (66-77 years).
Disease types also were reported: 1,461 patients had follicular lymphoma (FL; 37%), 1,192 had diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL; 30%), 823 had mantle cell lymphoma (MCL; 21%), and 443 had peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL; 11%).
At the time of alloHCT, about 85% of patients were chemosensitive, with the remainder being chemorefractory. The age groups had similar patient characteristics, with exceptions noted for unrelated donors, MCL, and RIC, which became increasingly overrepresented with age.
The results showed that NRM at 1 year was 13% for young patients, 20% for middle-age patients, and 33% for elderly patients (P less than .001). Overall survival at 3 years followed an inverse trend, decreasing with age from 60% in young patients to 54% in middle-age patients, before dropping more dramatically to 38% in the elderly (P less than .001).
In contrast to these significant associations between age and survival, relapse risk at 3 years remained relatively consistent, with young patients at 30%, middle-age patients at 31%, and elderly patients at 28% (P = .355).
The investigators noted that the risk of NRM increased most dramatically between middle age and old age, with less significant differences between the middle-age and young groups. They suggested that “age per se should have a limited impact on the indication for alloHCT for NHL in patients up to age 65 years.”
The increased risk with elderly status could not be fully explained by comorbidities, although these were more common in elderly patients. After analyzing information from a subset of patients, the investigators concluded that “the presence of comorbidities is a significant risk factor for NRM and survival, but this does not fully explain the outcome disadvantages in our [elderly] group.” Therefore, age remains an independent risk factor.
“The information provided in this cohort of patients with NHL, the largest reported to date, is useful and relevant, especially in the era of evolving therapies,” the investigators wrote. They added that the information is “even more relevant now with the availability of treatment with ... chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells ... after relapse post-alloHCT.”
The investigators reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Kyriakou C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.08.025.
Elderly patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) are more likely to die, but not relapse, within 1 year of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT), compared with younger or middle-age patients, according to investigators.
Comorbidities also increased risks of nonrelapse mortality (NRM) at 1 year, but to a lesser extent than that of elderly status, reported lead author Charalampia Kyriakou, MD, PhD, of the department of haematology at University College London Hospital and London North West University Healthcare NHS Trust, and her colleagues.
“Although alloHCT is feasible and effective in very old patients, the increased NRM risk must be taken into account when assessing the indication for alloHCT for NHL in this age group,” the investigators wrote in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
This decision is becoming more common, they noted. “With the advent of reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) strategies and other improvements in transplantation technology, alloHCT is being increasingly considered in elderly patients with [relapsed and refractory] NHL.”
The retrospective study analyzed 3,919 patients with NHL who underwent alloHCT between 2003 and 2013. Patients were sorted into three age groups: young (18-50 years), middle age (51-65 years), or elderly (66-77 years).
Disease types also were reported: 1,461 patients had follicular lymphoma (FL; 37%), 1,192 had diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL; 30%), 823 had mantle cell lymphoma (MCL; 21%), and 443 had peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL; 11%).
At the time of alloHCT, about 85% of patients were chemosensitive, with the remainder being chemorefractory. The age groups had similar patient characteristics, with exceptions noted for unrelated donors, MCL, and RIC, which became increasingly overrepresented with age.
The results showed that NRM at 1 year was 13% for young patients, 20% for middle-age patients, and 33% for elderly patients (P less than .001). Overall survival at 3 years followed an inverse trend, decreasing with age from 60% in young patients to 54% in middle-age patients, before dropping more dramatically to 38% in the elderly (P less than .001).
In contrast to these significant associations between age and survival, relapse risk at 3 years remained relatively consistent, with young patients at 30%, middle-age patients at 31%, and elderly patients at 28% (P = .355).
The investigators noted that the risk of NRM increased most dramatically between middle age and old age, with less significant differences between the middle-age and young groups. They suggested that “age per se should have a limited impact on the indication for alloHCT for NHL in patients up to age 65 years.”
The increased risk with elderly status could not be fully explained by comorbidities, although these were more common in elderly patients. After analyzing information from a subset of patients, the investigators concluded that “the presence of comorbidities is a significant risk factor for NRM and survival, but this does not fully explain the outcome disadvantages in our [elderly] group.” Therefore, age remains an independent risk factor.
“The information provided in this cohort of patients with NHL, the largest reported to date, is useful and relevant, especially in the era of evolving therapies,” the investigators wrote. They added that the information is “even more relevant now with the availability of treatment with ... chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells ... after relapse post-alloHCT.”
The investigators reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Kyriakou C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.08.025.
FROM BIOLOGY OF BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION
Key clinical point:
Major finding: One-year nonrelapse mortality (NRM) was 13% for young patients, 20% for middle-age patients, and 33% for elderly patients (P less than .001).
Study details: A retrospective analysis of 3,919 patients with NHL who underwent alloHCT between 2003 and 2013.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Kyriakou C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.08.025.
Study challenges LVEF assessment before DLBCL treatment
Measuring left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before administering doxorubicin-based chemotherapy doesn’t appear to add clinically meaningful information, according to an analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients.
Current guidelines recommend prescreening with either echocardiography or multiple-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan to identify asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction before administering doxorubicin-containing chemotherapy, since doxorubicin is known for its cardiotoxicity.
But other studies have challenged the usefulness of routine LVEF screening in DLBCL patients.
In the current study, Deborah L. Enns, PhD, and her colleagues at Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle reviewed the medical records of 291 patients diagnosed with DLBCL between 2001 and 2013.
In total, 206 patients with normal LVEF and 8 patients with low LVEF received doxorubicin (P = .006). But while that association appears to support routine prescreening to inform clinical decision making, the link disappeared when the researchers factored out previous cardiac disease (P = .51).
“It is possible that previous [heart failure] may have played a larger role in shaping treatment decisions than did LVEF test results alone,” the researchers wrote. The report is in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Innovations, Quality & Outcomes.
In addition, for patients who had their LVEF measured, the researchers found no difference in posttreatment incidence of heart failure based on whether patients received doxorubicin (7.0%) or did not (6.8%). The same was true for patients with LVEF values of less than 50% before treatment (13% vs. 14%).
The researchers noted that there are several reasons why LVEF prescreening may not be needed before treatment in DLBCL. For instance, DLBCL patients typically receive low cumulative doses of doxorubicin. Also, doxorubicin’s high efficacy in DLBCL should be balanced with the relatively low risk of death from heart failure due to doxorubicin treatment, at around 4% after 5 years for patients without preexisting cardiac conditions.
“We recommend that the policy of routinely performing prescreening LVEF measurements in all patients with DLBCL before administering anthracycline-based chemotherapy treatments be reevaluated,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Enns DL et al. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018 Aug 3;2(3):277-85.
Measuring left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before administering doxorubicin-based chemotherapy doesn’t appear to add clinically meaningful information, according to an analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients.
Current guidelines recommend prescreening with either echocardiography or multiple-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan to identify asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction before administering doxorubicin-containing chemotherapy, since doxorubicin is known for its cardiotoxicity.
But other studies have challenged the usefulness of routine LVEF screening in DLBCL patients.
In the current study, Deborah L. Enns, PhD, and her colleagues at Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle reviewed the medical records of 291 patients diagnosed with DLBCL between 2001 and 2013.
In total, 206 patients with normal LVEF and 8 patients with low LVEF received doxorubicin (P = .006). But while that association appears to support routine prescreening to inform clinical decision making, the link disappeared when the researchers factored out previous cardiac disease (P = .51).
“It is possible that previous [heart failure] may have played a larger role in shaping treatment decisions than did LVEF test results alone,” the researchers wrote. The report is in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Innovations, Quality & Outcomes.
In addition, for patients who had their LVEF measured, the researchers found no difference in posttreatment incidence of heart failure based on whether patients received doxorubicin (7.0%) or did not (6.8%). The same was true for patients with LVEF values of less than 50% before treatment (13% vs. 14%).
The researchers noted that there are several reasons why LVEF prescreening may not be needed before treatment in DLBCL. For instance, DLBCL patients typically receive low cumulative doses of doxorubicin. Also, doxorubicin’s high efficacy in DLBCL should be balanced with the relatively low risk of death from heart failure due to doxorubicin treatment, at around 4% after 5 years for patients without preexisting cardiac conditions.
“We recommend that the policy of routinely performing prescreening LVEF measurements in all patients with DLBCL before administering anthracycline-based chemotherapy treatments be reevaluated,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Enns DL et al. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018 Aug 3;2(3):277-85.
Measuring left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before administering doxorubicin-based chemotherapy doesn’t appear to add clinically meaningful information, according to an analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients.
Current guidelines recommend prescreening with either echocardiography or multiple-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan to identify asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction before administering doxorubicin-containing chemotherapy, since doxorubicin is known for its cardiotoxicity.
But other studies have challenged the usefulness of routine LVEF screening in DLBCL patients.
In the current study, Deborah L. Enns, PhD, and her colleagues at Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle reviewed the medical records of 291 patients diagnosed with DLBCL between 2001 and 2013.
In total, 206 patients with normal LVEF and 8 patients with low LVEF received doxorubicin (P = .006). But while that association appears to support routine prescreening to inform clinical decision making, the link disappeared when the researchers factored out previous cardiac disease (P = .51).
“It is possible that previous [heart failure] may have played a larger role in shaping treatment decisions than did LVEF test results alone,” the researchers wrote. The report is in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Innovations, Quality & Outcomes.
In addition, for patients who had their LVEF measured, the researchers found no difference in posttreatment incidence of heart failure based on whether patients received doxorubicin (7.0%) or did not (6.8%). The same was true for patients with LVEF values of less than 50% before treatment (13% vs. 14%).
The researchers noted that there are several reasons why LVEF prescreening may not be needed before treatment in DLBCL. For instance, DLBCL patients typically receive low cumulative doses of doxorubicin. Also, doxorubicin’s high efficacy in DLBCL should be balanced with the relatively low risk of death from heart failure due to doxorubicin treatment, at around 4% after 5 years for patients without preexisting cardiac conditions.
“We recommend that the policy of routinely performing prescreening LVEF measurements in all patients with DLBCL before administering anthracycline-based chemotherapy treatments be reevaluated,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Enns DL et al. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018 Aug 3;2(3):277-85.
FROM MAYO CLINIC PROCEEDINGS: INNOVATIONS, QUALITY & OUTCOMES
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Among diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients who had LVEF measured, the incidence of heart failure post treatment did not differ between patients who received doxorubicin and those who did not (P = 1.0).
Study details: A retrospective analysis of 291 patients diagnosed with DLBCL between 2001 and 2013.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no competing interests.
Source: Enns DL et al. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018 Aug 3;2(3):277-85.
Ibrutinib discontinuation harms survival in CLL
Discontinuing ibrutinib therapy because of disease progression was associated with worse survival, according to a real-world study of ibrutinib dosing in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients.
Researchers at the University of Rochester Wilmot Cancer Institute in New York, who performed the single-center study, also found that optimal dosing early on in treatment has a significant impact on disease progression.
“Treating physicians need to be aware of these outcomes when initiating therapy on patients with high-risk CLL or lymphoma, as well as those with significant comorbidities or immune deficiencies,” AnnaLynn M. Williams. MS, and her colleagues reported in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
The researchers examined the impact of ibrutinib discontinuation and dose adherence on overall and progression-free survival in 170 patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma and CLL treated with the drug at the Wilmot Cancer Institute between Jan. 1, 2014, and Dec. 1, 2016.
The study comprised 115 patients with CLL, 23 patients with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, 21 patients with mantle cell lymphoma, and 11 patients with other non-Hodgkin lymphomas. The median age of patients who started ibrutinib was 68 years, and the median treatment duration was 14.3 months. About a third of patients were taking ibrutinib as a first-line treatment.
Overall, 51 patients (30%) permanently discontinued ibrutinib during the study period, with more than half of the discontinuations stemming from adverse events or comorbidities. About 35% of the discontinuations were due to disease progression.
Median overall survival after discontinuation due to disease progression was 1.7 months. When patients discontinued for other reasons, median overall survival was not reached, compared with stopping for disease progression (P = .0008).
The researchers reported that among patients who discontinued for nonprogression reasons, 67% were alive after 1 year. Among CLL patients, 80% were alive after 1 year.
Among 20 patients who had a dose adherence of less than 80% in the first 8 weeks, the researchers found worse progression-free survival (P = .002) and overall survival (P = .021). Among CLL patients only, progression-free survival was significantly worse (P = .043) but overall survival was not (P = .816).
The study also included five patients who reduced their ibrutinib dose in the first 8 weeks – down to 280 mg in two patients, 140 mg in two patients, and 420 mg in one patient. Again, the researchers observed worse progression-free survival (P = .004) and overall survival (P = .014), compared with patients who maintained their dosing level.
Interrupting ibrutinib dosing had an impact on survival but not as much as discontinuation. Among 10 patients who interrupted therapy for more than a week and then restarted, progression-free survival was worse, compared with those who stayed on treatment continuously (P = .047), but overall survival was not significantly worse (P = .577).
“This would suggest that the ideal treatment strategy would be to recommend initiation of therapy at standard dosing and interruption as needed as directed in the [Food and Drug Administration] label,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and the Cadregari Endowment Fund. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Williams AM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.10.005.
Discontinuing ibrutinib therapy because of disease progression was associated with worse survival, according to a real-world study of ibrutinib dosing in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients.
Researchers at the University of Rochester Wilmot Cancer Institute in New York, who performed the single-center study, also found that optimal dosing early on in treatment has a significant impact on disease progression.
“Treating physicians need to be aware of these outcomes when initiating therapy on patients with high-risk CLL or lymphoma, as well as those with significant comorbidities or immune deficiencies,” AnnaLynn M. Williams. MS, and her colleagues reported in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
The researchers examined the impact of ibrutinib discontinuation and dose adherence on overall and progression-free survival in 170 patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma and CLL treated with the drug at the Wilmot Cancer Institute between Jan. 1, 2014, and Dec. 1, 2016.
The study comprised 115 patients with CLL, 23 patients with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, 21 patients with mantle cell lymphoma, and 11 patients with other non-Hodgkin lymphomas. The median age of patients who started ibrutinib was 68 years, and the median treatment duration was 14.3 months. About a third of patients were taking ibrutinib as a first-line treatment.
Overall, 51 patients (30%) permanently discontinued ibrutinib during the study period, with more than half of the discontinuations stemming from adverse events or comorbidities. About 35% of the discontinuations were due to disease progression.
Median overall survival after discontinuation due to disease progression was 1.7 months. When patients discontinued for other reasons, median overall survival was not reached, compared with stopping for disease progression (P = .0008).
The researchers reported that among patients who discontinued for nonprogression reasons, 67% were alive after 1 year. Among CLL patients, 80% were alive after 1 year.
Among 20 patients who had a dose adherence of less than 80% in the first 8 weeks, the researchers found worse progression-free survival (P = .002) and overall survival (P = .021). Among CLL patients only, progression-free survival was significantly worse (P = .043) but overall survival was not (P = .816).
The study also included five patients who reduced their ibrutinib dose in the first 8 weeks – down to 280 mg in two patients, 140 mg in two patients, and 420 mg in one patient. Again, the researchers observed worse progression-free survival (P = .004) and overall survival (P = .014), compared with patients who maintained their dosing level.
Interrupting ibrutinib dosing had an impact on survival but not as much as discontinuation. Among 10 patients who interrupted therapy for more than a week and then restarted, progression-free survival was worse, compared with those who stayed on treatment continuously (P = .047), but overall survival was not significantly worse (P = .577).
“This would suggest that the ideal treatment strategy would be to recommend initiation of therapy at standard dosing and interruption as needed as directed in the [Food and Drug Administration] label,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and the Cadregari Endowment Fund. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Williams AM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.10.005.
Discontinuing ibrutinib therapy because of disease progression was associated with worse survival, according to a real-world study of ibrutinib dosing in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients.
Researchers at the University of Rochester Wilmot Cancer Institute in New York, who performed the single-center study, also found that optimal dosing early on in treatment has a significant impact on disease progression.
“Treating physicians need to be aware of these outcomes when initiating therapy on patients with high-risk CLL or lymphoma, as well as those with significant comorbidities or immune deficiencies,” AnnaLynn M. Williams. MS, and her colleagues reported in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
The researchers examined the impact of ibrutinib discontinuation and dose adherence on overall and progression-free survival in 170 patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma and CLL treated with the drug at the Wilmot Cancer Institute between Jan. 1, 2014, and Dec. 1, 2016.
The study comprised 115 patients with CLL, 23 patients with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, 21 patients with mantle cell lymphoma, and 11 patients with other non-Hodgkin lymphomas. The median age of patients who started ibrutinib was 68 years, and the median treatment duration was 14.3 months. About a third of patients were taking ibrutinib as a first-line treatment.
Overall, 51 patients (30%) permanently discontinued ibrutinib during the study period, with more than half of the discontinuations stemming from adverse events or comorbidities. About 35% of the discontinuations were due to disease progression.
Median overall survival after discontinuation due to disease progression was 1.7 months. When patients discontinued for other reasons, median overall survival was not reached, compared with stopping for disease progression (P = .0008).
The researchers reported that among patients who discontinued for nonprogression reasons, 67% were alive after 1 year. Among CLL patients, 80% were alive after 1 year.
Among 20 patients who had a dose adherence of less than 80% in the first 8 weeks, the researchers found worse progression-free survival (P = .002) and overall survival (P = .021). Among CLL patients only, progression-free survival was significantly worse (P = .043) but overall survival was not (P = .816).
The study also included five patients who reduced their ibrutinib dose in the first 8 weeks – down to 280 mg in two patients, 140 mg in two patients, and 420 mg in one patient. Again, the researchers observed worse progression-free survival (P = .004) and overall survival (P = .014), compared with patients who maintained their dosing level.
Interrupting ibrutinib dosing had an impact on survival but not as much as discontinuation. Among 10 patients who interrupted therapy for more than a week and then restarted, progression-free survival was worse, compared with those who stayed on treatment continuously (P = .047), but overall survival was not significantly worse (P = .577).
“This would suggest that the ideal treatment strategy would be to recommend initiation of therapy at standard dosing and interruption as needed as directed in the [Food and Drug Administration] label,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and the Cadregari Endowment Fund. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Williams AM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.10.005.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA AND LEUKEMIA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Median overall survival after discontinuation of ibrutinib due to disease progression was 1.7 months.
Study details: A single-institution study of 170 patients with CLL or non-Hodgkin lymphoma who were taking ibrutinib.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and the Cadregari Endowment Fund. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
Source: Williams AM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.10.005.
Entospletinib falls short in relapsed/refractory DLBCL
Entospletinib, a selective inhibitor of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk), showed a dismal rate of progression-free survival and a high rate of adverse events in a cohort of previously treated patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Entospletinib was evaluated in an open-label, single-agent, phase 2 trial (NCT01799889) with five relapsed/refractory patient cohorts: chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), follicular lymphoma, other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphomas, mantle cell lymphoma, and DLBCL.
John M. Burke, MD, of Rocky Mountain Cancer Centers in Aurora, Colo., and his colleagues reported on the current analysis, which looked specifically at the 43 patients in the trial with previously treated DLBCL. Patients received at least one starting dose of 800 mg of entospletinib orally twice daily. The findings were published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
In a previous report on the relapsed/refractory CLL cohort, the investigational agent demonstrated clinical activity with acceptable toxicity (Blood. 2015 Apr 9;125[15]:2336-43).
In the current report, the rate of progression-free survival (PFS) at 16 weeks was 3.6% and the median PFS was 1.5 months. None of the patients in the study achieved a complete or partial response to treatment, and just five patients had stable disease.
All patients in the study eventually discontinued treatment and the median treatment duration was 1 month.
“The lack of activity of Syk inhibition in patients with relapsed DLBCL is in contrast to what would have been expected from preclinical data,” the investigators wrote. “Although it is unclear why entospletinib monotherapy lacked activity in the present study, it is possible that resistance to Syk inhibition played a role. Potential mechanisms of resistance of DLBCL to Syk inhibition include transcriptional upregulation of Syk mediated by FOXO1 and PTEN depletion.”
The investigators said that Syk inhibition in combination with BCL2 inhibitors could potentially overcome this resistance. Another approach, they suggested, would be to offer entospletinib in combination with Janus kinase (JAK) 1/3 inhibition.
“Based on results of the preclinical data, the efficacy of entospletinib in combination will be evaluated in future clinical trials,” the investigators wrote.
The rate of adverse events was high in the DLBCL cohort. Forty-two patients (98%) experienced an adverse event and nearly three-quarters experienced a grade 3 event. Overall, 30% of the grade 3 adverse events were related to treatment. More than 40% of patients interrupted treatment because of adverse events, and 19% discontinued. Four patients experienced an adverse event that led to death.
While the lack of clinical activity may have surprised investigators, the safety profile was in line with other patient cohorts in the phase 2 study. In the CLL and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma cohorts, the rates of treatment interruption were 45% and 54%, respectively.
The study was supported by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Burke reported relationships with Gilead and other companies.
SOURCE: Burke JM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug;18(8):e327-e331.
Entospletinib, a selective inhibitor of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk), showed a dismal rate of progression-free survival and a high rate of adverse events in a cohort of previously treated patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Entospletinib was evaluated in an open-label, single-agent, phase 2 trial (NCT01799889) with five relapsed/refractory patient cohorts: chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), follicular lymphoma, other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphomas, mantle cell lymphoma, and DLBCL.
John M. Burke, MD, of Rocky Mountain Cancer Centers in Aurora, Colo., and his colleagues reported on the current analysis, which looked specifically at the 43 patients in the trial with previously treated DLBCL. Patients received at least one starting dose of 800 mg of entospletinib orally twice daily. The findings were published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
In a previous report on the relapsed/refractory CLL cohort, the investigational agent demonstrated clinical activity with acceptable toxicity (Blood. 2015 Apr 9;125[15]:2336-43).
In the current report, the rate of progression-free survival (PFS) at 16 weeks was 3.6% and the median PFS was 1.5 months. None of the patients in the study achieved a complete or partial response to treatment, and just five patients had stable disease.
All patients in the study eventually discontinued treatment and the median treatment duration was 1 month.
“The lack of activity of Syk inhibition in patients with relapsed DLBCL is in contrast to what would have been expected from preclinical data,” the investigators wrote. “Although it is unclear why entospletinib monotherapy lacked activity in the present study, it is possible that resistance to Syk inhibition played a role. Potential mechanisms of resistance of DLBCL to Syk inhibition include transcriptional upregulation of Syk mediated by FOXO1 and PTEN depletion.”
The investigators said that Syk inhibition in combination with BCL2 inhibitors could potentially overcome this resistance. Another approach, they suggested, would be to offer entospletinib in combination with Janus kinase (JAK) 1/3 inhibition.
“Based on results of the preclinical data, the efficacy of entospletinib in combination will be evaluated in future clinical trials,” the investigators wrote.
The rate of adverse events was high in the DLBCL cohort. Forty-two patients (98%) experienced an adverse event and nearly three-quarters experienced a grade 3 event. Overall, 30% of the grade 3 adverse events were related to treatment. More than 40% of patients interrupted treatment because of adverse events, and 19% discontinued. Four patients experienced an adverse event that led to death.
While the lack of clinical activity may have surprised investigators, the safety profile was in line with other patient cohorts in the phase 2 study. In the CLL and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma cohorts, the rates of treatment interruption were 45% and 54%, respectively.
The study was supported by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Burke reported relationships with Gilead and other companies.
SOURCE: Burke JM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug;18(8):e327-e331.
Entospletinib, a selective inhibitor of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk), showed a dismal rate of progression-free survival and a high rate of adverse events in a cohort of previously treated patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Entospletinib was evaluated in an open-label, single-agent, phase 2 trial (NCT01799889) with five relapsed/refractory patient cohorts: chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), follicular lymphoma, other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphomas, mantle cell lymphoma, and DLBCL.
John M. Burke, MD, of Rocky Mountain Cancer Centers in Aurora, Colo., and his colleagues reported on the current analysis, which looked specifically at the 43 patients in the trial with previously treated DLBCL. Patients received at least one starting dose of 800 mg of entospletinib orally twice daily. The findings were published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
In a previous report on the relapsed/refractory CLL cohort, the investigational agent demonstrated clinical activity with acceptable toxicity (Blood. 2015 Apr 9;125[15]:2336-43).
In the current report, the rate of progression-free survival (PFS) at 16 weeks was 3.6% and the median PFS was 1.5 months. None of the patients in the study achieved a complete or partial response to treatment, and just five patients had stable disease.
All patients in the study eventually discontinued treatment and the median treatment duration was 1 month.
“The lack of activity of Syk inhibition in patients with relapsed DLBCL is in contrast to what would have been expected from preclinical data,” the investigators wrote. “Although it is unclear why entospletinib monotherapy lacked activity in the present study, it is possible that resistance to Syk inhibition played a role. Potential mechanisms of resistance of DLBCL to Syk inhibition include transcriptional upregulation of Syk mediated by FOXO1 and PTEN depletion.”
The investigators said that Syk inhibition in combination with BCL2 inhibitors could potentially overcome this resistance. Another approach, they suggested, would be to offer entospletinib in combination with Janus kinase (JAK) 1/3 inhibition.
“Based on results of the preclinical data, the efficacy of entospletinib in combination will be evaluated in future clinical trials,” the investigators wrote.
The rate of adverse events was high in the DLBCL cohort. Forty-two patients (98%) experienced an adverse event and nearly three-quarters experienced a grade 3 event. Overall, 30% of the grade 3 adverse events were related to treatment. More than 40% of patients interrupted treatment because of adverse events, and 19% discontinued. Four patients experienced an adverse event that led to death.
While the lack of clinical activity may have surprised investigators, the safety profile was in line with other patient cohorts in the phase 2 study. In the CLL and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma cohorts, the rates of treatment interruption were 45% and 54%, respectively.
The study was supported by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Burke reported relationships with Gilead and other companies.
SOURCE: Burke JM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug;18(8):e327-e331.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The rate of progression-free survival at 16 weeks was 3.6% with a median PFS of 1.5 months.
Study details: An analysis of 43 relapsed/refractory DLBCL patients who received single-agent entospletinib.
Disclosures: The study was supported by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Burke reported relationships with Gilead and other companies.
Source: Burke JM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug;18(8):e327-e331.