User login
VALOR: Baby step forward or misstep in AML?
SAN FRANCISCO – Adding vosaroxin to cytarabine chemotherapy increased overall survival in first relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia in the phase III VALOR study.
The difference in this primary endpoint, however, failed to achieve statistically significance (median 7.5 months vs. 6.1 months; P = .06), lead study author Dr. Farhad Ravandi reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
More patients receiving vosaroxin (Qinprezo) and cytarabine than cytarabine alone achieved complete remission (CR) (30.1% vs. 16.3%; P < .0001).
The benefit was significant across all subgroups (age at least 60 years, refractory disease, early and late relapse), except in those aged younger than 60 years, he said.
Vosaroxin is an investigational, first-in-class anticancer quinolone derivative that was granted fast track designation by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for the potential treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in combination with cytarabine.
Despite missing its primary endpoint, Dr. Ravandi argued during a press briefing that VALOR was a positive trial and that the survival benefit with combination vosaroxin was “highly significant.” He described relapsed/refractory AML as the equivalent of metastatic cancer, with patients presenting with disease “all over their body, right from day 1.”
“In solid tumors, we are excited about a 1- or 2-month survival improvement and I don’t see why we shouldn’t be excited in AML as well,” said Dr. Ravandi of the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
He suggested that the bar has been set high in AML because about 40% of patients are cured and that great leaps forward remain rare. “We should not discount the small steps forward in treating our patients and providing better treatment options,” he said.
Press briefing moderator Dr. David Steensma of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, agreed that change is often incremental in AML but countered that the magnitude of benefit wasn’t great.
“AML is a really difficult population, no question about it, but there’s also no question that seven and a half months is pretty crummy and we need to do better than that,” Dr. Steensma said.
VALOR randomly assigned 711 adult patients from 124 sites in 15 countries to IV cytarabine 1 g/m² on days 1-5 plus placebo or IV vosaroxin 90 mg/m² on days 1 and 4 for induction and 70 mg/m² for subsequent cycles. Patients had AML refractory to initial induction therapy or were in first relapse, defined as relapse within 90 days to 24 months after first CR or CR with incomplete platelet recovery.
In all, 30.1% of patients in the vosaroxin group and 29% in the placebo group underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation (ASCT). In those younger than 60 years, rates were 46.2% and 45.4%.
When stratified by age, there was a significant overall survival benefit with the vosaroxin combination for patients aged 60 years and older, who accounted for two-thirds of the study population (median 7.1 months vs. 5.0 months; hazard ratio, 0.75; P = .003), Dr. Ravandi said.
There was no survival advantage in patients younger than 60 years (median 9.1 months vs. 7.9 months; HR, 1.08, P = .60).
In a preplanned analysis censored for ASCT, median overall survival was significantly better in patients receiving the vosaroxin combination versus cytarabine alone (6.7 months vs. 5.3 months; HR, 0.83; P = .02).
“The benefit may be underestimated by the high rate of [ASCT], particularly in the younger patients,” Dr. Ravandi concluded during the formal presentation of the late-breaking abstract. “These data support the use of vosaroxin in combination with cytarabine as a new standard for salvage therapy in older patients with relapsed or refractory AML.”
During the discussion following the presentation, session comoderator Dr. Jonathan Friedberg of the University of Rochester Medical Center in Rochester, N.Y., asked, “How do you reconcile the observation that the patients you wanted to get to transplant got there, and yet you’re blaming the transplant for poor outcomes?”
Dr. Ravandi responded that transplantation is an issue in all AML studies and that a much larger study would have been needed to show a survival difference regardless of transplant status.
Treatment-related adverse events were more common in patients on vosaroxin and were mostly infection related. Stomatitis was identified as a dose-limiting toxicity in previous studies and occurred at any grade in 49% of vosaroxin patients and 19% of controls and at grade 3/4 in 15% and 3%.
Other notable grade 3/4 events were febrile neutropenia (47% vs. 33%) and thrombocytopenia (24% vs. 25%). This increase in toxicity did not translate into worse all-cause mortality at either 30 or 60 days, Dr. Ravandi said.
Sunesis Pharmaceuticals funded the study. Dr. Ravandi and several coauthors reported financial ties with Sunesis. Dr Steensma reported financial ties with several companies. Dr. Friedberg reported no disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – Adding vosaroxin to cytarabine chemotherapy increased overall survival in first relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia in the phase III VALOR study.
The difference in this primary endpoint, however, failed to achieve statistically significance (median 7.5 months vs. 6.1 months; P = .06), lead study author Dr. Farhad Ravandi reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
More patients receiving vosaroxin (Qinprezo) and cytarabine than cytarabine alone achieved complete remission (CR) (30.1% vs. 16.3%; P < .0001).
The benefit was significant across all subgroups (age at least 60 years, refractory disease, early and late relapse), except in those aged younger than 60 years, he said.
Vosaroxin is an investigational, first-in-class anticancer quinolone derivative that was granted fast track designation by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for the potential treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in combination with cytarabine.
Despite missing its primary endpoint, Dr. Ravandi argued during a press briefing that VALOR was a positive trial and that the survival benefit with combination vosaroxin was “highly significant.” He described relapsed/refractory AML as the equivalent of metastatic cancer, with patients presenting with disease “all over their body, right from day 1.”
“In solid tumors, we are excited about a 1- or 2-month survival improvement and I don’t see why we shouldn’t be excited in AML as well,” said Dr. Ravandi of the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
He suggested that the bar has been set high in AML because about 40% of patients are cured and that great leaps forward remain rare. “We should not discount the small steps forward in treating our patients and providing better treatment options,” he said.
Press briefing moderator Dr. David Steensma of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, agreed that change is often incremental in AML but countered that the magnitude of benefit wasn’t great.
“AML is a really difficult population, no question about it, but there’s also no question that seven and a half months is pretty crummy and we need to do better than that,” Dr. Steensma said.
VALOR randomly assigned 711 adult patients from 124 sites in 15 countries to IV cytarabine 1 g/m² on days 1-5 plus placebo or IV vosaroxin 90 mg/m² on days 1 and 4 for induction and 70 mg/m² for subsequent cycles. Patients had AML refractory to initial induction therapy or were in first relapse, defined as relapse within 90 days to 24 months after first CR or CR with incomplete platelet recovery.
In all, 30.1% of patients in the vosaroxin group and 29% in the placebo group underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation (ASCT). In those younger than 60 years, rates were 46.2% and 45.4%.
When stratified by age, there was a significant overall survival benefit with the vosaroxin combination for patients aged 60 years and older, who accounted for two-thirds of the study population (median 7.1 months vs. 5.0 months; hazard ratio, 0.75; P = .003), Dr. Ravandi said.
There was no survival advantage in patients younger than 60 years (median 9.1 months vs. 7.9 months; HR, 1.08, P = .60).
In a preplanned analysis censored for ASCT, median overall survival was significantly better in patients receiving the vosaroxin combination versus cytarabine alone (6.7 months vs. 5.3 months; HR, 0.83; P = .02).
“The benefit may be underestimated by the high rate of [ASCT], particularly in the younger patients,” Dr. Ravandi concluded during the formal presentation of the late-breaking abstract. “These data support the use of vosaroxin in combination with cytarabine as a new standard for salvage therapy in older patients with relapsed or refractory AML.”
During the discussion following the presentation, session comoderator Dr. Jonathan Friedberg of the University of Rochester Medical Center in Rochester, N.Y., asked, “How do you reconcile the observation that the patients you wanted to get to transplant got there, and yet you’re blaming the transplant for poor outcomes?”
Dr. Ravandi responded that transplantation is an issue in all AML studies and that a much larger study would have been needed to show a survival difference regardless of transplant status.
Treatment-related adverse events were more common in patients on vosaroxin and were mostly infection related. Stomatitis was identified as a dose-limiting toxicity in previous studies and occurred at any grade in 49% of vosaroxin patients and 19% of controls and at grade 3/4 in 15% and 3%.
Other notable grade 3/4 events were febrile neutropenia (47% vs. 33%) and thrombocytopenia (24% vs. 25%). This increase in toxicity did not translate into worse all-cause mortality at either 30 or 60 days, Dr. Ravandi said.
Sunesis Pharmaceuticals funded the study. Dr. Ravandi and several coauthors reported financial ties with Sunesis. Dr Steensma reported financial ties with several companies. Dr. Friedberg reported no disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – Adding vosaroxin to cytarabine chemotherapy increased overall survival in first relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia in the phase III VALOR study.
The difference in this primary endpoint, however, failed to achieve statistically significance (median 7.5 months vs. 6.1 months; P = .06), lead study author Dr. Farhad Ravandi reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
More patients receiving vosaroxin (Qinprezo) and cytarabine than cytarabine alone achieved complete remission (CR) (30.1% vs. 16.3%; P < .0001).
The benefit was significant across all subgroups (age at least 60 years, refractory disease, early and late relapse), except in those aged younger than 60 years, he said.
Vosaroxin is an investigational, first-in-class anticancer quinolone derivative that was granted fast track designation by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for the potential treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in combination with cytarabine.
Despite missing its primary endpoint, Dr. Ravandi argued during a press briefing that VALOR was a positive trial and that the survival benefit with combination vosaroxin was “highly significant.” He described relapsed/refractory AML as the equivalent of metastatic cancer, with patients presenting with disease “all over their body, right from day 1.”
“In solid tumors, we are excited about a 1- or 2-month survival improvement and I don’t see why we shouldn’t be excited in AML as well,” said Dr. Ravandi of the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
He suggested that the bar has been set high in AML because about 40% of patients are cured and that great leaps forward remain rare. “We should not discount the small steps forward in treating our patients and providing better treatment options,” he said.
Press briefing moderator Dr. David Steensma of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, agreed that change is often incremental in AML but countered that the magnitude of benefit wasn’t great.
“AML is a really difficult population, no question about it, but there’s also no question that seven and a half months is pretty crummy and we need to do better than that,” Dr. Steensma said.
VALOR randomly assigned 711 adult patients from 124 sites in 15 countries to IV cytarabine 1 g/m² on days 1-5 plus placebo or IV vosaroxin 90 mg/m² on days 1 and 4 for induction and 70 mg/m² for subsequent cycles. Patients had AML refractory to initial induction therapy or were in first relapse, defined as relapse within 90 days to 24 months after first CR or CR with incomplete platelet recovery.
In all, 30.1% of patients in the vosaroxin group and 29% in the placebo group underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation (ASCT). In those younger than 60 years, rates were 46.2% and 45.4%.
When stratified by age, there was a significant overall survival benefit with the vosaroxin combination for patients aged 60 years and older, who accounted for two-thirds of the study population (median 7.1 months vs. 5.0 months; hazard ratio, 0.75; P = .003), Dr. Ravandi said.
There was no survival advantage in patients younger than 60 years (median 9.1 months vs. 7.9 months; HR, 1.08, P = .60).
In a preplanned analysis censored for ASCT, median overall survival was significantly better in patients receiving the vosaroxin combination versus cytarabine alone (6.7 months vs. 5.3 months; HR, 0.83; P = .02).
“The benefit may be underestimated by the high rate of [ASCT], particularly in the younger patients,” Dr. Ravandi concluded during the formal presentation of the late-breaking abstract. “These data support the use of vosaroxin in combination with cytarabine as a new standard for salvage therapy in older patients with relapsed or refractory AML.”
During the discussion following the presentation, session comoderator Dr. Jonathan Friedberg of the University of Rochester Medical Center in Rochester, N.Y., asked, “How do you reconcile the observation that the patients you wanted to get to transplant got there, and yet you’re blaming the transplant for poor outcomes?”
Dr. Ravandi responded that transplantation is an issue in all AML studies and that a much larger study would have been needed to show a survival difference regardless of transplant status.
Treatment-related adverse events were more common in patients on vosaroxin and were mostly infection related. Stomatitis was identified as a dose-limiting toxicity in previous studies and occurred at any grade in 49% of vosaroxin patients and 19% of controls and at grade 3/4 in 15% and 3%.
Other notable grade 3/4 events were febrile neutropenia (47% vs. 33%) and thrombocytopenia (24% vs. 25%). This increase in toxicity did not translate into worse all-cause mortality at either 30 or 60 days, Dr. Ravandi said.
Sunesis Pharmaceuticals funded the study. Dr. Ravandi and several coauthors reported financial ties with Sunesis. Dr Steensma reported financial ties with several companies. Dr. Friedberg reported no disclosures.
AT ASH 2014
Key clinical point: Vosaroxin plus cytarabine failed to significantly improve overall survival in relapsed or refractory AML, but may offer older patients a new option.
Major finding: Median overall survival was 7.5 months for vosaroxin plus cytarabine vs. 6.1 months for cytarabine alone (HR, 0.865; P = .06).
Data source: Randomized, phase III trial in 711 patients with first relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia.
Disclosures: Sunesis Pharmaceuticals funded the study. Dr. Ravandi and several coauthors reported financial ties with Sunesis. Dr Steensma reported financial ties with several companies. Dr. Friedberg reported no disclosures.
Brentuximab changes landscape for post-transplant Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients
SAN FRANCISCO – Early post-transplant brentuximab vedotin dramatically slows Hodgkin’s lymphoma progression in patients at high risk for relapse or progression, the phase III AETHERA study shows.
After a median follow-up of about 28 months, the primary end point of progression-free survival (PFS) per independent review increased from a median of 24 months with placebo and best supportive care (BSC) to 43 months with brentuximab and BSC (Hazard ratio, 0.57; P = .001).
Per investigator assessment, median PFS was 16 months with placebo and had not been reached with brentuximab (HR, 0.50),Dr. Craig Moskowitz reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The benefit of brentuximab maintenance was consistent across every subgroup. Historically, roughly half of patients who undergo an autologous stem cell transplant will relapse.
“Once this study is published, in patients who met eligibility criteria to be on this study - and once again I’ll remind you that’s remission duration less than one year, disease outside the lymph node system, or primary refractory disease - in my opinion, this will be the standard of care,” Dr. Moskowitz said during a press briefing.
Brentuximab, an anti-CD30 antibody conjugate, is already approved in the U.S. for the management of Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) after failure of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) or at least two prior lines of multi-agent chemotherapy in patients ineligible for ASCT.
Brentuximab is also indicated for systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma after failure of at least one multi-agent chemotherapy regimen.
In September it was announced that AETHERA met its primary end point, but this was the first full look at the absolute survival rates and safety data.
The 2-year PFS rate for the brentuximab and placebo groups is now 63% vs. 51% per independent review and 65% vs. 45% per investigator.
“The bottom line is there’s a 20% difference in progression-free survival at 2 years upon investigator review. This has never been seen in patients with relapsed, refractory lymphoma, let alone Hodgkin lymphoma,” Dr. Moskowitz, clinical director of hematology oncology at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said.
Overall survival data are immature, but was the same in both groups at 2 years (P = .62). The likelihood of showing a survival difference was not expected because 85% of patients who relapsed on the placebo arm crossed over to brentuximab, as allowed per protocol, and it’s known that brentuximab alone in auto-transplant failures improves outcomes by at least a year, he said. Also, twice as many patients who failed placebo received a second transplant.
Dr. Moskowitz stressed that nearly every patient in the trial had at least three risk factors that would place them at high risk of treatment failure and that studies have shown that for patients with this many risk factors, the chance of being cured by an auto-transplant is about 25%. The risk factors are: relapsed less than 12 months or refractory to frontline therapy, best response of partial remission or stable disease to most recent salvage therapy, extranodal disease at pre-ASCT relapse, B symptoms at pre-ASCT relapse, or two or more prior salvage therapies.
Press briefing moderator Dr. Brad Kahl of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, said Aethera is the first study to show a significant benefit for a post-transplant strategy.
“The biggest question in my mind is whether the application of maintenance brentuximab vedotin is just delaying the inevitable relapse, so the patients will still relapse, just later, or has the brentuximab taken patients who are destined to relapse and turned them into a cured patient,” Dr. Kahl said. “We don’t know the answer to that question. That will become apparent with more time.”
Dr. Moscowitz observed that relapses almost never happen after two year, adding, “So if you’re in remission at two years after stem cell transplantation for Hodgkin lymphoma, you are likely to be cured.”
AETHERA enrolled 329 patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma and randomly assigned them after ASCT to brentuximab vedotin 1.8 mg/kg or placebo given every 3 weeks for up to 16 cycles, plus BSC. All patients were required to have achieved a complete response, partial remission, or stable disease to salvage therapy prior to ASCT. Their median age was 32 years and 53% were male.
Roughly 60% were refractory to upfront therapy, 43% in the brentuximab arm and 48% of controls had received 2 or more prior systemic therapies, and a third in each arm had extranodal involvement.
Consolidation therapy with brentuximab was generally well tolerated, Dr. Moskowitz said. Peripheral sensory neuropathy was the most common side effect, experienced at any grade in 67% on brentuximab vs. 19% of controls and at grade 3 in 13% vs. 1%. There were no grade 4 events and 85% of patients had resolution or improvement with dose reductions or stopping the drug.
Other adverse events in the brentuximab and control groups were neutropenia (35% vs. 12%), upper respiratory tract infections (26% vs. 23%), and fatigue (24% vs. 18%). Two patients died within 40 days of dosing with brentuximab, one from treatment-related acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with pneumonitis and one following an episode of treatment-related acute pancreatitis that had resolved at the time of death, he reported.
Based on the results, study sponsor Seattle Genetics is expected to seek approval for brentuximab in this consolidation setting in the first half of 2015, according to a statement from the company. The ongoing phase III ECHELON-1 and ECHELON 2 trials in HL and mature T-cell lymphomas are looking at the use of brentuximab in frontline disease.
SAN FRANCISCO – Early post-transplant brentuximab vedotin dramatically slows Hodgkin’s lymphoma progression in patients at high risk for relapse or progression, the phase III AETHERA study shows.
After a median follow-up of about 28 months, the primary end point of progression-free survival (PFS) per independent review increased from a median of 24 months with placebo and best supportive care (BSC) to 43 months with brentuximab and BSC (Hazard ratio, 0.57; P = .001).
Per investigator assessment, median PFS was 16 months with placebo and had not been reached with brentuximab (HR, 0.50),Dr. Craig Moskowitz reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The benefit of brentuximab maintenance was consistent across every subgroup. Historically, roughly half of patients who undergo an autologous stem cell transplant will relapse.
“Once this study is published, in patients who met eligibility criteria to be on this study - and once again I’ll remind you that’s remission duration less than one year, disease outside the lymph node system, or primary refractory disease - in my opinion, this will be the standard of care,” Dr. Moskowitz said during a press briefing.
Brentuximab, an anti-CD30 antibody conjugate, is already approved in the U.S. for the management of Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) after failure of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) or at least two prior lines of multi-agent chemotherapy in patients ineligible for ASCT.
Brentuximab is also indicated for systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma after failure of at least one multi-agent chemotherapy regimen.
In September it was announced that AETHERA met its primary end point, but this was the first full look at the absolute survival rates and safety data.
The 2-year PFS rate for the brentuximab and placebo groups is now 63% vs. 51% per independent review and 65% vs. 45% per investigator.
“The bottom line is there’s a 20% difference in progression-free survival at 2 years upon investigator review. This has never been seen in patients with relapsed, refractory lymphoma, let alone Hodgkin lymphoma,” Dr. Moskowitz, clinical director of hematology oncology at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said.
Overall survival data are immature, but was the same in both groups at 2 years (P = .62). The likelihood of showing a survival difference was not expected because 85% of patients who relapsed on the placebo arm crossed over to brentuximab, as allowed per protocol, and it’s known that brentuximab alone in auto-transplant failures improves outcomes by at least a year, he said. Also, twice as many patients who failed placebo received a second transplant.
Dr. Moskowitz stressed that nearly every patient in the trial had at least three risk factors that would place them at high risk of treatment failure and that studies have shown that for patients with this many risk factors, the chance of being cured by an auto-transplant is about 25%. The risk factors are: relapsed less than 12 months or refractory to frontline therapy, best response of partial remission or stable disease to most recent salvage therapy, extranodal disease at pre-ASCT relapse, B symptoms at pre-ASCT relapse, or two or more prior salvage therapies.
Press briefing moderator Dr. Brad Kahl of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, said Aethera is the first study to show a significant benefit for a post-transplant strategy.
“The biggest question in my mind is whether the application of maintenance brentuximab vedotin is just delaying the inevitable relapse, so the patients will still relapse, just later, or has the brentuximab taken patients who are destined to relapse and turned them into a cured patient,” Dr. Kahl said. “We don’t know the answer to that question. That will become apparent with more time.”
Dr. Moscowitz observed that relapses almost never happen after two year, adding, “So if you’re in remission at two years after stem cell transplantation for Hodgkin lymphoma, you are likely to be cured.”
AETHERA enrolled 329 patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma and randomly assigned them after ASCT to brentuximab vedotin 1.8 mg/kg or placebo given every 3 weeks for up to 16 cycles, plus BSC. All patients were required to have achieved a complete response, partial remission, or stable disease to salvage therapy prior to ASCT. Their median age was 32 years and 53% were male.
Roughly 60% were refractory to upfront therapy, 43% in the brentuximab arm and 48% of controls had received 2 or more prior systemic therapies, and a third in each arm had extranodal involvement.
Consolidation therapy with brentuximab was generally well tolerated, Dr. Moskowitz said. Peripheral sensory neuropathy was the most common side effect, experienced at any grade in 67% on brentuximab vs. 19% of controls and at grade 3 in 13% vs. 1%. There were no grade 4 events and 85% of patients had resolution or improvement with dose reductions or stopping the drug.
Other adverse events in the brentuximab and control groups were neutropenia (35% vs. 12%), upper respiratory tract infections (26% vs. 23%), and fatigue (24% vs. 18%). Two patients died within 40 days of dosing with brentuximab, one from treatment-related acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with pneumonitis and one following an episode of treatment-related acute pancreatitis that had resolved at the time of death, he reported.
Based on the results, study sponsor Seattle Genetics is expected to seek approval for brentuximab in this consolidation setting in the first half of 2015, according to a statement from the company. The ongoing phase III ECHELON-1 and ECHELON 2 trials in HL and mature T-cell lymphomas are looking at the use of brentuximab in frontline disease.
SAN FRANCISCO – Early post-transplant brentuximab vedotin dramatically slows Hodgkin’s lymphoma progression in patients at high risk for relapse or progression, the phase III AETHERA study shows.
After a median follow-up of about 28 months, the primary end point of progression-free survival (PFS) per independent review increased from a median of 24 months with placebo and best supportive care (BSC) to 43 months with brentuximab and BSC (Hazard ratio, 0.57; P = .001).
Per investigator assessment, median PFS was 16 months with placebo and had not been reached with brentuximab (HR, 0.50),Dr. Craig Moskowitz reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The benefit of brentuximab maintenance was consistent across every subgroup. Historically, roughly half of patients who undergo an autologous stem cell transplant will relapse.
“Once this study is published, in patients who met eligibility criteria to be on this study - and once again I’ll remind you that’s remission duration less than one year, disease outside the lymph node system, or primary refractory disease - in my opinion, this will be the standard of care,” Dr. Moskowitz said during a press briefing.
Brentuximab, an anti-CD30 antibody conjugate, is already approved in the U.S. for the management of Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) after failure of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) or at least two prior lines of multi-agent chemotherapy in patients ineligible for ASCT.
Brentuximab is also indicated for systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma after failure of at least one multi-agent chemotherapy regimen.
In September it was announced that AETHERA met its primary end point, but this was the first full look at the absolute survival rates and safety data.
The 2-year PFS rate for the brentuximab and placebo groups is now 63% vs. 51% per independent review and 65% vs. 45% per investigator.
“The bottom line is there’s a 20% difference in progression-free survival at 2 years upon investigator review. This has never been seen in patients with relapsed, refractory lymphoma, let alone Hodgkin lymphoma,” Dr. Moskowitz, clinical director of hematology oncology at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said.
Overall survival data are immature, but was the same in both groups at 2 years (P = .62). The likelihood of showing a survival difference was not expected because 85% of patients who relapsed on the placebo arm crossed over to brentuximab, as allowed per protocol, and it’s known that brentuximab alone in auto-transplant failures improves outcomes by at least a year, he said. Also, twice as many patients who failed placebo received a second transplant.
Dr. Moskowitz stressed that nearly every patient in the trial had at least three risk factors that would place them at high risk of treatment failure and that studies have shown that for patients with this many risk factors, the chance of being cured by an auto-transplant is about 25%. The risk factors are: relapsed less than 12 months or refractory to frontline therapy, best response of partial remission or stable disease to most recent salvage therapy, extranodal disease at pre-ASCT relapse, B symptoms at pre-ASCT relapse, or two or more prior salvage therapies.
Press briefing moderator Dr. Brad Kahl of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, said Aethera is the first study to show a significant benefit for a post-transplant strategy.
“The biggest question in my mind is whether the application of maintenance brentuximab vedotin is just delaying the inevitable relapse, so the patients will still relapse, just later, or has the brentuximab taken patients who are destined to relapse and turned them into a cured patient,” Dr. Kahl said. “We don’t know the answer to that question. That will become apparent with more time.”
Dr. Moscowitz observed that relapses almost never happen after two year, adding, “So if you’re in remission at two years after stem cell transplantation for Hodgkin lymphoma, you are likely to be cured.”
AETHERA enrolled 329 patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma and randomly assigned them after ASCT to brentuximab vedotin 1.8 mg/kg or placebo given every 3 weeks for up to 16 cycles, plus BSC. All patients were required to have achieved a complete response, partial remission, or stable disease to salvage therapy prior to ASCT. Their median age was 32 years and 53% were male.
Roughly 60% were refractory to upfront therapy, 43% in the brentuximab arm and 48% of controls had received 2 or more prior systemic therapies, and a third in each arm had extranodal involvement.
Consolidation therapy with brentuximab was generally well tolerated, Dr. Moskowitz said. Peripheral sensory neuropathy was the most common side effect, experienced at any grade in 67% on brentuximab vs. 19% of controls and at grade 3 in 13% vs. 1%. There were no grade 4 events and 85% of patients had resolution or improvement with dose reductions or stopping the drug.
Other adverse events in the brentuximab and control groups were neutropenia (35% vs. 12%), upper respiratory tract infections (26% vs. 23%), and fatigue (24% vs. 18%). Two patients died within 40 days of dosing with brentuximab, one from treatment-related acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with pneumonitis and one following an episode of treatment-related acute pancreatitis that had resolved at the time of death, he reported.
Based on the results, study sponsor Seattle Genetics is expected to seek approval for brentuximab in this consolidation setting in the first half of 2015, according to a statement from the company. The ongoing phase III ECHELON-1 and ECHELON 2 trials in HL and mature T-cell lymphomas are looking at the use of brentuximab in frontline disease.
AT ASH 2014
Key clinical point: Brentuximab vedotin given immediately post-transplant significantly improves progression-free survival in patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma at high risk for progression.
Major finding: Median progression-free survival per independent review was 24 months with placebo vs. 43 months with brentuximab (HR, 0.57; P = .001).
Data source: Randomized, double-blind, phase III study in 329 patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Disclosures: Seattle Genetics sponsored the study. Dr. Moskowitz reported research funding from Genentech and Merck, and research funding from and consultancy for Seattle Genetics. Several co-authors reported financial ties with industry, including employment with or equity ownership in Seattle Genetics.
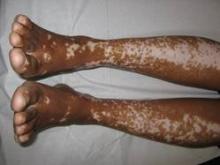
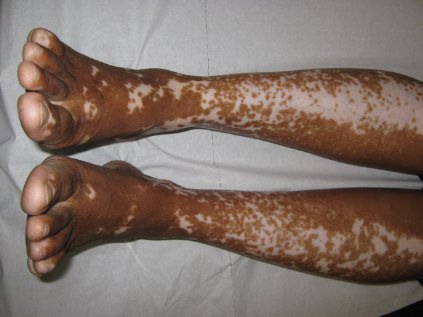
Vitiligo, alopecia more likely in GVHD when donor is female and recipient is male
The development of vitiligo or alopecia areata is not common in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease, but it is significantly more likely to occur when the donor was female, especially when the recipient was male, according to a report published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Dermatology.
Fifteen case reports and small series in the literature have reported the development of vitiligo or alopecia areata after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, most often among patients who first developed chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after the procedure. To further explore the frequency of these two skin autoimmune manifestations in GVHD and to identify associated risk factors, researchers performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adult and pediatric patients referred to the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center for GVHD in 2004-2013.
They identified 15 GVHD patients with vitiligo (4.9%) and 2 with alopecia areata (0.7%); one of these patients had both skin disorders. Most of the 15 patients had undergone stem-cell transplantation to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (5 patients) or acute leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (5 patients), and most had had a human leukocyte antigen–identical donor. Twelve of the 15 developed the skin disorder after having GVHD for more than 1 year, said Rena C. Zuo of the National Cancer Institute’s dermatology branch and her associates.
"Notably, CML accounts for only about 300 of 7,892 (3.8%) allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantations per year in the United States, a relative minority among indicated diseases," they said.
In what they described as the first study to identify an association between donor/recipient sex mismatch and the development of concomitant autoimmunity in patients with chronic GVHD, the investigators found that 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors, 2 of whom had previously given birth; the gender of the donor in the 15th case was unknown. Nine of these 14 recipients were male, "resulting in a female-to-male sex mismatch in [at least] 64% of cases," Ms. Zuo and her colleagues said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 Sept. 10 [doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1550]).
Both parous female donors and donor-recipient sex mismatch are known risk factors for GVHD. The risk of autoimmunity in female-to-male transplants "may reflect the activity of skin-homing donor T cells specific for recipient minor histocompatibility antigens encoded by Y-chromosome genes, a mechanism previously implicated in both GVHD and graft-versus-tumor responses," the investigators added.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
The development of vitiligo or alopecia areata is not common in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease, but it is significantly more likely to occur when the donor was female, especially when the recipient was male, according to a report published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Dermatology.
Fifteen case reports and small series in the literature have reported the development of vitiligo or alopecia areata after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, most often among patients who first developed chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after the procedure. To further explore the frequency of these two skin autoimmune manifestations in GVHD and to identify associated risk factors, researchers performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adult and pediatric patients referred to the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center for GVHD in 2004-2013.
They identified 15 GVHD patients with vitiligo (4.9%) and 2 with alopecia areata (0.7%); one of these patients had both skin disorders. Most of the 15 patients had undergone stem-cell transplantation to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (5 patients) or acute leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (5 patients), and most had had a human leukocyte antigen–identical donor. Twelve of the 15 developed the skin disorder after having GVHD for more than 1 year, said Rena C. Zuo of the National Cancer Institute’s dermatology branch and her associates.
"Notably, CML accounts for only about 300 of 7,892 (3.8%) allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantations per year in the United States, a relative minority among indicated diseases," they said.
In what they described as the first study to identify an association between donor/recipient sex mismatch and the development of concomitant autoimmunity in patients with chronic GVHD, the investigators found that 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors, 2 of whom had previously given birth; the gender of the donor in the 15th case was unknown. Nine of these 14 recipients were male, "resulting in a female-to-male sex mismatch in [at least] 64% of cases," Ms. Zuo and her colleagues said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 Sept. 10 [doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1550]).
Both parous female donors and donor-recipient sex mismatch are known risk factors for GVHD. The risk of autoimmunity in female-to-male transplants "may reflect the activity of skin-homing donor T cells specific for recipient minor histocompatibility antigens encoded by Y-chromosome genes, a mechanism previously implicated in both GVHD and graft-versus-tumor responses," the investigators added.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
The development of vitiligo or alopecia areata is not common in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease, but it is significantly more likely to occur when the donor was female, especially when the recipient was male, according to a report published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Dermatology.
Fifteen case reports and small series in the literature have reported the development of vitiligo or alopecia areata after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, most often among patients who first developed chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after the procedure. To further explore the frequency of these two skin autoimmune manifestations in GVHD and to identify associated risk factors, researchers performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adult and pediatric patients referred to the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center for GVHD in 2004-2013.
They identified 15 GVHD patients with vitiligo (4.9%) and 2 with alopecia areata (0.7%); one of these patients had both skin disorders. Most of the 15 patients had undergone stem-cell transplantation to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (5 patients) or acute leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (5 patients), and most had had a human leukocyte antigen–identical donor. Twelve of the 15 developed the skin disorder after having GVHD for more than 1 year, said Rena C. Zuo of the National Cancer Institute’s dermatology branch and her associates.
"Notably, CML accounts for only about 300 of 7,892 (3.8%) allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantations per year in the United States, a relative minority among indicated diseases," they said.
In what they described as the first study to identify an association between donor/recipient sex mismatch and the development of concomitant autoimmunity in patients with chronic GVHD, the investigators found that 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors, 2 of whom had previously given birth; the gender of the donor in the 15th case was unknown. Nine of these 14 recipients were male, "resulting in a female-to-male sex mismatch in [at least] 64% of cases," Ms. Zuo and her colleagues said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 Sept. 10 [doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1550]).
Both parous female donors and donor-recipient sex mismatch are known risk factors for GVHD. The risk of autoimmunity in female-to-male transplants "may reflect the activity of skin-homing donor T cells specific for recipient minor histocompatibility antigens encoded by Y-chromosome genes, a mechanism previously implicated in both GVHD and graft-versus-tumor responses," the investigators added.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Female-to-male stem cell donation ups the risk for vitiligo in GVHD.
Major finding: 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors (the gender of the 15th donor was unknown), and 9 of these 14 recipients were male.
Data source: A retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adults and children with chronic GVHD, 15 of whom developed vitiligo or alopecia areata.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
Monosomal karyotype, high prognostic risk score predicted transplantation failure
Monosomal karyotype and high prognostic risk according to the revised International Prognostic Scoring System are independent predictors of relapse and mortality in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia who undergo allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, according to findings from the GITMO (Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo) registry.
Treatment failure after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation may be from transplant complications or relapse. To understand the predictors of failure, investigators studied outcomes in 519 patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation between 2000 and 2011.
Those with monosomal karyotype had a 49% relapse rate and a 10% 5-year overall survival rate; both rates were significantly worse, compared with patients without monosomal karyotype (P less than .001 for each). Those considered high or very-high risk based on the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R), had 39% and 23% 5-year overall survival, respectively, and 23% and 39% relapse rates, respectively (P less than .001 in all cases vs. patients not at high or very-high risk), Dr. Matteo G. Della Porta of Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia, Italy and colleagues reported on behalf of the GITMO.
Age of 50 years or older and high hematopoietic cell transplantation-comorbidity index scores were independent predictors of nonrelapse mortality (P = .02; P = .017, respectively), they found (Blood 2014 [doi:10.1182/blood-2013-12-542720]).
Accounting for various combinations of patients’ ages, IPSS-R category, monosomal karyotype, and high hematopoietic cell transplantation–comorbidity index, the 5-year probability of survival after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation ranged from 0 to 94%. The analyses performed reinforce the concept that allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation – the only potentially curative treatment for MDS – "offers optimal eradication of myelodysplastic hematopoiesis when the procedure is performed before MDS patients progress to advanced disease stages," the investigators concluded.
The investigators reported having no disclosures.
Monosomal karyotype and high prognostic risk according to the revised International Prognostic Scoring System are independent predictors of relapse and mortality in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia who undergo allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, according to findings from the GITMO (Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo) registry.
Treatment failure after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation may be from transplant complications or relapse. To understand the predictors of failure, investigators studied outcomes in 519 patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation between 2000 and 2011.
Those with monosomal karyotype had a 49% relapse rate and a 10% 5-year overall survival rate; both rates were significantly worse, compared with patients without monosomal karyotype (P less than .001 for each). Those considered high or very-high risk based on the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R), had 39% and 23% 5-year overall survival, respectively, and 23% and 39% relapse rates, respectively (P less than .001 in all cases vs. patients not at high or very-high risk), Dr. Matteo G. Della Porta of Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia, Italy and colleagues reported on behalf of the GITMO.
Age of 50 years or older and high hematopoietic cell transplantation-comorbidity index scores were independent predictors of nonrelapse mortality (P = .02; P = .017, respectively), they found (Blood 2014 [doi:10.1182/blood-2013-12-542720]).
Accounting for various combinations of patients’ ages, IPSS-R category, monosomal karyotype, and high hematopoietic cell transplantation–comorbidity index, the 5-year probability of survival after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation ranged from 0 to 94%. The analyses performed reinforce the concept that allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation – the only potentially curative treatment for MDS – "offers optimal eradication of myelodysplastic hematopoiesis when the procedure is performed before MDS patients progress to advanced disease stages," the investigators concluded.
The investigators reported having no disclosures.
Monosomal karyotype and high prognostic risk according to the revised International Prognostic Scoring System are independent predictors of relapse and mortality in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia who undergo allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, according to findings from the GITMO (Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo) registry.
Treatment failure after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation may be from transplant complications or relapse. To understand the predictors of failure, investigators studied outcomes in 519 patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation between 2000 and 2011.
Those with monosomal karyotype had a 49% relapse rate and a 10% 5-year overall survival rate; both rates were significantly worse, compared with patients without monosomal karyotype (P less than .001 for each). Those considered high or very-high risk based on the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R), had 39% and 23% 5-year overall survival, respectively, and 23% and 39% relapse rates, respectively (P less than .001 in all cases vs. patients not at high or very-high risk), Dr. Matteo G. Della Porta of Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia, Italy and colleagues reported on behalf of the GITMO.
Age of 50 years or older and high hematopoietic cell transplantation-comorbidity index scores were independent predictors of nonrelapse mortality (P = .02; P = .017, respectively), they found (Blood 2014 [doi:10.1182/blood-2013-12-542720]).
Accounting for various combinations of patients’ ages, IPSS-R category, monosomal karyotype, and high hematopoietic cell transplantation–comorbidity index, the 5-year probability of survival after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation ranged from 0 to 94%. The analyses performed reinforce the concept that allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation – the only potentially curative treatment for MDS – "offers optimal eradication of myelodysplastic hematopoiesis when the procedure is performed before MDS patients progress to advanced disease stages," the investigators concluded.
The investigators reported having no disclosures.
FROM BLOOD
Major finding: Patients with a monosomal karyotype had a 49% relapse rate and a 10% 5-year overall survival rate, and those considered high or very-high risk based on the IPSS-R, had 39% and 23% 5-year overall survival, respectively, and 23% and 39% relapse rates, respectively.
Data source: An analysis of GITMO registry data.
Disclosures: The investigators reported having no disclosures.