User login
Undiagnosed COPD may change heart function before heart attacks occur
, data from a clinical trial suggest.
The finding could represent an opportunity for early intervention, Rita Pavasini, MD, wrote in COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
“Early change of the right ventricular function, as detected by reduced right ventricular strain and reduced fractional area change, is present in [these] patients,” wrote Dr. Pavasini of Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Ferrara, Cona, Italy. “Further studies are warranted to determine whether these alterations can be reversed or modulated by an early identification and treatment and whether targeting early right ventricular strain reduction results in better clinical outcomes in these comorbid patients.”
Dr. Pavasini and colleagues reported a prespecified subanalysis of the Screening for COPD in ACS Patients (SCAP) trial, which showed that screening patients admitted for acute coronary syndromes with respiratory measures could identify those at risk for undiagnosed COPD. The substudy examined the echocardiographic characteristics of these patients.
SCAP comprised 137 patients who were current or past smokers. At baseline, 29% had a COPD diagnosis. However, most displayed airflow limitation (59% mild, 38% moderate). All underwent transthoracic echocardiogram at baseline and at 6 months.
At baseline, fractional area change (FAC) was already significantly lower in patients with occult COPD than in those without it (38% vs. 44%). Patients with undiagnosed COPD also had significantly reduced right ventricular strain (RVS) (–15 vs. –20).
“Interestingly, the inferior location of myocardial infarction did not influence the results,” the authors said. “Indeed, RVS and FAC did not differ between patients with inferior location of myocardial infarction vs. those without inferior location.”
At 6 months, these differences were unabated. FAC was still significantly lower among those with COPD (37% vs. 46%), and RVS still significantly less (–16 vs. –20). Systolic pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP) was also significantly higher in patients with concomitant COPD (35 vs. 27 mm Hg).
“The early impairment in RVS might reflect the impact of endothelial dysfunction, increased arterial stiffness and inflammation on right heart function, rather than only hypoxia, and even more in a population with mainly mild to moderate COPD,” the team said. “Thus, it is highly probable that sPAP in patients with undiagnosed COPD is mainly determined by concomitant pulmonary disease, which did not differ between acute and chronic phase.”
On the whole, the data suggest that the impairment of right ventricular strain was primarily related to the undiagnosed COPD, and not the cardiovascular event, they said,
“These data are consistent with the observed impairment of RVS and indirectly confirms that undiagnosed COPD determines early changes in the structure and function of the right heart.”
Dr. Pavasini had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Pavasini R et al. COPD 2019 Jul 21. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2019.16451059.
, data from a clinical trial suggest.
The finding could represent an opportunity for early intervention, Rita Pavasini, MD, wrote in COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
“Early change of the right ventricular function, as detected by reduced right ventricular strain and reduced fractional area change, is present in [these] patients,” wrote Dr. Pavasini of Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Ferrara, Cona, Italy. “Further studies are warranted to determine whether these alterations can be reversed or modulated by an early identification and treatment and whether targeting early right ventricular strain reduction results in better clinical outcomes in these comorbid patients.”
Dr. Pavasini and colleagues reported a prespecified subanalysis of the Screening for COPD in ACS Patients (SCAP) trial, which showed that screening patients admitted for acute coronary syndromes with respiratory measures could identify those at risk for undiagnosed COPD. The substudy examined the echocardiographic characteristics of these patients.
SCAP comprised 137 patients who were current or past smokers. At baseline, 29% had a COPD diagnosis. However, most displayed airflow limitation (59% mild, 38% moderate). All underwent transthoracic echocardiogram at baseline and at 6 months.
At baseline, fractional area change (FAC) was already significantly lower in patients with occult COPD than in those without it (38% vs. 44%). Patients with undiagnosed COPD also had significantly reduced right ventricular strain (RVS) (–15 vs. –20).
“Interestingly, the inferior location of myocardial infarction did not influence the results,” the authors said. “Indeed, RVS and FAC did not differ between patients with inferior location of myocardial infarction vs. those without inferior location.”
At 6 months, these differences were unabated. FAC was still significantly lower among those with COPD (37% vs. 46%), and RVS still significantly less (–16 vs. –20). Systolic pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP) was also significantly higher in patients with concomitant COPD (35 vs. 27 mm Hg).
“The early impairment in RVS might reflect the impact of endothelial dysfunction, increased arterial stiffness and inflammation on right heart function, rather than only hypoxia, and even more in a population with mainly mild to moderate COPD,” the team said. “Thus, it is highly probable that sPAP in patients with undiagnosed COPD is mainly determined by concomitant pulmonary disease, which did not differ between acute and chronic phase.”
On the whole, the data suggest that the impairment of right ventricular strain was primarily related to the undiagnosed COPD, and not the cardiovascular event, they said,
“These data are consistent with the observed impairment of RVS and indirectly confirms that undiagnosed COPD determines early changes in the structure and function of the right heart.”
Dr. Pavasini had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Pavasini R et al. COPD 2019 Jul 21. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2019.16451059.
, data from a clinical trial suggest.
The finding could represent an opportunity for early intervention, Rita Pavasini, MD, wrote in COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
“Early change of the right ventricular function, as detected by reduced right ventricular strain and reduced fractional area change, is present in [these] patients,” wrote Dr. Pavasini of Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Ferrara, Cona, Italy. “Further studies are warranted to determine whether these alterations can be reversed or modulated by an early identification and treatment and whether targeting early right ventricular strain reduction results in better clinical outcomes in these comorbid patients.”
Dr. Pavasini and colleagues reported a prespecified subanalysis of the Screening for COPD in ACS Patients (SCAP) trial, which showed that screening patients admitted for acute coronary syndromes with respiratory measures could identify those at risk for undiagnosed COPD. The substudy examined the echocardiographic characteristics of these patients.
SCAP comprised 137 patients who were current or past smokers. At baseline, 29% had a COPD diagnosis. However, most displayed airflow limitation (59% mild, 38% moderate). All underwent transthoracic echocardiogram at baseline and at 6 months.
At baseline, fractional area change (FAC) was already significantly lower in patients with occult COPD than in those without it (38% vs. 44%). Patients with undiagnosed COPD also had significantly reduced right ventricular strain (RVS) (–15 vs. –20).
“Interestingly, the inferior location of myocardial infarction did not influence the results,” the authors said. “Indeed, RVS and FAC did not differ between patients with inferior location of myocardial infarction vs. those without inferior location.”
At 6 months, these differences were unabated. FAC was still significantly lower among those with COPD (37% vs. 46%), and RVS still significantly less (–16 vs. –20). Systolic pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP) was also significantly higher in patients with concomitant COPD (35 vs. 27 mm Hg).
“The early impairment in RVS might reflect the impact of endothelial dysfunction, increased arterial stiffness and inflammation on right heart function, rather than only hypoxia, and even more in a population with mainly mild to moderate COPD,” the team said. “Thus, it is highly probable that sPAP in patients with undiagnosed COPD is mainly determined by concomitant pulmonary disease, which did not differ between acute and chronic phase.”
On the whole, the data suggest that the impairment of right ventricular strain was primarily related to the undiagnosed COPD, and not the cardiovascular event, they said,
“These data are consistent with the observed impairment of RVS and indirectly confirms that undiagnosed COPD determines early changes in the structure and function of the right heart.”
Dr. Pavasini had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Pavasini R et al. COPD 2019 Jul 21. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2019.16451059.
FROM COPD: JOURNAL OF CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
COPD adds complexity to shared decision making for LDCT lung cancer screening
research suggests.
Jonathan M. Iaccarino, MD, of the pulmonary center at the Boston University, and coauthors reported the results of a secondary analysis of patient-level outcomes from 75,138 low-dose CT (LDCT) scans in 26,453 participants in the National Lung Screening Trial (Chest 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.06.016).
Currently, LDCT screening is recommended annually for high-risk smokers aged 55-80 years. The National Lung Screening Trial showed that this screening achieved a 20% relative reduction in lung cancer mortality and 6.7% relative reduction in overall mortality in this group. The guidelines stress the importance of shared decision making, with discussion of the risks and benefits of screening.
Dr. Iaccarino and colleagues point out that decision aids for shared decision making need to include important baseline characteristics, such as the presence of COPD, as these can complicate the risk and benefit analysis.
In this study, they found that 14.2% of LDCT scans performed led to a subsequent diagnostic study and 1.5% resulted in an invasive procedure. In addition, 0.3% of scans resulted in a procedure-related complication, and in 89 cases (0.1%), this procedure-related complication was serious.
At the patient level, nearly one-third (30.5%) received a diagnostic study, 4.2% underwent an invasive procedure – 41% of whom ultimately were found not to have lung cancer – 0.9% had a procedure-related complication, and 0.3% had a serious procedure related complication. Furthermore, among those who experienced a serious complication, 12.5% were found not to have lung cancer.
“Our study analyzes cumulative outcomes at the level of the individual patient over the three years of LDCT screening during the NLST, showing higher rates of diagnostic procedures, invasive procedures, complications and serious complications than apparent when data is presented at the level of the individual test,” the authors wrote.
The 4,632 participants with COPD were significantly more likely to undergo diagnostic studies (36.2%), have an invasive procedure (6%), experience a procedure-related complication (1.5%) and experience a serious procedure-related complication (0.6%) than were participants without COPD. However, they also had a significantly higher incidence of lung cancer diagnosis than did participants without COPD (6.1% vs. 3.6%).
“While most decision aids note the risks of screening may be increased in those with COPD, our study helps quantify these increased risks as well as the increased likelihood of a lung cancer diagnosis, a critical advance given that providing personalized (rather than generic) information results in more accurate risk perception and more informed choices among individuals considering screening,” the authors wrote. “With the significant change in the balance of benefits and risks of screening in patients with COPD, it is critical to adjust the shared decision-making discussions accordingly.”
They also noted that other comorbidities, such as heart disease, vascular disease, and other lung diseases, would likely affect the balance of risk and benefit of LDCT screening, and that there was a need for further exploration of screening in these patients.
Noting the study’s limitations, the authors pointed that their analysis focused on outcomes that were not the primary outcomes of the National Lung Screening trial, and that they relied on self-reported COPD diagnoses.
The study was supported by the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the Charles A. King Trust, and Edith Nourse Rogers Memorial Veterans Hospital. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Iaccarino JM et al. CHEST 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.06.016.
research suggests.
Jonathan M. Iaccarino, MD, of the pulmonary center at the Boston University, and coauthors reported the results of a secondary analysis of patient-level outcomes from 75,138 low-dose CT (LDCT) scans in 26,453 participants in the National Lung Screening Trial (Chest 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.06.016).
Currently, LDCT screening is recommended annually for high-risk smokers aged 55-80 years. The National Lung Screening Trial showed that this screening achieved a 20% relative reduction in lung cancer mortality and 6.7% relative reduction in overall mortality in this group. The guidelines stress the importance of shared decision making, with discussion of the risks and benefits of screening.
Dr. Iaccarino and colleagues point out that decision aids for shared decision making need to include important baseline characteristics, such as the presence of COPD, as these can complicate the risk and benefit analysis.
In this study, they found that 14.2% of LDCT scans performed led to a subsequent diagnostic study and 1.5% resulted in an invasive procedure. In addition, 0.3% of scans resulted in a procedure-related complication, and in 89 cases (0.1%), this procedure-related complication was serious.
At the patient level, nearly one-third (30.5%) received a diagnostic study, 4.2% underwent an invasive procedure – 41% of whom ultimately were found not to have lung cancer – 0.9% had a procedure-related complication, and 0.3% had a serious procedure related complication. Furthermore, among those who experienced a serious complication, 12.5% were found not to have lung cancer.
“Our study analyzes cumulative outcomes at the level of the individual patient over the three years of LDCT screening during the NLST, showing higher rates of diagnostic procedures, invasive procedures, complications and serious complications than apparent when data is presented at the level of the individual test,” the authors wrote.
The 4,632 participants with COPD were significantly more likely to undergo diagnostic studies (36.2%), have an invasive procedure (6%), experience a procedure-related complication (1.5%) and experience a serious procedure-related complication (0.6%) than were participants without COPD. However, they also had a significantly higher incidence of lung cancer diagnosis than did participants without COPD (6.1% vs. 3.6%).
“While most decision aids note the risks of screening may be increased in those with COPD, our study helps quantify these increased risks as well as the increased likelihood of a lung cancer diagnosis, a critical advance given that providing personalized (rather than generic) information results in more accurate risk perception and more informed choices among individuals considering screening,” the authors wrote. “With the significant change in the balance of benefits and risks of screening in patients with COPD, it is critical to adjust the shared decision-making discussions accordingly.”
They also noted that other comorbidities, such as heart disease, vascular disease, and other lung diseases, would likely affect the balance of risk and benefit of LDCT screening, and that there was a need for further exploration of screening in these patients.
Noting the study’s limitations, the authors pointed that their analysis focused on outcomes that were not the primary outcomes of the National Lung Screening trial, and that they relied on self-reported COPD diagnoses.
The study was supported by the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the Charles A. King Trust, and Edith Nourse Rogers Memorial Veterans Hospital. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Iaccarino JM et al. CHEST 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.06.016.
research suggests.
Jonathan M. Iaccarino, MD, of the pulmonary center at the Boston University, and coauthors reported the results of a secondary analysis of patient-level outcomes from 75,138 low-dose CT (LDCT) scans in 26,453 participants in the National Lung Screening Trial (Chest 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.06.016).
Currently, LDCT screening is recommended annually for high-risk smokers aged 55-80 years. The National Lung Screening Trial showed that this screening achieved a 20% relative reduction in lung cancer mortality and 6.7% relative reduction in overall mortality in this group. The guidelines stress the importance of shared decision making, with discussion of the risks and benefits of screening.
Dr. Iaccarino and colleagues point out that decision aids for shared decision making need to include important baseline characteristics, such as the presence of COPD, as these can complicate the risk and benefit analysis.
In this study, they found that 14.2% of LDCT scans performed led to a subsequent diagnostic study and 1.5% resulted in an invasive procedure. In addition, 0.3% of scans resulted in a procedure-related complication, and in 89 cases (0.1%), this procedure-related complication was serious.
At the patient level, nearly one-third (30.5%) received a diagnostic study, 4.2% underwent an invasive procedure – 41% of whom ultimately were found not to have lung cancer – 0.9% had a procedure-related complication, and 0.3% had a serious procedure related complication. Furthermore, among those who experienced a serious complication, 12.5% were found not to have lung cancer.
“Our study analyzes cumulative outcomes at the level of the individual patient over the three years of LDCT screening during the NLST, showing higher rates of diagnostic procedures, invasive procedures, complications and serious complications than apparent when data is presented at the level of the individual test,” the authors wrote.
The 4,632 participants with COPD were significantly more likely to undergo diagnostic studies (36.2%), have an invasive procedure (6%), experience a procedure-related complication (1.5%) and experience a serious procedure-related complication (0.6%) than were participants without COPD. However, they also had a significantly higher incidence of lung cancer diagnosis than did participants without COPD (6.1% vs. 3.6%).
“While most decision aids note the risks of screening may be increased in those with COPD, our study helps quantify these increased risks as well as the increased likelihood of a lung cancer diagnosis, a critical advance given that providing personalized (rather than generic) information results in more accurate risk perception and more informed choices among individuals considering screening,” the authors wrote. “With the significant change in the balance of benefits and risks of screening in patients with COPD, it is critical to adjust the shared decision-making discussions accordingly.”
They also noted that other comorbidities, such as heart disease, vascular disease, and other lung diseases, would likely affect the balance of risk and benefit of LDCT screening, and that there was a need for further exploration of screening in these patients.
Noting the study’s limitations, the authors pointed that their analysis focused on outcomes that were not the primary outcomes of the National Lung Screening trial, and that they relied on self-reported COPD diagnoses.
The study was supported by the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the Charles A. King Trust, and Edith Nourse Rogers Memorial Veterans Hospital. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Iaccarino JM et al. CHEST 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.06.016.
FROM CHEST
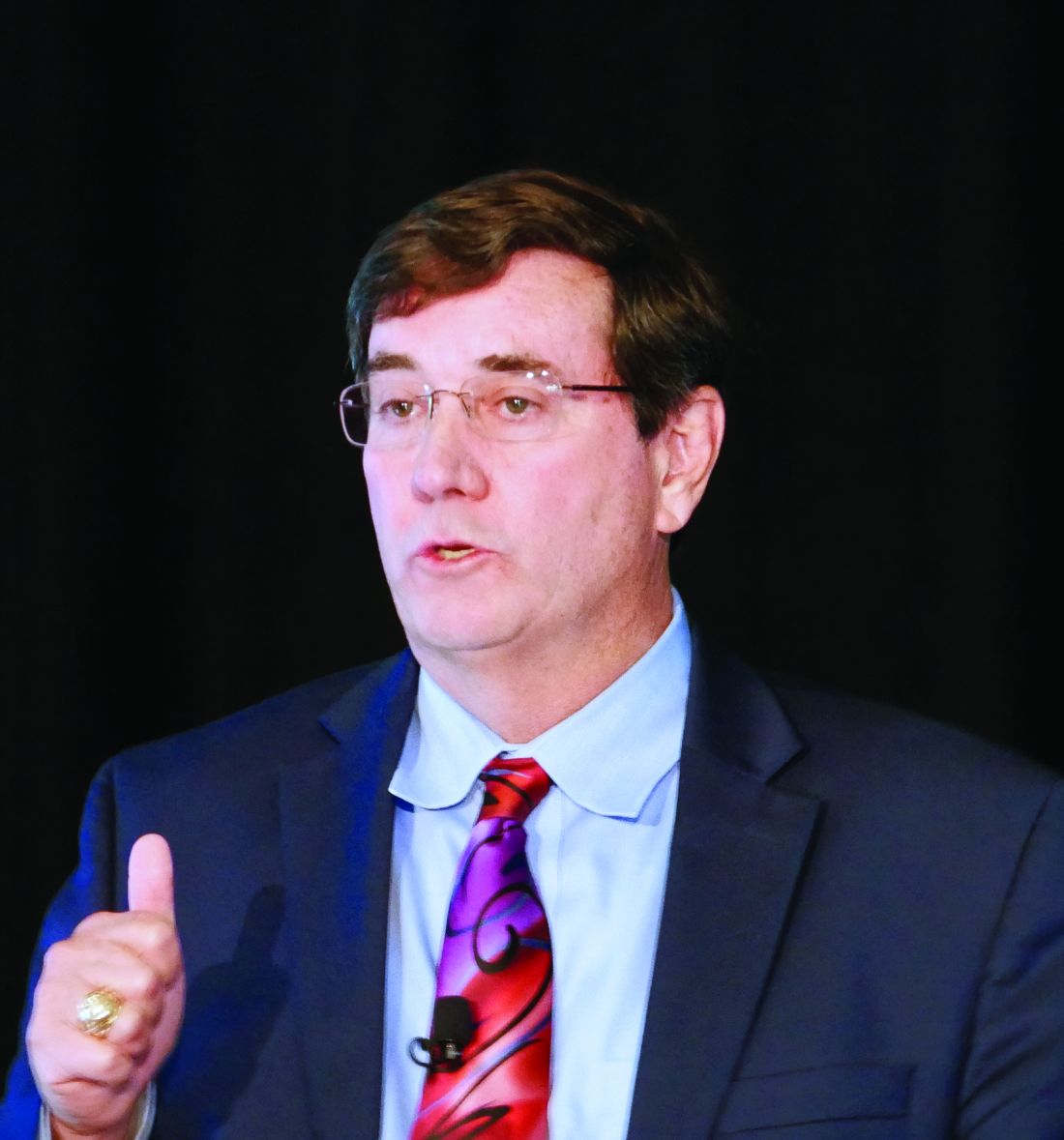
Best inhaler for COPD is the one the patient will use
ORLANDO –
That’s according to Gabriel Ortiz, MPAS, PA-C, DFAAPA, a speaker at the Cardiovascular & Respiratory Summit by Global Academy for Medical Education.
There are several treatment options available in inhaler form for patients with COPD, including short-acting and long-acting beta2-agonists (SABA/LABA), short-acting and long-acting antimuscarinics (SAMA/LAMA), combination therapy, and triple therapy. But education and training on how to use an inhaler is also important, Mr. Ortiz said in his presentation.
Providers should help a patient choose an inhaler they are most likely to use. “It’s difficult to actuate and inhale, so there’s a lot of education that goes into that,” said Mr. Ortiz, of Pediatric Pulmonary Services in El Paso, Texas. “What we do for our patients is, we educate them, we tell them to demonstrate it, then bring [the] inhaler back on the next visit and demonstrate to us every time.”
“Make sure that they demonstrate because, as patients get older, they may lose their ability to actuate and inhale,” he added.
Adherence to therapy should also be considered before changing from a current therapy, he added. Mr. Ortiz described a scenario in which a prescription was filled, but because of the cost, the patient reduced the dose by half to make the therapy last longer.
“We could be the best providers in the world, prescribing the best medication in the world. If the medication doesn’t get to where we need it, it’s not going to help anybody,” he said.
Providers should also use nonpharmacological treatments to prevent or keep COPD from progressing. Smoking cessation is key to reducing the risk of developing COPD, and it is not clear whether e-cigarettes aid in smoking cessation, despite companies that market these products making that claim. “We have a huge e-cigarette epidemic here,” he said.
Instead, Mr. Ortiz recommended identifying which patients are current tobacco users, encouraging them to quit, determining whether the patient is willing to make a commitment to cut down on tobacco use or stop entirely, helping draft a quit plan and obtaining intra- and extratreatment social support for smoking cessation, and scheduling follow-up. Providers should discuss smoking cessation at each visit, and it may take multiple visits before a patient is willing to consider quitting, he said.
Another measure providers can take is making sure patients with COPD have received influenza and pneumococcal vaccinations because this can lower the risk of respiratory tract infections. Physical activity, training in exercise, nutritional support, and pulmonary rehabilitation can improve their health status, dyspnea, and exercise tolerance. While C-level evidence shows education alone is not effective according to Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines, providers working with patients through self-management interventions have been shown to improve health status and decrease COPD-related hospitalizations.
Oxygen therapy has been effective for patients with severe resting chronic hypoxia and improves survival, said Mr. Ortiz. For patients who gradually decline in health despite treatment, palliative, hospice, and end-of-life care may be an option. “Remember that as acute exacerbations continue, that increases the risk of death,” he said. “We want to try and prevent [those] exacerbations and improve quality of life.”
During follow-up visits, providers should continue performing spirometry tests annually to measure decline in forced expiratory volume in 1 second, information on symptoms that have presented since the previous visit, details of any exacerbations that occurred, and current smoking status. When making decisions to adjust therapy, providers should examine the effectiveness of the current regimen and consider the dose of prescribed medications, whether the patient is adhering to the regimen, inhaler technique, and any side effects.
Mr. Ortiz reports also being a paid employee for Thermo Fisher, a biotechnology product development company based in Waltham, Mass. Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
ORLANDO –
That’s according to Gabriel Ortiz, MPAS, PA-C, DFAAPA, a speaker at the Cardiovascular & Respiratory Summit by Global Academy for Medical Education.
There are several treatment options available in inhaler form for patients with COPD, including short-acting and long-acting beta2-agonists (SABA/LABA), short-acting and long-acting antimuscarinics (SAMA/LAMA), combination therapy, and triple therapy. But education and training on how to use an inhaler is also important, Mr. Ortiz said in his presentation.
Providers should help a patient choose an inhaler they are most likely to use. “It’s difficult to actuate and inhale, so there’s a lot of education that goes into that,” said Mr. Ortiz, of Pediatric Pulmonary Services in El Paso, Texas. “What we do for our patients is, we educate them, we tell them to demonstrate it, then bring [the] inhaler back on the next visit and demonstrate to us every time.”
“Make sure that they demonstrate because, as patients get older, they may lose their ability to actuate and inhale,” he added.
Adherence to therapy should also be considered before changing from a current therapy, he added. Mr. Ortiz described a scenario in which a prescription was filled, but because of the cost, the patient reduced the dose by half to make the therapy last longer.
“We could be the best providers in the world, prescribing the best medication in the world. If the medication doesn’t get to where we need it, it’s not going to help anybody,” he said.
Providers should also use nonpharmacological treatments to prevent or keep COPD from progressing. Smoking cessation is key to reducing the risk of developing COPD, and it is not clear whether e-cigarettes aid in smoking cessation, despite companies that market these products making that claim. “We have a huge e-cigarette epidemic here,” he said.
Instead, Mr. Ortiz recommended identifying which patients are current tobacco users, encouraging them to quit, determining whether the patient is willing to make a commitment to cut down on tobacco use or stop entirely, helping draft a quit plan and obtaining intra- and extratreatment social support for smoking cessation, and scheduling follow-up. Providers should discuss smoking cessation at each visit, and it may take multiple visits before a patient is willing to consider quitting, he said.
Another measure providers can take is making sure patients with COPD have received influenza and pneumococcal vaccinations because this can lower the risk of respiratory tract infections. Physical activity, training in exercise, nutritional support, and pulmonary rehabilitation can improve their health status, dyspnea, and exercise tolerance. While C-level evidence shows education alone is not effective according to Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines, providers working with patients through self-management interventions have been shown to improve health status and decrease COPD-related hospitalizations.
Oxygen therapy has been effective for patients with severe resting chronic hypoxia and improves survival, said Mr. Ortiz. For patients who gradually decline in health despite treatment, palliative, hospice, and end-of-life care may be an option. “Remember that as acute exacerbations continue, that increases the risk of death,” he said. “We want to try and prevent [those] exacerbations and improve quality of life.”
During follow-up visits, providers should continue performing spirometry tests annually to measure decline in forced expiratory volume in 1 second, information on symptoms that have presented since the previous visit, details of any exacerbations that occurred, and current smoking status. When making decisions to adjust therapy, providers should examine the effectiveness of the current regimen and consider the dose of prescribed medications, whether the patient is adhering to the regimen, inhaler technique, and any side effects.
Mr. Ortiz reports also being a paid employee for Thermo Fisher, a biotechnology product development company based in Waltham, Mass. Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
ORLANDO –
That’s according to Gabriel Ortiz, MPAS, PA-C, DFAAPA, a speaker at the Cardiovascular & Respiratory Summit by Global Academy for Medical Education.
There are several treatment options available in inhaler form for patients with COPD, including short-acting and long-acting beta2-agonists (SABA/LABA), short-acting and long-acting antimuscarinics (SAMA/LAMA), combination therapy, and triple therapy. But education and training on how to use an inhaler is also important, Mr. Ortiz said in his presentation.
Providers should help a patient choose an inhaler they are most likely to use. “It’s difficult to actuate and inhale, so there’s a lot of education that goes into that,” said Mr. Ortiz, of Pediatric Pulmonary Services in El Paso, Texas. “What we do for our patients is, we educate them, we tell them to demonstrate it, then bring [the] inhaler back on the next visit and demonstrate to us every time.”
“Make sure that they demonstrate because, as patients get older, they may lose their ability to actuate and inhale,” he added.
Adherence to therapy should also be considered before changing from a current therapy, he added. Mr. Ortiz described a scenario in which a prescription was filled, but because of the cost, the patient reduced the dose by half to make the therapy last longer.
“We could be the best providers in the world, prescribing the best medication in the world. If the medication doesn’t get to where we need it, it’s not going to help anybody,” he said.
Providers should also use nonpharmacological treatments to prevent or keep COPD from progressing. Smoking cessation is key to reducing the risk of developing COPD, and it is not clear whether e-cigarettes aid in smoking cessation, despite companies that market these products making that claim. “We have a huge e-cigarette epidemic here,” he said.
Instead, Mr. Ortiz recommended identifying which patients are current tobacco users, encouraging them to quit, determining whether the patient is willing to make a commitment to cut down on tobacco use or stop entirely, helping draft a quit plan and obtaining intra- and extratreatment social support for smoking cessation, and scheduling follow-up. Providers should discuss smoking cessation at each visit, and it may take multiple visits before a patient is willing to consider quitting, he said.
Another measure providers can take is making sure patients with COPD have received influenza and pneumococcal vaccinations because this can lower the risk of respiratory tract infections. Physical activity, training in exercise, nutritional support, and pulmonary rehabilitation can improve their health status, dyspnea, and exercise tolerance. While C-level evidence shows education alone is not effective according to Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines, providers working with patients through self-management interventions have been shown to improve health status and decrease COPD-related hospitalizations.
Oxygen therapy has been effective for patients with severe resting chronic hypoxia and improves survival, said Mr. Ortiz. For patients who gradually decline in health despite treatment, palliative, hospice, and end-of-life care may be an option. “Remember that as acute exacerbations continue, that increases the risk of death,” he said. “We want to try and prevent [those] exacerbations and improve quality of life.”
During follow-up visits, providers should continue performing spirometry tests annually to measure decline in forced expiratory volume in 1 second, information on symptoms that have presented since the previous visit, details of any exacerbations that occurred, and current smoking status. When making decisions to adjust therapy, providers should examine the effectiveness of the current regimen and consider the dose of prescribed medications, whether the patient is adhering to the regimen, inhaler technique, and any side effects.
Mr. Ortiz reports also being a paid employee for Thermo Fisher, a biotechnology product development company based in Waltham, Mass. Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM CARPS 2019
Statin use linked to less depression, anxiety in ACOS patients
based on data from approximately 9,000 patients.
Although asthma–COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) has been associated with depression, the effects of oral and inhaled corticosteroids on anxiety and depression in these patients have not been well investigated, wrote Jun-Jun Yeh, MD, of Ditmanson Medical Foundation Chia-Yi (Taiwan) Christian Hospital, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, the researchers analyzed 9,139 ACOS patients including 1,252 statin users and 7,887 nonstatin users; 62% were male.
The statin users had significantly lower risk of both anxiety and depression than did the nonstatin users (adjusted hazard ratio 0.34 for anxiety and 0.36 for depression) after researchers controlled for factors including age, sex, comorbidities, and medications. Statin users experienced a total of 109 anxiety or depression events over an average of 8 years’ follow-up, while nonstatin users experienced a total of 1,333 anxiety or depression events over an average of 5 years’ follow-up.
The incidence density rate of anxiety was 11/1,000 person-years for statin users and 33/1,000 person-years for nonstatin users. The incidence density rate of depression was 3/1,000 person-years for statin users and 9/1,000 person-years for nonstatin users.
Significantly lower risk of anxiety and depression also were observed in statin users, compared with nonstatin users, in subgroups of men, women, patients younger than 50 years, and patients aged 50 years and older. The risks of anxiety and depression were lower in statin users versus nonstatin users across all subgroups with or without inhaled or oral corticosteroids.
Overall, the statin users were significantly younger, had more comorbidities, and were more likely to use inhaled or oral corticosteroids than were the nonstatin users.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective nature of the study and a lack of information on prescribed daily doses of medication, the researchers noted. However, the results support those from previous studies and suggest that “the anti-inflammatory effect of statins may attenuate anxiety and depression in ACOS patients, even in the late stages of the disease,” although the exact mechanism of action remains unknown and larger, randomized, controlled trials are needed, they said.
The study was supported by grants from a variety of organizations in Taiwan, China, and Japan. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Yeh JJ et al. J Affect Disord. 2019 Jun 15; 253:277-84.
based on data from approximately 9,000 patients.
Although asthma–COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) has been associated with depression, the effects of oral and inhaled corticosteroids on anxiety and depression in these patients have not been well investigated, wrote Jun-Jun Yeh, MD, of Ditmanson Medical Foundation Chia-Yi (Taiwan) Christian Hospital, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, the researchers analyzed 9,139 ACOS patients including 1,252 statin users and 7,887 nonstatin users; 62% were male.
The statin users had significantly lower risk of both anxiety and depression than did the nonstatin users (adjusted hazard ratio 0.34 for anxiety and 0.36 for depression) after researchers controlled for factors including age, sex, comorbidities, and medications. Statin users experienced a total of 109 anxiety or depression events over an average of 8 years’ follow-up, while nonstatin users experienced a total of 1,333 anxiety or depression events over an average of 5 years’ follow-up.
The incidence density rate of anxiety was 11/1,000 person-years for statin users and 33/1,000 person-years for nonstatin users. The incidence density rate of depression was 3/1,000 person-years for statin users and 9/1,000 person-years for nonstatin users.
Significantly lower risk of anxiety and depression also were observed in statin users, compared with nonstatin users, in subgroups of men, women, patients younger than 50 years, and patients aged 50 years and older. The risks of anxiety and depression were lower in statin users versus nonstatin users across all subgroups with or without inhaled or oral corticosteroids.
Overall, the statin users were significantly younger, had more comorbidities, and were more likely to use inhaled or oral corticosteroids than were the nonstatin users.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective nature of the study and a lack of information on prescribed daily doses of medication, the researchers noted. However, the results support those from previous studies and suggest that “the anti-inflammatory effect of statins may attenuate anxiety and depression in ACOS patients, even in the late stages of the disease,” although the exact mechanism of action remains unknown and larger, randomized, controlled trials are needed, they said.
The study was supported by grants from a variety of organizations in Taiwan, China, and Japan. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Yeh JJ et al. J Affect Disord. 2019 Jun 15; 253:277-84.
based on data from approximately 9,000 patients.
Although asthma–COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) has been associated with depression, the effects of oral and inhaled corticosteroids on anxiety and depression in these patients have not been well investigated, wrote Jun-Jun Yeh, MD, of Ditmanson Medical Foundation Chia-Yi (Taiwan) Christian Hospital, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, the researchers analyzed 9,139 ACOS patients including 1,252 statin users and 7,887 nonstatin users; 62% were male.
The statin users had significantly lower risk of both anxiety and depression than did the nonstatin users (adjusted hazard ratio 0.34 for anxiety and 0.36 for depression) after researchers controlled for factors including age, sex, comorbidities, and medications. Statin users experienced a total of 109 anxiety or depression events over an average of 8 years’ follow-up, while nonstatin users experienced a total of 1,333 anxiety or depression events over an average of 5 years’ follow-up.
The incidence density rate of anxiety was 11/1,000 person-years for statin users and 33/1,000 person-years for nonstatin users. The incidence density rate of depression was 3/1,000 person-years for statin users and 9/1,000 person-years for nonstatin users.
Significantly lower risk of anxiety and depression also were observed in statin users, compared with nonstatin users, in subgroups of men, women, patients younger than 50 years, and patients aged 50 years and older. The risks of anxiety and depression were lower in statin users versus nonstatin users across all subgroups with or without inhaled or oral corticosteroids.
Overall, the statin users were significantly younger, had more comorbidities, and were more likely to use inhaled or oral corticosteroids than were the nonstatin users.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective nature of the study and a lack of information on prescribed daily doses of medication, the researchers noted. However, the results support those from previous studies and suggest that “the anti-inflammatory effect of statins may attenuate anxiety and depression in ACOS patients, even in the late stages of the disease,” although the exact mechanism of action remains unknown and larger, randomized, controlled trials are needed, they said.
The study was supported by grants from a variety of organizations in Taiwan, China, and Japan. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Yeh JJ et al. J Affect Disord. 2019 Jun 15; 253:277-84.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF AFFECTIVE DISORDERS
COPD eosinophil counts predict steroid responders
Triple therapy with an inhaled corticosteroid is particularly helpful for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who have high baseline eosinophil counts, a trial involving more than 10,000 patients found.
Former smokers received greater benefit from inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) than did current smokers, reported lead author Steven Pascoe, MBBS, of GlaxoSmithKline and colleagues. The investigators noted that these findings can help personalize therapy for patients with COPD, which can be challenging to treat because of its heterogeneity. The study was published in Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
The phase 3 IMPACT trial compared single-inhaler fluticasone furoate–umeclidinium–vilanterol with umeclidinium-vilanterol and fluticasone furoate–vilanterol in patients with moderate to very severe COPD at high risk of exacerbation. Of the 10,333 patients involved, approximately one-quarter (26%) had one or more severe exacerbations in the previous year and half (47%) had two or more moderate exacerbations in the same time period. All patients were symptomatic and were aged 40 years or older. A variety of baseline and demographic patient characteristics were recorded, including blood eosinophil count, smoking status, and others. Responses to therapy were measured with trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), symptom scoring, and a quality of life questionnaire.
After 52 weeks, results showed that higher baseline eosinophil counts were associated with progressively greater benefits in favor of triple therapy. For patients with baseline blood eosinophil counts of at least 310 cells per mcL, triple therapy was associated with about half as many moderate and severe exacerbations as treatment with umeclidinium-vilanterol (rate ratio = 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.47-0.66). For patients with less than 90 cells per mcL at baseline, the rate ratio for the same two regimens was 0.88, but with a confidence interval crossing 1 (0.74-1.04). For fluticasone furoate–vilanterol vs. umeclidinium-vilanterol, high baseline eosinophil count again demonstrated its predictive power for ICS efficacy, again with an associated rate ratio of 0.56 (0.47-0.66), compared with 1.09 (0.91-1.29) for patients below the lower threshold. Symptom scoring, quality of life, and FEV1 followed a similar trend, although the investigators noted that this was “less marked” for FEV1. Although the trend held regardless of smoking status, benefits were more pronounced among former smokers than current smokers.
“In former smokers, ICS benefits were observed at all blood eosinophil counts when comparing triple therapy with umeclidinium-vilanterol, whereas in current smokers no ICS benefit was observed at lower eosinophil counts, less than approximately 200 eosinophils per [mcL],” the investigators wrote.
“Overall, these results show the potential use of blood eosinophil counts in conjunction with smoking status to predict the magnitude of ICS response within a dual or triple-combination therapy,” the investigators concluded. “Future approaches to the pharmacological management of COPD should move beyond the simple dichotomization of each clinical or biomarker variable, toward more complex algorithms that integrate the interactions between important variables including exacerbation history, smoking status, and blood eosinophil counts.”
The study was funded by GlaxoSmithKline. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, CSA Medical, and others.
SOURCE: Pascoe S et al. Lancet Resp Med. 2019 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30190-0.
Triple therapy with an inhaled corticosteroid is particularly helpful for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who have high baseline eosinophil counts, a trial involving more than 10,000 patients found.
Former smokers received greater benefit from inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) than did current smokers, reported lead author Steven Pascoe, MBBS, of GlaxoSmithKline and colleagues. The investigators noted that these findings can help personalize therapy for patients with COPD, which can be challenging to treat because of its heterogeneity. The study was published in Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
The phase 3 IMPACT trial compared single-inhaler fluticasone furoate–umeclidinium–vilanterol with umeclidinium-vilanterol and fluticasone furoate–vilanterol in patients with moderate to very severe COPD at high risk of exacerbation. Of the 10,333 patients involved, approximately one-quarter (26%) had one or more severe exacerbations in the previous year and half (47%) had two or more moderate exacerbations in the same time period. All patients were symptomatic and were aged 40 years or older. A variety of baseline and demographic patient characteristics were recorded, including blood eosinophil count, smoking status, and others. Responses to therapy were measured with trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), symptom scoring, and a quality of life questionnaire.
After 52 weeks, results showed that higher baseline eosinophil counts were associated with progressively greater benefits in favor of triple therapy. For patients with baseline blood eosinophil counts of at least 310 cells per mcL, triple therapy was associated with about half as many moderate and severe exacerbations as treatment with umeclidinium-vilanterol (rate ratio = 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.47-0.66). For patients with less than 90 cells per mcL at baseline, the rate ratio for the same two regimens was 0.88, but with a confidence interval crossing 1 (0.74-1.04). For fluticasone furoate–vilanterol vs. umeclidinium-vilanterol, high baseline eosinophil count again demonstrated its predictive power for ICS efficacy, again with an associated rate ratio of 0.56 (0.47-0.66), compared with 1.09 (0.91-1.29) for patients below the lower threshold. Symptom scoring, quality of life, and FEV1 followed a similar trend, although the investigators noted that this was “less marked” for FEV1. Although the trend held regardless of smoking status, benefits were more pronounced among former smokers than current smokers.
“In former smokers, ICS benefits were observed at all blood eosinophil counts when comparing triple therapy with umeclidinium-vilanterol, whereas in current smokers no ICS benefit was observed at lower eosinophil counts, less than approximately 200 eosinophils per [mcL],” the investigators wrote.
“Overall, these results show the potential use of blood eosinophil counts in conjunction with smoking status to predict the magnitude of ICS response within a dual or triple-combination therapy,” the investigators concluded. “Future approaches to the pharmacological management of COPD should move beyond the simple dichotomization of each clinical or biomarker variable, toward more complex algorithms that integrate the interactions between important variables including exacerbation history, smoking status, and blood eosinophil counts.”
The study was funded by GlaxoSmithKline. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, CSA Medical, and others.
SOURCE: Pascoe S et al. Lancet Resp Med. 2019 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30190-0.
Triple therapy with an inhaled corticosteroid is particularly helpful for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who have high baseline eosinophil counts, a trial involving more than 10,000 patients found.
Former smokers received greater benefit from inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) than did current smokers, reported lead author Steven Pascoe, MBBS, of GlaxoSmithKline and colleagues. The investigators noted that these findings can help personalize therapy for patients with COPD, which can be challenging to treat because of its heterogeneity. The study was published in Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
The phase 3 IMPACT trial compared single-inhaler fluticasone furoate–umeclidinium–vilanterol with umeclidinium-vilanterol and fluticasone furoate–vilanterol in patients with moderate to very severe COPD at high risk of exacerbation. Of the 10,333 patients involved, approximately one-quarter (26%) had one or more severe exacerbations in the previous year and half (47%) had two or more moderate exacerbations in the same time period. All patients were symptomatic and were aged 40 years or older. A variety of baseline and demographic patient characteristics were recorded, including blood eosinophil count, smoking status, and others. Responses to therapy were measured with trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), symptom scoring, and a quality of life questionnaire.
After 52 weeks, results showed that higher baseline eosinophil counts were associated with progressively greater benefits in favor of triple therapy. For patients with baseline blood eosinophil counts of at least 310 cells per mcL, triple therapy was associated with about half as many moderate and severe exacerbations as treatment with umeclidinium-vilanterol (rate ratio = 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.47-0.66). For patients with less than 90 cells per mcL at baseline, the rate ratio for the same two regimens was 0.88, but with a confidence interval crossing 1 (0.74-1.04). For fluticasone furoate–vilanterol vs. umeclidinium-vilanterol, high baseline eosinophil count again demonstrated its predictive power for ICS efficacy, again with an associated rate ratio of 0.56 (0.47-0.66), compared with 1.09 (0.91-1.29) for patients below the lower threshold. Symptom scoring, quality of life, and FEV1 followed a similar trend, although the investigators noted that this was “less marked” for FEV1. Although the trend held regardless of smoking status, benefits were more pronounced among former smokers than current smokers.
“In former smokers, ICS benefits were observed at all blood eosinophil counts when comparing triple therapy with umeclidinium-vilanterol, whereas in current smokers no ICS benefit was observed at lower eosinophil counts, less than approximately 200 eosinophils per [mcL],” the investigators wrote.
“Overall, these results show the potential use of blood eosinophil counts in conjunction with smoking status to predict the magnitude of ICS response within a dual or triple-combination therapy,” the investigators concluded. “Future approaches to the pharmacological management of COPD should move beyond the simple dichotomization of each clinical or biomarker variable, toward more complex algorithms that integrate the interactions between important variables including exacerbation history, smoking status, and blood eosinophil counts.”
The study was funded by GlaxoSmithKline. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, CSA Medical, and others.
SOURCE: Pascoe S et al. Lancet Resp Med. 2019 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30190-0.
FROM LANCET RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
New COPD subtypes help refine risk
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is often heterogeneous in its presentation and prognosis, and neither pulmonary function tests nor CT alone are always adequate to characterize a patient’s disease. a study has found.
In a paper published in CHEST, Jinkyeong Park, MD, PhD, of Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital in Goyang, South Korea, and colleagues looked at data from 9,080 subjects enrolled in the COPDGene study, an observational cohort of longtime smokers with and without COPD. By assessing visually defined patterns of emphysema with quantitative imaging features and spirometry data, the researchers identified 10 distinct subtypes of COPD (including no disease) and noted significant differences in mortality and progression among them.
Dr. Park and colleagues found that patients in the subgroups with quantitative but no visual emphysema and those with visual but not quantitative emphysema represented unique groups with mild COPD that were both at risk for progression – but with likely different underlying mechanisms. Current smokers, women, and whites were more common among subjects showing visually defined emphysema without quantitative evidence. “Many of the subjects in the visual-only emphysema subtype have areas of low lung density due to emphysema masked by smoking-induced lung inflammation,” the researchers wrote.
Overall 5-year mortality differed significantly among the groups (P less than .01) and was highest in the three groups with moderate to severe centrilobular emphysema. Patients with paraseptal and moderate to severe centrilobular emphysema showed substantial progression of emphysema over 5 years, compared with individuals with no CT abnormality (P less than .05).
“These results suggest that the combination of visual and quantitative CT features, which may reflect different underlying pathobiological processes in COPD, may provide a superior approach to classify individuals with COPD, compared to the use of visual or quantitative CT features alone,” the researchers wrote.
The study received funding from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Three of the study’s coauthors reported conflicts of interest in the form of patent applications or financial support from pharmaceutical firms. The COPDGene Project receives pharmaceutical industry and U.S. government support.
SOURCE: Park J et al. CHEST. 2019 Jul 5. doi:10:1016/j.chest.2019.06.15.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is often heterogeneous in its presentation and prognosis, and neither pulmonary function tests nor CT alone are always adequate to characterize a patient’s disease. a study has found.
In a paper published in CHEST, Jinkyeong Park, MD, PhD, of Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital in Goyang, South Korea, and colleagues looked at data from 9,080 subjects enrolled in the COPDGene study, an observational cohort of longtime smokers with and without COPD. By assessing visually defined patterns of emphysema with quantitative imaging features and spirometry data, the researchers identified 10 distinct subtypes of COPD (including no disease) and noted significant differences in mortality and progression among them.
Dr. Park and colleagues found that patients in the subgroups with quantitative but no visual emphysema and those with visual but not quantitative emphysema represented unique groups with mild COPD that were both at risk for progression – but with likely different underlying mechanisms. Current smokers, women, and whites were more common among subjects showing visually defined emphysema without quantitative evidence. “Many of the subjects in the visual-only emphysema subtype have areas of low lung density due to emphysema masked by smoking-induced lung inflammation,” the researchers wrote.
Overall 5-year mortality differed significantly among the groups (P less than .01) and was highest in the three groups with moderate to severe centrilobular emphysema. Patients with paraseptal and moderate to severe centrilobular emphysema showed substantial progression of emphysema over 5 years, compared with individuals with no CT abnormality (P less than .05).
“These results suggest that the combination of visual and quantitative CT features, which may reflect different underlying pathobiological processes in COPD, may provide a superior approach to classify individuals with COPD, compared to the use of visual or quantitative CT features alone,” the researchers wrote.
The study received funding from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Three of the study’s coauthors reported conflicts of interest in the form of patent applications or financial support from pharmaceutical firms. The COPDGene Project receives pharmaceutical industry and U.S. government support.
SOURCE: Park J et al. CHEST. 2019 Jul 5. doi:10:1016/j.chest.2019.06.15.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is often heterogeneous in its presentation and prognosis, and neither pulmonary function tests nor CT alone are always adequate to characterize a patient’s disease. a study has found.
In a paper published in CHEST, Jinkyeong Park, MD, PhD, of Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital in Goyang, South Korea, and colleagues looked at data from 9,080 subjects enrolled in the COPDGene study, an observational cohort of longtime smokers with and without COPD. By assessing visually defined patterns of emphysema with quantitative imaging features and spirometry data, the researchers identified 10 distinct subtypes of COPD (including no disease) and noted significant differences in mortality and progression among them.
Dr. Park and colleagues found that patients in the subgroups with quantitative but no visual emphysema and those with visual but not quantitative emphysema represented unique groups with mild COPD that were both at risk for progression – but with likely different underlying mechanisms. Current smokers, women, and whites were more common among subjects showing visually defined emphysema without quantitative evidence. “Many of the subjects in the visual-only emphysema subtype have areas of low lung density due to emphysema masked by smoking-induced lung inflammation,” the researchers wrote.
Overall 5-year mortality differed significantly among the groups (P less than .01) and was highest in the three groups with moderate to severe centrilobular emphysema. Patients with paraseptal and moderate to severe centrilobular emphysema showed substantial progression of emphysema over 5 years, compared with individuals with no CT abnormality (P less than .05).
“These results suggest that the combination of visual and quantitative CT features, which may reflect different underlying pathobiological processes in COPD, may provide a superior approach to classify individuals with COPD, compared to the use of visual or quantitative CT features alone,” the researchers wrote.
The study received funding from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Three of the study’s coauthors reported conflicts of interest in the form of patent applications or financial support from pharmaceutical firms. The COPDGene Project receives pharmaceutical industry and U.S. government support.
SOURCE: Park J et al. CHEST. 2019 Jul 5. doi:10:1016/j.chest.2019.06.15.
FROM CHEST
Patients with COPD at heightened risk for community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are at a significantly increased risk for hospitalization for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), compared with patients without COPD, a large prospective study has found.
Jose Bordon, MD, and colleagues aimed to define incidence and outcomes of COPD patients hospitalized with pneumonia in the city of Louisville, Ky., and to extrapolate the burden of disease in the U.S. population. They conducted a secondary analysis of data from the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study, a prospective population-based cohort study of all hospitalized adults with CAP who were residents in the city of Louisville, Ky., from June 1, 2014, to May 31, 2016.
COPD prevalence in the city of Louisville was derived via data from the 2014 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) as well as from the 2014 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS). In addition, the researchers analyzed clinical outcomes including time to clinical stability (TCS), length of hospital stay (LOS), and mortality, according to Dr. Bordon, an infectious disease specialist at Providence Health Center, Washington, and colleagues on behalf of the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study Group.
The researchers found an 18-fold greater incidence of community-acquired pneumonia in patients with COPD, compared with non-COPD patients.
A total of 18,246 individuals aged 40 and older with COPD were estimated to live in Louisville, Ky. The researchers found that 3,419 COPD patients were hospitalized due to CAP in Louisville during the 2-year study period. COPD patients, compared with non-COPD patients, were more likely to have a history of heart failure, more ICU admissions, and use of mechanical ventilation, compared with patients without COPD. The two groups had similar pneumonia severity index scores, and 17% received oral steroids prior to admission. COPD patients had more pneumococcal pneumonia, despite receiving pneumococcal vaccine significantly more often than non-COPD patients.
The annual incidence of hospitalized CAP was 9,369 cases per 100,000 COPD patients in the city of Louisville. In the same period, the incidence of CAP in patients without COPD was 509 per 100,000, a more than 18-fold difference.
Although the incidence of CAP in COPD patients was much higher than in those without, the difference didn’t appear to have an impact on clinical outcomes. There were no clinical differences among patients with vs. without COPD in regard to time to reach clinical improvement and time of hospital discharge, and in-hospital mortality was not statistically significantly different between the groups, the authors reported. The mortality of COPD patients during hospitalization, at 30 days, at 6 months, and at 1 year was 5.6% of patients, 11.9%, 24.3%, and 33.0%, respectively vs. 6.6%, 14.2%, 24.2%, and 30.1% in non-COPD patients. However, 1-year all-cause mortality was a significant 25% greater among COPD patients, as might be expected by the progression and effects of the underlying disease.
“[Our] observations mean that nearly 1 in 10 persons with COPD will be hospitalized annually due to CAP. This translates into approximately 500,000 COPD patients hospitalized with CAP every year in the U.S., resulting in a substantial burden of approximately 5 billion U.S. dollars in hospitalization costs,” the researchers stated.
“Modifiable factors associated with CAP such as tobacco smoking and immunizations should be health interventions to prevent the burden of CAP in COPD patients,” even though “pneumococcal vaccination was used more often in the COPD population than in other CAP patients, but pneumococcal pneumonia still occurred at a numerically higher rate,” they noted.
The study was supported by the University of Louisville, Ky., with partial support from Pfizer. The authors reported having no conflicts.
SOURCE: Bordon JM et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019 Jun 26; doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.06.025.
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are at a significantly increased risk for hospitalization for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), compared with patients without COPD, a large prospective study has found.
Jose Bordon, MD, and colleagues aimed to define incidence and outcomes of COPD patients hospitalized with pneumonia in the city of Louisville, Ky., and to extrapolate the burden of disease in the U.S. population. They conducted a secondary analysis of data from the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study, a prospective population-based cohort study of all hospitalized adults with CAP who were residents in the city of Louisville, Ky., from June 1, 2014, to May 31, 2016.
COPD prevalence in the city of Louisville was derived via data from the 2014 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) as well as from the 2014 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS). In addition, the researchers analyzed clinical outcomes including time to clinical stability (TCS), length of hospital stay (LOS), and mortality, according to Dr. Bordon, an infectious disease specialist at Providence Health Center, Washington, and colleagues on behalf of the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study Group.
The researchers found an 18-fold greater incidence of community-acquired pneumonia in patients with COPD, compared with non-COPD patients.
A total of 18,246 individuals aged 40 and older with COPD were estimated to live in Louisville, Ky. The researchers found that 3,419 COPD patients were hospitalized due to CAP in Louisville during the 2-year study period. COPD patients, compared with non-COPD patients, were more likely to have a history of heart failure, more ICU admissions, and use of mechanical ventilation, compared with patients without COPD. The two groups had similar pneumonia severity index scores, and 17% received oral steroids prior to admission. COPD patients had more pneumococcal pneumonia, despite receiving pneumococcal vaccine significantly more often than non-COPD patients.
The annual incidence of hospitalized CAP was 9,369 cases per 100,000 COPD patients in the city of Louisville. In the same period, the incidence of CAP in patients without COPD was 509 per 100,000, a more than 18-fold difference.
Although the incidence of CAP in COPD patients was much higher than in those without, the difference didn’t appear to have an impact on clinical outcomes. There were no clinical differences among patients with vs. without COPD in regard to time to reach clinical improvement and time of hospital discharge, and in-hospital mortality was not statistically significantly different between the groups, the authors reported. The mortality of COPD patients during hospitalization, at 30 days, at 6 months, and at 1 year was 5.6% of patients, 11.9%, 24.3%, and 33.0%, respectively vs. 6.6%, 14.2%, 24.2%, and 30.1% in non-COPD patients. However, 1-year all-cause mortality was a significant 25% greater among COPD patients, as might be expected by the progression and effects of the underlying disease.
“[Our] observations mean that nearly 1 in 10 persons with COPD will be hospitalized annually due to CAP. This translates into approximately 500,000 COPD patients hospitalized with CAP every year in the U.S., resulting in a substantial burden of approximately 5 billion U.S. dollars in hospitalization costs,” the researchers stated.
“Modifiable factors associated with CAP such as tobacco smoking and immunizations should be health interventions to prevent the burden of CAP in COPD patients,” even though “pneumococcal vaccination was used more often in the COPD population than in other CAP patients, but pneumococcal pneumonia still occurred at a numerically higher rate,” they noted.
The study was supported by the University of Louisville, Ky., with partial support from Pfizer. The authors reported having no conflicts.
SOURCE: Bordon JM et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019 Jun 26; doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.06.025.
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are at a significantly increased risk for hospitalization for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), compared with patients without COPD, a large prospective study has found.
Jose Bordon, MD, and colleagues aimed to define incidence and outcomes of COPD patients hospitalized with pneumonia in the city of Louisville, Ky., and to extrapolate the burden of disease in the U.S. population. They conducted a secondary analysis of data from the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study, a prospective population-based cohort study of all hospitalized adults with CAP who were residents in the city of Louisville, Ky., from June 1, 2014, to May 31, 2016.
COPD prevalence in the city of Louisville was derived via data from the 2014 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) as well as from the 2014 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS). In addition, the researchers analyzed clinical outcomes including time to clinical stability (TCS), length of hospital stay (LOS), and mortality, according to Dr. Bordon, an infectious disease specialist at Providence Health Center, Washington, and colleagues on behalf of the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study Group.
The researchers found an 18-fold greater incidence of community-acquired pneumonia in patients with COPD, compared with non-COPD patients.
A total of 18,246 individuals aged 40 and older with COPD were estimated to live in Louisville, Ky. The researchers found that 3,419 COPD patients were hospitalized due to CAP in Louisville during the 2-year study period. COPD patients, compared with non-COPD patients, were more likely to have a history of heart failure, more ICU admissions, and use of mechanical ventilation, compared with patients without COPD. The two groups had similar pneumonia severity index scores, and 17% received oral steroids prior to admission. COPD patients had more pneumococcal pneumonia, despite receiving pneumococcal vaccine significantly more often than non-COPD patients.
The annual incidence of hospitalized CAP was 9,369 cases per 100,000 COPD patients in the city of Louisville. In the same period, the incidence of CAP in patients without COPD was 509 per 100,000, a more than 18-fold difference.
Although the incidence of CAP in COPD patients was much higher than in those without, the difference didn’t appear to have an impact on clinical outcomes. There were no clinical differences among patients with vs. without COPD in regard to time to reach clinical improvement and time of hospital discharge, and in-hospital mortality was not statistically significantly different between the groups, the authors reported. The mortality of COPD patients during hospitalization, at 30 days, at 6 months, and at 1 year was 5.6% of patients, 11.9%, 24.3%, and 33.0%, respectively vs. 6.6%, 14.2%, 24.2%, and 30.1% in non-COPD patients. However, 1-year all-cause mortality was a significant 25% greater among COPD patients, as might be expected by the progression and effects of the underlying disease.
“[Our] observations mean that nearly 1 in 10 persons with COPD will be hospitalized annually due to CAP. This translates into approximately 500,000 COPD patients hospitalized with CAP every year in the U.S., resulting in a substantial burden of approximately 5 billion U.S. dollars in hospitalization costs,” the researchers stated.
“Modifiable factors associated with CAP such as tobacco smoking and immunizations should be health interventions to prevent the burden of CAP in COPD patients,” even though “pneumococcal vaccination was used more often in the COPD population than in other CAP patients, but pneumococcal pneumonia still occurred at a numerically higher rate,” they noted.
The study was supported by the University of Louisville, Ky., with partial support from Pfizer. The authors reported having no conflicts.
SOURCE: Bordon JM et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019 Jun 26; doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.06.025.
FROM CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND INFECTION
C-reactive protein testing reduced antibiotic prescribing in patients with COPD exacerbation
, according to a recent randomized, controlled trial.
Point-of-care C-reactive protein (CRP) testing led to fewer antibiotic prescriptions at the initial consultation, according to investigators participating in the PACE study, a multicenter, open-label trial of more than 600 patients with COPD enrolled at one of 86 general practices in the United Kingdom.
Patient-reported antibiotic use over the next 4 weeks was more than 20 percentage points lower for the group managed with the point-of-care strategy, compared with those who received usual care, according to the investigators, led by Christopher C. Butler, FMedSci, of the Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences at the University of Oxford (England).
Less antibiotic use and fewer prescriptions did not compromise patient-reported, disease-specific quality of life, added Dr. Butler and colleagues. Their report appears in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In the United States and in Europe, more than 80% of COPD patients with acute exacerbations will receive an antibiotic prescription, according to Dr. Butler and coauthors.
“Although many patients who have acute exacerbations of COPD are helped by these treatments, others are not,” wrote the investigators, noting that in one hospital-based study, about one in five such exacerbations were thought to be due to noninfectious causes.
The present study included patients at least 40 years of age who presented to a primary care practice with an acute exacerbation and at least one of the three Anthonisen criteria (increased dyspnea, sputum production, and sputum purulence) intended to guide antibiotic therapy in COPD. A total of 325 were randomly assigned to the CRP testing group, and 324 to a group that received just usual care.
Antibiotic use was reported by fewer patients in the CRP testing group, compared with the usual-care group (57.0% vs. 77.4%; adjusted odds ratio, 0.31, 95% confidence interval, 0.20-0.47), the investigators reported.
Only 47.7% of patients in the CRP-guided group received antibiotic prescriptions at the initial consultation, vs. 69.7% of patients in the usual care group.
Hospitalizations over 6 months of follow-up were reported for 8.6% and 9.3% of patients in the CRP-guided and usual-care groups, respectively, while diagnoses of pneumonia were recorded for 3.0% and 4.0%. There was no clinically important difference between groups in the rate of antibiotic-related adverse effects.
“The evidence from our trial suggests that CRP-guided antibiotic prescribing for COPD exacerbations in primary care clinics may reduce patient-reported use of antibiotics and the prescribing of antibiotics by clinicians,” Dr. Butler and colleagues said in a discussion of these results.
Findings from the study by Dr. Butler and colleagues are “compelling enough” to support C-reactive protein (CRP) testing to guide antibiotic use in patient who have acute exacerbations of COPD, wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
“The trial achieved its objective, which was to show that CRP testing safely reduces antibiotic use,” stated Allan S. Brett, MD, and Majdi N. Al-Hasan, MB,BS, of the department of medicine at the University of South Carolina, Columbia.
Point-of-care testing of CRP could be applied even more broadly in clinical practice, Dr. Brett and Dr. Al-Hasan wrote, since testing has been shown to reduce prescribing of antibiotics for suspected lower respiratory tract infections and other common presentations in patients with no COPD.
“Whether primary care practices in the United States would embrace point-of-care CRP testing is another matter, given the regulatory requirements for in-office laboratory testing and uncertainty about reimbursement,” they noted.
Reduced antibiotic prescribing in patients with COPD likely has certain benefits, including reducing risk of Clostridioides difficile colitis, according to the authors.
By contrast, the current study did not determine which COPD patients might benefit from antibiotics, if any, nor which antibiotic might be warranted for those patients.
The study was supported by the Health Technology Assessment Program of the UK National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Butler reported disclosures related to Roche Molecular Systems and Roche Molecular Diagnostics, among others.
SOURCE: Butler CC et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 10;381:111-20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1803185.
, according to a recent randomized, controlled trial.
Point-of-care C-reactive protein (CRP) testing led to fewer antibiotic prescriptions at the initial consultation, according to investigators participating in the PACE study, a multicenter, open-label trial of more than 600 patients with COPD enrolled at one of 86 general practices in the United Kingdom.
Patient-reported antibiotic use over the next 4 weeks was more than 20 percentage points lower for the group managed with the point-of-care strategy, compared with those who received usual care, according to the investigators, led by Christopher C. Butler, FMedSci, of the Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences at the University of Oxford (England).
Less antibiotic use and fewer prescriptions did not compromise patient-reported, disease-specific quality of life, added Dr. Butler and colleagues. Their report appears in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In the United States and in Europe, more than 80% of COPD patients with acute exacerbations will receive an antibiotic prescription, according to Dr. Butler and coauthors.
“Although many patients who have acute exacerbations of COPD are helped by these treatments, others are not,” wrote the investigators, noting that in one hospital-based study, about one in five such exacerbations were thought to be due to noninfectious causes.
The present study included patients at least 40 years of age who presented to a primary care practice with an acute exacerbation and at least one of the three Anthonisen criteria (increased dyspnea, sputum production, and sputum purulence) intended to guide antibiotic therapy in COPD. A total of 325 were randomly assigned to the CRP testing group, and 324 to a group that received just usual care.
Antibiotic use was reported by fewer patients in the CRP testing group, compared with the usual-care group (57.0% vs. 77.4%; adjusted odds ratio, 0.31, 95% confidence interval, 0.20-0.47), the investigators reported.
Only 47.7% of patients in the CRP-guided group received antibiotic prescriptions at the initial consultation, vs. 69.7% of patients in the usual care group.
Hospitalizations over 6 months of follow-up were reported for 8.6% and 9.3% of patients in the CRP-guided and usual-care groups, respectively, while diagnoses of pneumonia were recorded for 3.0% and 4.0%. There was no clinically important difference between groups in the rate of antibiotic-related adverse effects.
“The evidence from our trial suggests that CRP-guided antibiotic prescribing for COPD exacerbations in primary care clinics may reduce patient-reported use of antibiotics and the prescribing of antibiotics by clinicians,” Dr. Butler and colleagues said in a discussion of these results.
Findings from the study by Dr. Butler and colleagues are “compelling enough” to support C-reactive protein (CRP) testing to guide antibiotic use in patient who have acute exacerbations of COPD, wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
“The trial achieved its objective, which was to show that CRP testing safely reduces antibiotic use,” stated Allan S. Brett, MD, and Majdi N. Al-Hasan, MB,BS, of the department of medicine at the University of South Carolina, Columbia.
Point-of-care testing of CRP could be applied even more broadly in clinical practice, Dr. Brett and Dr. Al-Hasan wrote, since testing has been shown to reduce prescribing of antibiotics for suspected lower respiratory tract infections and other common presentations in patients with no COPD.
“Whether primary care practices in the United States would embrace point-of-care CRP testing is another matter, given the regulatory requirements for in-office laboratory testing and uncertainty about reimbursement,” they noted.
Reduced antibiotic prescribing in patients with COPD likely has certain benefits, including reducing risk of Clostridioides difficile colitis, according to the authors.
By contrast, the current study did not determine which COPD patients might benefit from antibiotics, if any, nor which antibiotic might be warranted for those patients.
The study was supported by the Health Technology Assessment Program of the UK National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Butler reported disclosures related to Roche Molecular Systems and Roche Molecular Diagnostics, among others.
SOURCE: Butler CC et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 10;381:111-20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1803185.
, according to a recent randomized, controlled trial.
Point-of-care C-reactive protein (CRP) testing led to fewer antibiotic prescriptions at the initial consultation, according to investigators participating in the PACE study, a multicenter, open-label trial of more than 600 patients with COPD enrolled at one of 86 general practices in the United Kingdom.
Patient-reported antibiotic use over the next 4 weeks was more than 20 percentage points lower for the group managed with the point-of-care strategy, compared with those who received usual care, according to the investigators, led by Christopher C. Butler, FMedSci, of the Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences at the University of Oxford (England).
Less antibiotic use and fewer prescriptions did not compromise patient-reported, disease-specific quality of life, added Dr. Butler and colleagues. Their report appears in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In the United States and in Europe, more than 80% of COPD patients with acute exacerbations will receive an antibiotic prescription, according to Dr. Butler and coauthors.
“Although many patients who have acute exacerbations of COPD are helped by these treatments, others are not,” wrote the investigators, noting that in one hospital-based study, about one in five such exacerbations were thought to be due to noninfectious causes.
The present study included patients at least 40 years of age who presented to a primary care practice with an acute exacerbation and at least one of the three Anthonisen criteria (increased dyspnea, sputum production, and sputum purulence) intended to guide antibiotic therapy in COPD. A total of 325 were randomly assigned to the CRP testing group, and 324 to a group that received just usual care.
Antibiotic use was reported by fewer patients in the CRP testing group, compared with the usual-care group (57.0% vs. 77.4%; adjusted odds ratio, 0.31, 95% confidence interval, 0.20-0.47), the investigators reported.
Only 47.7% of patients in the CRP-guided group received antibiotic prescriptions at the initial consultation, vs. 69.7% of patients in the usual care group.
Hospitalizations over 6 months of follow-up were reported for 8.6% and 9.3% of patients in the CRP-guided and usual-care groups, respectively, while diagnoses of pneumonia were recorded for 3.0% and 4.0%. There was no clinically important difference between groups in the rate of antibiotic-related adverse effects.
“The evidence from our trial suggests that CRP-guided antibiotic prescribing for COPD exacerbations in primary care clinics may reduce patient-reported use of antibiotics and the prescribing of antibiotics by clinicians,” Dr. Butler and colleagues said in a discussion of these results.
Findings from the study by Dr. Butler and colleagues are “compelling enough” to support C-reactive protein (CRP) testing to guide antibiotic use in patient who have acute exacerbations of COPD, wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
“The trial achieved its objective, which was to show that CRP testing safely reduces antibiotic use,” stated Allan S. Brett, MD, and Majdi N. Al-Hasan, MB,BS, of the department of medicine at the University of South Carolina, Columbia.
Point-of-care testing of CRP could be applied even more broadly in clinical practice, Dr. Brett and Dr. Al-Hasan wrote, since testing has been shown to reduce prescribing of antibiotics for suspected lower respiratory tract infections and other common presentations in patients with no COPD.
“Whether primary care practices in the United States would embrace point-of-care CRP testing is another matter, given the regulatory requirements for in-office laboratory testing and uncertainty about reimbursement,” they noted.
Reduced antibiotic prescribing in patients with COPD likely has certain benefits, including reducing risk of Clostridioides difficile colitis, according to the authors.
By contrast, the current study did not determine which COPD patients might benefit from antibiotics, if any, nor which antibiotic might be warranted for those patients.
The study was supported by the Health Technology Assessment Program of the UK National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Butler reported disclosures related to Roche Molecular Systems and Roche Molecular Diagnostics, among others.
SOURCE: Butler CC et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 10;381:111-20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1803185.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Sicker COPD patients may be more likely to initiate arformoterol
according to study to identify predictors of its use. In addition to being sicker, being treated by a pulmonologist rather than a primary care physician and being white were factors that increased a patient’s likelihood of receiving nebulized arformoterol.
Patients less likely to receive the nebulized version of this long-acting beta2 adrenoreceptor agonist (LABA) were African Americans, patients with psychiatric comorbidities, and patients eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid.
“Studies have shown that 40% to 71% of Medicare beneficiaries receive no maintenance treatment for COPD. Although a recent longitudinal study on Medicare populations reported that use of maintenance medications has been improving, in general, it is recognized that Medicare beneficiaries with COPD remain undertreated,” Todd P. Gilmer, PhD, from the department of family medicine and public health at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote.
The investigators identified patients with COPD using Medicare administrative data; of these patients, 11,887 were arformoterol users, and 450,178 were control patients who did not use arformoterol. Patients were included in the study if they had at least one claim for COPD medication and were continuously enrolled in Medicare Parts A, B, and D. The cohort consisted of mostly white women aged 70 years or older, and 47% were dual-eligible to receive both Medicare and Medicaid benefits. A subgroup of 1,778 arformoterol users were also identified for analysis who were hospitalized and discharged within 30 days of using arformoterol, as well as a subgroup of 21,910 control patients with hospitalizations.
The researchers found COPD-related hospitalization (odds ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-1.39; P less than .001), exacerbation (OR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.26-1.41; P less than .001), use of a systemic corticosteroid (OR, 1.50; 95% CI, 1.43-1.57; P less than .001) or methylxanthine (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.28-1.47; P less than .001), use of oxygen therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.93-2.09; P less than .001), pulmonologist care (OR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.34-1.46; P less than .001), and respiratory therapist care (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.11-1.36; P less than .001) strongly predicted arformoterol use, while racial/ethnic minority status, psychiatric comorbidity (OR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.56-0.76; P less than .001), acquired immune deficiency syndrome (OR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.52-0.94; P less than .01), and dual-eligibility for Medicare and Medicaid (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.70-0.77; P less than .001) lowered the odds of arformoterol use (P less than .001). In the subgroup of patients with hospitalizations, COPD-related admission (OR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.55-2.14; P less than .001), exacerbation (OR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.88-3.63; P less than .001)m and inpatient care from a pulmonologist (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.58-2.01; P less than .001) predicted arformoterol use.
“Given the results of this study, increasing access to nebulized maintenance therapy is warranted for select populations with COPD including racial/ethnic minorities, the dual-eligible, and those with certain comorbidities, such as psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Gilmer and colleagues wrote in their study. “Future studies are needed to explore the optimal time to initiate nebulized maintenance therapy, and the potential differential impact of early versus late initiation on patient outcomes.”
Researchers noted that, although their results may seem initially counterintuitive given that COPD has a higher prevalence in men, 56% of the beneficiaries in their Medicare data were women who were 65 years or older, and the results are consistent with other studies that show similar gender distribution findings for maintenance treatment patterns among COPD patients receiving Medicare.
“Since most Medicare beneficiaries with COPD are older than 70 years of age, the higher percentage of women than men in our two cohorts can be explained by the age distributions that ensued as a result of applying our various inclusion and exclusion criteria,” they said.
This study was funded by Sunovian. Dr. Gilmer and one coauthor are paid employees of University of California San Diego, which receives research funding from Advance Health Solutions. Another coauthor is an advisory board member for Advance Health Solutions and a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, and Pulmonix. Two other coauthors are paid employees of Advance Health Solutions, and another is a paid employee of Sunovion.
SOURCE: Gilmer TP et al. COPD. 2019 Jun 19. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2019.1618256.
according to study to identify predictors of its use. In addition to being sicker, being treated by a pulmonologist rather than a primary care physician and being white were factors that increased a patient’s likelihood of receiving nebulized arformoterol.
Patients less likely to receive the nebulized version of this long-acting beta2 adrenoreceptor agonist (LABA) were African Americans, patients with psychiatric comorbidities, and patients eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid.
“Studies have shown that 40% to 71% of Medicare beneficiaries receive no maintenance treatment for COPD. Although a recent longitudinal study on Medicare populations reported that use of maintenance medications has been improving, in general, it is recognized that Medicare beneficiaries with COPD remain undertreated,” Todd P. Gilmer, PhD, from the department of family medicine and public health at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote.
The investigators identified patients with COPD using Medicare administrative data; of these patients, 11,887 were arformoterol users, and 450,178 were control patients who did not use arformoterol. Patients were included in the study if they had at least one claim for COPD medication and were continuously enrolled in Medicare Parts A, B, and D. The cohort consisted of mostly white women aged 70 years or older, and 47% were dual-eligible to receive both Medicare and Medicaid benefits. A subgroup of 1,778 arformoterol users were also identified for analysis who were hospitalized and discharged within 30 days of using arformoterol, as well as a subgroup of 21,910 control patients with hospitalizations.
The researchers found COPD-related hospitalization (odds ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-1.39; P less than .001), exacerbation (OR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.26-1.41; P less than .001), use of a systemic corticosteroid (OR, 1.50; 95% CI, 1.43-1.57; P less than .001) or methylxanthine (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.28-1.47; P less than .001), use of oxygen therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.93-2.09; P less than .001), pulmonologist care (OR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.34-1.46; P less than .001), and respiratory therapist care (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.11-1.36; P less than .001) strongly predicted arformoterol use, while racial/ethnic minority status, psychiatric comorbidity (OR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.56-0.76; P less than .001), acquired immune deficiency syndrome (OR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.52-0.94; P less than .01), and dual-eligibility for Medicare and Medicaid (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.70-0.77; P less than .001) lowered the odds of arformoterol use (P less than .001). In the subgroup of patients with hospitalizations, COPD-related admission (OR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.55-2.14; P less than .001), exacerbation (OR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.88-3.63; P less than .001)m and inpatient care from a pulmonologist (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.58-2.01; P less than .001) predicted arformoterol use.
“Given the results of this study, increasing access to nebulized maintenance therapy is warranted for select populations with COPD including racial/ethnic minorities, the dual-eligible, and those with certain comorbidities, such as psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Gilmer and colleagues wrote in their study. “Future studies are needed to explore the optimal time to initiate nebulized maintenance therapy, and the potential differential impact of early versus late initiation on patient outcomes.”
Researchers noted that, although their results may seem initially counterintuitive given that COPD has a higher prevalence in men, 56% of the beneficiaries in their Medicare data were women who were 65 years or older, and the results are consistent with other studies that show similar gender distribution findings for maintenance treatment patterns among COPD patients receiving Medicare.
“Since most Medicare beneficiaries with COPD are older than 70 years of age, the higher percentage of women than men in our two cohorts can be explained by the age distributions that ensued as a result of applying our various inclusion and exclusion criteria,” they said.
This study was funded by Sunovian. Dr. Gilmer and one coauthor are paid employees of University of California San Diego, which receives research funding from Advance Health Solutions. Another coauthor is an advisory board member for Advance Health Solutions and a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, and Pulmonix. Two other coauthors are paid employees of Advance Health Solutions, and another is a paid employee of Sunovion.
SOURCE: Gilmer TP et al. COPD. 2019 Jun 19. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2019.1618256.
according to study to identify predictors of its use. In addition to being sicker, being treated by a pulmonologist rather than a primary care physician and being white were factors that increased a patient’s likelihood of receiving nebulized arformoterol.
Patients less likely to receive the nebulized version of this long-acting beta2 adrenoreceptor agonist (LABA) were African Americans, patients with psychiatric comorbidities, and patients eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid.
“Studies have shown that 40% to 71% of Medicare beneficiaries receive no maintenance treatment for COPD. Although a recent longitudinal study on Medicare populations reported that use of maintenance medications has been improving, in general, it is recognized that Medicare beneficiaries with COPD remain undertreated,” Todd P. Gilmer, PhD, from the department of family medicine and public health at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote.
The investigators identified patients with COPD using Medicare administrative data; of these patients, 11,887 were arformoterol users, and 450,178 were control patients who did not use arformoterol. Patients were included in the study if they had at least one claim for COPD medication and were continuously enrolled in Medicare Parts A, B, and D. The cohort consisted of mostly white women aged 70 years or older, and 47% were dual-eligible to receive both Medicare and Medicaid benefits. A subgroup of 1,778 arformoterol users were also identified for analysis who were hospitalized and discharged within 30 days of using arformoterol, as well as a subgroup of 21,910 control patients with hospitalizations.
The researchers found COPD-related hospitalization (odds ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-1.39; P less than .001), exacerbation (OR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.26-1.41; P less than .001), use of a systemic corticosteroid (OR, 1.50; 95% CI, 1.43-1.57; P less than .001) or methylxanthine (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.28-1.47; P less than .001), use of oxygen therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.93-2.09; P less than .001), pulmonologist care (OR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.34-1.46; P less than .001), and respiratory therapist care (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.11-1.36; P less than .001) strongly predicted arformoterol use, while racial/ethnic minority status, psychiatric comorbidity (OR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.56-0.76; P less than .001), acquired immune deficiency syndrome (OR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.52-0.94; P less than .01), and dual-eligibility for Medicare and Medicaid (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.70-0.77; P less than .001) lowered the odds of arformoterol use (P less than .001). In the subgroup of patients with hospitalizations, COPD-related admission (OR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.55-2.14; P less than .001), exacerbation (OR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.88-3.63; P less than .001)m and inpatient care from a pulmonologist (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.58-2.01; P less than .001) predicted arformoterol use.
“Given the results of this study, increasing access to nebulized maintenance therapy is warranted for select populations with COPD including racial/ethnic minorities, the dual-eligible, and those with certain comorbidities, such as psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Gilmer and colleagues wrote in their study. “Future studies are needed to explore the optimal time to initiate nebulized maintenance therapy, and the potential differential impact of early versus late initiation on patient outcomes.”
Researchers noted that, although their results may seem initially counterintuitive given that COPD has a higher prevalence in men, 56% of the beneficiaries in their Medicare data were women who were 65 years or older, and the results are consistent with other studies that show similar gender distribution findings for maintenance treatment patterns among COPD patients receiving Medicare.
“Since most Medicare beneficiaries with COPD are older than 70 years of age, the higher percentage of women than men in our two cohorts can be explained by the age distributions that ensued as a result of applying our various inclusion and exclusion criteria,” they said.
This study was funded by Sunovian. Dr. Gilmer and one coauthor are paid employees of University of California San Diego, which receives research funding from Advance Health Solutions. Another coauthor is an advisory board member for Advance Health Solutions and a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, and Pulmonix. Two other coauthors are paid employees of Advance Health Solutions, and another is a paid employee of Sunovion.
SOURCE: Gilmer TP et al. COPD. 2019 Jun 19. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2019.1618256.
FROM COPD: JOURNAL OF CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
Risk of cardiac events jumps after COPD exacerbation
particularly in older individuals, new research has found.
In Respirology, researchers report the outcomes of a nationwide, register-based study involving 118,807 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who experienced a major adverse cardiac event after an exacerbation.
They found that the risk of any major cardiac adverse event increased 270% in the 4 weeks after the onset of an exacerbation (95% confidence interval, 3.60-3.80). The strongest association was seen for cardiovascular death, for which there was a 333% increase in risk, but there was also a 257% increase in the risk of acute MI and 178% increase in the risk of stroke.
The risk of major adverse cardiac events was even higher among individuals who were hospitalized because of their COPD exacerbation (odds ratio, 5.92), compared with a 150% increase in risk among those who weren’t hospitalized but were treated with oral corticosteroids and 108% increase among those treated with amoxicillin with enzyme inhibitors.
The risk of a major cardiac event after a COPD exacerbation also increased with age. Among individuals younger than 55 years, there was a 131% increase in risk, but among those aged 55-69 years there was a 234% increase, among those aged 70-79 years the risk increased 282%, and among those aged 80 years and older it increased 318%.
Mette Reilev, from the department of public health at the University of Southern Denmark, Odense, and coauthors suggested that acute exacerbations were associated with elevated levels of systemic inflammatory markers such as fibrinogen and interleukin-6, which were potently prothrombotic and could potentially trigger cardiovascular events.
“Additionally, exacerbations may trigger type II myocardial infarctions secondary to an imbalance in oxygen supply and demand,” they wrote.
The authors raised the question of whether cardiovascular prevention strategies should be part of treatment recommendations for people with COPD, and suggested that prevention of COPD exacerbations could be justified even on cardiovascular grounds alone.
“Studies investigating the effect of cardiovascular treatment on the course of disease among COPD exacerbators are extremely scarce,” they wrote. “Thus, it is currently unknown how to optimize treatment and mitigate the increased risk of [major adverse cardiovascular events] following the onset of exacerbations.”
However, they noted that prednisolone treatment for more severe exacerbations may have a confounding effect, as oral corticosteroids could induce dyslipidemia, hypertension, and hyperglycemia, and increase long-term cardiovascular risk.
Six authors declared funding from the pharmaceutical industry – three of which were institutional support – unrelated to the study.
SOURCE: Reilev M et al. Respirology. 2019 Jun 21. doi: 10.1111/resp.13620.
particularly in older individuals, new research has found.
In Respirology, researchers report the outcomes of a nationwide, register-based study involving 118,807 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who experienced a major adverse cardiac event after an exacerbation.
They found that the risk of any major cardiac adverse event increased 270% in the 4 weeks after the onset of an exacerbation (95% confidence interval, 3.60-3.80). The strongest association was seen for cardiovascular death, for which there was a 333% increase in risk, but there was also a 257% increase in the risk of acute MI and 178% increase in the risk of stroke.
The risk of major adverse cardiac events was even higher among individuals who were hospitalized because of their COPD exacerbation (odds ratio, 5.92), compared with a 150% increase in risk among those who weren’t hospitalized but were treated with oral corticosteroids and 108% increase among those treated with amoxicillin with enzyme inhibitors.
The risk of a major cardiac event after a COPD exacerbation also increased with age. Among individuals younger than 55 years, there was a 131% increase in risk, but among those aged 55-69 years there was a 234% increase, among those aged 70-79 years the risk increased 282%, and among those aged 80 years and older it increased 318%.
Mette Reilev, from the department of public health at the University of Southern Denmark, Odense, and coauthors suggested that acute exacerbations were associated with elevated levels of systemic inflammatory markers such as fibrinogen and interleukin-6, which were potently prothrombotic and could potentially trigger cardiovascular events.
“Additionally, exacerbations may trigger type II myocardial infarctions secondary to an imbalance in oxygen supply and demand,” they wrote.
The authors raised the question of whether cardiovascular prevention strategies should be part of treatment recommendations for people with COPD, and suggested that prevention of COPD exacerbations could be justified even on cardiovascular grounds alone.
“Studies investigating the effect of cardiovascular treatment on the course of disease among COPD exacerbators are extremely scarce,” they wrote. “Thus, it is currently unknown how to optimize treatment and mitigate the increased risk of [major adverse cardiovascular events] following the onset of exacerbations.”
However, they noted that prednisolone treatment for more severe exacerbations may have a confounding effect, as oral corticosteroids could induce dyslipidemia, hypertension, and hyperglycemia, and increase long-term cardiovascular risk.
Six authors declared funding from the pharmaceutical industry – three of which were institutional support – unrelated to the study.
SOURCE: Reilev M et al. Respirology. 2019 Jun 21. doi: 10.1111/resp.13620.
particularly in older individuals, new research has found.
In Respirology, researchers report the outcomes of a nationwide, register-based study involving 118,807 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who experienced a major adverse cardiac event after an exacerbation.
They found that the risk of any major cardiac adverse event increased 270% in the 4 weeks after the onset of an exacerbation (95% confidence interval, 3.60-3.80). The strongest association was seen for cardiovascular death, for which there was a 333% increase in risk, but there was also a 257% increase in the risk of acute MI and 178% increase in the risk of stroke.
The risk of major adverse cardiac events was even higher among individuals who were hospitalized because of their COPD exacerbation (odds ratio, 5.92), compared with a 150% increase in risk among those who weren’t hospitalized but were treated with oral corticosteroids and 108% increase among those treated with amoxicillin with enzyme inhibitors.
The risk of a major cardiac event after a COPD exacerbation also increased with age. Among individuals younger than 55 years, there was a 131% increase in risk, but among those aged 55-69 years there was a 234% increase, among those aged 70-79 years the risk increased 282%, and among those aged 80 years and older it increased 318%.
Mette Reilev, from the department of public health at the University of Southern Denmark, Odense, and coauthors suggested that acute exacerbations were associated with elevated levels of systemic inflammatory markers such as fibrinogen and interleukin-6, which were potently prothrombotic and could potentially trigger cardiovascular events.
“Additionally, exacerbations may trigger type II myocardial infarctions secondary to an imbalance in oxygen supply and demand,” they wrote.
The authors raised the question of whether cardiovascular prevention strategies should be part of treatment recommendations for people with COPD, and suggested that prevention of COPD exacerbations could be justified even on cardiovascular grounds alone.
“Studies investigating the effect of cardiovascular treatment on the course of disease among COPD exacerbators are extremely scarce,” they wrote. “Thus, it is currently unknown how to optimize treatment and mitigate the increased risk of [major adverse cardiovascular events] following the onset of exacerbations.”
However, they noted that prednisolone treatment for more severe exacerbations may have a confounding effect, as oral corticosteroids could induce dyslipidemia, hypertension, and hyperglycemia, and increase long-term cardiovascular risk.
Six authors declared funding from the pharmaceutical industry – three of which were institutional support – unrelated to the study.
SOURCE: Reilev M et al. Respirology. 2019 Jun 21. doi: 10.1111/resp.13620.
FROM RESPIROLOGY